Auto-Stellar
1,2,3Student, Department of Mechatronics Engineering New Horizon Institute of Technology and Management, Thane, University of Mumbai, India
4Professor, Department of Mechatronics Engineering New Horizon Institute of Technology and Management, Thane, University of Mumbai, India

Abstract - Astronomy is becoming a new booming field of science. With the end of exploration on Earth, scientists have begun to take a keen interest in what is not in this world. Just by being able to observe the countless stars in our galaxy and discover new horizons in the universe. Telescopes have become one of the basic tools used by every aspiring scientist. Now that it is quite easy to point a telescope at the sky, doing so is equally busy. After many research and technological advances we. The first was able to mount a GoTo that would tell you exactly what you were aiming at in the sky. Now while these mounts are useful, they are also expensive. The purpose of this project is to build a low-cost equatorial telescope mount using an Arduino DUE board. The project uses a variety of basic electronic equipment and some 3D printing. The idea is to create a commercially available cheaper and build-to-build alternative to the GOTO/Star Tracker products produced by Skywatcher, Orion, Vixen, and others. At the heart of the system is an Arduino DUE board, loaded with software that is constantly being developed to add functionality. The project tends to solve tracking issues for adult astronomers to capture and research space objects with a cheap and customizable setup.
Keywords: Astronomy, Telescope, GOTO, Arduino, 3D printing, Equatorial.
1.INTRODUCTION
GOTO refers to a type of telescope mount and associated softwarethatcanautomaticallypointthetelescopeatauserselectedastronomicalobject.BothGoTobaseaxleshavea motor and computer control. GoTo mounts are calibrated before use. When enabled, the user's latitude, longitude, time,anddatecanbequeried.Youcanalsogetthisdatafrom aGPSreceiverattachedtoyourtelescopeorbuiltintothe telescopemountitself.Also,themountcontrollercanhave itsownreal-timeclock.
1.1 History of AUTO/GOTO telescopes:
The first computerized telescopes were developed in the 1970sandweremainlyusedbyprofessionalastronomers. However,withtheadventofmoreadvancedtechnologyand thereductionofelectronicscosts,automatictelescopeshave become more affordable and accessible to amateur astronomers in recent years. Today's most popular
automatictelescopemanufacturersincludeCelestron,Meade Instruments,OrionTelescopes&Binoculars
1.2 Functionality
Automated telescopes are equipped with electronic motorsthatcontrolthemovementofthetelescopemounts, allowing for precise movement and tracking of celestial objects.Italsohasacomputerizedsystemthatcanstorea databaseoffamouscelestialobjects,souserscaneasilyfind and track these objects without manually entering coordinates.Someadvancedautomatedtelescopescanalso beremotelycontrolled,allowingremoteobservation.
2. OBJECTIVE
The Auto-Stellar is an inexpensive and build-to-build alternativetocommerciallyavailableGOTO(computerized telescopes) for equatorial mounts. That armature helps astronomers capture and explore space objects with an inexpensive and customizable setup. A cost efficient, customizable,andalternativesolutionforreadilyavailable GoTomounts(startrackers).Itwillsolvethetrackingissue whichisacommonproblemfacedbyrookieastronomers
3. SCOPE
This project can find and track a database of 250 stellar masses in the northern and southern hemispheres. Observation logs are kept for each observation, including temperature, location, etc. This is independent operation and/or computer/tablet assisted operation. Provides an accurate and fast alignment method for an "always-at-aglance" experience. Auto-Stellar is an idea to make GOTO telescopesmoreaffordable.Itisagoodwaytolearnalotof new things, such as elevation and elevation coordinates, localsiderealtime,earthmotion,Arduinocoding,andmuch more.Telescopesarecustomizedbasedonyourneeds.AutoStellarhasthepotentialtochangethemarket.Inexpensive for amateur astronomers and Astro photographers with a budgetofuptoRs23,000.
4. PROJECT DESIGN
Auto-Stellarisanopensource(GOTO)ArduinoDuebased telescope control system. Built as a stand-alone system,
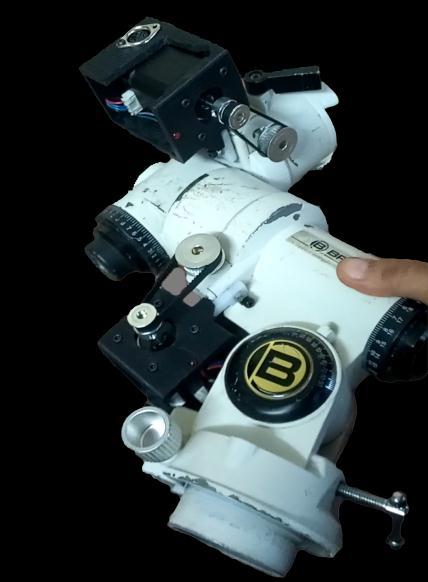
Auto-Stellar does not require a computer, tablet, mobile phone or internet connection to operate and deliver stunningviews.Basically,wehaveadatabasecontainingthe best 250 stellar masses (the messier catalog and Hidden Treasure)and200starstocalculatetheirpositioninthesky and show the telescope. The implemented alignment procedureallowsforan"always-on-eye"experiencewhen rotatingtoaselectedobject,andwhenanobjectentersthe eye, the system tracks it. However, if you want to take advantageofelectronicdevices,Auto-StellarusesBluetooth communication(wirelesssetup)toconnecttoallelectronic devicesandacceptcommandsbasedontheMEADELX200 communicationprotocol.Thesystemworkswithavarietyof stepper motorsandcan be connected tobothDIY mounts and commercial products such as Skywatcher, MEADE, Orion, and Vixen. The project aims to solve the issue of tracking heavenly objects in the sky for photographic and researchpurposes.
4.1. Components:
ArduinoDueOriginal
NextionEnhanced5.0”HMITouchDisplay
RTCDS3231RealTimeClock
GPSuBloxNeo6M
PS2joystickforArduino
DHT22TemperatureSensor
HC-05BluetoothModule
DRV8825MotorDriver2x
StepperMotorsNEMA17x2
PrototypeElectronicboard(PCB)
20Tooth&36ToothPulleys
TimingBelt

BuckConverter
MemoryCardReader
12V1ADCAdapter
3DPrintedCase&MotorMount
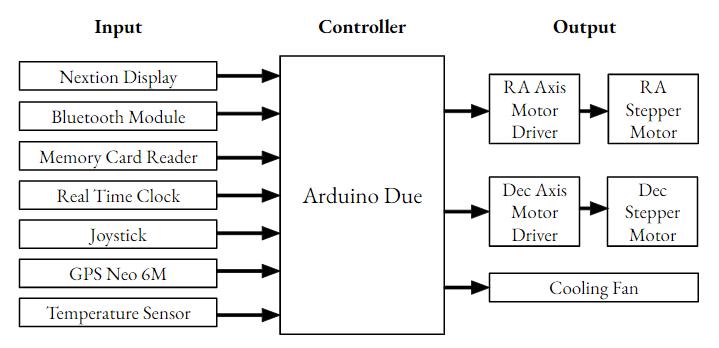
4.2. Input Block:
The input block has all the sensors and input peripheral devices given in the block diagram. All these inputs are given to the Arduino DUE microcontroller. It has a touch screendisplaywithaGUIprogramloadedinit.
4.3. Controller Block:
The controller block has an Arduino Due with the main program loaded in it. It performs all the calculations and givestheoutputtothemotordriverofRightAscensionand Declinationaxes.Ithastheinformationabouttheequatorial mountandtheGPSdatacollectedfromtheGPS.
4.4. Output Block:
Theoutputblockconsistingofmotordriversgivethepulses to stepper motors according to the Arduino DUE’s calculationthatistheequatorialcoordinatesoftheobjectin the sky. The right ascension and declination axis are the coordinatesoftheequatorialcoordinatessystem.
5. OBSERVATIONS
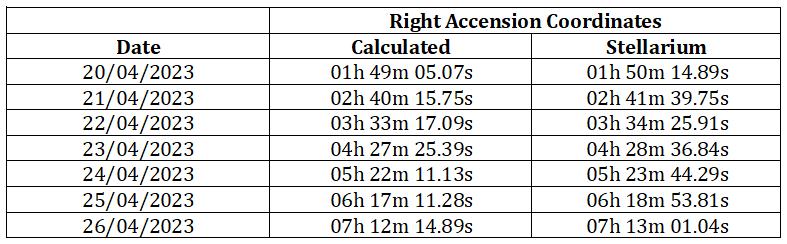
Object:Moon:
Period:20thAprilto26thApril
Coordinates:RightAscension
Table -1: RightAscensionCoordinates
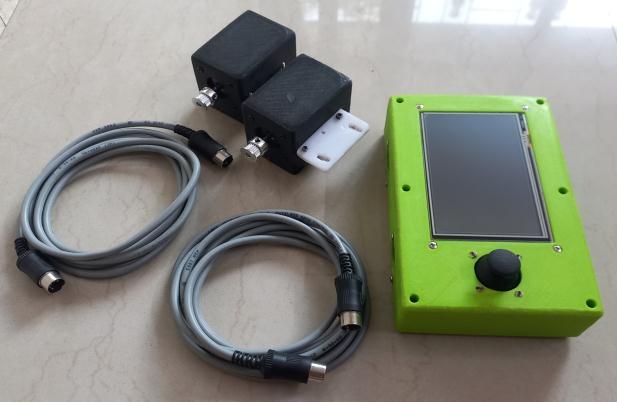
Fig
-1: ConnectionsetupforAuto-Stellar
Theblockdiagramconsistsofthreeblocks:
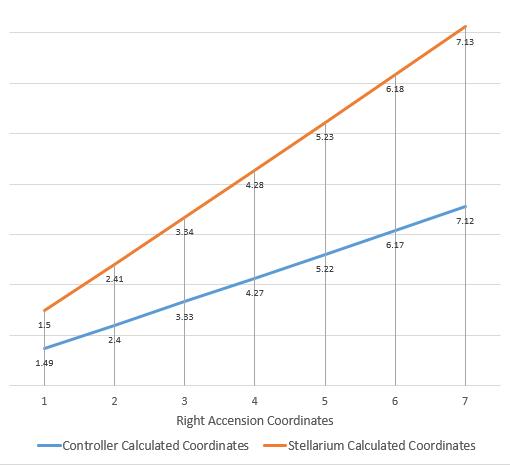
Chart-1:CalculatedCoordinatesofStellariumandControllers
Abovechartrepresentstheerrorofhandheldcontrollerin comparison with Stellarium for Moon’s right accension coordinates over a period of 20th April to 26th April. This errorcanbeminimizedbyaligningandcalibratingthesetup in real time, to get the maximum positioning and tracking accuracy.

GoTo telescopes are useful tools for both amateur and professional astronomers. They simplify the process of locating and tracking celestial objects, allowing users to spendmoretimeobservingandlesstimeadjustingtelescope mounts. They may be more expensive than hand-held telescopes and require more technical expertise, but the advantagestheyoffermakethemaworthwhileinvestment forthoseseriousaboutastronomy.
intheoppositedirection.Thisrequiresa"meridianflip"in whichthetelescopeismovedtotheothersideofthemount andre-alignedwiththecelestialpole.
So,tocounterthisproblemAuto-Stellarisfitwithmotorized tracking systems thatallows the project to followcelestial objects as they move across the sky. This is important for observing objects that move relatively quickly, such as planetsandcomets.

6. CONCLUSIONS

Auto-Stellarmustbeaccuratelyalignedwiththecelestialpole in order to track objects smoothly. Polar alignment is a critical step that must be performed carefully, as any misalignmentcancauseobjectstodriftoutofview.
Equatorialmountsaredesignedtoworkataspecificlatitude, and adjustment may be necessary if you plan to use the mountinalocationwithadifferentlatitude.Thisadjustment ensuresthatthemountremainsaccuratelyalignedwiththe celestialpole.
Another important aspect is the Meridian flip Due to the rotation of the Earth, objects observed with an equatorial mountwilleventuallycrossthemeridianandbegintomove
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[5] I H Kurniawan, M Irfan, A Aminudin, Bosscha Observatory, Bandung Technology Institute, “GOTO TelescopeMotionControlSystemRightAscensionand DeclinationDirectionwithThreeModesofSpeedUsing MicrocontrollerATMega2560”inMSCEIS2019,October 12, Bandung, Indonesia Copyright © 2020 EAI DOI 10.4108/eai.12-10-2019.2296306

ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
ARCEducators
rDUINOScopeCommunity
KhaireyNouhe
DessislavGouzgounov
REFERENCES
[1] Patent Number: 4,764,881 COMPUTER CONTROLLED
ALTAZIMUTHTELESCOPEMOUNTInventor:GilbertH. Gagnon,SanMarcos,Calif.DateofPatent:Aug.16,1988
[2] AshishVanjani,SagarAtre,MITWorldPeaceUniversity, Pune,“AltAzTelescopeMountDesign”inInternational ResearchJournalofEngineeringandTechnology(IRJET)
e-ISSN:2395-0056Volume:07Issue:08,Aug2020,pISSN:2395-0072
[3] GauravV.Bhawde,AkshayKadam,DavidLobo,Roshan Gawade, Shardul Mhatre, “Design, Fabrication and Analysis of Automatic Telescopic Mount” Article in International Journal of Analytical, Experimental and FiniteElementAnalysis(IJAEFEA),Issue.1,Vol.5,March 2018 e-ISSN: 2394-5141, p-ISSN: 2394-5133, pp 8-12 DOI:10.26706/IJAEFEA.1.5.20180306
[4] SusanaMart´ın-Ruiz,FranciscoJ.Aceituno,MiguelAbril, Luis P. Costillo, Antonio Garc´ıa, Jos´e Luis de la Rosa, IsabelBustamante,JuanGutierrez-Soto,H´ectorMag´an, Jos´e Luis Ramos, Marcos Ubierna, “T35: A Small Automatic Telescope for Long-Term Observing Campaigns”HindawiPublishingCorporationAdvances inAstronomyVolume2010,ArticleID869810,7pages doi:10.1155/2010/869810
© 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.226 |

