International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023
2395-0072
1 Assistant Professor, Department of Information Technology, Meenakshi College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India
2-5Student, Department of Information Technology, Meenakshi College of Engineering, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India ***
Abstract -An AI-based smart plant management system is designed for plant farming in the greenhouse. The idea is to measure the soil’s moisture content and provide an automatic watering system to maintain the soil moisture level for the plant shown.The major goals are to increase the soil’sproductivity and to regulate the amount of water used by each plant, planted in the soil. Soil Moisture Sensor (SMS), Temperature Sensor (TS), Automatic Water System (AWS), Water Flow Controller (WFC), Solar Panel, and Battery are the hardware devices used. An AI-powered control and management algorithm is deployed for the smart management of plants in this work and also a database is created to house all of the plant data required for the management A web application is developed that enables remote monitoring of the plant management system.
sensor will used. To calculate the values of soil Moisture leveloftheplant/tree.
In our proposed work a smart plant management system in green house environment is developed, using the Control & Management Algorithm. For improving the soil productivity the control part of the algorithm is usedand to maintain the water level the management part of the algorithmisused.Finally,throughtheWebappdeveloped, the AI will alert the user incase if any problem is encountered in the automatic watering system, to check thestatusoftheplantinthegreenhouse
a.AI→DATABASE→INSTRUCTION→WEB→ALERTSMS.
b. AI→AUTOMATIC WATER SYSTEM→WATER FLOW CONTROLLER→WEBAPP.
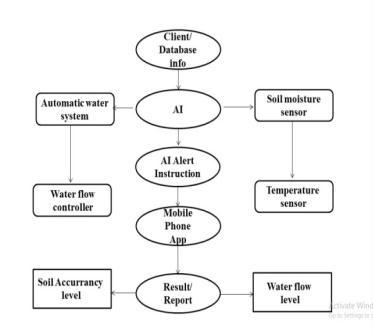
c. AI→SOIL MOISTURE SENSOR→TEMPERATURE SENSOR→WEBAPP.
Above are the various AI connectives with devices. A web applicationisdesigned forcontrollingand monitoring the AIbasedsystem.
2.PERFORMING STATE (PS) and
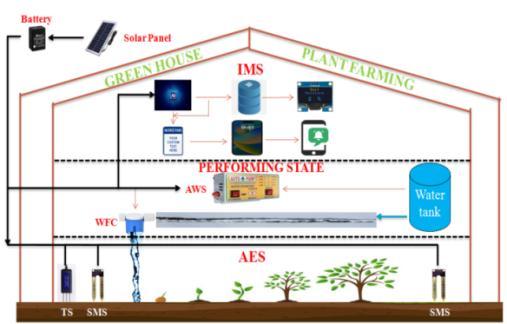
The setting of greenhouse plant farming can be improved with an intelligent plant management technology. By controlling the required devices, we will construct an experimentalanalysisofsoilaccuracylevelandwaterflow level.Theproject's"CONTROLANDMANAGEMENT(C&M) ALGORITHM" is its main contribution, which accurately identifiesthesoilandwaterlevel.Thetechniqueisdivided into the following three modules: 1.INFORMATION MODULE SYSTEM (IMS),
3. ANALYSIS OF EXECUTION STATE (AES) for this purpose. The experimental setup shows the details of the first three techniques. Each plant and tree has been assigned a special plant ID in this intelligent plant system (for instance, "plant name: mango; plant ID: CMM03) that ismaintainedinadatabase.
[1]IntheexistingworkaDeepLearning basedalgorithm is used in maintaining the soil Productivity. In the DL based approaches a Long-Short Term memory Network was used in connecting the hardware devices. Smart farming involvetheuseofsmartMeters,WirelesssensorNetwork, Aerial vehicles, Smart camera Node, soil Moisture WSN, Satellite Imagery etc. In this project using so many sensorsLike Temperature, Humidity and soil Moisture
4
4.1.
The first step is the pre-process of the information which is done in the Information Module system (IMS).In this
modulethe AI will be connected with different hardware devices that are required. All the information about the plantsis stored in the database and a database is created. AIgetsitsneededinformationfromthisdatabase.

This MySQL database system contains the details about the plant and is accessible using the MySQL software.
automatic water system and a water flow controller attached to it. A Web app's AI will be linked to the AI whichwilldetectthesoilmoisturelevelusingthesensor.
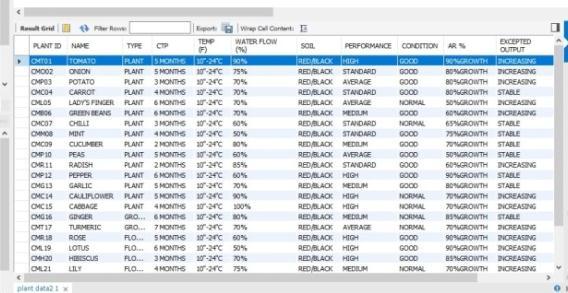
The following table shows a database list of a variety of plants, including ground plants, flowers, greenhouse plants, etc. Each data list will be represented byauniqueplantID,suchas(Onion-CMO02).
ForthesmartplantingsystemanArduinoUNO is used,itcommunicateswiththeArduinoIDEtogetthedata from the sensors. Additionally, a Web app that is connectedwillautomaticallyalertandnotify.Anditserves asabridgebetweentheArduinoNanoBoardandtheweb app.

To regulate the load, for powering the lighting system,motor,orsolenoid.Weutilizethe5Vrelaymodule. Asidefromthat,itcanswitchbetweenACandDCvoltages. The relay's specs determine the maximum voltage and currentthatthe5Vrelaymodulecanregulate.
The second module is the Performing State, here the connectivity among the water storage and Automatic water system (AWS) and Water Flow controller(WFC) is established. In this step AI monitors the flow of water to the soiland maintains the flow to be less than or equal to (<=)Averageflowlevel50-60%ofwaterlevelAccuracy.

The Arduino UNO kit has been designed to communicate with devices in order to regulate programmer’s functional specifications. It also has an
The Third step is the On-Process which is carried out in the Analysis of Execution state module. In this modulethe soil moisture sensor will detect the soil Accuracy/Water level, and if any decrease in moisture level is noticed the AI will detect it and send an alert notification to theWeb app.

Thesoilmoisturesensormeasureshowmoistthe soil is. Two parallel-aligned probes are present in this sensor. This sensor's detecting method involves running current through its probes and measuring the resistance present in the space between them. Less water is present whenthesoilisdry.Probesshowmoreresistanceandless current flow through this water. Similar to this, more water-containing soil conducts electricity through these sensors, causing less resistance to be observed. By using this resistance, the sensor's controlling module determinesthemoisturelevel.
STEP10 :CONDITION5-Watermotorandwater system
STEP11 :>>MANAGEMENTALGO<<(6-10)
STEP12 :CONDITION6-AutomatedWatersystem (AWS)connectedwithWaterFlow Controller(WFC)
STEP13 :CONDITION7-Attachsolarpanelwith batteryforpowerchargetoSMS
STEP14 :ON-PROCESSofAES,AIINSTRUCTION BASED.

STEP15 :CONDITION8-processingwithsensor
STEP16 :CONDITION9-AImonitoringthesensor
STEP17 :CONDITION10-HenceAIAlertto WebApp
STEP18 :SwitchcaseREPORT(C&M)
Inthisproject,usingawebapplicationofsitewill be used a Node MCU ESP8266 of Wi-Ficonnected to Arduino uno of kit. It will be programmed for user can create or using existing to see the plant status and have alert message to particular Web number or manually setuptheWebnumber.Alsoshowna plantIDReportand detailsforparticularplantsystem.
STEP1 :Pre-ProcessofIMS
STEP2 :AIconnected
STEP3 :>>CONTROLALGO<<(1-5)
STEP4 :AIcheckinDATABASE
STEP5 :CONDITION1-aboutPlantDetails
STEP6 :CONDITION2-AIinstructiontoWeb
STEP7 :CONDITION3-WebapptoAlerta messageis
a. Seednameand b. PerimeterofDistance.
STEP8 :WORKINGPROCESSofPerformingstate, AIProgrammed.
STEP9 :CONDITION4-AIconnectedwithAWS
STEP19 :PRE-PROCESS
STEP20 :WORKINGPROCESS
STEP21 :ON-PROCESS
5. SYSTEM FLOW CHART
This project's work will serve as a smart plant managementsystem forgreenhousefarming,andprojectrelated experimental work will be used to maintain the garden. For instance, when there is no water flow in the soil,AI/SMSwillrecognizeitandsendanotificationtothe Web app. Additionally, theWeb app will inform on whether the water flow is increasing or decreasing. All of these experimental labor procedures will be based on algorithmrequirementsforcertaingreenhouseplants.
This project effort uses artificial intelligence to represent the goal of smart planting for greenhouse farming. The IMS'sfirststageisthepre-processingphase,duringwhich the AI will be linked to various hardware and need components. All plant-related information is kept in a database.AIisabletoaccessinformationfromdatabases.

The second stage of the AI working process is the connection between the water storage and the automatic water system (AWS) and water flow controller (WFC). Water is flowing into the soil for less than or equal to (=) to an average flow level of between 50% and 60% of the accuracyofthewaterlevel.
Thethirdphaseoftheon-processanalysisisthedetection of the soil moisture sensor, the soil accuracy/water level will be decreased, and AI will identify and alert a notificationtotheWebapp.

plant management technique can be designed in such a way it can be extended to actual farming in large scale landsandfarmerscanbeprofitedfromthissmartplanting technique
Ourinvolvementinthisprojectasstudentsofinformation technologyofengineeringwillbehelpfulforGREENhouse farming and gardening with the aid of fully experimental procedurethatissuccessfullyoperating.
[1] V. Nasir and F. Sassani, “A review on deep learning in machining and tool monitoring: Methods, opportunities, and challenges,” Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol.,vol.115,no.9,pp.2683–2709,May2021.
[2] L.-R. Jácome-Galarza, M.-A. Realpe-Robalino, J. Paillacho-Corredores, and J.-L. Benavides-Maldonado, “Timeseriesinsensordatausingstateof-the-artdeep learning approaches: A systematic literature review,” in Communication, Smart Technologies and Innovation for Society. Singapore: Springer, 2022, pp. 503–514.
[3] A.KhannaandS.Kaur,“EvolutionofInternetofThings (IoT)anditssignificantimpactinthefieldofprecision agriculture,” Comput. Electron. Agricult., vol. 157, no. 1,pp.218–231,2019.
Figure6wasobtainedwhenaprototypeordatagathering module was being tested utilizing solar power, a renewable source of energy. The prototype testing was conducted correctly, and the required safety measures weretakentoensure effectivedata transfer.Basedonthe datagathered,dataaresubmittedintheArduinoboard.
The project's experimental results show that the plant growth rate is consistent with the ambient environment. The main findings of this investigation agree with our expectedresultseventhoughthesoilmoistureduringthe experiment was around 65%.The project's goal is to determine the soil moisture level accurately using the sensor, once this is done, the automatic water flow range will be regulated by AI of AES to maintain the moisture content of the soil required by the plant sown in the soil This research will be beneficial for greenhouse farming and gardening maintenance systems. In future the smart
[4] M. Catelani, L. Ciani, A. Bartolini, C. Del Rio, G. Guidi, and G. Patrizi, “Reliability analysis of wireless sensor networkforsmartfarmingapplications,”Sensors,vol. 21,no.22,p.7683,Nov.2021.
[5] M.Lezoche,J.E.Hernandez, M.D.M.E.AlemanyDíaz, H.Panetto,andJ.Kacprzyk,“Agri-food4.0:Asurveyof the supply chains and technologies for the future agriculture,”Comput.Ind.,vol.117,May2020,Art.no. 103187.
[6] T. Ojha, S. Misra, and N. S. Raghuwanshi, “Wireless sensor networks for agriculture: The state-of-the-art in practice and future challenges,” Comput. Electron. Agric.,vol.118,pp.66–84,Oct.2015.
[7] R. Rayhana, G. G. Xiao, and Z. Liu, “Printed sensor technologies for monitoring applications in smart farming: A review,” IEEE Trans. In strum. Meas., vol. 70,pp.1–19,2021.
[8] K.Alibabaeietal.,“Areviewofthechallengesofusing deep learning algorithms to support decision-making
in agricultural activities,” Remote Sens., vol. 14, no. 3, p.638,Jan.2022.
[9] K. Alibabaei, P. D. Gaspar, and T. M. Lima, “Crop yield estimation using deep learning based on climate big data and irrigation scheduling,” Energies, vol. 14, no. 11,p.3004,May2021.
[10] K. Alibabaei, P. D. Gaspar, E. Assunção, S. Alirezazadeh, and T. M. Lima, “Irrigation optimization withadeepreinforcementlearningmodel:Casestudy on a site in Portugal,” Agricult. Water Manage., vol. 263,Apr.2022,Art.no.107480.
