Indian Sign Language Recognition using Vision Transformer based Convolutional Neural Network
Sunil G. Deshmukh1, Shekhar M. Jagade21Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Maharashtra Institute of Technology, Aurangabad 431010, Maharashtra, India
2Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Sri N B Navale Sinhgad College of Engineering, Solapur413255, Maharashtra, India
Abstract - Hand gesture recognition (HGR) is a popular issue in the areas of learning algorithms and visual recognition. Certain Human-Computer Interactions technologies also need HGR. Traditional machine learning techniquesandintricateconvolutionalneuralnetworks(CNN) have been employed to HGR up till now. Despite the fact that theseapproachesworkadequatelywellonHGR,weemployed a more modern model, vision transformer, in this research. Vision Transformer (ViT) is created to enhance CNN's performance. ViT has a strong similarity to CNN, but its classification work utilizes distinct layers. The ViT was performed to gesture datasets via learning algorithms. In trials, a testing dataset having crossed test strategy is evaluated, and classification accuracy is employed as productivity metric. According to test findings, the presented approachframeworkattainsanachievedaccuracyof99.88% ontheimagedatabaseused,whichisconsiderablyhigherthan thestate-of-the-art.Theablationstudyalsosupportstheclaim that the convolutional encoding increases accuracy on HGR.
Key Words: Convolutional neural network, Vision transformer (ViT), Transfer learning, Training of images, Accuracy, Hand gesture, Human-computer interaction (HCI).
1. INTRODUCTION
Directcontactisbecomingthemostpopularwayforusers and machines to communicate. People connect with one another naturally and intuitively through contactless techniques including sound as well as body actions. The versatilityandefficacyofthesecontactlesscommunication techniqueshavemotivatedseveralresearcherstoadopting themtofurtherHCI.Gesturesareasignificantpartofhuman language and an essential non-contact communication technique.Wearabledatagloveswerefrequentlyusedinthe pasttograbthepositionsandanglesofeveryuser'sjointsas theymoved.
Thecomplexityandpriceofawornsensorhavelimitedthe extensive application of such a technology. Gesture recognition refers to a computer's ability to understand gesturesand executespecifiedinstructionsin response to suchmotions.ThemaingoalofHGRistoestablishasystem
that can identify, analyze, and communicate information basedonspecificmotions[1].

Techniques for recognizing gestures on the basis of contactless visual inspection are now prominent. This is becausetheiraccessibilityandprice.Handgesturesarean expressive communication technique employed in the healthcare, entertainment, and educational sectors of the economy,aswellastoassistpeoplewithspecialneedsand the elderly. For the purpose of identifying hand gestures, handtrackingwhichcombinesanumberofcomputervision operations such as hand segmentation, detection, and trackingiscrucial.HGRareusedtoconveyinformationor emotionsinsignlanguagetothosewhohavehearingloss. The major problem is that the typical person may easily misinterpret the message. AI and computer vision developmentsmaybeutilizedtoidentifyandcomprehend signlanguage.
Withtheassistanceofmoderntechnology,thetypicalperson maylearntorecognizesignlanguage.Thisarticleintroduces a deep learning-based technique for hand gesture identification.Inthisregard,operatingthesystemremotely necessitatestheuseofgestures.Thedevicesrecordhuman motions and recognize them as the ones that are used to control them. The movements employ a variety of modes, includingstaticanddynamicmodes.Thestaticgesturesare maintainedwhilethedynamicgesturesshifttovariousareas whenthemachineisbeingcontrolled.So,ratherthanusing static gestures, it is essential to identify or recognize dynamic motions. The camera that is connected to the apparatusinitiallycapturespeople'smovements[2].
Whenthe backdropof anymotionsthatwereidentifiedis removed,thegesture'sforegroundisgathered.Tolocateand eliminate the noises in the foreground gesture, filtering techniquesareapplied.Thesenoise-removedgesturesare comparedtopre-storedandtaughtmovementsinorderto verify the meaning of the gestures. The automotive and consumer electronics sectors utilize a gesture-based machineoperatingsystemthatdoesn'trequireanyhuman input. Static and dynamic gestures, as well as online and offlineactions,canallbeclassifiedashumangestures.The machine'siconscanbechangedusingofflinegestures,but
thesystemormenuwheretheitemsareshowncannotbe altered.Themovementsoftheinternetcausethemachine's symbolstoshiftortiltinavarietyofways.
Online gestures are significantly more useful than offline gestures in real-time machine operating systems. These strategiesrequiredalargenumberoftrainingsamplesand couldnothandlelargetrainingdatasets.Thisflawisfixedby suggestingViT-basedCNNinthisstudy.Thecomplexityof thistechniqueislow,anditdoesnotrequireabigamountof datatotrain.Theincorporationofadeeplearningalgorithm and a cutting-edge segmentation approach into a HGR system is an original component of the proposed study. Enhancinguserstocommunicatebyprogrammingsoftware morereceptivetouserdemandsisthefundamentalaimof human-computerinteraction(HCI).Gesturesareintentional, suggestivebodymovementsthatincludethephysicalaction of the hands, wrists, face, shoulders, and face with the intention of engaging with the surroundings or conveying the relevant information. The creation of human-centric interfaces is made possible by hand gesture recognition (HGR),acrucialjobinHCIandahighlyhelpfulmethodfor computerstocomprehendhumanbehavior

A vital part of our everyday lives is being able to communicateeffectively.Peoplewhoaredeafordumbfind itchallengingtoengagewithpeopleduetotheirincapacity totalkandlisten.Oneofthemosteffectiveandwell-known techniquesisarguablytheuseofhandgestures,sometimes referredtoassignlanguage.Programsthatcanidentifysign language motions and movements must be developed in orderfordeafanddumbpeopletocommunicatemoreeasily withthosewhodonotunderstandsignidioms.Thepurpose of this study is to employ sign languages as a first step in removingthe barrierto communication betweenhearingimpairedanddeafpeople.Whenemployedtosolvepicture recognitionissuesincomputervision,modern(CNN)yield successful performance.The mosteffective wayto build a completeCNNnetworkisviatheuseoftransferlearning.In a broad range of fields, including automation, machine learning is used. Aspects of artificial intelligence include techniquesformeasuring,recording,detecting,monitoring, identifying,ordiagnosingphysicalphenomena.Moreover,a varietyofsensors,suchasvision-basedsensors,capacitive sensors, and motion-based sensors can record hand movements[3].
Data Glove Techniques: Glove-basedsensorsaretheonly technologies that can handle the complex needs of handbased input for HCI. In order to determine the hand postures,thisapproachusesmechanicaloropticalsensors thataremountedtoagloveandtranslatefingerflexionsinto electricalimpulses.Thefollowingdisadvantagesrenderthis innovation less well-liked: The user is required to carry a burdenofwiresthatarelinkedtotheprocessoranditalso needscalibratingandsetupprocesses,thuscontactwiththe computer-controlled surroundings lacks its ease and
naturalness.TechniquesthatarebasedonvisionApproaches basedonsystemvisionhavetheabilitytoobtainmorenonintrusive, natural solutions since they are based on how peopleinterpretinformationabouttheirenvironment.While itischallengingtocreateavision-basedinterfaceforgeneral use, it is possible to do so for a controlled environment without facing many difficulties, such as accuracy and processingspeed[4].
Heapetal.[5]developedadeformable3Dhandmodel,and they surface-mapped the whole hand using PCA from training instances. Real-time tracking is made possible by locatingthemostlikelytobedistortedmodelthatmatches thepicture.Whilemoreprocessingisnecessarytoextract valuablehighermetadata,suchaspointingdirection,ithas beenshownthatsucharepresentationisquitesuccessfulat precisely locating and tracking the hand in pictures. Nevertheless, the approach is not scale and rotation invariant and cannot tackle the obstruction issue. Compositionalmethodsareusedintoidentifyhandposture. Configurationsofpartsserveasthefoundationforahand posture depiction. Characteristics are classified in accordance with the perceptual principles of grouping to providealistofpotentialcandidatecompositions.Basedon overlappedsub-domains,thesesubgroupsprovideasparse pictureofthehandposition.
Anovelmethodforidentifyingstaticmotionsinchallenging circumstancesbasedonwristband-basedcontourfeatures wasproposed byLeeetal.[6].Pairof black wristbands is appliedtobothhandstoproperlydividethehandarea.By theuseofamatchingalgorithm,thegestureclassisdetected. Whenthebackgroundcolourreappears,thesystemfailsto effectively segregate the hand region. For the purpose of detecting static hand gestures, Chevtchenko et al. [7] optimized a coalitation of characteristics and dimensions usingamulti-objectiveevolutionaryalgorithm.Upto97.63 percentidentificationaccuracywasreachedon36gesture posturesfromtheMUdataset.Theaforementionedaccuracy wasattainedutilizingaholdoutcross-validationtestandthe combined Gabor filter and Zernike moment features. A varietyofgeometriccharacteristicsincludingangle,distance, andcurvaturefeatureswerealsoproducedbythecontourof thehandmotion,andtheseaspectswereclassifiedaslocal descriptors.Followingthat,localdescriptorswereimproved using the Fisher vector, and gesture recognition was accomplished using a support vector machine classifier. DeepfeaturesfromAlexNet'sfullyconnectedlayerandVGG 16 were used to recognize sign language. The obtained attributes were classified using the SVM classifier. The recognitionperformancewasestimatedtobe70%usinga conventional dataset and the leave-one-subject-out crossvalidationtest.TheresultsshowthatforRGBinputphotos, detection performance is constrained by background variation,humannoise,andhighinter-classsimilarityinASL gesturepostures.
Parvathyetal.[8],theauthorsdeploya vision-basedHGR system to extract key characteristics from radar-based pictures before categorizing them with a 96.5% accuracy SVM classifier. Deep learning models based on (CNN) architecture have attracted more interest in human computationandobjectdetection.Convolutionalfiltersare used by CNN to extract the key details of an image's subjecttheobjectclassificationconvolutionprocessesthat coverimportantattributesshouldthereforebeminimized. TheauthorsZhanetal.[9]havesuggestedaCNNmodelfor thereal-timeHGR.Thismodel'saccuracywas98.76%using adatasetof500photosand9distincthandmotions.They also suggested a double dimensional (2D) CNN model for dynamicHGRthatincludesofmaxandminresolutionsubnetworks,whichwaslaterdemonstratedtohaveattainedan accuracyof98.2%onthesamedataset.
FordynamicHGRthatincorporatesactionsaswellasmotion sensing,thesuggested worksare not appropriate.So,it is necessarytoinvestigatetheselectionofreliableclassifiers and suitable hyper-parameters for the same. Adithya and Rajesh[10]suggestadeepCNNarchitectureforHGR.The suggested architecture avoids detecting and segmenting handsincollectedpictures.Theauthorstestedthesuggested architectureontheNUShandpostureandAmericanFinger spelling A datasets, achieving accuracy of 94.26% and 99.96%,respectively.TheauthorsIslametal.[11]developed aCNNmodelwithdataaugmentationforstaticHGR.Inthis case, 8000 photographs from the dataset are utilized for training, whereas 1600 images are used for testing after being divided into 10 classes. The dataset has been augmented using various data augmentations such as zooming, re-scaling, rotation, shearing, height, and width shifting.
Neethu et al. [12] used a cutting-edge deep CNN model to performhandmotionrecognitionandHGR.Here,thehand andfingerphotosareseparatedintoseparatemaskimages, whicharesubsequentlysenttoCNN forclassificationinto severalgroups.Theresultsdemonstratethatthesuggested CNN model produced a 90.7% recognition accuracy. Wu [13],suggestedadoublechannelCNN(DC-CNN)modelfor HGR. The hand gesture photos and hand edge images are createdherebypre-processingthesourcephotographs.The CNNchannelsthencategoriesthesepicturesusingtwofeeds. These pictures are then sent into two CNN channels for classification.ThesuggestedDC-CNNdemonstratedaccuracy of98.02%and97.29%ontheJochen-TrieschDatabaseand theNAOCamerahandpostureDatabase,respectively.The suggested DC-CNN approach has not been tested with complicatedbackdroppictures.Furtherfeaturesarebeing added to make the model more versatile. The model's applicabilitytodynamicHGRmustbeinvestigated.
Lai and Yanushkevich [14] proposed a mix of CNN and recurrentneuralnetwork(RNN)forautonomousHGRbased ondepthandskeletondata.RNNisutilizedtoprocessthe

skeletondatainthiscase,whereasCNNisusedtoanalyze the depth data. Using the dynamic hand gesture-14/28 dataset, the suggested model attained an accuracy of 85.46%. The presented approach may be expanded to recognizehumanactivities,whichisanintriguingsubjectto investigate.Baoetal.[15]suggestedadeepCNNmodelfor smallHGRdirectlyfrompictureswithoutsegmentationor pre-processing.ThesuggestedHGRnetworkcandistinguish betweenuptosevengroups.Thesuggestedmodelattained accuracy of 97.1% for simple backdrop and 85.3% for complicatedbackground,respectively.Ithasbeensaidthat the proposed solution has the benefit of being able to be implementedinreal-time
A realistic and effective way for creating the model's contourswhicharethenevaluatedwiththepicturedatais produced by using quadrics to create the 3D model. An Unscented Kalman filter (UKF), which reduces the geometrical uncertainty between the profiles and edges retrievedfromthepictures,isusedtopredictthepostureof the hand model. Although giving more accuracy than the enhancedKalmanfilter,theUKFallowsforfasterframerates than more complex estimating techniques like particle filtering.Thehandgesturerecognitionjobmaydependona variety of input data types and combinations, much like other computer vision-related tasks. As a result, methodologiesdescribedintheliteraturemaygenerallybe dividedintotwocategories:monotonicandmultifunctional. To address the action and sign language recognition challenges, the authors of suggest transformer-based methods that are comparable to ours. An input translator and recognizing paradigm that resembles the Faster Rstructure CNN's uses a slightly adapted variant of the transformer architecture. A data extractor and a transformer-like framework are combined to recognize actionsinreal-time.Thetemporallinkagesarenotexplicitly modelled since it uses 1D convolutional layers between consecutive decoder blocks rather than any kind of positional encoding. On the contrary side, in our method, positional encodings is used to encapsulate the temporal featuresontheframesorder(PE)[16].
The CNNs is the state-of-the-art in machine learning and extensively employed for various image identification applications,haveastrongcompetitorintheshapeofVision Transformer(ViT).Intermsofaccuracyandcomputational efficiency,ViTmodelsperformedapproximatelyfourtimes better than the most advanced CNNs currently available. New vision transformer frameworks have also exhibited surprising skills, reaching equivalent and even superior performance than CNNs on several computer vision applications,despiteconvolutionalneuralnetworkshaving longsincedominatingtheareaofmachinelearning.
Here,ithasbeenresearchedanddevelopedaTransformerbasedframeworktorecognizehandgesturesinthisarticle. In a sense, we take use of the Transformer architecture's
recentground-breakingworkinsolvingmanycomplicated ML issues, as well as its enormous potential to use more input parallel processing with attentive mechanisms. To solvetheissuesmentionedabove,VisionTransformers(ViT) might be regarded as an acceptable architecture. The presented Vision Transformer-based Hand Gesture Recognizing(ViTHGR)frameworkmayaddressissueswith assessment accuracy and training time that are often encounteredwhenusingothernetworkslikethetraditional MLtechniques.Asaresult,theprimarysignalisdividedinto smaller sections using a certain window opening in the recommendedViT-HGRtopology,andoneofthesesegments isthensenttotheViTforadditionalassessment.
2. VISION TRANSFORMER (ViT)

TheadventofVisionTransformer(ViT)putsCNN,thestateof-the-art in computer vision that is so often used in a variety of image identification applications, into intense competition.Convolutionalneuralnetworks(CNNs)cannot competewiththeViTmodelsintermsofprocessingpower, effectiveness,andaccuracy.Modernperformancecriteriafor transformer topologies in the area of natural language processing.
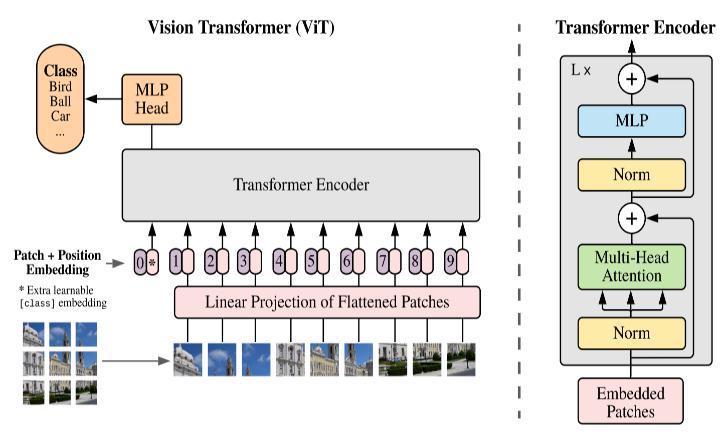
In certain computer vision tasks, the transformer outperformsexistingconvolutionapproaches[10].Avision transformerisatransformerusedspecificallyforacomputer visionjob(ViT).ViTsperformimpressivelyandwithgreat promiseincomputervisionapplications.ViTofferstwokey advantages: 1) Self-attention method, in which the model interpretsawidevarietyofinputseeds(tokens)inanallencompassing context. 2) The capacity to practice challenging activities. The ViT concept is shown in Fig. 1, where initial photos are patched together in line with the prototypemodel.Patchesarethensentimmediatelyintothe layer of the straight projections. The procedure of patch embeddingiscarriedoutinthesecondstep.Thesequencing of the inserted patches now includes the class token. As a result, patches grow in size by one. Positional embedding additionallyaddsembeddedpatchestothedatabasespatial sequencingofpatches.Lastly,theencoderlayerservesasthe first transformer layer and is given patch embedding and positioningofencodingwithaclasstoken.Themostcrucial part of a transformer, notably in ViT, is encoding. The feeding forward layer receives the output of the attentive layer,whichthenproducestheencoder'sfinaloutcome[17].
The ViT encoder has many stages, and each component consistsofthreesignificantprocessingcomponents:
1. Layer Norm
2. Multi-head Attention Network (MSP)
3. Multi-Layer Perceptions (MLP)
1. Layer Norm helps the model adjust to the differences between the training pictures while keepingthetrainingphaseontrack.
2. AnetworkcalledtheMulti-headAttentionNetwork (MSP) creates attention mappings from the integrated visual signals that are provided. These concentration maps assist the network in concentrating on the image's most crucial areas, suchasobject(s).Theideaofattentionmappingis similar to that explored in the research on conventional computer recognition (e.g., saliency mapsandalpha-matting).
3. TheGaussianErrorsLinearUnit(GELU)isthelast layerofthetwo-layerclassificationnetworkknown asMLP.ThefinalMLPblock,commonlyknownas theMLPhead,servesasthetransformer'soutput. Data augmentationmaybeusedonthisoutputto providecategorizationlabels.
Thetransformer'sarchitecturalhasbeenpreserved,andthe majority of the alterations relate to how the photos are alteredbeforebeingsenttothetransformer.WhereasVision Transformer (ViT) uses pictures as its input, NLP-based modelstakeasequenceofwordsasinput.Imagesaresplit into2Dpatchesofagivensizetoaccountforthisdisparity (usually16x16).Priortothepatchesbeingsuppliedtothe Transformer as a flattened 1D sequence, recommends utilizing linear projections on flattened 2D patches and positional embedding to get patch embedding while
retaining positional information (just like tokens). The Transformer Encoder, which is composed of an attention layer and a Multi-Layer-Perceptron, receives a series of patches as input in the basic model's architecture (MLP). This is then sent to a MLP that is not connected to the encoder, and this MLP eventually produces a probability distribution of all the classes. The picture is initially run through a featured extruder, which identifies crucial characteristics that describe the image and normalizes images across RGB channels while maintaining mean and standard deviations. The ViT model is then applied to the picture,witheachlayerteachingthemodelthatsomething newbeforeproducingtheresult[17].
Vaswani et al. [18] served as an inspiration for the Transformersencodingimage.Apictureissplitintosmall patches, each of which is linearly embedded, positional embeddings are added, and the resultant sequences of matricesaresenttoatypicalTransformerencoding.Ithas beenusedtheconventionalmethodforaddinganadditional trainable"classifyingtoken"tothesequencesasawaytodo classification.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Inthisarticle,theinterpretationofpredefinedIndiansign languages is examined. The suggested strategy may aid disabledindividualsinconversingwithnormalindividuals. IntheperspectiveoftheIndianlanguage,thedatasetutilized forresearchisastaticISLdatabasewithdigitandalphabetic signals.Functioningwiththetransformerencodingdoesnot need any data preparation. ViT assists the model in enhancing its performance. The performance of the suggestedtechniqueisshowninTable1.Recallisthetotal proportion of entries that were mistakenly categorized as negative,calculatedby(“equation2”)dividingthenumberof realpositivesbythesummationoftruepositivesandfalse negatives. Precision and F-1 score are calculated by “equation1”and“equation3”,respectively.

Mathematically,thereportcanberepresentedinasimilar manneras;
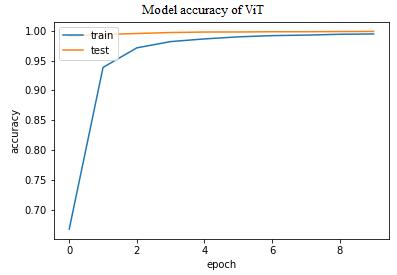
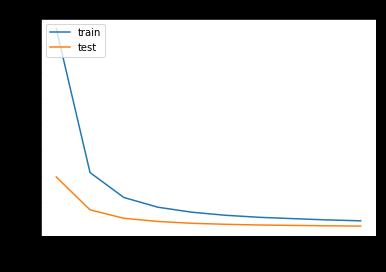
As seen in Fig. 2. the proposed model demonstrates great convergencethroughoutthetrainingandvalidationphases. The samples were evaluated by means of the ViT model. These are the testing accuracy results for ten epochs. The totalaverageaccuracywas99.88%;asshowninFig.2.outof the 48281imagesutilizedfortesting,3531werecorrectly categorized,while165weremisclassified.Itisseenthatthe ViTmodelperformedhavinggoodindexofaccuracylevel. FromFig.3itcanbeobservedthattheconvergencetimeand losses are minimized. Table 2 displays the training loss, percentageaccuracy,validationaccuracy,andvalidationloss astheyoccurredwiththeresponsetime.
ModelaccuracyofViTmodel
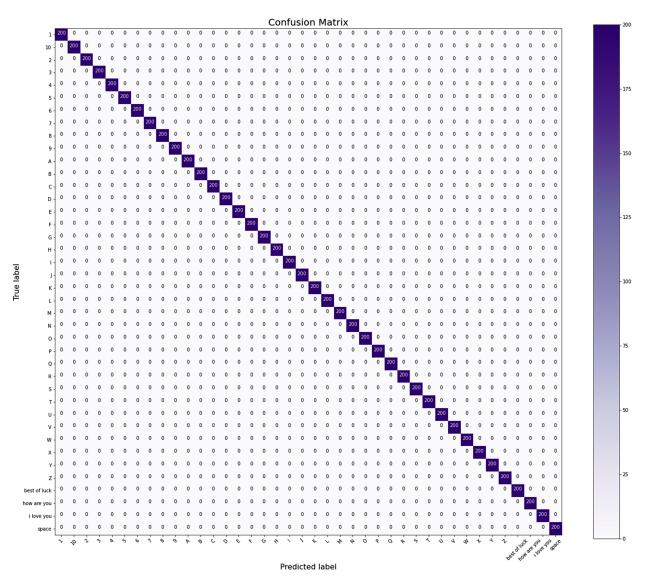
A confusion matrix is also plotted in Fig. 4. A confusion matrix displays the real positives and negatives identified duringtheexecutionofthealgorithm.Thisillustrateswhere thealgorithmwentwrongaswellasthenumberofaccurate exclusionsandfalsepositives.Thegenuinelabelingisshown ontheyaxisandtheanticipatedlabelingisdisplayedonthe xaxis.Theconfusionmatrixhelpstodeterminewhetheror notthebulkofthemodel'spredictionsaretrue.
4. CONCLUSION
In this research, the viability of the ViT approach for the categorizationoftheHGRisinvestigated.Theshortcomings of the Convolutional networks were addressed using the newlyintroducedstrategyknownasViT.ThesuggestedViTHGR system can categorize a significant variety of hand gesturescorrectlyfromstartwithoutthenecessityofdata augmentingand/ortransferlearning,henceovercomingthe retrainingtimeissueswithrecurrentplatforms.Accordingto testfindings,thepresentedapproachframeworkattainsan achievedaccuracyof99.88%ontheimagedatabaseused, whichisconsiderablyhigherthanthestate-of-the-art.The ablationstudyalsosupportstheclaimthattheconvolutional encodingincreasesaccuracyonHGR.Innextresearch,more pre-trainedViTalgorithmswillbeutilizedforthepurposeof improving the accuracy of hand gesture identification. Furthermore,additionalhandgesturedatasetsaswellasthe MLP mixing models will be employed in future investigations.
REFERENCES
[1] Z.Ren,J.Yuan,J.Meng,andZ.Zhang,“Robustpart-based hand gesture recognition using kinect sensor,” IEEE transactions on multimedia, vol. 15, no. 5, 2013, pp. 1110–1120.
[2] S. Ahmed, K. D. Kallu, S. Ahmed, and S. H. Cho, “Hand gestures recognition using radar sensors for humancomputer-interaction: A review,” Remote Sens, vol. 13,no.3,Feb.2021.
[3] VandenBergh,M.,&VanGool,L,“CombiningRGBand ToFcamerasforreal-time3Dhandgestureinteraction,”

In 2011 IEEE workshop on applications of computer vision(WACV),January2011,pp.66-72,
[4] Karbasi, M.; Bhatti, Z.; Nooralishahi, P.; Shah, A.; Mazloomnezhad,S.M.R,“Real-timehandsdetection in depthimagebyusingdistancewithKinectcamera,”Int. J.InternetThings,Vol. 4,2015,pp.1
6.
[5] A.J.Heap,D.C.Hogg,“Towards3-Dhandtrackingusing adeformable model,” In 2nd International Face and GestureRecognitionConference(1996),pp140–45.
[6] D.LeeandW.You,“Recognitionofcomplexstatichand gestures by using the wristband‐based contour features,”IETImageProcessing,vol.12,no.1,2018,pp. 80–87.
[7] S. F. Chevtchenko, R. F. Vale, and V. Macario, “Multiobjective optimization for hand posture recognition,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 92, 2018, pp. 170–181.
[8] Parvathy P, Subramaniam K, Prasanna Venkatesan G, Karthikaikumar P, Varghese J, Jayasankar T, “Developmentofhandgesturerecognitionsystemusing machine learning,” J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 12(6):2021,6793–6800.

[9] Zhan F, “Hand gesture recognition with convolution neural networks,” In: 2019 IEEE 20th international conference on information reuse and integration for datascience(IRI),2019,pp295–298
[10] Adithya V, Rajesh R, “A deep convolutional neural networkapproachforstatichandgesturerecognition,” Procedia Computer Science third international conferenceoncomputingandnetworkcommunications (CoCoNet’19)171,2020,pp.2353–2361.
[11] Islam MZ, Hossain MS, ul Islam R, Andersson K, “Static hand gesture recognition using convolutional neuralnetworkwithdataaugmentation,”.In:2019joint 8thinternationalconferenceoninformatics,electronics vision(ICIEV)and20193rdinternationalconferenceon imaging,visionpatternrecognition(icIVPR),2019,pp. 324–329.
[12] Neethu PS, Suguna R, Sathish D, “An efficient method for human hand gesture detection and recognition using deep learning convolutional neural networks,”SoftComput,vol.24(20),2020,pp.15239–15248,.
[13] WuXY,“Ahandgesturerecognitionalgorithmbasedon dc-cnn”, Multimed Tools Appl, vol. 79(13), 2020, pp. 9193–9205.
[14]Lai K, Yanushkevich SN, “Cnn+rnn depth and skeletonbaseddynamichandgesturerecognition,”In: 2018 24th international conference on pattern recognition(ICPR),2018,pp3451–3456
[15] Bao P, Maqueda AI, del-Blanco CR, García N, “Tiny handgesturerecognitionwithoutlocalizationviaadeep convolutionalnetwork,”.IEEETransConsumerElectron, vol.63(3),2017,pp.251–257.
[16] Song, L.; Hu, R.M.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, Y.L.; Gong, L.Y, “Real-time 3d hand gesture detection from depth images”, Adv. Mater. Res, Vol. 756, 2013, pp. 4138–4142
[17] Cheng, P. M., and Malhi, H. S. “Transfer learning with convolutional neural networks for classification of abdominal ultrasound images,” Journal of digital imaging,Springer, Vol.30(2),2017,pp.234-243
[18] Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, Ł. and Polosukhin, I. “Attention is all you need”, In: 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), LongBeach,CA,USA,2017,pp.1-15
BIOGRAPHIES
Sunil G. Deshmukh acquired the B.E. degree in Electronics Engineering from Dr. Babasaheb AmbedkarMarathwadaUniversity, Aurangabad in 1991 and M.E. degreeinElectronicsEngineering from Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University (BAMU), Aurangabadin2007.Currently,he is pursuing Ph.D. from Dr. BabasahebAmbedkarMarathwada University,Aurangabad, India.He is the professional member of ISTE,Hisareasofinterestsinclude image processing, Humancomputerinteraction.

Shekhar M. Jagade secured the B.E. degree in Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering from Government Engineering College, Aurangabad in 1990 and M.E. degree in Electronics and CommunicationEngineeringfrom Swami Ramanand Teerth MarathwadaUniversity,Nandedin 1999 and Ph.D from Swami Ramanand Teerth Marathwada University,Nandedin2008.Hehas published nine paper in international journals and three papers in international conferences. He is working as a vice-principal in the N. B. Navale Sinhgad College of Engineering, Kegaon-Solapur, Maharashtra, India. He is the professional memberofISTE,ComputerSociety of India, and Institution of Engineers India. His field of interests includes image processing, micro-electronics, Human-computerinteraction.


