Rider Ready- Bike parts purchase portal with smart cart
Harshit Parasrampuria1, Manali Rathod2, Pratik Sherlekar3 , Pranav Temkar4 ,Prof. Amruta Sankhe5
1Harshit Parasrampuria, Dept. of Information Technology Engineering, Atharva College of Engineering 2Manali Rathod, Dept. of Information Technology Engineering, Atharva College of Engineering 3Pratik Sherlekar, Dept. of Information Technology Engineering, Atharva College of Engineering 4Pranav Temkar, Dept. of Information Technology Engineering, Atharva College of Engineering
5Prof. Amruta Sankhe, Dept. of Information Technology, Atharva College of Engineering, Maharshtra, India ***
Abstract - This paper presents the design and implementationof a bike parts purchasing portal thatutilizes the Apriori algorithm for cart recommendations. The association rules were trained by minimum support=3, minimum confidence=20%andminimumlengthswere9,7and 6,5. The portal provides an easy and convenient platform for customers to purchase bike parts and also has the option to book for installation services. The Apriori algorithm is employedto analyze customer purchase behaviorandsuggest items that are frequently bought together, thus enhancingthe customer shopping experience. The chatbot is integrated to provide instant support for customers and assist with their purchases. The portal is user-friendly and aims to simplify the process of purchasing bikeparts,makingitaone-stop-shopfor all biking needs.
Key Words: Bike, apriori, chatbot, workshop, website, filtering, php, comparative analysis.
1. INTRODUCTION
Riding a motorcycle is a passion for many and requires constant maintenance to keep it in top shape. With the increase in the number of riders, there is also a growing demand for motorcycle parts and accessories. However, findingtherightpartsandmakingthepurchasecanoftenbe a time-consuming and challenging task. To address this problem,anewportalforpurchasingmotorcyclepartshas beendeveloped.ThisportalutilizestheApriorialgorithmfor cart recommendations and has a chatbot for customer support.Italsoprovidestheoptiontobookforpartfittings, making it a comprehensive solution for all motorcyclerelatedneeds.TheuseoftheApriorialgorithmensuresthat customers receive relevant and personalized recommendations,streamliningthepurchasingprocess.The integration of a chatbot provides instant support and enhancestheoverallcustomerexperience.Thispaperaims to present the design and implementation of this unique portal,offeringaone-stop-shopforallmotorcyclepartsand accessories.
1.1-Need
Indiahasthelargestnumberoftwowheeledvehiclesinthe world and hence the largest number of consumers who frequentlyneedtoreplacecertainparts.Goingtoacompany garageisnotalwaysfeasiblesopeoplerelyonindependent motorgarages.Itfrequentlyleadstogaragesusingsubpar components and cause accidents and increased costs. Our portal will ensure that the parts are purchased from the actual manufacturers who made their vehicles. While purchasing the product the customers can also select the vendors for the garages to replace the parts that they purchased. In this way vendors get new business and the customersgetassurancethatthepartstheypurchasedare authentic.Thevendorswhohaveofflinestoresgetachance tointegratetheirbusinesswithtechandbecomeapartof themoderntechbusinessworld.
2. Application
Everypersonwhousesabikecanusetheportaltopurchase partsthatrequireperiodicreplacementlikeengineoil,brake wiresandmanymore.Peoplewhowanttopurchasespare partscanpurchaseindividualproductsandkeepthemfor emergency. The smart cart option gives users a recommendation on which products are frequently purchasedwiththeirproductssotheyhaveabettercartof products that is learnt from collective intelligence. The vendorsbasedonlocationcanbebookedforconsultationor to fit the parts that have been purchased. Portal is also a vendoraggregatorwherethevendorsgettheirownloginids andtheycangetbusinessesandacceptorrejecttheorder themselves.Theycanalsoviewtheordersofothervendors which will promote healthy competition and result in competitivepricesfortheusers.
3. Literature Survey

A. Car Recommendation System for Dealers in Different European Countries
This paper discusses the creation of a car recommendation system for various European countries
using collaborative filtering (CF). Unlike content-based filtering, which relies on the attributes of an item, CF recommends items based on each user's historical information.Thisapproachwaschosenduetoitsadvantage inpersonalizedrecommendations.Theusermodelwasbuilt using data on brand, model, car sales, and country. The model calculates the similarity between business pairs to providerecommendations.Ourmodelsuccessfullypredicted the top 5 selling cars in each country with a mean square error(MSE)of8.086.Whenpredictingandtestingcarswith arankhigherthan3,theMSEwas0.4241379.However,due toalackofdata,theMSEofthefullmodelwasslightlyhigh.
B. Multi-Context Recommendation Systems (CARS) in Autonomous Driving and Other Applications
Recommendationsystems(RS)playacrucialrolein enhancing user experience by providing instantaneous suggestions for desired items. Context-aware recommendation systems (CARS) aim to optimize the RS further by considering various contextual factors such as locationandtime.Byincorporatingmulti-contexts,CARSadd morenuancetotheprocessofpredictingitems,resultingin morepersonalizedrecommendations.Thispaperexplores the foundations of recommendation systems, including categories, evaluation metrics, datasets, and challenges. Additionally,thepaperhighlightstheeffectivenessofCARS inautonomousdrivingbypresentingthreeCARSmodelsand their experimental results. The study shows that multicontexts provide drivers with more personalized options, allowing them to make intelligent decisions while on the road.
C. ROS2-based Gadgets for Motorcyclists
In this paper, we introduce a collection of motorcyclegadgetsintendedtoenhancethesafety,comfort, anduserexperienceofmotorcyclists.Theimplementationof thesegadgetswastestedinasimulationenvironment,and the results of these tests are presented herein. The set of gadgetsincludesasmarthelmet,ahapticjacket,andapairof hapticgloves.Thesmarthelmetisequippedwithapairof smartglassesandaheadset,whilethehapticjacketfeatures vibrationmotorsandLEDindicators.Additionally,thehaptic gloveseachincludeavibrationmotor.
D. Smart Security Systems for motorbikes
The objective of this paper is to present the development of a universal algorithm for an intelligent safety system designed for motorcycles. Additionally, the paper discusses the creation of a prototype to enable the final implementation and tuning of the algorithm. The prototype comprises an IoT Kit that uses an ARM M3+ microcontroller,aGPSmoduleforpositionevaluation,and

bothGSMandBluetoothmodulesforcommunication.The articlealsoprovidesadetaileddescriptionofthedesignand functionofanAndroidapplication,whichservesasaGUIfor Bluetooth communication between a smartphone and the safetyprototype.
4. Proposed approach
Theproposedapproachforthemotorcyclepartspurchase portal involves the integration of multiple technologies to provideanenhancedcustomerexperience.Firstly,userhas tologinusingtheuseridorgenerateanewone.Aftereach transactionontheusersside,dataiscollectedandanalyzed usingtheApriorialgorithmtogenerateitem-itemassociation rulesandmakepersonalizedcartrecommendations.There will be an option to log in for the admins to manage the website and prevent fraud. The catalogue will be editable directly through the interface and not dependent on the backend team for every minor update. Additionally, the portaloffersanoptiontobookpartfittingsoffline,allowing customerstoreceiveprofessionalinstallationservices.These orders will be approved or rejected by the vendors themselves through specialized login ids. Customers also have an option to book vendors to fit the parts they have purchased.Bybringingtogetherthesefeatures,theproposed approach aims to create a comprehensive solution for purchasingmotorcycle parts andaccessories,streamlining the process and providing a convenient platform for customersandvendorswhowillgetnewcustomers.
5. Methodology A. Dataset
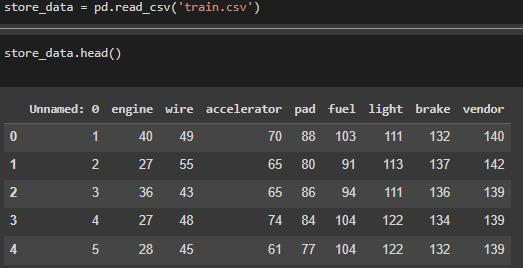
Thedatasetiscollectedfrompurchasesmadebyusersonthe website.Thetransactionsthatwerefinalizedwerestoredina different database, When the database grew to sufficient numberoftransactions,thetransactionswereextractedtoa csvfile.Thiscsvfilecontainedthetransactionswhichwillbe usedtogeneratetheassociationrules.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
B. Pre-processing
The data was pre-processed by removing incomplete transactionsandtransactionsthatwerefraudulentaswellas duplicate in nature. The rows were numbered and the columnswererenamedsothatthedatalabelscanbeselected atthetimeofgeneratingrules.
C. Apriori Algorithm
Apriori algorithm predefined class apyori was used to generatetheassociationrules.Thefunctionwaspredefined and hence the support, confidence and length of the association rules needed to be selected according the requirement.Thesupportwas3,confidencewas20%andthe lengthswere9,7,6,5fordifferentlengthsofassociationrules generation.
5. ALGORITHMS USED
5.1 Apriori Algorithm
Fig.codefortheapriorialgorithm
D. Results
Theresultswere12associationrules.5rulesoflength9,3 rulesoflength7,2rulesoflength6and2rulesoflength5. The rules were frequent item datasets. Hence the results werereadyandenteredintotheprioritytable.Duetothis, therecommendedproductsaccordingtopreviousdataare nowdisplayedbeforeotherproducts.
Aprioriisapopulardataminingalgorithmthatisusedfor discoveringfrequentitemsetsandassociationrulesinlarge datasets. The algorithm is based on the Apriori principle, whichisusedtoprunethesearchspaceefficientlyandreduce thenumberofcandidaterulesthatneedtobeevaluated.The algorithmconsistsoftwophases:thecandidategeneration phaseandthecandidateevaluationphase.Inthecandidate generationphase,thealgorithmgeneratesasetofcandidate itemsetsoflengthkbasedonthefrequentitemsetsoflength k-1.Thisisdonebyjoiningeachfrequentitemsetwithitself andpruninganyresultingitemsetsthatarenotfrequent.The algorithmthencountsthesupportofeachcandidateitemset, whichisthenumberoftransactionsthatcontaintheitemset. Ifthesupportofacandidateitemsetisgreaterthanorequal totheminimumsupportthreshold,itisaddedtothesetof frequent itemsets. In the candidate evaluation phase, the algorithm generates association rules from the frequent itemsets.Foreachfrequentitemset,thealgorithmgenerates allpossiblenon-emptysubsetsandcomputestheconfidence of each rule. The confidence of a rule is the ratio of the support of the rule's antecedent and consequent to the supportoftherule'santecedent.Iftheconfidenceofaruleis greaterthanorequaltotheminimumconfidencethreshold, theruleisaddedtothesetofassociationrules.Apriorihas somelimitations,suchashighcomputationalcomplexityand sensitivity to the minimum support threshold. To address theselimitations,severalvariationsandimprovementsofthe algorithm have been proposed, such as FP-growth and ECLAT. However, Apriori remains a popular and effective algorithmforassociationrulemininginvariousdomains.
A. Apriori Principle
The Apriori principle is a concept used in the Apriori algorithm, which is a popular data mining algorithm for discoveringassociationrulesinlargedatasets.Theprinciple isbasedontheobservationthatifasetofitemsisfrequent, thenallofitssubsetsmustalsobefrequent.Inotherwords,if agroupofitemsoccursfrequentlytogetherinadataset,then any subset of that group must also occur frequently. This principle is important because it allows the algorithm to efficientlyprunethesearchspaceandreducethenumberof candidate itemsets that need to be considered. By only consideringfrequentitemsets,theApriorialgorithmisableto focus on the most relevant relationships between items, which greatly improves its efficiency and effectiveness.[5][6][7][8]
B. Candidate itemset
Acandidateitemsetisasetofitemsthatisgeneratedduring thefirstphaseoftheApriorialgorithm.Thisphaseiscalled
thecandidategenerationphase,anditinvolvesgeneratingall possible combinations of items up to a certain length. The candidateitemsetsarethenevaluatedinthesecondphaseto determinetheirfrequencyandfilteroutinfrequentitemsets. The remaining frequent itemsets are used to generate association rules. The size of the candidate itemset grows rapidlyasthelengthofthe itemset increases,and this can leadtoacombinatorialexplosion.Toaddressthisissue,the ApriorialgorithmusestheAprioriprinciple,whichstatesthat if an itemset is frequent, then all its subsets must also be frequent.Thisprincipleenablesthealgorithmtoefficiently prunethesearchspaceandreducethenumberofcandidate itemsetsthatneedtobeevaluated.[9][10]
C. Frequent itemset
Infrequentitemsetmining,afrequentitemsetreferstoaset of itemsthatfrequentlyappear together ina transactional database. It is used as the basis for generating association rulesindatamining.Thefrequencyofanitemsetismeasured bythenumberoftransactionsthatcontainalltheitemsinthe set.Afrequentitemsetcanbeofanysize,fromasingleitem toseveralitems.Findingfrequentitemsetsisanimportant stepinmarketbasketanalysisandotherapplications,asit helpsidentifypatternsandrelationshipsbetweenitems.The Apriorialgorithm,forexample,generatesfrequentitemsets in a systematic way, by first identifying all frequent single items and then gradually extending them to larger itemsets.[11][12]
5.2 Priority Algorithm
A priority algorithm is a commonly used technique for assigningimportanceorsignificancetoasetofitemssuchas tasks, projects, or research papers. It works by evaluating differentfactorssuchasurgency,potentialimpact,andthe amountofeffortrequiredtocompleteatask.Byanalyzing thesefactors,thealgorithmassignsapriorityvaluetoeach itemwhichhelpsindividualsororganizationstodetermine whichitemsrequirethemostattentionandresources.For instance,inprojectmanagement,apriorityalgorithmisused toprioritizetasksandallocateresourcesefficiently.Urgent tasksaregivenahigherpriorityandaddressedfirst,while tasksthatcanwaitareassignedalowerpriority.Similarly,in academicresearch,apriorityalgorithmcanhelpresearchers prioritize research papers to read and evaluate by consideringfactorssuchasrelevancetotheirresearch,the reputation of the authors, and the significance of the findings. In general, the use of a priority algorithm helps individuals and organizations to manage their resources effectivelyandachievetheirgoalsefficiently.Byfocusingon the most important or urgent items, they can increase productivity,meetdeadlines,andultimatelyachievesuccess. Thespecificfactorsconsideredinapriorityalgorithmmay varydependingonthecontextandgoalsoftheindividualor organization,buttheoverallobjectiveremainsthesame-to
assignpriorityvaluesthatreflecttherelativeimportanceof eachitem.[13][14][15][16][17][18]

6. Architecture
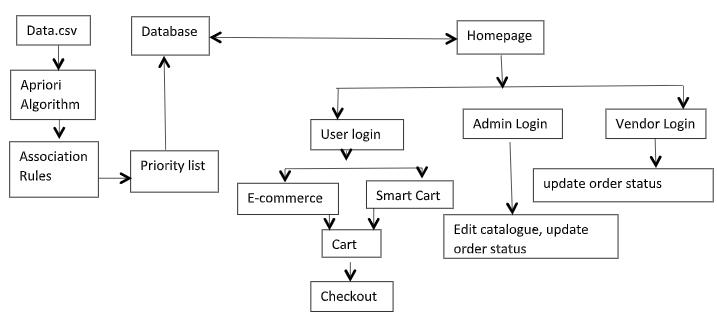
Fig.architectureoftheproject
7. Methodology
Awebsiteusingphpforthebackendwascreated.Navigation baritemssuchasecommerce,userlogin,vendorloginand adminloginwereadded.Thebackendwasdoneinsqlwhere multiple tables were created to store the permanent data such as the products, categories and user accounts. Every singledataentryinthetablescanbeeditedordeletedwith the exception of the transaction saving database which storestheusertransactionstotrainapriorialgorithm.The admin portal has a graphical interface to edit the product description and pictures. The different categories can be switchedofffromtheadminloginitselfincasetheproductis not is stock. The chatbot and the payment gateway were addedseparately.[3][4]
The apriori algorithm was used to generate the frequent associationrulesbasedonadatabasetrain.csvgeneratedby extractingthetransactiondatafrombikw_transaction.sql.
Thecodewaswritteninpython3andtherulesweremined withaminimumsupportof0.019andconfidenceof20%.
13rulesweregeneratedandthesizeoftheitemsetsvaried between 4-8 items. The results were then extracted in a separatecsvfilesandintegratedintotheportal.[1][2]
8. Software Requirements
1.OperatingSystem:Windows10orlater
2.Server:XAMPP7.4
3.ProgrammingLanguages:
PHP7.0andabove
HTML3.0andabove
CSS
JavaScript
Python3.10
4.FileFormats: CommaSeparatedValues(CSV)
9. Results
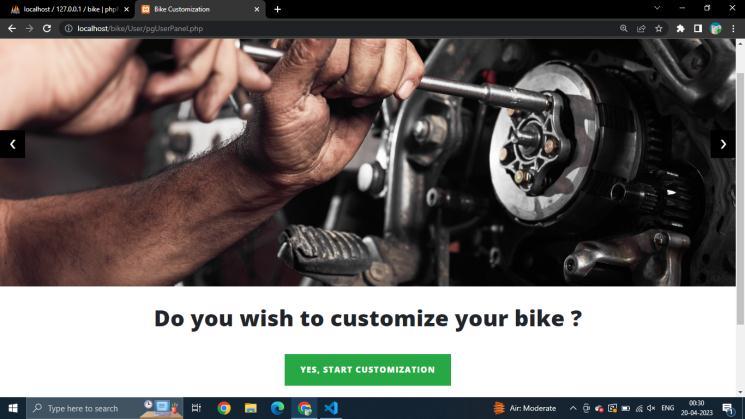
Thewebsitestartswithastartcustomizingpagewhichhas thesmartcartrecommendations.
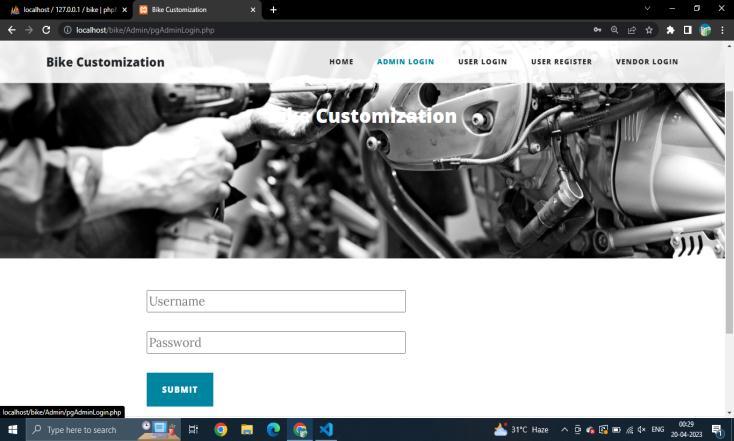

The login page for admin, user and vendor are different. Logincanbedonebyenteringcorrectuseridandpassword combination
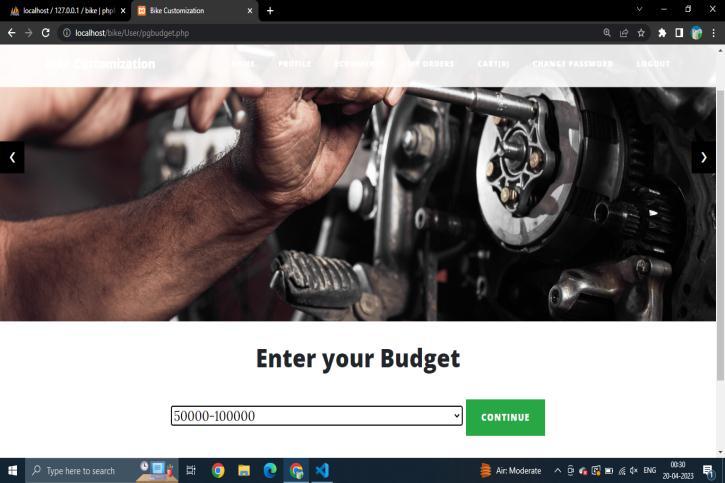
Theproductsareshownaccordingthebudgetselected by the user. The budget can be selected using a simple dropdownmenu.
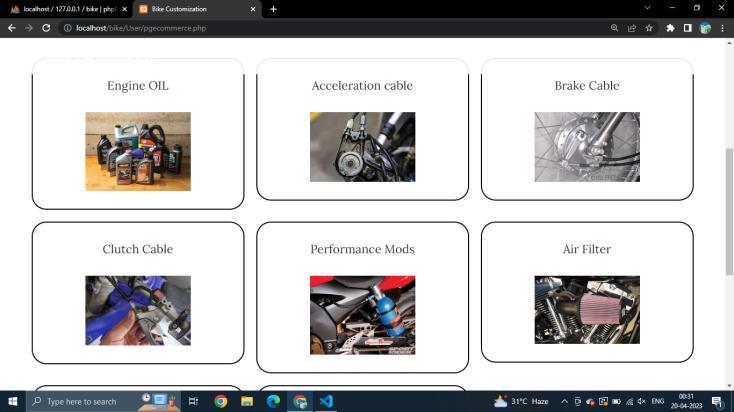
Ecommercesectioncandifferentcategoriesincaseauser wants to be specific with their purchase and not buy accordingtothesmartcart.
After completing the purchase users are redirected to the cartpagewheretheycanreviewandedittheirorders.
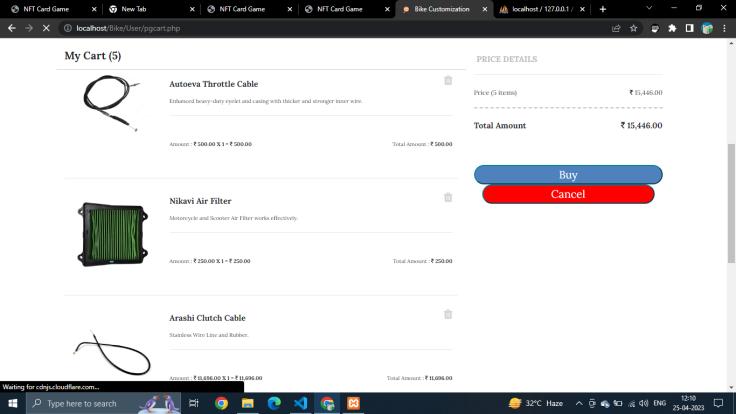
Cart
Thenthebuynowclickredirectstheuserstotherazorpay transactiongatewaywherethepaymentcanbemadebyany method accepted by the gateway or simply click cash on deliveryoption.
11. CONCLUSIONS
Theprojectwassuccessfullyimplementedandalltheinitial requirements were fulfilled. The smart cart recommendations are retrained every time there is a significant increase inthe number of transactionsand the recommendationsarehelpful.Thewebsiteisresponsiveand fast, users can use it through their phone too. The order trackingisaccurateandtherearenoactivebugs.
12. REFERENCES
[1] T. Deekshitha, M. Venkatesan, and S. Vijayalakshmi, "DesignandImplementationofaWebPortalforPurchasing Bike Parts with Smart Cart," International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 1653-1659,2021.
[2] S.V.S.S.Satyanarayana,P.S.Reddy,andP.V.S.S.S.G. Gupta,"SmartShoppingCartSystemforEfficientShopping," International Journal of Innovative Technology and ExploringEngineering,vol.8,no.6S,pp.1049-1052,2019.
[3] M. V. Kumar, R. Vinodh Kumar, and B. Anjaneyulu, "DevelopmentofaWeb-basedE-commerceSystemforBike Parts," International Journal of Advanced Research in ComputerScienceandSoftwareEngineering,vol.9,no.3,pp. 443-447,2019.
[4] S. Kumar andA. Kumar,"Designand Development of Online Bike Parts Purchase Portal with Smart Cart," InternationalJournalofComputerSciencesandEngineering, vol.9,no.6,pp.383-389,2021.
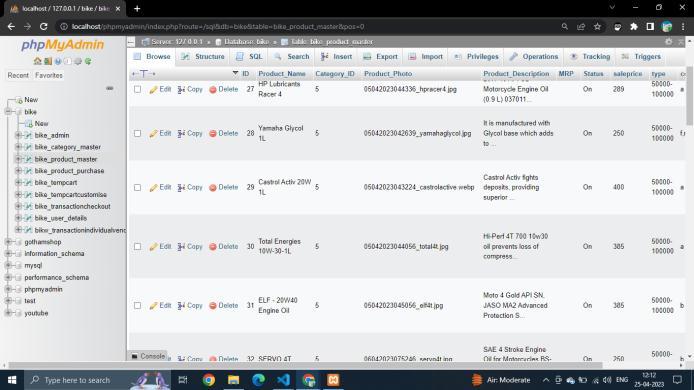
Fig.Database
All of the customer data is stored/retrieved from the sql databaseaccessiblefromthephpmyadminpage.Thereare differenttableswithmultipleattributes.
10. Future Scope
Addingmorevendorsiskeytogivingusersabetterchoice among them. We also wish to add a feedback form for grievancesrelatedtothevendorsandaratingsystembased on 5 star grading after completion of each order. The number of orders completed by each vendor will also be displayed and discount coupon application will be added. The product list will be expanded to more products and categoriessouserswillhaveanevenlargerpoolofproducts tochoosefrom.Customersupportintheformofachatbot forsimplequeriesandhumaninteractionincaseoflarger querieswillbeadded.Thetrainingofthedatawillbedone via fp-tree algorithm to manage with the scaling of the project.
[5] H. Garg and N. Gupta, "A Comprehensive Study on EcommerceWebsitesandCustomerSatisfaction,"Journalof Applied Engineering Research, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 328-333, 2018.
[6] R.KaurandS.Dhiman,"AStudyofUserPerceptionand ExpectationtowardsOnlineShopping,"InternationalJournal ofScientificResearchinComputerScience,Engineeringand InformationTechnology,vol.6,no.1,pp.24-28,2021.
[7] N. N. Al-Madi and M. A. Almulla, "Factors Affecting OnlineShoppingBehavior:AStudyofKuwaitiConsumers," JournalofInternetBankingandCommerce,vol.25,no.2,pp. 1-19,2020.
[8] Priority-Based Scheduling Algorithm for Real-Time Systems" by R. S. Panda and R. K. Sahoo, published in the International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security(IJCSNS),Vol.8,No.4,April2008.
[9] Liu,B.,Hsu,W.,&Ma,Y.(1999).Integratingclassification and association rule mining. In Proceedings of the Fourth

International
Volume:
InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryandData Mining(KDD-99)(pp.80-86).
[10] Savasere,A.,Omiecinski,E.,&Navathe,S.(1995).An efficient algorithm for mining association rules in large databases. In Proceedings of the 21st International ConferenceonVeryLargeDataBases(VLDB)(pp.432-444).
[11] Park,J.S.,Chen,M.S.,&Yu,P.S.(1995).Aneffective hash-based algorithm for mining association rules. In Proceedings of the 1995 ACM SIGMOD International ConferenceonManagementofData(pp.175-186).
[12] Han,J.,Pei,J.,&Yin,Y.(2000).Miningfrequentpatterns without candidate generation. In Proceedings of the 2000 ACMSIGMODInternationalConferenceonManagementof Data(pp.1-12).
[13] Zhang, H., & Ramakrishnan, R. (2002). Optimal grid layoutfordatamining:acasestudyoftheApriorialgorithm. In Proceedings of the 2002 ACM SIGMOD International ConferenceonManagementofData(pp.567-578).
[14] Priority-Based Scheduling Algorithm for Real-Time Systems" by R. S. Panda and R. K. Sahoo, published in the International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security(IJCSNS),Vol.8,No.4,April2008.
[15] A Dynamic Priority Queue Algorithm for Real-Time Embedded Systems" by H. Abeni, M. Caccamo, and L. Palopoli,publishedintheProceedingsoftheIEEEReal-Time SystemsSymposium,2003.
[16] Priority-Based Scheduling in Real-Time Systems: A Survey"byC.C.HsuandW.K.Shih,publishedintheJournal ofSystemsandSoftware,Vol.81,No.9,September2008.
[17] APriority-BasedAlgorithmforResourceAllocationin CloudComputing"byH.Wang,Y.Zhang,andX.Li,published in the Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International ConferenceonCloudComputingandIntelligenceSystems.
[18] AnImprovedPriority-BasedSchedulingAlgorithmfor Real-TimeSystems"byM.H.JafriandM.S.Bhatia,published in the Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT).

