International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net
1 Asst. Professor, Dept. of Computer Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Maharashtra, India
2 B.E. student, Dept. of Computer Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Maharashtra, India
3 B.E. student, Dept. of Computer Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Maharashtra, India
4 B.E. student, Dept. of Computer Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Maharashtra, India
5 B.E. student, Dept. of Computer Engineering, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Technology, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - Air pollution is a growing concern worldwide, and it has serious implications on human health, the environment, and the economy. In this project, we explore the prediction of Air Quality Index (AQI) using the Random Forest algorithm. AQI is a measureofairpollutionthatisusedtocommunicatethe health risks associated with breathing polluted air. We use historical data collected from various air quality monitoring stations in a city and apply the Random Forest algorithm to predict AQI. This study aims to predict the AQI using machine learning algorithms. The AQI is a crucial indicator of air quality, and accurate forecasting can help mitigate the negative effects of air pollution on human health and the environment. The study utilizes data from air quality monitoring stations andmeteorologicalsensorstotrainandevaluatevarious machine learning models, including Random Forest, Support Vector Regression, and Artificial Neural Networks. The accuracy of the algorithm is measured using the root mean square error . The mean square error and themeanabsoluteerro).Theresultsindicate that the Random Forest algorithm performs well in predictingAQIandhasthepotentialto beusedasatool to monitor air quality and help in making decisions to reduce air pollution. The findings of this study can be usedbypolicymakers,cityplanners,andenvironmental agencies to design effective strategies to combat air pollution.
Keywords: Prediction, Machine Learning, Random Forest, Air Quality, P.M 2.5 , Root mean squared error( RMSE), Mean Squared error(MSE),mean absolute error (MAE)
Airpollutionisapervasiveproblemthataffectsmillions of people worldwide, resulting in adverse health outcomes, environmental degradation, and economic losses. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that air pollution causes around 7 million premature deaths annually, making it one of the leading global health risks (WHO, 2021). Air Quality Index (AQI) is a measure of air pollution that provides information on
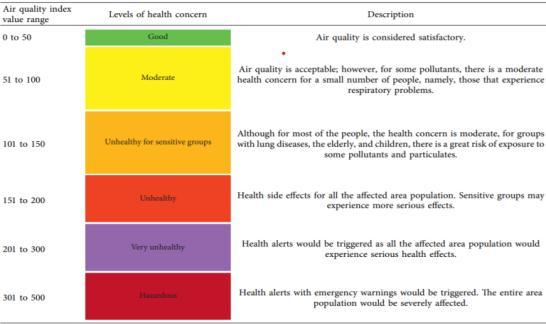
theairqualitystatusandassociatedhealthrisks.AQIisa numerical value ranging from 0 to 500, and it is calculated based on the levels of major air pollutants such as particulate matter (PM), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide(NO2),andsulfurdioxide(SO2).
Variousapproacheshavebeendevelopedtomonitorand manage air quality, including regulatory policies, emissioncontrols,andairqualityforecasting.Airquality forecasting aims to predict future AQI levels using statistical and machine learning models based on historical data and meteorological factors. Machine learning techniques such as Linear Regression, support vector regression (SVR), and decision trees have been appliedtoairqualityforecasting.RandomForest(RF)is a powerful machine learning algorithm that has been usedforAQIpredictioninrecentstudies.
• Airqualityforecastingthatusesmachinelearningto predicttheairqualityindexforagivenregion.
• To achieve better performance than the standard regressionmodels.
• Our goal is for the model to accurately predict Air QualityIndexforIndiaasawhole.
• By forecasting Air Quality Index, we can track the mainpollutantscausingpollutantsandthelocations acrossIndiathatareseverelyaffectedbypollutants.
• By creating a easily operated graphical user interfacewewillhelptheusertokeepatrackofthe airqualityindexanditsattributeonasinglescreen.
AQIisanimportantenvironmentalindicatorthatisused to inform public health and policy decisions. The proposed System using an Enhanced approach using ANN (Artificial Neural Network) is tested using the dataset of list 5 years (2013-2018). The results are compared with previous methods results. These
methods are Random Forest, Linear regression, XG boost , K Nearest Neighbour Regression, ANN .The proposedenhancedmethodforAQIadvantagesoverthis methods.Whencomparedtovariousothermethods,our model gave the most precise forecasts. This technique makes it simple and accurate for meteorologists to forecast the weather and the AQI in the future. Fine material (PM 2.5) may be significant because, once its levelintheairissomewhathigh,itposesaseriousthreat topeople'shealth.Smallairborneparticles,knownasPM 2.5,reducevisibilityandhighlevelsmaketheairlooklike fog.
Clean the data and remove any missing or inconsistent values. There are various techniques which are used in data preprocessing i.e data cleaning , data integration & data transformation, data reduction, data encoding. The overall goal aim of data preprocessing is to insure that the data is ready for analysis or machine learning and thatitwillproduceaccurateandmeaningfulresults.
Select the relevant features from the dataset that can impact air quality. This can be done using statistical techniques or domain knowledge. There are several techniques for feature selection, such as filter methods, wrapper methods, and embedding methods. Filter methodsinvolveevaluatingtherelevanceofeachfeature basedonsomestatisticalmeasure,suchascorrelationor mutual information, and selecting the top-ranked features. Wrapper methods involve selecting features based on the performance of a machine learning algorithm, such as decision trees or SVM, with a particularsubsetoffeatures.Embeddedmethodsinvolve incorporating feature selection into the learning algorithm itself, such as with regularization techniques likeLassoorRidgeregression.

Collect data on various air quality parameters such as particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5), sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), ozone (O3), carbon monoxide (CO),etc.foragivenlocationatdifferenttimes.Thisdata can be obtained of India from local environmental agenciesoronlinesources.
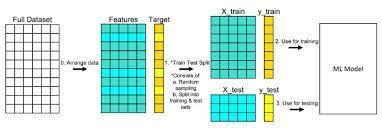
Train-test split is a technique used in machine learning to evaluate the performance of a model on unseen data. Theprocessinvolvessplittingadatasetintotwoparts:a training set and a testing set. The training set is used to train the model, and the testing set is used to evaluate the model's performance. The goal is to train a model that can generalize well to new, unseen data. The splitting of the dataset can be done randomly or using a specifictechniquesuchasstratifiedsampling,wherethe split is done in a way that preserves the proportion of classesorvaluesintheoriginaldataset.
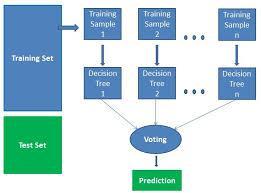
Build a random forest model using the training data. Random forest is an ensemble method that combines multiple decision trees and reduces overfitting. It
belongs to the ensemble learning family of algorithms, which combines multiple models to make better predictions than any individual model. The basic idea behind the random forest algorithm is to build a collectionofdecisiontreesand combinetheiroutputsto makeafinalprediction.Eachdecisiontreeintheforestis trained on a different subset of the original data and a randomsubsetofthefeatures.Bycreatingdifferenttrees based on different data subsets and features, random forest reduces the risk of overfitting and improves the accuracyandstabilityofthepredictions. Whenmakinga prediction, each decision tree in the forest predicts the outcomeindependently,andthefinalpredictionismade bycombiningtheoutputsofallthetrees.Inclassification tasks,thepredictionistypicallybasedonamajorityvote of the trees, while in regression tasks, the prediction is typicallybasedontheaverageoftheoutputsofthetrees.
4)Grid search: Use a grid search to try out all possible combinations of hyperparameters. Grid search is a techniquethatallowsyoutodefineabigvarietyofutility value for every hyperparameter and then conductes the evaluationforthemodelforallpossiblecombinationsof thesevalues.
5) Cross-validation: Perform k-fold cross-validation on each combination of hyperparameters to get a more accurate estimate of the model's performance. Crossvalidation helps to reduce the risk of overfitting and provides a more reliable estimate of the model's performance.
6)Evaluate performance: After completing the grid search and cross-validation, select the hyperparameters thatgivethebestperformanceonthevalidationset.
7)Test on new data: Finally, test the model with the selected hyperparameters on a new test dataset to evaluateitsperformanceinreal-worldscenarios.
Random forest is a popular machine learning algorithm used for regression and classification tasks. It is widely used for air quality index prediction due to its ability to handle non-linear relationships between the input variables and the target variable. However, it is important to evaluate the performance of the Random Forestmodeltoensureitsaccuracyandreliability. some commonly used evaluation metrics for a Random Forest model:
Hyperparametertuningisanessentialstepinoptimizing the performance of a Random Forest model for air quality index prediction. Here are the steps you can followforhyperparametertuninginRandomForest:

1)Split the data: Divide your dataset into a training set andavalidationset.Youcanusea70-30splitora80-20 split,dependingonthesizeofyourdataset.
2)Define hyperparameters: Select the hyperparameters totune.InRandomForest,someofthehyperparameters that can be tuned include the number of trees in the forest, the depth of each tree, the minimum number of samples required to split an internal node, and the maximum number of features to consider when looking forthebestsplit.
3)Chooseametric:Selecta performancemetricthatyou want to optimize. For air quality index prediction, you can use metrics like mean squared error (MSE), mean absoluteerror(MAE),orR-squared(R2).
1)Mean Squared Error (MSE): MSE measures the mean squared difference between the predicted and actual values.LowervaluesofMSEindicatebetterperformance ofthemodel
2) Mean Absolute Error(MAE): MAE measures the average absolute difference between the predicted and actualAQIvalues.
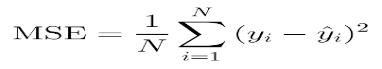
3) Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): RMSE measures the average squared difference between the predicted andactualAQIvalues,andittakesthesquarerootofthe result.
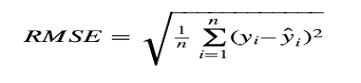
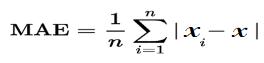
4)Rsquared(R^2): R-squared is a degree of the way properly the version suits the data.. It measures the proportion of the variance in the AQI values that can be explained by the model. R-squared values range from 0 to1,withavalueof1indicatingaperfectfit.
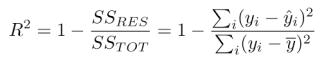
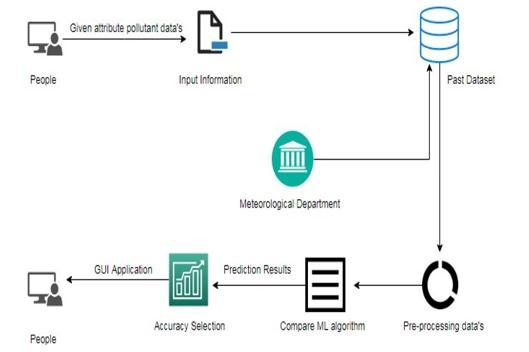
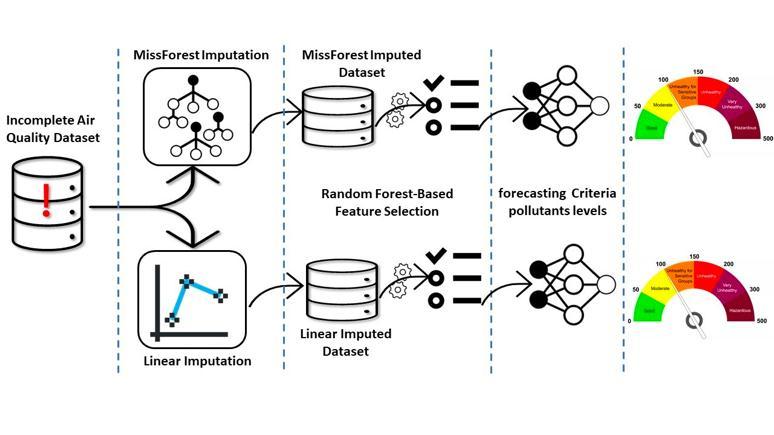
The figure below shows the system configuration of the proposed system. To train the model first the dataset is preprocessed. After pre-processing feature extraction is done for the dataset from which we get training data. These Training data are then passed into various data science model. Next, you'll finally check the PM2.5 pollutant range predictions to predict whether the air quality levels are good or good enough to deploy the model. Otherwise, , you will have to redeploy the model anddataset.
In this project , we have shown how using Random ForestAlgorithmwehaveobtainedpreciseandaccurate results for Air Quality Index . we have used parameters suchasMAE,MSEandRMSE.



MAE: 36.326655063 86365
MSE: 2704.4949219 76799
RMSE: 52.0047586474 23785
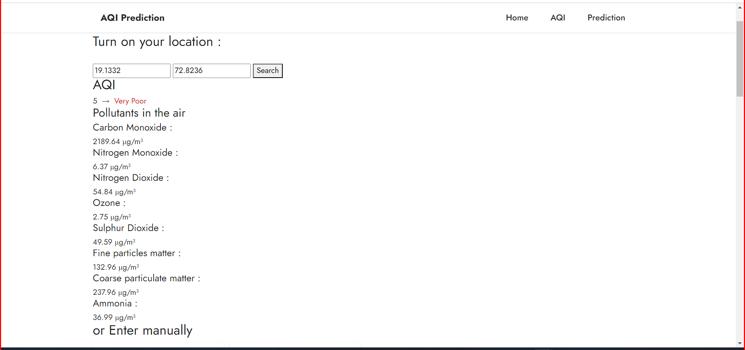
The below representation shows us the categorical division by Environmental Protection Agency(EPA) for AQI HereusingaGraphicalUserInterface(GUI),Wehave established our results in the most simplest form using randomforestalgorithmwiththebestaccuratywecould have achieved. The User Interface shows various fields which helps us to find Air Quality Index based on the data feededinit.
In conclusion, random forest is a powerful machine learningalgorithmthatcan be used for air qualityindex prediction.Itisapopularmethodforitsabilitytohandle complex, high-dimensional datasets and to identify important features for prediction. By using random forest to analyze various air quality parameters, such as temperature, humidity, and particulate matter concentrations,itispossibletoaccuratelypredicttheair qualityindexata givenlocationandtime.However,itis important to note that prediction accuracy can be affectedbythequalityandquantityofdatausedtotrain the model, as well as other external factors such as weatherconditionsandhumanactivity.
Thisprojectwasconducted andalltheevaluationswere implemented under the guidance of Prof Dipak Gaikar , Department of Computer Engineering at MCT’S Rajiv GandhiInstituteofTechnology,Mumbai,India.
[1] Dragomir, Elia Georgiana. "Air quality index prediction using K-nearest neighbor technique no. 1 (2010):103-108.

[2] Carbajal-Hernández, José Juan "Assessment and prediction of air quality using fuzzy logic and autoregressive models." Atmospheric Environment 60 (2012):37-50.
[3] Kumar, Anikender and P. Goyal, “ Forcasting of daily air quality index in Delhi”, Science of th Total Environment409,no.24(2011):5517-5523.
[4]SinghKunwarPetal.“Linearandnonlinearmodelling approaches for urban air quality prediction, “ Science of theTotalEnvironment426(2012):244-255.
[5] Sivacoumar R, et al, “ Air pollution modelling for an industrial complexandmodel performance evaluation “, EnvironmentalPollution111.3(2001):471-477
[6] Gokhale sharad and Namita Raokhande, “Performance evaluation of air quality models for predicting PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations at urban traffic intersection during winter period”, Science of the totalenvironment394.1(2008):9-24.
[7]Bhanarkar,A.D.,etal,“Assessmentofcontributionof SO2 and NO2 from different sources in Jamshedpur region, India, “Atmospheric Environment 39.40(2005):7745- India." Atmospheric Environment 39.40(2005):7745-7760.
[8] Singh Kunwar P., Shikha Gupta and Premanjali Rai, “ Identifying pollution sources and prediction urban air quality using ensemble learning methods”, Atmospheric environment80(2013):426-437.
[9] Wang Jun, and Sundar A. Christopher, “Intercomparison between satellite derived aerosol optical thickness and PM2. 5 Mass: Impliances for air quality studies”,Geophysical research letters30.21(2003).
[10] Sharma M E A McBean and U.Ghosh, “Prediction of atmospheric sulphate deposition at sensitive receptors in northern India”, Atmospheric Environment 29.16(1995):2157-2162
[11] T. Madan, S. Sagar, and D. Virmani, “Air quality prediction using machine learning algorithms –a review,” in 2020 2nd International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking(ICACCCN),2020,pp.140–145.
[12] C. Li, Y. Li, and Y. Bao, “Research on air quality prediction based on machine learning,” in 2021 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Human-ComputerInteraction(ICHCI),2021,pp.77–81.