X-Ray Disease Identifier
1Rohan Darji, Dept of Information Technology, Atharva College of Engineering
2Siddhant Chavan, Dept of Information Technology, Atharva College of Engineering
3Harsh Chauhan, Dept of Information Technology, Atharva College of Engineering
4Parth Khanolkar, Dept of Information Technology, Atharva College of Engineering
5Prof. Amruta Sankhe, Dept of Information Technology, Atharva College of Engineering, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - Numerous lung diseases are frequently been diagnosedgloballyandtheglobalpandemicCOVID-19acted in addition to affecting the lifestyle of the people. It is essentialtoprovideawell-timeddiagnosisfordiseaseslike Emphysema, Effusion, Pneumonia, Edema, etc., for this variousimage-processingmodelsaredeveloped.Oneofthe promising research areas in the medicinal field is Medical Image analysis which delivers quick and accurate results along with providing decisions with their appropriate diagnosis.
Inspiredbyrecentresearchonimageanalysisthatcorrelates the findings in chest x-ray images, we have developed an approachthatusestheexistingdeeplearningmodel –the VGG19classificationmodeltoprocesstheX-rayimagesand diagnose them according to the respective disease and providebasicknowledgeaboutthem.Astheimplementation tool,Jupyter notebookisusedandthismodel hastheNIH (National Institute of Health) X-ray image dataset. Experiments have shown that the classification method applied in this system is able to detect the findings in the diseasesmoreeffectivelyandwithanaccuracyofabove60% formostofthediseases.
Key Words: VGG19, Deep Learning, X-Ray images, ClassificationMethods.
1. INTRODUCTION
Alterationsintheenvironment,lifestyle,andotherfactors are causing a rapid increase in the effect of diseases on humanhealth.Thecountrieswheremillionsofpeopleare facingpovertyandairpollutionareespeciallyendangered withtheriskofgettingseverallungdiseases.Accordingto the estimation of WHO, over 4 million premature deaths haveoccurredannuallyfromlungdiseasesincludingasthma, pneumonia, and Emphysema. Therefore, it is essential to implement diagnostic systems that will help in detecting lungdiseasesandprovidingarespectivediagnosis.During the global pandemic, pneumonia i.e. - breathing and lung problemwereattheirpeak.Itbecamecrucialforalltoearly detectthefindingsinthelungsandforthispurposemachine learninganddeeplearningplayedavitalrolewhichhelped millionsofpeopleworldwide.
Ingeneral,forthepredictionofdiseases,wetrytouseeither X-ray,CT,orMRIscantechniquesfortakingdecisionsonthe appropriate disease but with the help of deep learning methodologies there has been ease for all the doctors, radiologists as well as other researches by giving them a direction for the detection of lung diseases. With this advancement in technology and the use of AI, successful researchandviableresultshelptosavecountlesslives by estimatingdiseasesinremoteareaswithouttheuseofheavy machinery. Thus, a system capable of predicting lung diseases and diagnosing them with good accuracy will reducetheloadonalldoctorsbyhelpingthemtoworkmore effectivelyandsmoothly.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW

2.1 CNN-based Deep Learning Model for Chest X-ray Health Classification Using TensorFlow (2020)[1]
The article discusses the use of machine vision, image processing techniques, and deep learning algorithms as diagnostic tools for respiratory ailments, specifically pneumonia. These tools are more accurate, portable, and cost-effective, makingthem efficientfor physicianstouse. Artificialintelligenceandmachinelearningareconsidered the most accurate methodologies for identifying and classifying health issues, including pneumonia. The study focusesontrainingasystemtodistinguishbetweenhealthy anddiseasedlungsbasedonasetofparameterssuchasthe dataset'ssizeandthemodelandneuralnetworkattributes. TheMobileNetV2pre-trainedneuralnetworkmodelisused as a backbone for feature extraction, enabling accurate results in object detection and semantic segmentation without prior features. The convolutional neural network was trained and analysed to classify lungs based on the outputlabels:NORMALandPNEUMONIA,achievingaccurate resultsofover90%duringtesting.Thestudyconcludesthat theMobileNetV2convolutionalneuralnetworkmodeloffers accurate results and several advantages, including high accuracy,evenwithoutpriorfeatures.
2.2 The use of digital pathology and image analysis in clinical trials. (2019)[2]
Thearticlediscussesthepotentialofdigitalpathologyand imageanalysistoprovidegreateraccuracy,reproducibility, andstandardizationofpathology-basedtrialentrycriteria and endpoints. Image analysis can identify, extract, and quantify features in greater detail than pathologist assessment, potentially leading to improved prediction models and tasks beyond manual capability. The article providesanoverviewoftheutilityofsuchtechnologiesin clinical trials, discussing potential applications, current challenges, limitations, and unanswered questions that requireaddressingbeforeroutineadoptioninsuchstudies. Machine learning methods can facilitate accurate quantitative assessment of digital images, potentially exceeding human observer performance levels. Central laboratory image analysis should be considered in study design for standardized results, although inter-platform variationbetweenindividualcentersisapotentialsourceof bias.Thearticleconcludesthatdigitalpathologyandimage analysis technologies can play a role in central review, training, and image analysis, improving the assessment of standardpathologicalfeaturesorextractingnovelinsightsin clinicaltrials.
2.3 Customized VGG19 Architecture for Pneumonia Detection in Chest X-Rays. (2021)[3]
Pneumonia is a significant illness in both children and aged humans due to lung infections. Early diagnosis is necessary for timely treatment. A Deep-Learning System (DLS)isproposedtodiagnoselungabnormalitiesusingchest X-rayimages.Traditionaldiagnosisbyaskilledradiologist canbetime-consumingandmayleadtobiaseddisparities, affecting judgment. Computer Assisted Evaluation (CAE) procedures are proposed to help clinicians identify the diseaseanditsinfectionrateusingchestradiographs.The proposedworkemploysacustomizedVGG19architecture andEnsemble ofFeaturesScheme (EFS)to achieve better classificationresults.Thetaskistoclassifyimagedatasets into normal/pneumonia categories. The performance of VGG19 was better than other DLS, based on Transfer Learning-based classification. EFS is then implemented to improveVGG19'sdiagnosticability.Theexperimentalresults indicate that the proposed system has the potential to accurately diagnose pneumonia using chest X-ray images, aidingintimelytreatment.
2.4
Thearticlepresentsaproposedsystemfortheassistance ofradiologistsinthedetectionoflungdiseasesusingdeep learningmodels.Thesystemisdesignedtoclassifychestxrayimagesandaccuratelyidentifyanyabnormalitiespresent

inthelungs. The proposed applicationusesdeeplearning CNNmodelstodetectchestorlungdiseasesfromchestx-ray images.ThearticlediscussestheuseofmodelslikeVgg16 andVgg19topredictlungdiseasefromchestx-rayimages and determine which model gives the best accuracy and performance. The proposed system aims to benefit rural areaswhereradiologistsarenoteasilyavailable.Theauthors gathered several infected lung images and normal lung images to train the deep learning model using a CNN algorithm.Theyachievedaclassificationaccuracyof95.0% when applied to the test dataset through various experiments conducted on the proposed model. The proposed system can be used for the prediction of lung cancerfromreal-worldchestx-rayimagesandassistinthe earlydetectionoflungdiseases,providinganeffectiveway for expert diagnosis of lung diseases using deep learning models.
3. PROBLEM STATEMENT
With an increasing world population, more people are living with chronic medical conditions that require monitoringtomaintaingoodhealthandlongevity.Autopsies and their related tests and equipment are expensive and requirespecializedtrainingandeducation,makingitdifficult formanypeopletoperformthisjob.Thesystemwillbeable to assist radiologists in their diagnoses and provide diagnosesinremoteareaswithaminimumaccuracyof80%.
Thesolutionaimstoreducetheworkloadofradiologists, whoneedtoundergo7yearsofformalmedicaleducationand oftenworkinchallengingconditions.Medicalprofessionals use X-ray, CT, or MRI scans to predict diseases, but specialized knowledge is needed to detect abnormalities. Thus,wegottheideatocreateanX-rayanalysissystemthat providesbasicanalysisandpredictionsofdiseasesbasedona known database, even in remote areas with efficient accuracy,makingitmoreaccessibleforpatientsandreducing theburdenonradiologists.
4. METHODOLOGY
4.1 Dataset
Datasetiscollectedfrom[5],whichcontainedchestX-ray imagesofanormalpersonandinfectedperson.Thedatabase contained 5606 total images of chest X-Ray of 13 lung diseases; namely Cardiomegaly, Emphysema, Effusion, Hernia,Pneumothorax,Atelectasis,PleuralThickening,Mass, Edema,Consolidation,Infiltration,Fibrosis,Pneumonia;and NormalchestX-Rayimages.Imagesareasfollows:
Analysis of Data
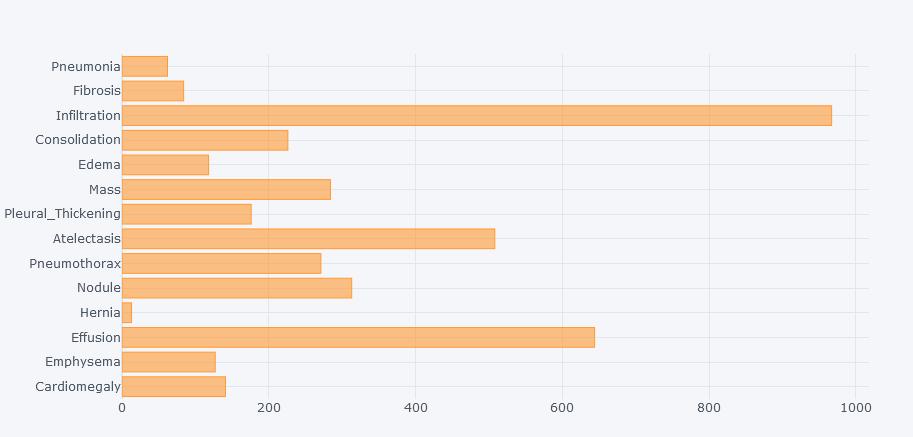
Thefigure.2depictsabargraphthatshowstheanalysisof imagesinourdatasetwhichwascollectedfromtheNational InstituteofTechnology.Thedistributionofimagesamongthe 14diseasesisclearlyshowninthebargraph.
4.2 Pre-processing
X-ray images may have varying resolutions, which can affect the performance of a machine learning model. Therefore,itisimportanttoresizetheimagestoaconsistent size before training the model. We achieved this by using imageresizingtechniques.Furthermore,X-rayimagesmay havedifferentlightingconditionsandcontrasts,whichcan alsoaffecttheperformanceofamachinelearningmodel.So, itisimportanttonormalizetheimagestoreducetheeffectof thesevariations.Weachievedthisbysubtractingthemean anddividingbythestandarddeviationoftheimageintensity values.Tofurtherimprovetheperformanceofthemachine learningmodel,itisoftenbeneficialtoaugmentthedata.We didthisbyapplyingrandomtransformationstotheimages, such as rotations, translations, or flips, to increase the diversityofthedata.
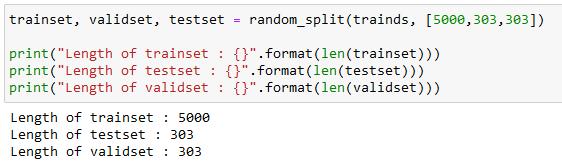
Fig.3 Splitting the Data set
4.3 Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
A neural network is called a convolutional neural network,designedtohandlemultidimensionaldatasuchas imageandtimeseriesdata.Duringthetrainingprocess,this includes the extraction of features and weight calculation duringthetraining.Theidentityofsuchnetworksisobtained by the use of a convolution operator, which is useful for solvingcomplextasks[6].
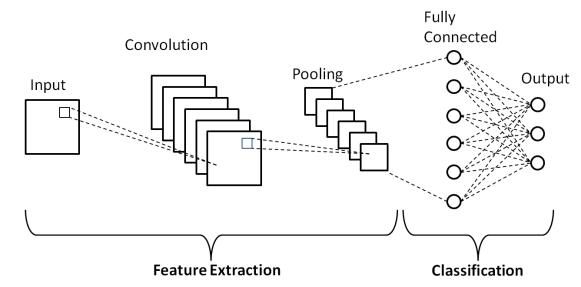
The CNN architecture consists of several convolutional layers,followedbypoolinglayersandfullyconnectedlayers. The convolutional layers extract features from the X-ray images,whilethepoolinglayersreducethesizeofthefeature maps.Thefullyconnectedlayersclassifytheimagesbasedon theextractedfeatures.
Duringtraining,theCNNlearnstorecognizepatternsin theX-rayimagesthatareassociatedwithnormalorabnormal conditions.Themodelisevaluatedusingaseparatetestsetof X-rayimagesthatwerenotusedduringtraining.
Theresultsoftheprojectcanbeevaluatedusingmetricssuch as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. Accuracy measures the proportion of correct predictions, while precisionmeasurestheproportionoftruepositivesamongall positivepredictions.Recallmeasurestheproportionoftrue positivesthatwerecorrectlyidentified,whiletheF1scoreis theharmonicmeanofprecisionandrecall.

4.4 Vgg-19 Pretrained Model
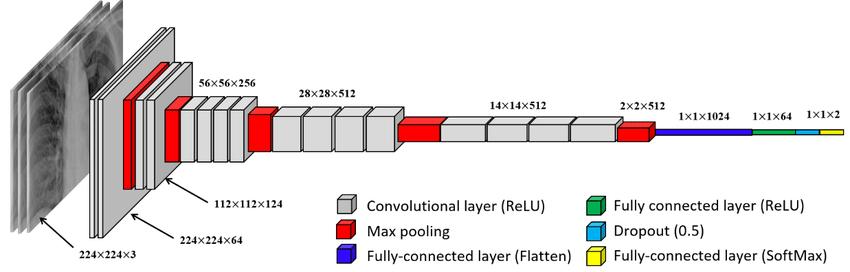
VGG19isaconvolutionalneuralnetworkmodelthatwas proposed by researchers at the Visual Geometry Group (VGG)attheUniversityofOxford.Itisanextensionofthe VGG16model,withtheadditionofthreemoreconvolutional layersandonemorefullyconnectedlayer.TheVGG19model hasatotalof19layers,including16convolutionallayersand 3fullyconnectedlayers.
The VGG19 model architecture consists of a series of convolutional layers with 3x3 filters, followed by maxpoolinglayerswith2x2filters.Thenumberoffiltersinthe convolutionallayersincreasesaswemovedeeperintothe network,from64filtersinthefirstlayerto512filtersinthe last few layers. The model also uses a rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation function after each convolutional layer. ThefullyconnectedlayersoftheVGG19modelarelikethose of the VGG16 model. The first two fully connected layers eachhave4,096neurons,whilethelastfullyconnectedlayer has1,000neurons,correspondingtothenumberofclasses intheImageNetdatasetforwhichthemodelwasoriginally trained.TheVGG19modelhasbeentrainedonlarge-scale imageclassificationtasks,suchastheImageNetdataset,and hasachievedstate-of-the-artperformanceonthesetasks.It has also been used in a variety of other computer vision tasks, such as object detection, segmentation, and style transfer.OneofthemainadvantagesoftheVGG19modelis itssimplicityandeaseofuse.Thearchitectureofthemodel iseasytounderstandandmodify,makingitapopularchoice for researchers and practitioners in the computer vision community.Additionally,theVGG19modelhasarelatively small number of parameters compared to more complex models,whichmakesiteasiertotrainonlimitedhardware resources. Overall, the VGG19 model is a powerful and versatileconvolutionalneuralnetworkarchitecturethathas beenwidelyusedinavarietyofcomputervisiontasks.
testing sets. the training set is used to train the machine learningmodel.ThisinvolvesfeedingtheX-rayimagesinto the model, which will learn to recognize patterns in the images that are associated with infected or non-infected lungs.Themodelisoptimizedusingalossfunction,which measures how well the model is performing at the classification task. The optimization process involves adjusting the weights of the model to minimize the loss function.
VGG-19istheutilizedpre-trainedneuralnetworkmodel.It is the backbone of the system. The main blocks are called convolutional blocks; hence, it is a convolutional neural network.
5. DATA AND RESULTS
The model used is trained in 30 epochs of the dataset whichyieldsthefollowingresults.
Fig.5 Vgg-19 Model Architecture[8]
4.4 Training Model
Training a machine learning model for X-ray images involvesseveralsteps.Thefirststepistocollectadatasetof X-ray images, where each image is labeled as infected or non-infected. Then, the dataset is split into training and
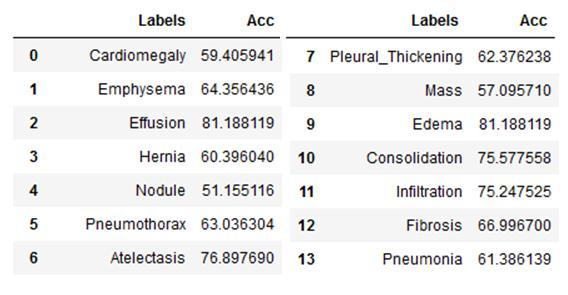
Thesearethevalidationdatasetaccuracythatproducethe above-mentionedaccuracyresultsforthediseases.

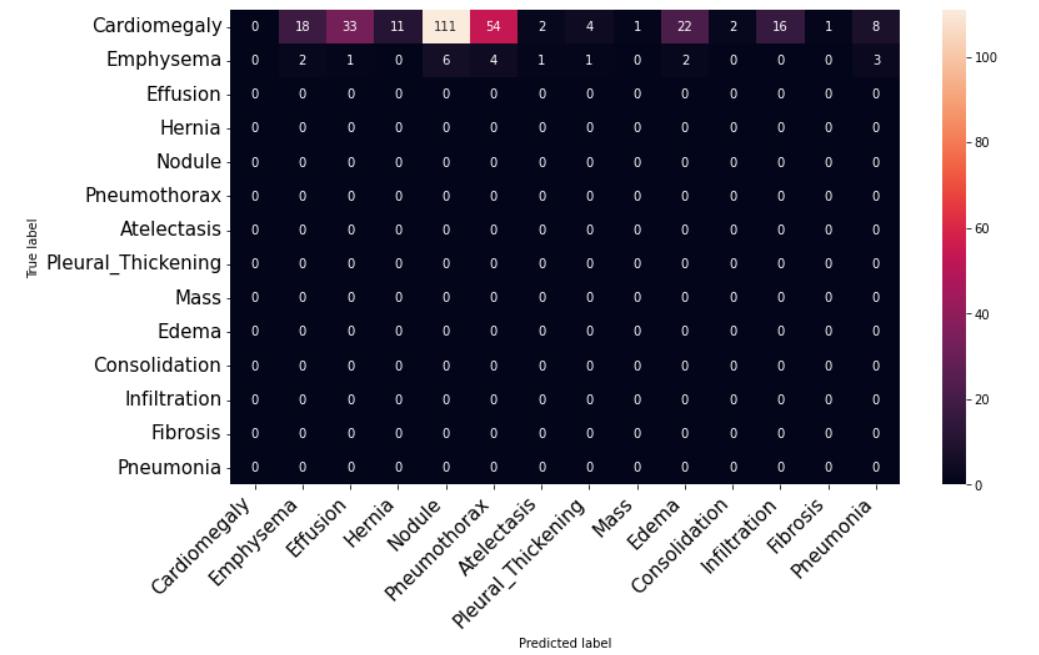
Fig.7showstheconfusionmatrix.Theconfusionmatrix showsthesummaryofthesystem’scapabilitiesaftertesting the whole training set. To briefly explain the confusion matrix,theY-axisshowsthefieldsofdiseasesthatrepresent truelabelsandtheX-axisshowsthefieldsofdiseasesthat representpredictedlabels.
6. SAMPLE OUTPUTS
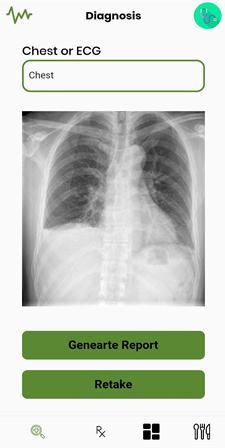
Upon entering the data in the appropriate fields and uploadingtheX-rayimageasshowninthefig.8wecanclick ongeneratereporttogettheanalysisoftheX-ray.

Afterclickingongeneratereporttheimageuploadedbythe userisprocessedandthefinalreportisbeingdisplayedon thenextscreenalongwithdiseasepredicted,findingandthe precautions.Itisshowninthefig.9below.

7. CONCLUSION
ByusingadeepCNNarchitectureandappropriatedata pre-processing,themodelcouldachievehighperformancein
classifyingX-raysintodiseasecategories.Theconvolution neuralnetworkparticularlyutilizingtheVGG-19offerednot only accurate results but also offered advantages as well suchaslowcomputingpowerneededfortheprocessingof data.Themainobjectiveofpresentresearchesistoclassifya certainx-rayimageatafastratewhichisachieved.Accurate results are proven in the percentage range during testing which is above 60% for majority of the diseases. A single modelusedtotrainandclassifymultiplediseaseswillyield resultsbutthetrainingofthemodelisresourceintensive
8. FUTURE WORK
For Future work, different models can be trained to providemoreaccurateresultsandmorediseasediagnoses. DifferentCNNmodelscanbeimplementedtogivebetterand faster results. Patients’ medical history can be stored on cloud services so that it is accessible to the hospital or doctor. It can also provide patients with easy and secure access to their medical records. This can help doctors in givingabetterdiagnosiswithconsiderationtothepatient’s previous diseases. Our application can provide 80% accuracy for some of the diseases predicted. With tie ups with medical practitioners, we may be able increase the accuracyofotherdiseasestested.Theapplicationcanalsobe used to aid in remote areas, whether a patient should get tested by a more advanced hospital. This project can be furtherextendedtoaddressotherradiologyrelatedanalysis. AIapplicationsfordiseaseprediction/diagnosesholdsgreat promisebutfurtherresearchisneeded.
REFERENCES
[1] Tobias, Rogelio Ruzcko. (2020). CNN-based Deep Learning Model for Chest X-ray Health Classification UsingTensorFlow.10.1109/RIVF48685.2020.9140733.
[2] Pell R, Oien K, Robinson M, Pitman H, Rajpoot N, Rittscher J, Snead D, Verrill C; UK National Cancer ResearchInstitute(NCRI)Cellular-MolecularPathology (CM-Path)qualityassuranceworkinggroup.Theuseof digitalpathologyandimageanalysisinclinicaltrials.J Pathol Clin Res. 2019 Apr;5(2):81-90. doi: 10.1002/cjp2.127.Epub2019Mar25.PMID:30767396; PMCID:PMC6463857.
[3] Nilanjan Dey, Yu-Dong Zhang, V. Rajinikanth, R. Pugalenthi, N. Sri Madhava Raja, Customized VGG19 ArchitectureforPneumoniaDetectioninChestX-Rays, PatternRecognitionLetters,Volume 143,2021,Pages 67-74,ISSN0167-8655.
[4] Kumar, C & Geetha, Mrs & Raju, Srujan. (2020). COMPARITIVE ANALYSIS OF LUNG DISEASE DETECTION USING DEEP LEARNING MODELS. The International journal of analytical and experimental modalanalysis.12.3818.
[5] https://nihcc.app.box.com/v/ChestXrayNIHCC/folder/37178474737
[6] Tiwari,S.(2020).ABlurClassificationApproachUsing DeepConvolutionNeuralNetwork.InternationalJournal of Information System Modeling and Design (IJISMD), 11(1),93-111.

[7] https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Schematicdiagram-of-a-basic-convolutional-neural-network-CNNarchitecture-26_fig1_336805909
[8] https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Modified-VGG19-model-architecture_fig1_344398328
