Alzheimer Detection System
Hrutvik Rane, Swarali More, Ghanshyam Patel, Maitrey Phatak, Charmi ChaniyaraHrutvik Rane, Atharva College of Engineering, Maharashtra, India
Swarali More, Atharva College of Engineering, Maharashtra, India

Ghanshyam Patel, Atharva College of Engineering, Maharashtra, India
Maitrey Phatak, Atharva College of Engineering, Maharashtra, India
Charmi Chaniyara, Atharva College of Engineering, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract – Neurodegeneration in addition to poor communication between neuron synapses lead to Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most common form of dementia, damages the brain, resulting in impaired memory and ability to perform daily tasks due to damage to the brain. With the help of MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scans of brain images, with the help of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, we can diagnose and predict the disease and classify AD patients to determine if they will develop this deadly disease. future. To be. The main goal of all these actions is to save time and money for radiologists, doctors and nurses and to develop better predictive tools, information and diagnostics to assist patients with this disease. Recently, the usage of deep learning algorithms has been increasingly helpful in diagnosis of AD. This is because DL algorithms work on large datasets. In the paper, we have made use of convolution neural network to work with early detection and classifying of the disease. CNNs are popular because of their excellent performance in machine learning using a widerange of information.
Key Words: Neurological disorder, Alzheimer’s disease, Deep learning, MRI, Convolutional neural network, Brain imaging.
1.INTRODUCTION
Thenumberofdangerousdiseaseshasincreasedinrecent years due to demographic shifts in developing and developedcountries[1].Exceptforsomemedicationsthat halt the growth of the disorders, effective therapies for dementia and Alzheimer's disease are still elusive despite advancements in medical science. Therefore, preventing the spread of illnesses into their severe stages depends greatly on early detection [1,2]. Some of the serious diseasesthathavereceivedalotofattentioninthemental health field are dementia and Alzheimer's disease. This is because of its prevalence in the elderly and its negative impact on the elderly's ability to perform daily tasks. Dementia is memory loss or impairment that prevents mental health from being maintained due to aging or illness. It is characterized by changes in mental and behavioral disorders or stroke It is a syndrome that includesimpairedmemory, behaviorandthinkingandthe
loss of ability to perform daily activities [3,4]. Reports from WorldHealthOrganization(WHO)statethataround 47 million people across the world live with dementia. It could reach 82 million by 2030. The root cause of dementia is neurodegeneration and poor connections in thebrain,whichleadstopoordecisionmakingskills.Nonneurodegenerative mechanisms cause vascular dementia. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common and commonformsofdementia,accountingfor60%to70%of dementia cases. Age is a risk factor for AD, especially in peopleover theageof65. ADismorecommonlyfound in women than men. However, the aetiology of AD has not been correctly determined bythe medical personnel.. The mainidea is basedonthe combinationof extracellularAβ peptide and hyperphosphorylated tau protein in brain cells. These two patterns are biomarkers called amyloid plaques (aggregation of beta-amyloid fragments of neurons) and tangles (intracellular accumulation of tau proteinintheformoftwistedfilaments).
1.1 Common Symptoms
MemoryLoss:
The most common symptom of Alzheimer's disease is memory loss. These include forgetting recent events, forgetting names and faces, misplacing items, and repeatingquestions.
Difficultyinplanningandproblemsolving:
Alzheimer's patients often have problems planning and solvingproblems.Thiscancauseproblemswithtaskssuch as paying bills, managing finances, and completing daily tasks.
SpeechProblems:
Alzheimer's patients may have difficulty finding the right wordstoexpressthemselvesortounderstandwhatothers aresaying.
Moodandbehaviouralchanges:
Alzheimer's disease can cause changes in mood and behaviour, such as depression, anxiety, irritability, and apathy.
1.2 Neuroimaging Modalities:
The use of MRI to diagnose Alzheimer's disease has been the subject of research for many years. MRI (magneticresonanceimaging)isanon-invasivetechnique that provides detailed information about the brain. It is widelyusedinclinicalpracticeinthediagnosisandfollowup of Alzheimer's disease. Neurons and synapses are lost in the brain, and some brain areas shrink. MRI can detect thesechanges.

2. DATA USED
The data is being sourced from Alzheimer diagnosed dataset andaround6000imageswereusedforthemodel training. The dataset comprises of four types of classes non-demented Alzheimer,very milddementedAlzheimer, mild demented Alzheimer and moderate demented Alzheimer.
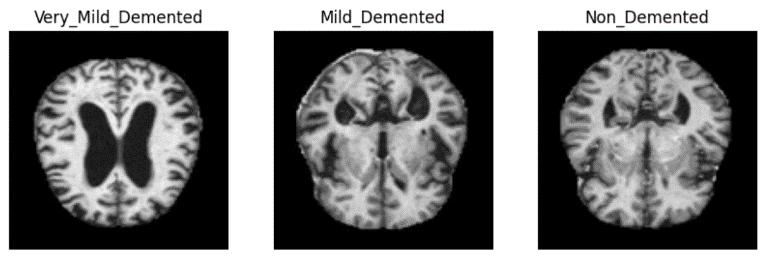
image manipulation that combines multiple scenes into a single image. It aids in resolving issues with overlapping pictures'size,contrast,andimagerotation.Combiningthe picture data from many photos and transforming them to the same coordinate system is known as image registration. It has several applications in clinical and medical research. Images taken for medical purposes can becollectedfromthesame personatthesametimeusing multiplemodels,orfromdifferentpersonsusingdifferent models. For optimum results, it's crucial to convert the MRI pictures in the file to the same width and height as they differ in size. Since the input image size of the CNN model is 224×224 pixels, this research reduces the MRI imageto224×224.
3.2 Convolution Neural Network
Convolution neural networks are a subset of deep neural networks which make use of convolutional layers for processing inputs for the included images. The convolutional layers of CNN compute the output of neurons connected to specific regions in the input and apply convolutional filters to the input. It assists in extracting spatial and temporal information from images. A weight-sharing method is used in CNN's convolutional layerstoreducetheoverallnumberofparameters.
3.2.1 Feature Extraction
Fig 1: InputImages
3. PROPOSED MODEL
In this section, we discuss our proposed model that consistsofCNNmodelandthefollowingsteps.
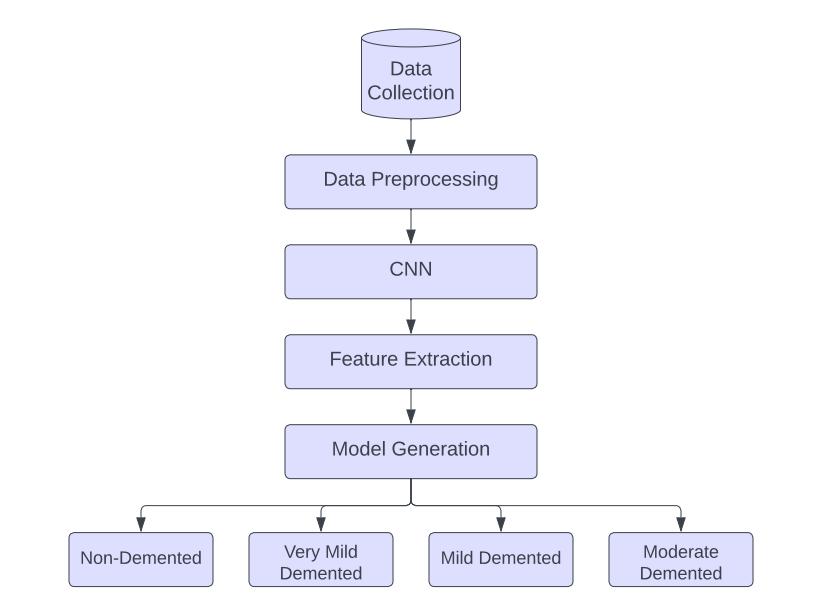
ThisworkusesaCNN-basedmodeltoextractkeyfeatures without human interference. The proposed architecture consists of four convolutional layers, a max-pooling layer, dropout, flatten and a fully connected layer. The output rangesfromnon-dementedtomoderatelydemented.
3.2.2 Layers
Convolutions
Using a kernel size of 45*45*45, convolution operations are performed on an image of 8-block size. There are two convolutional layers employed, and the first filter has 32 3*3kernels.Thekernel'ssizedenotesaneuron'sreceptive field, reinforcing the neurons' local link to the prior volume.
RectifiedLinearUnitandSoftmax
Fig 2: ProposedSystemArchitecture
3.1 Data preprocessing
Preprocessingisusedtoimproveimagedatabyremoving unwanted distortions and improving certain views that are important for further processing. Tagging is a type of
The Activation function of ReLU is defined [11] and the Softmax function let the model to express the inputs as a discrete probability distribution. In ReLUs the training timeissignificantlyfasterascomparetosigmoidunitsand hyperbolictangent[12].
Pooling Layer
The aggregation function max-pooling is used to obtain the maximum value, as determined by the kernel size,
input hxw size, and stride. The pooling approach effectively summarises the outputs of adjacent groups of the inputs in addition to reducing the inputs' dimensions [9]. When the picture size is very huge, this layer really performs down sampling, which minimises the spatial dimensions while maintaining valuable information and alsoreducesthenumberofparameters[10]inthiswork1 maxpoolinglayerisused.
Dropout
Theoutputofneuronswitharatiodropout,orprob-ability of r, is adjusted to 0 by the usage of dropout layers in the hidden layers. The forward pass and the backpropagation processes are not affected by the neurons that dropped out. Two dropout layers, with ratios of 0.25 and 0.5, have beenaddedtothedesignthatwesuggest.
FullConnectedLayer
The last layer, which we refer to as the FC layer, is fully connected; each of its neurons is connected to the layer above it,anditalso enhancesthetraining performance of CNN models since we flattened our matrix into a vector form and fed it into the fully connected layer. [19]. All activationsinthelayerbelowitarefullyconnectedtothis layer.
4. OUTPUT
The output consists of the MRI scan with the assigned label.

Labels can be from very mild, mild, moderate and non demented.Outputcan get verifiedby a neurosurgeonand addintoacccuracyofmodel.
The CNN network has several layers, including a convolutional, activation, pooling, and fully connected layer.TheactivationlayerappliestheRectifiedLinearUnit (ReLU) to increase the nonlinear properties in the CNN model because of its training speed. The first layer is the convolutional layer, which takes the input image using a kernel (ReLU) or filter and identifies the relationship betweentheimageandtheirfeatures(toidentifywhether the image is of an Alzheimer's patient or Normal). Since weflattenedourmatrixintoavectorformandsentitinto the fully connected layer, the fully connected layer ultimately enhances the training performance of the models. Using MRI images, CNN was employed in this study to identify and predict AD. at this model, we were able to train and test the model using 6000 photos while also achieving a test accuracy rate of 0.98% and a low proportion of test loss at a rate of 0.0667. We used four alternativeepochsizesthroughoutthemodel'stestingand training in order to compare the findings and determine which one produced the most accurate outcome. With respect to all three epochs, we improved test loss and accuracy by employing 30 epochs. Table 1 depict the outputandthenumberofepochsusedinCNN.
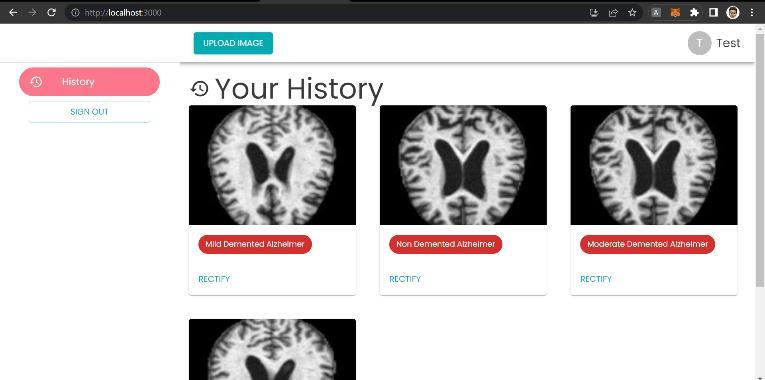
Fig 3: Output of the user Interface
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this study, we employed MRI scan pictures that were characterized as having moderate dementia, nondementia, or very mild dementia. We randomly selected 80% of the training data, while the remaining 20% were usedtovalidatethemodel.
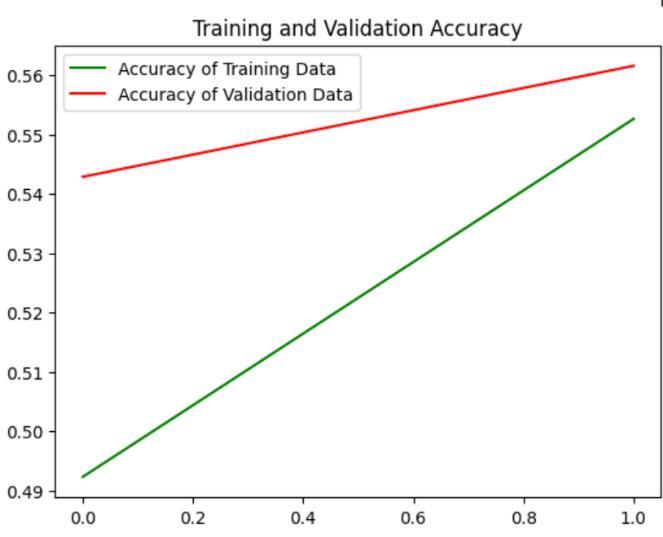
The accuracy and loss of the model's training and validation are shown in the following graph. In the following chart, training set is used to train the model, while the validation set is used to assess the model's performance.
6. CONCLUSIONS
Recent developments in biomedical engineering have madethestudyandinterpretationofmedicalpicturesone of the primary research fields [14], [15]. The usage and use of DL is one of the factors contributing to this advancement in the analysis of medical pictures [16]. In the last year, DL has been mostly employed for classification, and AI-based approaches are used to automatically diagnose AD in its early stages to meet the main objectives of doctors [17]. In order to identify AD patientsearly,anautomatedframeworkandclassification forAD utilizingMRIimagesis crucial.Inthisresearch,we use MRI scans to propose a convolutional neural network classification approach for AD. 98% accuracy is a huge accomplishment. A notable result was attained while dealing with an epoch size of 30, with an accuracy rate of 98%,outofalltheoutcomeswithvariousepochs.
Future work is something we anticipate and hope to encourage. Consequently, the outcome might be further enhanced by using deep convolutional neural networks, which have recently demonstrated their usefulness in neuroimagingstudies.Asaresult,thealgorithm'scapacity to identify AD would be greatly enhanced by the usage of deep CNN and large MRI scan pictures. Additionally, this deep learning technique offers invaluable information to the researcher in order to diagnose various types of diseases in addition to helping the doctor, carers, radiologist, and patients who are afflicted with this ailment.
REFERENCES
[1]BhagtaniA,ChoudhuryT,RajG,SharmaM.Anefficient survey to detect Alzheimer disease using data mining techniques. In: 2017 3rd International conference on applied and theoretical computing and communication technology(iCATccT).IEEE;2017
[2] Simons S, Abasolo D, Escudero J. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease from quadratic sample entropy of electroencephalogram.HealthcTechnolLett2015
[3] Sharma J, Kaur S. Gerontechnology-The study of alzheimer disease using cloud computing. In: 2017 International conference on energy, communication, data analyticsandsoftcomputing(ICECDS).IEEE;2017
[4] La Joie R, Bejanin A, Fagan AM, et al. Associations between[(18)F]AV1451tauPETandCSFmeasuresoftau pathologyinaclinicalsample.Neurology.2018
[5] Daza JC, Rueda A. Classification of Alzheimer’s disease in MRI using visual saliency information. In: Computing conference(CCC),2016IEEE11thColombian.IEEE;2016.
[6]ChupinM,GérardinE,CuingnetR,BoutetC,LemieuxL, Lehéricy S, Benali H, Garnero L, Colliot O. Fully automatic hippocampus segmentation and classification in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment appliedondatafromADNI.Hippocampus2009
[7] C. Patterson, World Alzheimer Report 2018-the State of the Art of Dementia Research: New Frontiers. London, U.K.:Alzheimer’sDiseaseInternational,2018
[8] D. Shen, G. Wu, and H. Suk, ‘‘Deep learning in medical imageanalysis,’’Annu.Rev.Biomed.Eng.,vol.19,pp.221–248,Jun.2017.
[9] Y. Lecun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, “Deep learning,” Nature, vol. 521, no. 7553, pp. 436–444, 2015, doi: 10.1038/nature14539.
[10] A. Krizhevsky and G. E. Hinton, “ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks,” pp.1–9.
[11]T.Wood,“SoftmaxFunctionDefinitionDeepAI.”2020.
[12]G.Hinton,“Dropout:ASimpleWaytoPreventNeural NetworksfromOverfitting,”vol.15,pp.1929–1958,2014.
[13]Y.Li,D.Shi,B.Ding,andD.Liu,“UnsupervisedFeature Learning for Human Activity Recognition Using SmartphoneSensors,”pp.99–100,2014.
[14]A.W.Salehi,P.Baglat,andG.Gupta,“MaterialsToday : Proceedings Review on machine and deep learning models for the detection and prediction of Coronavirus,” Mater. Today Proc., 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.245.
[15] K. Sethi, “Machine Learning Based Performance Evaluation System Based On Multi-Categorial Factors,” 2018FifthInt.Conf.Parallel,Distrib.GridComput.,pp.86–89,2018.

[16] S. M. Anwar, M. Majid, A. Qayyum, M. Awais, M. Alnowami, and M. K. Khan, “Medical Image Analysis using Convolutional Neural Networks: A Review,” J. Med. Syst., vol.42,no.11,2018,doi:10.1007/s10916-018-1088-1.
[17] K. Sethi, “Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms on Different Datasets,” no. Icic 2017, pp. 87–91,2018
