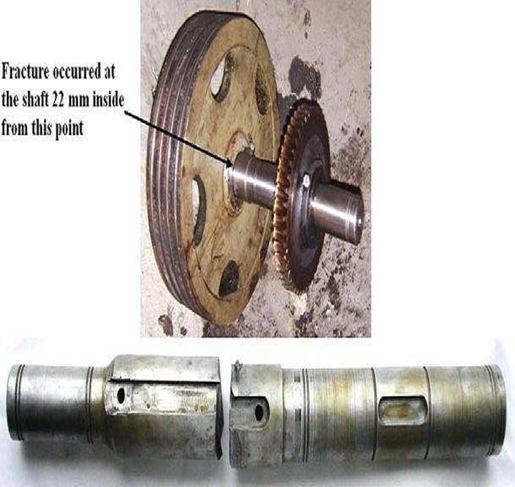
Review of shaft failure in Coil Car Assembly
Abstract - A spinning machine component known as a shaft transfers power from one place to another. Power transmission causes the shaft to receive torque, and reactions to the members it supports cause the shaft to receive a bending moment. The shaft was modified to include a discontinuity for crucial functional requirements. The shaft supports a variety of loading situations while it is in use (torsion, bending, axial, and combinations of these). In order to better understand failure and find ways to prevent it, a coil car shaft study was done. A visual inspection, hardness measurement, and investigation were carried out to determine the integrity of the failed axle shaft. The findings indicate that reversed bending fatigue caused the axle shaft to fracture and that fractures occasionally happened as a result of misalignment. A common cause of failure for many rotating equipment components isfatigue fracture.
We first check the load capacity of our existing shaft utilising theoretical and analytical techniques and typical shaft design calculations. Calculate the new shaft diameter in light of the findings. The load on the shaft considerably lowers as shaft diameter grows. The S-N curve is used to theoretically and analytically calculate the fatigue life of a shaftthatissubject tocyclic bendingstresses.Stresslevels in the shaft steps were found to be greater during the shaft investigation. We examine the effects of fillet and chamfer on shaft life and use them to disperse load. Also, the effect of a larger load acting area on shaft life is examined in this study
Key Words: shaft failure, maintenance techniques, heavy loading, industrial application, analytical solution

1.INTRODUCTION
A coil car is a material-handling device. This coil car instrument is frequently used in the steel and vital industries. The middle function of this type of material management tool is to load and sell off coils from mandrels. Transporting coils (or rolls) of sheet metal, mostnotablysteel,isdonewiththehelpofcoilcars,atype of rolling stock. The transport surface can be flat with supportplatesorspecificelements,suchasdouble-wedge cradles to support rounds such as ferrules or coils in the travel direction or also transverse, and one or more coils orrollsofstrapswithananti-rollsystemcanbeincluded. Thesevehiclesfirstappearedinthe1960s.Earlyexamples includethePennsylvaniaRailroadG40andG41classcars,
whichwerebuiltin1964-1965[1].TheG41hasacapacity of 2000 LBS and can carry 6 coils in a single rack system. ThisG41coilcarhasa self-weightof59200LBS.TheG41 coilcarhasatotalofeightwheels.G41hasatotallengthof 39feet2inchesandawidthof9feet8inches.Thecentral distancebetweenthetwowheelsisthreefeet.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
2.1 Deepan Marudachalam M.G, K.Kanthavel, R.Krishnaraj:
A shaft used in a spinning machine frequently fails, as discussed by Deepan Marudachalam M.G. Failure took place close to the shaft's change in cross section, where a relief groove is present. The forces and torques acting on the shaftarecomputedusing thedrivesystemto estimate thestressesoccurringatthefailureregion.Thefindingsof stress analysis using the finite element technique (FEM) arecomparedtothecalculatedvalues[2].Theleastsquare approach is used to determine the stress concentration factors at the failure cross section from the fatigue stress concentrationfactors.AccordingtoDeepanMarudachalam M.G., changing the position of the support and increasing theshaft'sfilletradiireducethestressconcentrationfactor while raising the endurance limit and fatigue factor of the shaft'ssafety.
OsmanAsidiscussesthefailureanalysisofarearaxleshaft fromacarthatwasinvolvedinanaccident.Theaxleshaft had split into two pieces, which was discovered. The investigation sought to determine whether the failure causedorcontributedtotheaccident.

2.2 A. Göksenli *, I.B. Eryürek
An elevator drive shaft failure analysis is carefully examined. Properties of the shaft's microstructure, mechanics, and chemistry are identified. After visually examiningthefracturesurface,ithasbeendeterminedthat the fracture was caused by torsional-bending fatigue. At the keyway edge, a fatigue crack has started. The shaft's forces and torques are calculated, and stresses at the fracture surface are estimated. The endurance limit, the fatigue safety factor, the shaft's fatigue cycle life, and the fatigue analysis are all computed. Due to poor keyway manufacturing or design (low radius of curvature), a high notch effect resulted from the shaft's fracture. Finally, the useofFEMtodescribetheimpactofchangingtheradiusof curvature on stress intensity and distribution clarifies the safety measures that must be done to avoid a failure of a similarnature.
Theshaft'smaterialwasdeterminedtobetypical.Although the material quality was good and failure was not caused by a material property, the average micro hardness, yield strength, and tensile strength were 157 HV, 349 MPa, and 527MPa.Whiletheactual radius was2mm,FEAindicated a stunning 5mm stress concentration at the shoulder's chamfer. A micro crack started along the chamfer as a result of the higher stress concentration and torsional vibration, and it developed in size as a result of ongoing stressandtorsionalvibration.
3.SUMMARY OF LITERATURE REVIEW

SR. NO AUTHOR FAILURE REASON Year
Shaftfailedasa resultoffatigue.
Fig -2:Elevatorshaftfailure
2.3 Jinfeng du Jun Liang Lei zhang
Thisessayexaminesthefailureanalysisofapowerboiler's shaft-mounted induced draught fan. It compares the manufactured shaft to the real design and discovers that the chamfer is less than what is indicated in the drawing. This intensifies the focus of stress. Furthermore stated is that aberrant torsional vibration and increased stress concentration are caused by the shaft's incorrect balance. Theinducedshaftcrackedasaresultofthevibrationsand alternate torsional loading, resulting in the ratchet-like profile.Twophasesmadeupthefullanalysis.
1.Performanceandfractureanalysisoffailedshafts
2. Study of the shaft's design, torsional resonance, and stress.
Low
radiusofthe curvatureof keyway
radiusof chamferlessthan thedesignradius
After visual and stereoscopic inspection, we were able to determinethatthefailureofourcoilcarshaftwascaused by severe stress and rotational bending. In order to reduce this shaft failure, we first verified whether our shaftdesignisappropriate. Wecomputetheexistingshaft designanalyticallyandtheoretically.
Theoretical Calculation of Existing Shaft
Data:
1.MotorSpecifications:
OMS315-Hydraulic ,RPM-285rpm,Power-15KW.
2.Diameteroftheshaft:
68 mm (Smallest diameter of Shaft is consider core diameterofshaft)
3.Material:
EN-9 FOS=3(Assume)
Step1-Permissibleshearstress
= = =51.66Mpa
(b)ShaftofCoilCar
ActualLoadingConditionofShaft
FreeBodyDiagramofShaft
BendingMomentDiagramofShaft
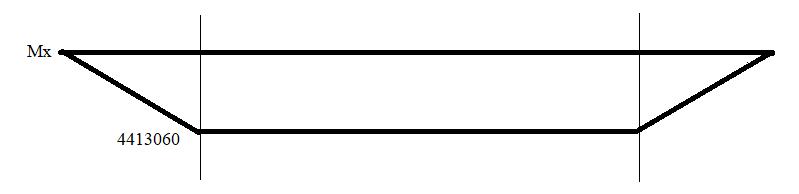

………... (1)
BendingmomentatpointA=0
( ) ( ) ( )
Byusingequation(1)weget,
Step3-BendingMomentcalculation

BendingMomentatpointA=0N.mm
BendingMomentatpointB=4413060N.mm
BendingMomentatpointC=4413060N.mm
BendingMomentatpointD=0N.mm
Step4-Torsionalmoment
T= T= T=502.590N.mm
Step5-Shaftdiameteronstrengthbasis (TORQUE) √( ) ( )
√( ) ( )
ByusingMaximumShearStresstheory, ( ) x = 71.94 Mpa > 51.66 Mpa(permissible/allowableshearstress)
Shaftisfailed.
Analytical Calculation Of Existing Shaft
ModelFormation-

Step2-Forcescalculation
ForcesactonpointB–24517N
ForcesactonpointC-24517N
Here, we processed the coil car shaft using the Ansys method. We use the solid work software to generate the model,importitintoAnsys,applytheappropriateloading conditions, and then compute the analytical coil car shaft
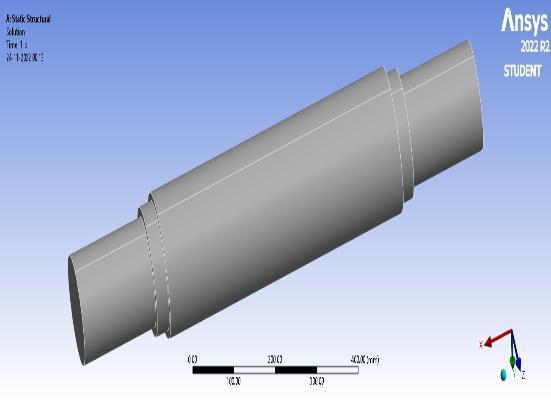
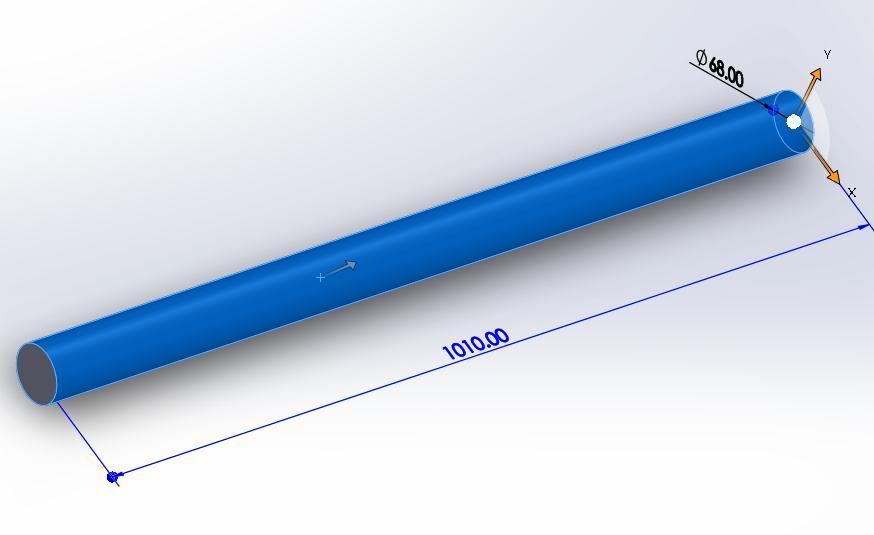
result. The shaft for the coil car is initially built in solid work with a 68 mm core diameter. Shaft steps are not included here because we do not account for them in the theoretical computation either. To develop the shaft design in Solid Work, we merely utilised the sketch and extrudetools
MeshingCondition-
Mesh creation is one of the most important steps in performing an accurate simulation with FEA. A mesh is madeupofnumerous parts withnodes whosecoordinate coordinatesinspacecanvarybasedonthekindofelement usedtorepresentthegeometry'sshape.Unevenformsare challenging for FEA solvers, while common shapes like cubes make it considerably simpler. Amorphous shapes are converted into "elements," which are more recognisable volumes, by the process of meshing. Determining which CAD model elements from your FEA simulation package, such as Mechanical, require meshes andwhichdonotiscritical.
CADgeometryistypicallyhighlycomplexanddetailedfor production needs. To save time, you might defeature, or eliminate, some of your geometry if you don't need every detail for a simulation. There are two categories for meshing techniques. For these uses, we're referring to 3D models.
1.Tetrahedalelementmeshingor“tet”

2.Hexahedralelementmeshingor“hex”
Fig4.1.3ShaftSolidworkModel
As soon as the 3D model is complete, we simply save the shaftasa.sldprtfile.Ansysimportsthis.sldprtfilewithout issue.Basedontheavailablecircumstances,wedesigneda 68 mm diameter by 1010 mm long shaft in solid work programme.
Material-
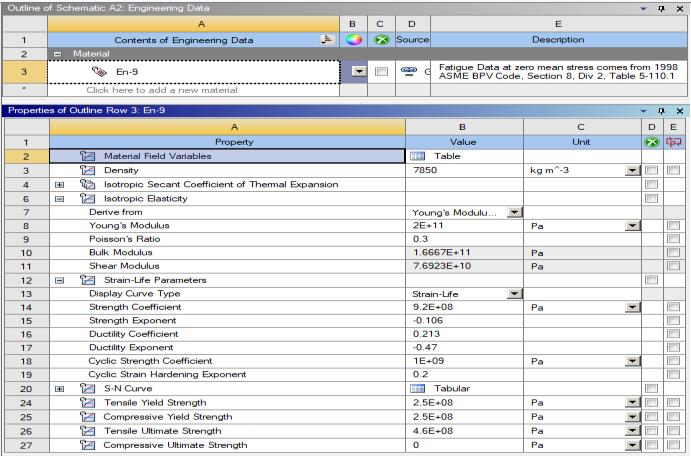
We used the static structure module in Ansys to analyse this coil car shaft issue. Before beginning the analysis, we must first think about the qualities of the materials. We added this material characteristic to Ansys because our shaftismadeofEn-9material.
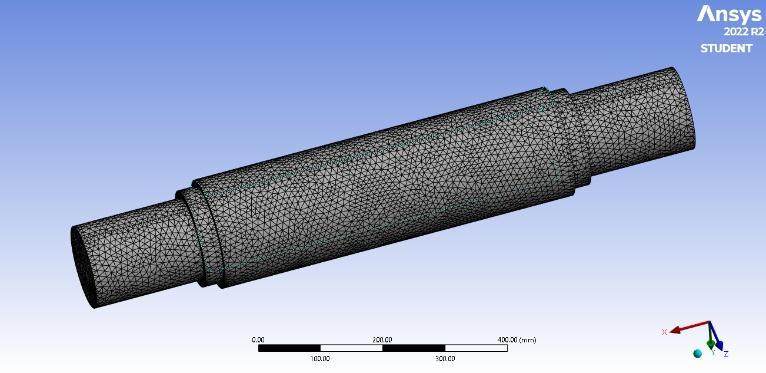
Hex or "brick" elements are more accurate than tet elements at lower element counts. The most effective option for complex geometry may be tet elements. We decided to use hexahedral element meshing in our analysisbecauseofthesimplicityofourgeometryandthe requirementforanaccurateresult.Startingwithafull-size mesh, we apply sizing commands and reduce the size to 0.01. By lowering the mesh size, this aids in producing betterresults.
Loadingcondition-
The weight on the hydraulic cylinder is actually transferredfromthecarriagetotheshaftandfinallytothe wheel, depending on the situation. A two-coil car, for instance, can carry up to eight tonnes of coil on a mill machine, but for the purposes of this analysis and improvement, we're going to apply ten tonnes of force on the four wheels of the shaft. We apportioned these 10
tonnesofweightsothat2.5tonnesofweightwereapplied totheshaftateachcorner ofthecarriage.Thus,oneshaft is capable of supporting a 5-ton load. We take the shaft without steps and point loads like the 5 tonnes of force operating on the shaft into account when analyzing the current shaft In order to come as close as feasible to the actualloadingcondition,wefixedtherightandleftsidesof the shaft under this loading scenario. We included rotational velocity in our coil car shaft study since, under this loading scenario, the gear linked to the front wheel shaft also generates momentum. We won't include the rear wheel shaft gear in our analysis because it was not installed. Other loading circumstances in rare wheels are thesame,withtheexceptionofgearcondition..
Visual inspection, stereoscope inspection, and material testing. Aside from that, hardness testing and available data show that our shaft failed due to bending moment, stressconcentration,andmisalignment.
We can clearly see from the analytical study that stress concentration is higher in the shaft step where area changes occur. This stress is reduced by using a proper radiusfilletorchamfer.Becausetherearenoradiusfillets intheexistingshaft,thestressinthatareaisgreater.This stressisreduced.
We also provide three material options as part of the study's requirements. En-9 was the best material for the shaft. For this shaft, we also use En-24 and C55 Mn75 materials. Based on the weight method, we can conclude thatEn-9materialisthebestformanufacturingshafts.
REFERENCES
[1] Deepan Marudachalam, M.G., Kanthavel, K. and Krishnaraj, R., 2011. Optimization of shaft design under fatigue loading using Goodman method.International Journal of Scientific & EngineeringResearch,2(8),p.1.
[2] 2Asi,O.,2006.Fatiguefailureofarearaxleshaftof an automobile.Engineering failure analysis,13(8), pp.1293-1302.
[3] Prajapati, H.R., Patel, B.P. and Patel, N.V., Investigation of Stress Concentration Factor for Keyway on Shaft under Different Loading Conditions:ACaseStudy.
[4] Xiaolei,X.andZhiwei,Y.,2009.Failureanalysisofa locomotive turbocharger main-shaft.Engineering FailureAnalysis,16(1),pp.495-502.
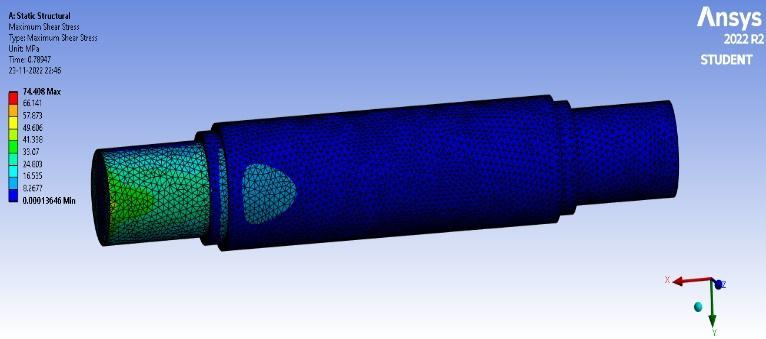
4.1.7StressConcentration
Using the proper material, meshing, and loading conditions, we move on to obtain results. As a result, we originally focused on the maximum shear stress value. since during the theoretical computations, we focused on themaximumshearstressvalue.
5. CONCLUSIONS
The idea conveyed by the shaft's design is that the shaft failed at the specified diameter. The stress decreases dramatically as the diameter of the shaft increases. After determining the final diameter of the shaft (80 mm), we increase the step by 10 mm (i.e 90 mm & 100 mm). In comparison to existing shaft diameters, the new shaft designprovidesalongerfatiguelife.

[5] Göksenli, A. and Eryürek, I.B., 2009. Failure analysis of an elevator drive shaft.Engineering failureanalysis,16(4),pp.1011-1019.
[6] Hariom, V.K. and Chandrababu, D., 2016. A review of fundamental shaft failure analysis.International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology,3(10),pp.389-395.
[7] V.B.Bhandari ,“Design of Machine Element” 1994 TataMcGrawHillPublicationCompanyLtd

