AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF SEVERITY GRADING IN DIABETIC RETINOPATHY USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK
Sharan. M 1, Rithik. S2, Lakshmi Priya. S 3
1Department of computer science and Engineering, Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, Tamil Nadu, Chennai
2Department of computer science and Engineering, Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, Tamil Nadu, Chennai
3Assistant Professor, Department of computer science and Engineering, Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, Tamil Nadu, Chennai ***

Abstract – The primary reason for middle-aged people's eyesight is age is diabetic retinopathy (DR). Early identification of the development of diabetic retinopathy can be very beneficial for clinical treatment. Although several different feature extraction various strategies have been put forth, and the classification job for retinal images is still tedious and time-consuming even for those trained clinicians. Hence, primary screening of DR is to avoid vision loss, it is advised that diabetic patients have this procedure performed at least once a year. Recently, deep convolutional neural networks have manifested superior performance in image classification compared to previous handcrafted feature-based image classification methods. As a result, a Random forest classifier has been developed that can distinguish the intricate elements required for classification, such as micro-aneurysms, exudate, and hemorrhages on the retina, and then automatically deliver a diagnosis without human input. Last but not least, a CNN-based automated DR screening approach for retinal pictures is suggested. This method displays the different phases of DR (Mild, Moderate, and Severe) as well as its attention map for the region that is most affected. It also reduces the workload of ophthalmologists. Thus the proposed system of CNN classifier gives a significant improvement in terms of speed and accuracy when compared to previous methods.
Key Words: Diabetic retinopathy (DR) Fundus Images (FIs),micro aneurysm (MA), Flame-shaped haemorrhages (FSHs), Convolutional Neural Network(CNN)
1. INTRODUCTION
Imageprocessingisaformofprocessingimagesthoseare either captured as pictures or frames for which the input is given as an image and the output of the image processing is also a picture associated with the image[1]. Image processing refers to digital image processing but the visual and analog processing is feasible as well[2]. Medical Image Processing is in which the images generatedfromthehuman bodyformedicalpurposesare subjected to processing. It helps easily to detect and
identifythedisease[3].DiabeticOneofthemainreasonsof retinal degeneration (DR) is sightlessness and there subsist valuable behaviours that hold back the development of the disease provided that it would be identifiedintheearlystage[4].Normalretinalassessment of the diabetic patients guarantees an early identification of DR, which considerably reduces the occurrence of blindness[5].Duetothehighprevalenceofdiabetes,mass screening takes a lot of time and requires a large number of qualified graders to carefully examine the fundus images looking for retinal abnormalities. Diabetes and otherdisorderslinkedtoagingandsocietyareontherise rightnow[6].Theissuesrelatingtotheeyescanbedivided into two main categories. The first is eye disease, such as cataract, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, and glaucoma. The second group is categorised as lifestyle-related diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, and atherosclerosis. Diabetescanharmtheeyesbydamagingtheretinalblood vessels, which can ultimately lead to visual loss. When diabetes is treated using prosthetic retinas, Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the name used to describe this condition[7].Oneofthetreatmentstoreducetheamount ofvisualmutilationprocessedbyDRhasbeenidentifiedas early detection and diagnosis, with a focus on routine medical examinations for the identification and supervision of this condition. During this method, retina images, also known as fundus images (FIs), are carefully processed using a medical imaging camera and are physically checked for the presence of DR objects by screeners and ophthalmologists. Diabetic Retinopathy is an eye condition that diabetes patients experience to a great extent. If a diabetic patient's blood sugar levels are too high, the blood vessels at the back of their eye will be destroyed,whichpreventstheretina fromgetting enough nutrients to adequately retain their vision [8]. One of the main reasons for visual loss worldwide is diabetic retinopathy, also known as DR [9]. It is one of the main causes of preventable blindness and vision impairment [10].The prevalence of DR among diabetic patients globally was found to be 7.62%–47.1% based on a metaanalysis of 35 studies from 35 different countries. The second category of DR severity is non-proliferative
diabetic retinopathy. NPDR and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).There are three levels of NPDR: mild, moderate,andserious.Microaneurysm(MA)anddot/blot haemorrhage (HA) are early stages of mild NPDR. As the illness advances, flame-shaped haemorrhage’s (FSHs), cotton-wool patches, and hard exudates (HEs) In the moderateNPDRstage,(CWSs)becomevisible.Manymore MAs, HAs, or venous beading (VB) arise in the severe NPDR stage[11]. The most advanced form of DR is called PDR. Neovascularization (NV), pre-retinal haemorrhage’s (PHs), vitreous haemorrhage’s (VH), and fibrous proliferation(FP),whichisthesourceoftractionalretinal detachment, are the important pathologies[12]. Early screeninganddiagnosisofDRinthesediabeticpeoplecan stop vision loss and blindness. However, there isn't an ophthalmologist nearby in a remote rural region[13]. Consequently, an automation software is developed that can screen and DR with pathology extraction using algorithms for digital picture processing[14]. It is anticipated that this software will be a useful tool for medical professionals with limited expertise in DR diagnosis.
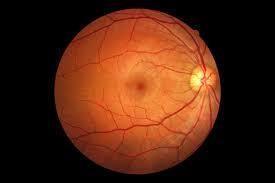
Fig.1.2:(a)NormalRetina (b)DiabeticRetina
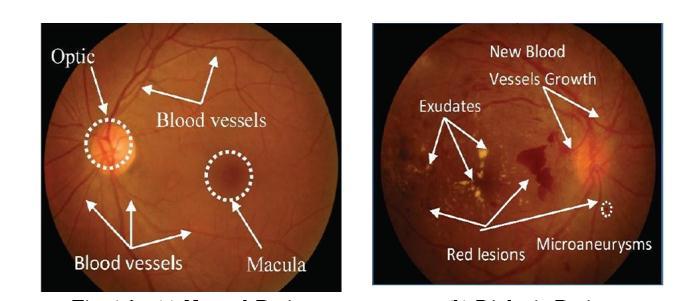
Fig.1.1:HumanRetina
Figure1.1illustratesthefundusimageofanormalhuman retina. The retina is made up of a thin layer of lightsensitive tissue that is located close to the optical nerve. Light beams are concentrated onto the retina, where they aresubsequentlysenttothebrainforinterpretationofthe images. The macula, a relatively tiny region, is located at themiddle ofthe retina.Thepossibilityofpinpointvision is due to the presence of this macula that plays a major role in reading, writing or recognition of face[15]. The retinaisinturnsurroundedbyperipheralretina.Without the presence of retina, efficient communication between theeyesandbrainarenotpossiblewhereasonlyvision is possiblethroughit.
Diabetic retinopathy typically affects both eyes. In the early stages of the sickness, those who are frequently affected by the disorder do not notice changes in their eyesight. But, when it worsens, it frequently has irreversible effects; including vision loss. Figure 1.2 illustratesthenormalretinaversusdiabeticretina.
In the stage of diabetic retinopathy, blood vessel fluid leakage into the eye causes scarring of the retina. The onset of is the first sign of diabetic retinopathy. Haemorrhage in the retina[16]. The methods, algorithms, andtechniquesused toidentifyhaemorrhagefromretinal images of diabetic retinopathy are reviewed and explained. A fundus image-based algorithm based on a universal logical approach has been developed to detect the presence of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) correlated lesions. It can distinguish between red and bright lesions and does not require any special pre- or post-processing. Several actions are carried out, and coloured retinal images are used to assess the various stages of diabetic retinopathy[17]. Micro aneurysms, which resemble small, secular pouches and look as tiny red dots, are brought on by a localised enlargement of the capillary walls. Another idea contends that the walls are brittle and prone to shattering, which might result in haemorrhages. Hard exudates are yellow lipid deposits that appear as vivid yellow lesions. The light, spherical region known as the optic disc is where the blood vessels initially develop. Visual acuity is greatest in the fovea, the central region of the retina. A mixture of interior components of microaneurysm detectors including macular centre and retinopathy-relatedlesiondetectionusingspecificallypreprocessing methods and applicant extractors are proposed[18]. The earliest stage of the illness is nonproliferative diabetic retinal disease, where the retinal blood vessels leak fluid or bleed. In NPDR, the arteries in the retina turn out to be very weak and they tend to be veryminuteanddotlikehaemorrhageswillbeseen.These types of weak blood vessels generally tend to swell or cause edema in the retinal image and it results in decreased vision. The symptoms of this disease will be mild or non-existent. Micro aneurysms, haemorrhages, hardexudates,macularedoema,andmacularischemiaare alterations brought on by NPDR that affect the eyes. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) is now present since the illness has advanced to that point. PDR causes circulationproblems,whichmakesomepartsoftheretina ischemic or oxygen-depleted. New blood vessels become part of the circulatory system that helps the retina maintain enough oxygen levels[19]. Neovascularization is thewordforthis.Bloodmayenterthevitreousandretina, causing spots or floaters that are consistent with visual loss.SDRcausesaberrantvasculargrowthandscartissue,

which can be major difficulties for glaucoma, immediate retinaldetachment,andgradualvisionloss.
1.2. Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Certainsymptomsofdiabeticretinopathyidentifiedbythe research community are the observation of spots, dots or cobweb-like dark strings floating in the vision of the patients. Some patients experience hazy vision and a cyclicalchangeintheireyesightfromblurrytoclear.Some patients may experience black or dark spots in their field ofvisioninadditiontohavingimpairednightvision,which can ultimately lead to visual loss[20]. The retinal vessels are connected for a few more reasons. According to reports, this happens when the blood capillaries in the retina change, impacting diabetes patients and even leadingtoeyesightloss.Oncertaincasesthepatientswith retinal vessels suffer swelling and also observe leak fluid thatcannotbereversedaffectingthepatientsinlarge.
2. METHODOLOGY AND ALGORITHMS
2.1 Modules
2.1.1. Pre-processing
i. Augmentation
Augmentation can add randomized rotations to input images so that a network is invariant to the presence of rotationininputimages.
Input:Retinalfundusimage
Output:Augmentedimages
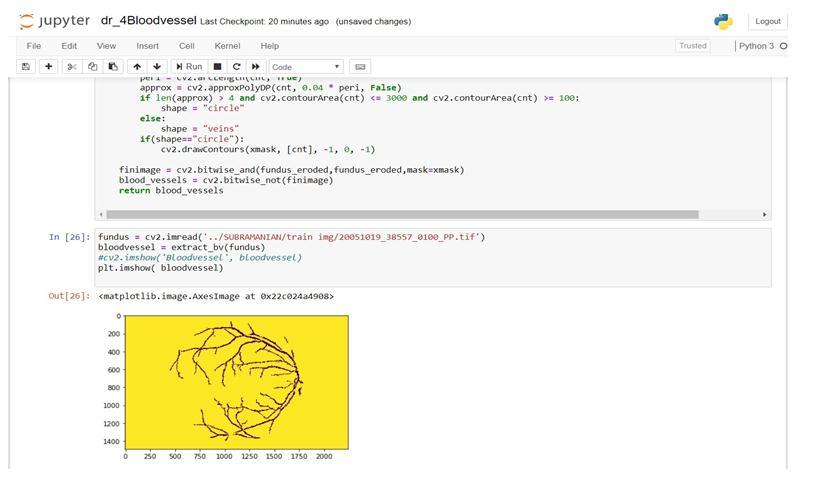
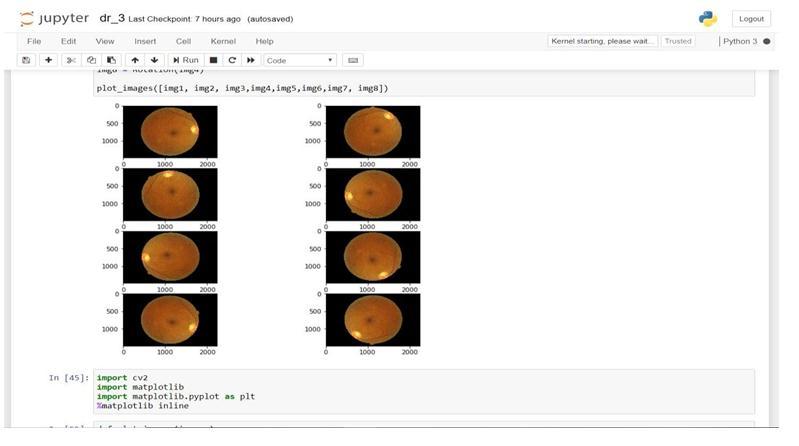
Figure2.1.1:Augmentationofretinalimage
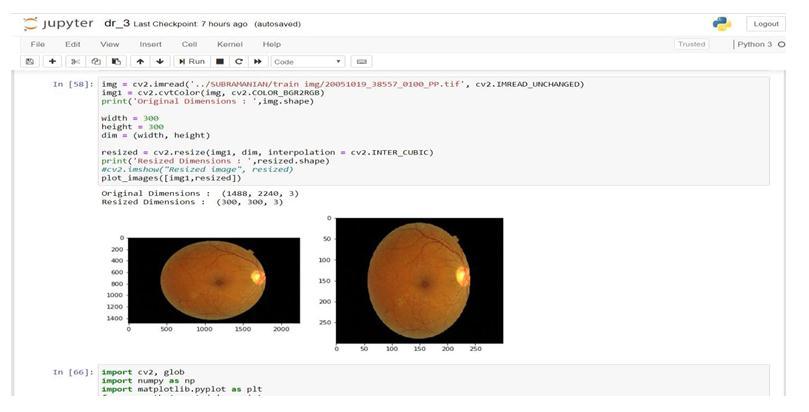
ii.ResizeandNormalize

Imageresizingincreasesor decreasesthetotal number of pixels.
Normalizationisa processthatchangestherangeofpixel intensityvalues.
Input:Augmentedimages
Output:Resizedimage
2.1.2. Segmentation
The tiny, elongated structures in the retina are blood vessels. By segmenting blood vessels in retinal images, early illness identification is made possible. Automating this process has various advantages, including reducing subjectivityandremovinglabor-intensivesteps.Theoptic disc,which representsthe beginningoftheoptic nerve, is where the fibres of retinal ganglion cells converge. At the opticdisc,theretina'smajorbloodarteriesalsoenter.The fovea, a 1.5 mm broad depression on the internal surface of the photoreceptor layer, is made entirely of cone photoreceptorsand istailoredforthe bestpossiblevisual acuity. The 0.5mm-diameter foveal avascular zone is a region inside the fovea (An area without any blood vessels).
Input:Resizedimage
Output: Image segmented with Blood vessel, Optic disc andFovea
2.1.3. Classification
The final test item class is then chosen by averaging the votes from numerous decision trees from a randomly chosenportionofthetrainingset.
Input:SegmentedImages
Output: Image with diseases (MA, Haemorrhages, Exudates)
3.1 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
This chapter discusses the overall system architecture anddetaileddescriptionofallmodules.
2.1.4. CNN Classifier
Convolutional neural networks are one sort of artificial neuralnetwork(CNN).Itemploysperceptron,atechnique for supervised learning, to examine data. Each individual neurontakesinavarietyofinputs,weighsthem,andthen sends the weighted result through an activation function toproduceanoutput.
Input:Imagewithdisease
Output:ImageclassifiedbasedonseverityofMA
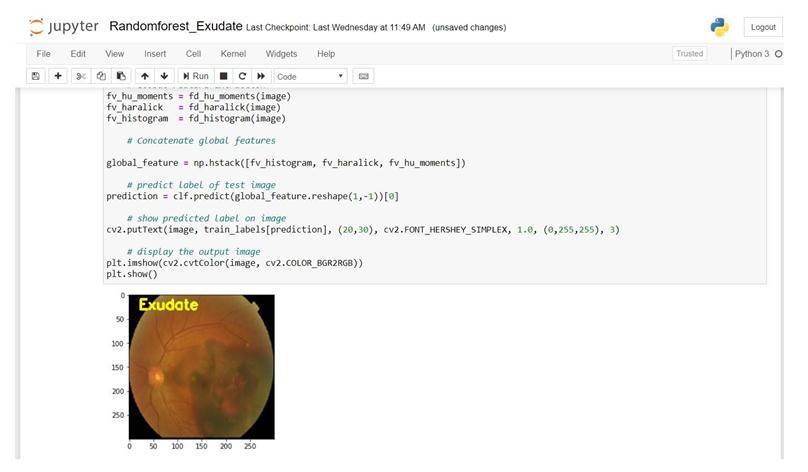
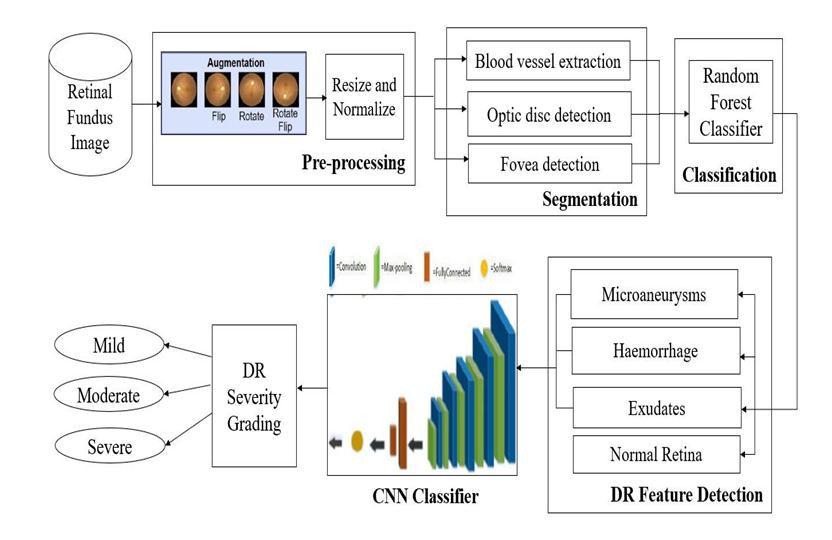
Figure3.1SystemArchitecture
Figure3.1describestheoverallsystemarchitectureofthe proposed DR detection with its severity from Retinal fundusimages.Thissystemstartswiththepre-processing stage where augmentation, resizing and normalization of retinal images is done. Several segmentations, including blood vessels, the optic disc, and the fovea, are found in thepre-processedimages.Usingarandomforestclassifier, the DR features are found in these segmented images. Finally for each DR feature detected the severity of the disease is calculated using the CNN classifier for better accuracy.
3.3 ALGORITHM
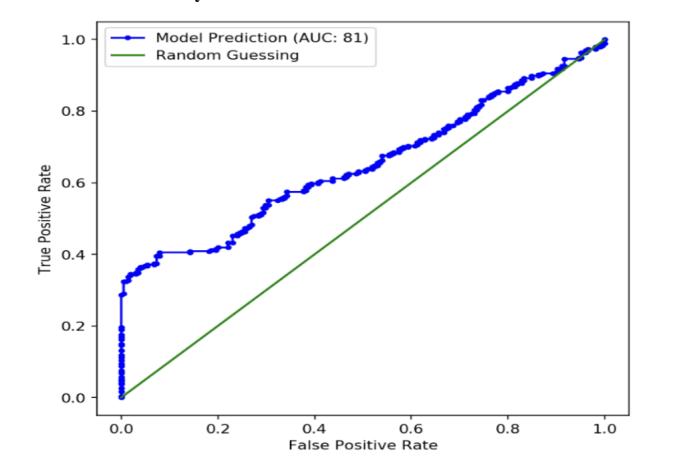
The Machine Learning system uses test data to assess the predictiveaccuracyofthetrainedmodelandtrainingdata to train models to recognize trends. By comparing predictions on the evaluation data set with actual values (also referred to as ground truth) using a variety of measures, machine learning systems assess their predictiveperformance.

• RandomForest
• ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(CNN)
Thismodelemploystwocrucialideasthatgiveitthename random rather than averaging the predictions of trees, whicharereferredtoasthe"forest"
• selecting at random from training sets when creatingtrees
