Android Malware Detection
Aasthaa Bohra1 , Gayatri Shahane2 , Sakshi Shelke3 , Dr. Shalu Chopra41,2,3INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY VESIT(of Mumbai University) Mumbai, India

4INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY, HOD VESIT(of Mumbai University) Mumbai, India ***
Abstract Android malware detection involves identifying malicious software on Android devices. This can be accomplished through various techniques such as signature-based detection and behavior-baseddetection.However,thesetechniques cannot detect unknown malware. Hence, we have used machine learning algorithms for malware detection. Machine learning-based malware detection uses algorithms to identify patterns and behaviors characteristic of malware, without relying on previously known signatures. This type of detection can be more effective in detecting unknown or evolving threats. It involves training machine learning models on large datasets of both benign and malicious software to identify common features. During runtime, the trained model is then appliedtoincomingfilestodetermineif theycontain malware. This type of detection is becoming increasinglypopularduetoitsabilitytoadapttonew threats in real-time. Machine learning-based malware detection involves using algorithms to automatically identify and classify malicious software based on patterns and behaviors. This can include supervised learning, where a model is trained on a dataset of labeled malware and benign samples. These methods have shown promising results in detecting previously unseen and evolving malware threats. However, they can also be prone to false positive and false negative errors, and it is important to properly validate and test models before deploying them in production environments. Malware detection using machine learning involves trainingamachinelearningmodelonalargedataset ofbenignand malicioussoftwaretoidentifypatterns and behaviors associated with malware. The model can then be used to analyze new, unknown software and determine if it is malicious or benign. Some commonly used machine learning algorithms for malware detection include decision trees, random forests,andneuralnetworks.
Keywords Android, Malware, Machine learningbased, Detection
I. INTRODUCTION
Malware is short for malicious software, refers to any programorcodedesignedtoharmorexploitacomputer
system. It can take the form of viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, and others. Malware can infect a computer by exploiting security vulnerabilities, tricking the user into installing it, or through phishing attacks. Its effects can range from annoying pop-up ads to serious data theft or destruction. To protect against malware, it is recommended to keep your operating system and software up to date, use a reliable antivirus program,becautiousofemailattachmentsandlinks,and usestrongpasswords.
Proliferation of mobile devices has led to an increase in the number of android malware cases. Various antimalware detection programs have been built to tackle these issues. Signature-based detection is a method for detectingAndroid malware bycomparing thecode ofan Android application against a database of known malwaresignatures.Ifamatchisfound,theapplicationis flaggedasmalicious.Thismethodisfastandreliable,but it only detects known malware, and new or unknown threats will not be detected. To improve the detection rate, signature-based detection is often combined with other methods such as behavioral analysis. Behavioral analysisisa methodfor detecting malwareby observing the behavior of an application during its execution. This approachlooksathowtheapplicationinteractswiththe operating system, network resources, and other applications, and checks for any unusual or malicious behavior. This method is more effective at detecting unknown or new malware, but it is also more resourceintensive and slower than signature-based detection. By combining behavioral analysis with signature-based detection, the overall accuracy of detecting malware can beimproved.
Machine learning-based Android malware detection is a method for detecting malicious files by using machine learning algorithms. These algorithms are trained on large datasets of known malware and benign files, and then use this training to identify new apps as malicious orbenign.Thismethodcanbemoreeffectiveatdetecting unknownornewmalware,asitcanidentifypatternsand relationships in the data that may not be immediately apparent. Additionally, machine learning algorithms can continually learn and adapt to new threats, improving their accuracy over time. Non-signature-based detection totally eliminates the attack window time and can also detect unknown, zero-day and modern malware which
gets totally undetected in signature-based detection techniques.
Insignature-basedmalwaredetection,antivirusprogram looksforsignaturewhichisnothingbutsequenceofbyte in a particular file to declare the file as malicious. For polymorphic and unknown viruses, signature-based detection system fails because polymorphic viruses are encrypted viruses and they are changing decryptor loop on each infection without changing actual code and for unknown viruses there is no signature present in antivirusdatabase.Hence,non-signaturebasedapproach to detect malware on the basis of an integrated feature set prepared by processing Portable executable (PE) file’s header fields values. The machine learning based methodutilizesthestructuralandbehavioralfeaturesof malware and benign programs to build a classification modeltoidentifyagivensampleprogramasmalwareor benign.
II. RELATED WORKS

A few methods for detection of malwares have been developedwhichwillbediscussedfurtherinthissection.
Studies on Android malware detection have aimed to develop and evaluate methods to detect and prevent malicious activity on Android devices. Machine learning algorithms, such as random forest and support vector machine, have been used to develop effective Android malware detectors. Dynamic analysis, which involves analyzingthe behavior ofan app whileitis running,has been shown to be an effective technique for detecting Android malware. Permission-based analysis, which involvesanalyzingthe permissionsrequested by an app, has been used to detect Android malware by identifying abnormal or excessive permission requests. Hybrid methods, which combine multiple techniques, such as staticanalysisanddynamicanalysis,havebeenshownto be more effective than using a single method alone. Performance evaluations have shown that machine learning-based approaches tend to have high accuracy and low false positive rates, while rule-based methods have lower accuracy but higher specificity. Real-time detection is an important aspect of Android malware detection, as malware can cause harm as soon as it is installedonadevice.
Overall, research on Android malware detection has focused on developing and evaluating techniques to detect malicious activity on Android devices, with machine learning-based approaches emerging as a promising solution. Zhou et al. collected 1260 malicious samples on Android markets before 2012 and took a detailed analysis using a variety of static and dynamic analysismethods[1],andthensummarizedthetimeline and development direction of the malware, and
generalized the malicious load and start up mode of thesesampleswhichinspiredalotofworkinthefieldof researchanddetectionofmalware.Theexistingresearch mainlyfocuseson two aspectsof dynamic detectionand static detection. The attempt to dynamically detect malwares mainly concentrated in the monitoring software system calls, network traffic and file access behavior.
The detection of malicious code can be done through statistical analysis of opcodes distribution using statistical method such as Pearson’s chi square procedure, post-hoc standardized testing, Crammer’s V [2]. They proposed static malcode detection using decision tree classification algorithm in chronological point of view. The dataset includes malwares from year 2000 to 2007. Training and testing of classifier with malwareuptorespectiveyearhasdoneandperformance hasevaluated.Theconceptoftextcategorizationusedfor detection of malware. They investigated imbalance problemaboutmaliciousandbenignfiles.
III. ANDROID DETECTION USING PERMISSIONS
Android malware detection using file permissions involvesanalyzingthepermissionsoffilesanddirectories on the device to identify any malicious behavior. Some techniques to detect malware using file permissions involve looking for files with permissions that are unexpected for a particular app or system file, files with superuser (root) permissions, as these can be used by malware to gain full control over the device,worldwritable files can be modified by any app or user on the device, which can be used by malware to persist on the device, files that have been recently modified, as this could indicate malicious activity and files for apps that are installed that request permissions that are not required for their intended functionality, as this could indicate malicious behavior. whether the app is a malicious or normal app based on patterns permission, the required permissions extracted statically. Most popular permissions are registered into class to define whether the permission is benign or malicious. The permissions of a class determine the benign and malicious app. Data mining develops the constructive pattern of permission to determine whether the android appismaliciousorbenign.Wehaveusedtheinformation of the Android app package and permissions to train various machine learning algorithms such as Random Forest, Gradient Boosting Classifier and Logistic Regression.TheproposedapproachinstalledtheAndroid application(APK) on Android devices to extract dynamic features such as networks behavior, memory consumption, computation power, time-space, battery, and binder; these features are used to classify malware. This dynamic approach captured network traffic
behaviors of running Android applications(APK) from differentandroiddevices.
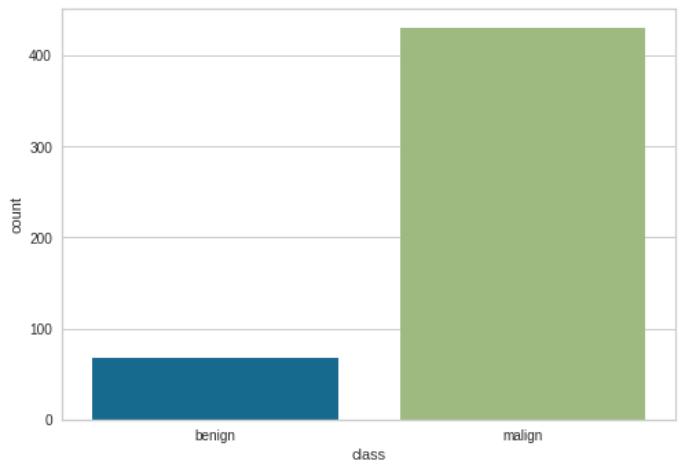
With AndroGuard, one can examine the structure of an APK, extract and analyze its components, and extract featuressuchaspermissions,activities,andservices.The library also provides a convenient API for accessing and manipulatingthedata,makingitausefultoolforsecurity researchers, Android developers, and anyone interested in analyzing Android applications. The Application Programming Interface (API) is used by the application forcommunication.Itisdefinedasacollectionofvarious rulesthatgovernscommunication.APICallsareacrucial factortodeterminewhetheranapplicationismalwareor benign. It can help in bringing attention to suspicious behaviour. The API Calls for each application were extracted using Androguard. It uses reverse engineering by analyzing the DEX file of each APK file. Then, the API Calls were converted into binary values (0 or 1) that indicatethepresenceofAPICallsinanAPK.Alargesetof permissions were extracted from Android application samples for malware detection. About 500 permissions features were extracted from the Android samples, includingbenignandmaliciousapplications.
Android permission feature
android.permission. CALL_PHONE
Description of the feature
Some apps can requestCALL_PHONE permission withoutnecessaryforthem.Ifthe user allows this permission request, theapplication will call phoneitself without notification.
Androidmalwarereferstoanytypeofmalicioussoftware thatisdesignedtoharmorexploittheAndroidoperating system, its apps, or the device it runs on. It can come in manyforms,includingviruses,Trojans,spyware,adware, ransomware, and more. These malicious programs can steal personal information, display unwanted advertisements, lock the device and demand payment, tracktheuser'slocationandactivities,andperformother harmfulactions.
An initial dataset containing various malware folders such as ransomware, spyware, adware,etc has been installedfromacybersecuritywebsite.Therearebenign foldersaswell.Toextractfeaturesfromtheandroidfiles, AndroGuard has been used. AndroGuard is a Python library for reverse engineering and analysis of Android applications. It provides tools for disassembling, decompiling, and analyzing Android APK files. With AndroGuard, one can examine the structure of an APK, extract and analyze its components, and extract features such as permissions, activities, and services. The library also provides a convenient API for accessing and manipulatingthedata,makingitausefultoolforsecurity researchers, Android developers, and anyone interested inanalyzingAndroidapplications.
android.permission.I NTERNET
The user can allow this permission request because he or she is not aware of this permission request’s importance. Every application does not require this permission request. It is dangerous because themalwareapplicationcansend private information to their websites.
android.permission. SEND_SMS
The application can send SMS message so that the money can be stolen by installing similar applicationswiththispermission request.

IV. TRAINING AND TESTING THROUGH ALGORITHMS

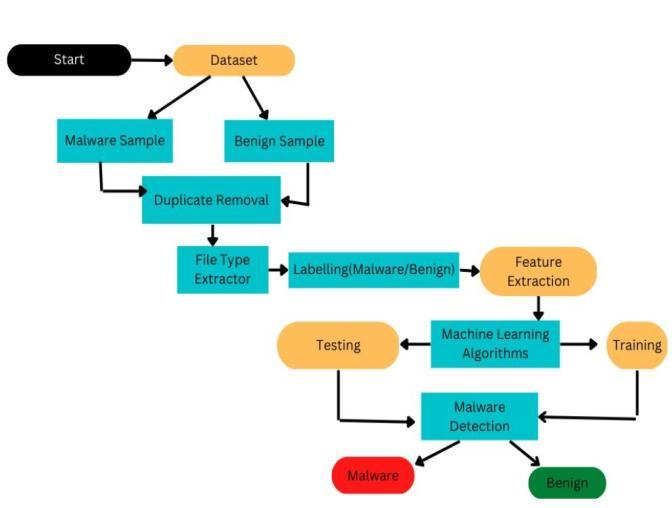
After classifying the dataset into benign and malware categories, our aim is to train a machine learning model usingandroidpermissionsfeature.Thissectiondiscusses thevariousmachinelearningalgorithmsusedtotrainthis modelforaccuratemalwaredetection.
LogisticRegressionisastatisticalmethodforanalyzinga dataset in which there are one or more independent variables that determine an outcome. The outcome is measured with a dichotomous variable (in which there are only two possible outcomes). It is used for binary classificationproblemsandpredictstheprobabilityofan event occurrence. The model is trained using maximum likelihood estimation and makes predictions using the logisticfunction.
Stackingofalgorithmsisanensemblelearningtechnique that combines multiple individual models to produce a better overall prediction. Itworks by traininga model to make predictions using the outputs (predictions) of several other models as input features. The final predictionismadebyameta-modelthatistrainedonthe outputsofthebasemodels.Thisprocesscanberepeated severaltimes,creatingastackingofmultiplelevels,hence the name "stacking". The idea is to use the strengths of each model toaddresstheweaknessesof others,leading to improved accuracy and stability compared to using a singlemodel.
V. PERFORMACE MEASUREMENT
Results of training the algorithms mentioned above are generated in the form of accuracy score, classification reportandconfusionmatrix.
Accuracy is a commonly used metric for evaluating the performance of a machine learning algorithm. It measures the proportion of correct predictions made by the algorithm compared to the total number of predictions. In binary classification problems, such as Android malware detection, accuracy is defined as the number of true positive (TP) and true negative (TN) predictionsdividedbythetotalnumberofpredictions:
Accuracy = (TP + TN) / (TP + TN + False Positive (FP) + FalseNegative(FN))
A Random Forest Classifier is an ensemble machine learning algorithm used for classification tasks. It builds multiple decision trees and combines their predictions through voting or averaging to increase accuracy and reduceoverfitting.
Gradient Boosting is a machine learning technique for regressionandclassificationproblems,whichproducesa prediction model in the form of an ensemble of weak prediction models, typically decision trees. It builds the model in a stage-wise fashion like other boosting methods do, and it generalizes them by allowing optimizationofanarbitrarydifferentiablelossfunction.
Fig3.AccuracyScoreofLogisticRegression
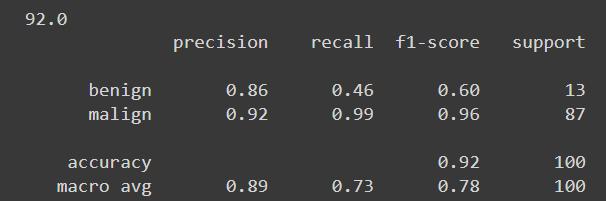
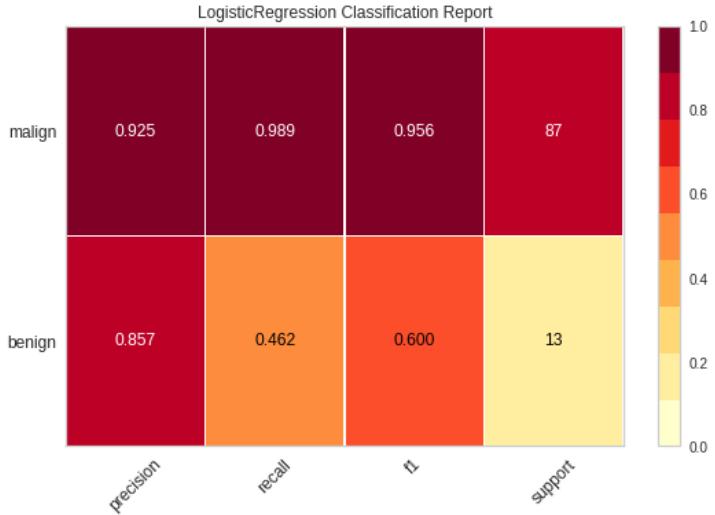
Figure 3 shows that the accuracy score of logistic regressioninourmodelis92percent.
In Android malware detection, a classification reportcan provide a summary of the performance of a machine learning algorithm in detecting malicious and benign
apps,basedonasetoffeaturesandalabelledtrainingset. By analyzing the precision, recall, F1-Score, and support for each class, practitioners can gain insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the algorithm and identify areasforimprovement.
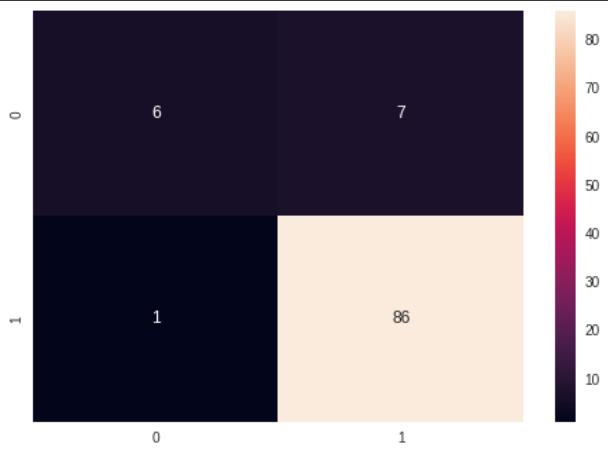
ConfusionMatrixoflogisticregressionshows86TP,6TN, 7FPand1FN.
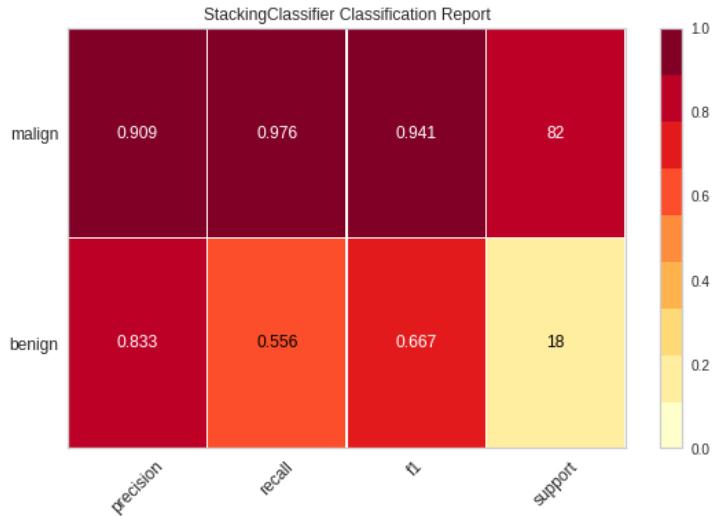
PerformanceReportoftheStackingModel–
According to the above classification report, logistic regression is giving promising results (and precisely identifying 92.5 percent malign and 85.5 percent benign files).
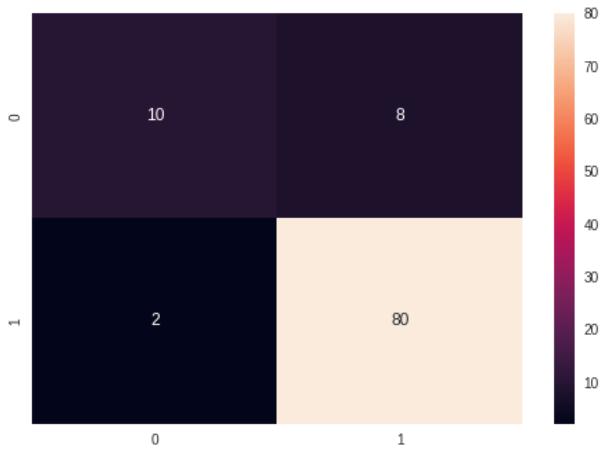
A Confusion Matrix is a tabular representation of the performanceofamachinelearningclassifier.Itprovidesa summary of the true positive (TP), false positive (FP), false negative (FN), and true negative (TN) predictions madebytheclassifierforabinaryclassificationproblem, or for each category in a multi-class classification problem.

Inabinaryclassificationproblem,theconfusionmatrixis usually a 2x2 table that summarizes the four types of predictions. The rows represent the actual class labels, whilethecolumnsrepresentthepredictedclasslabels.

VI. FUTURE WORKS
Inconclusion,malwaredetectionusingmachinelearning is a promising approach for identifying malicious software It has the advantage of being able to detect previously unseen malware, but it also has limitations such as the potential for false positive or false negative results. To achieve effective malware detection using machinelearning, it is important to have a large, diverse and up-to-date dataset for training the model, as well as ongoing monitoring and refinement of the model’s performance. Additionally, it is important to integrate multiple detection methods, including machine learning, forcomprehensivesecurity.
Incorporatingprivacyconsiderations:Asprivacybecomes an increasingly important concern, future work should

consider privacy-preserving techniques for malware detectiononAndroiddevices.
VII. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank the editor and the reviewer for enhancing the research paper with their insights and suggestions.

VIII. REFERENCES
https://www.unb.ca/cic/datasets/invesandmal2019.htm l
[1]ZHOU Y, JIANG X. Dissecting android malware: characterization and evolution [A]. Symposium on SecurityandPrivacy[C].Oakland:IEEE,2012.95-109.
[2] Bilar, D.(2007). Opcodes as predictor for malware. International Journal of Electronic Security and Digital Forensics,1(2),156-168.
