Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net


Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net

2,3,4,5, Fourth Year Civil Engineering Department , Government College Of Engineering , Jalgaon – 425001[MS] India ***
Abstract:- Extensivecomplexionclaysoilsarethetypes ofsoilsinwhichthevolumechangeswithrespectto the change in their water content. They have a geste of swelling and shrinking that is a serious hazard to structures erected over them. Extensive soils are abundantly being soil types in Ethiopia, particularly Addis Ababa. This paper shows the issues of an attempt to supports and stabilize extensive completion clay soil with plastic bottle strips. The plastic strips were prepared and added at three different mixing ratios (0.5%, 1.0% and 2.0%) by weight and in three different aspect rates (5.0 mm × 7.5 mm, 10mm × 15mm, 15mm ×20mm). The experimental results showed that there was a significant enhancement in shear strength parameters. The lump and desiccation cracking geste of the soil were also expressively reduced. There was a substantial reduction in the optimum moisture content and slight prolifiration in the maximum dry density. Stabilizing extensive complexion clay soils with waste plastic bottles contemporaneously solves the challenges of indecorous plastic waste recycling that is presently a teething problem in at most developing countries. The results attained from this study positively suggest that addition of this material in extensive soils would be effective for ground improvement/enhancement in geotechnicalengineering.
Keywords:- Extensive Soil, Clay Soil, Plastic Strips, Soil Stabilization.
Extensivecomplexionsoilsaretypesofsoilsshow asignificantchangeinvolumeoncetheycomeincontact withhumidity. Theyexpandwhenexposedtoredundant waterandshrinkinhotrainfallconditionswherethereis a scare quantum of water. geste of sweeling and shrinkageofextensivecomplexionsoilsinturnaffectthe stability of structures that is erected over these soils causing a serious hazard it majoraly affects the bearing capacity and strength of foundations by uplift as they swell and may beget from cracks to discriminational movements to structural faiures [1].In order to make on extensive soil they need to be stabilized to reduce their
lump and ameliorate their mechanical capacities. Soil Stabilization is the process by which the engineering parcels of the soil are bettered and its made further permeability and connection eventuality and increase the shear capacity. [2]. The system is substantially espousedfortraceandplainstable.Itisusedtodropthe soils unqualified characteristics similar as construction.They can easily linked in the field in dry seasonastheyshowdeepcrackofpolygonal.
In order to make soil stabilization goes way over to encouraging operasion of weak sol and reducing the uneconomical process of weak soil relief . Occasionally ,soil stabilization is used for mega city and suburban to make them further noise absorbing . [3].Different styles have been developed preliminary to stabilizes we can infelicitous soil . Some os these styles includes mechanical stabilization , cement stabilization , lime stabilization ,bituminous stabilization, chemical stabilization, thermal stabilization, as well as grouting stabilization by geotextile and fabrics.[4].Using plasticks for this purpose contemporaneously solves the challenges of indecorous plastic waste recycling gthat is presently a teething problem this in turn causes serious damage to beast factory and mortal lives. Polythene Terephathalate (PET) bottles are conventionally plastic bottlestheypresentlyarelargeemployee.
The materials include plastic bags and bottels that were cutted into small three different size strips, using bladesandscissors.Expansivesoilthatwassievedinthe sievingmachinesusingdifferentsizesieves.
Thecharacterizationofsoilsampletakenforthe study included flyspeck size distribution, Atterberg limit and specific gravity of soil tests .The sample soil taken was settled in order to take The bottles and strips were
“STABILAZATIONProf. V. T. Patil1 , Sandip Pukale2 , Pankaj Satpute3 , Imtiyaz Hussain4, Khusboo Waghmare5 1HOD Civil Engineering Department
cleaned properly after collection and bags and bottels were cut into three different sized and shapes strips, manuallyusingscissorsandblades) (Figure 1).Thestrip sizesareshownin Table 1
out any other contaminations and gratuitous patches. It was also prepare for testing according. Once sample medication was done, sieve analysis and hydrometer analysis work conducted to study the flyspeck size distribution of the soil the test was done as per (7) and (8) respectively. We performed plastic limit test, liquid limit test and liquidity indextest to check the behaviour ofsoil.

Free swell test, standard proctor compaction test, direct shear test, Unconfined Compressive Strength (UCS) test and California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test were carried out in order to study these changes of these particularplasticbottleand bagsstripsontheextensive clay soil. The various methods to determine specific standards used to perform these testes are listed in Table 3
By performing the Atterberg limit test. The test was carried out as per(9) using Casagrande outfit . Specific graveness of the soil on the other hand was determined fromthespecificgravitytestinthelaboratory.Aspecific gravity cup and vaccum pump by used to carry out the testasper(10).Thespecificgravitywastakenastherate of viscosity of the soil to the viscosity of water at same temperature.
The plastic strips, which are anticipated to act as soil mounts, were added to the soil in three different possibilities and percentages (0.5%, 1% and 2%) by massofthesoil. Table 2 showsthetreatmentlevelsused for each of these strip while carrying out the study. Percentage by mass represents the rate of mass of plastic to mass of these soil sample taken as a percentage.
The swelling and lumping of the soil sample was studiedbyconductingwiththehelpof freeswelltest.In this test, a 10 g of oven-dried soil sample passing through a number of 40 sieve (425 µm) was put into a graduated free-swell jar which has capacity of 100 ml, and filled with water. The sample was kept undisturbed until it reached its maximum swelling level. Then the recorded value was calculated with respect to the original 10 ml volume and expressed in percentage.
Figure 2 showsfreeswelljars forsettling.TheMDDand OMC were determined by performing standard proctor compactiontest.Inthistest,thesoilwascompactusinga test mould and a rammer at different water contents untilthewetdensitystarteddecreasing (Figure 3).

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056


Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The response of consolidated and the drained soil samplesforthedirectsheartest,andtheresultsinshear strength of the soil were found by performing direct sheartest.Thetestwasconductedbyscrewingainstant at a controlled strength ratio on a single shear plane which is determine by configuration of the outfit. Generally, three samples were tested, each under a different normal cargo load, to demonstrate its effect of surchargeandstructuralloaduponshearresistanceand displacement both relegation. The shear results at the three normal loads are plotted on single graph and linearlyfittedtoobtainresulttheaverageshearstrength (C) of the soil, whereas the angle of internal friction (φ) iscalculatedfromthepitch(slope)ofthelinethatisused to fit the shear strength values. Figure 4 demonstrate the procedures of a direct shear test. Cohesive soils can be estimated grounded based on their shear resistance when confinement to compressive load with no confinement. The unconfined compressive strength (UCS) test was used to determine the shear capacity of the sample soil under contraction . The sample was extracted and cut into the standard cylindrical shape. The UCS machine was used to compress these and both the applied load and change in its length of the sample wererecorded.Thevalueswereobservedandcomputed to get the sample representative value. Figure 5 shows the Unified Compressive Strength test machine and sample.
California Bearing Ratio test was performed to find the penetration strength of a compacted soil relative to crushedrock type, whichis assumed to bean excellent base-course material. The results of a CBR test help to understand the parameters like shear strength and bearing capacity of a soil . The test follows a Indian Standard light weight compaction procedure combined with a doubled penetration thatisapplied bya machine that applies a plunger load. This test was used to simulate the effect of surcharge and excessive moisture on the compacted soil by putting a standard load that represents surcharge and soaking the mould for four days

3.1. Characterization of Soil
Thesoilspecific gravitywhichistheratioofthemass of the soil vs equal volume of water weight. The test conducted is used to find out specific gravity in the extensiveclaysoilsamplebasedonASTMD8954.


The dry density of the soil mass changes with the water content for various types of soil and compactive efforts . with the increase in water content , moisture filmsareformedaroundthesoilparticleswhichincrease in soil mass workability . As the soil particles are replaced by the water the unit weight of water the density begins to decrease . The mass of the compacted soilandthevolumeofmouldgivesthebulkdensity,and using water content we can find the dry density
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
.Compactioncanbeappliedtoimprovethe propertiesof anexistingsoilorintheprocessofplacingthefilms.
The compaction was applied with different percentage of plastic content by the weight of the soil this was supported out with the same percentage of water content[5%,10%,15%,20%] Figure 6. The comparison of MDD and OMC is plotted at different water content anddrydensitiesvalue. Figure 7., Table 5.
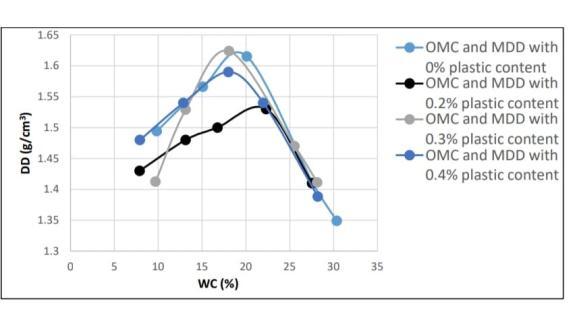
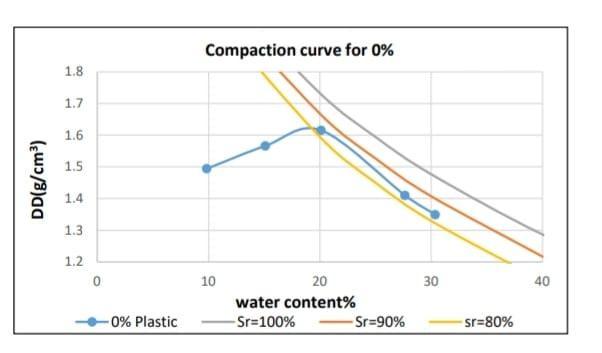
The main challenge of extensive soil is its volume variation in its different moisture conditions. As the water content increases, the soil begins to swell and its volumeincreasesinawiderangefromtheactualvolume. This property happens at a particle level, when the plastics strips was proposed to act as a physical agent and was anticipated to drop the swelling evenly of the soil. For the visual experiment during trails and the conclusion for free swelling test for the soil containing different chance of plastics strips . the reduction in swelling is a sole effect of the physical commerce betweenthesoilandthestrip.Thefreeswellisobserved to be 160 which accordingly to ASTM is classified as vertically largely extensive soil size of 5x7.5mm strip contain interpretation of swelling test results for each plasticsstrips Table 6.Thistestusessampleof10gmina standardgraduatedfreeswelljarthereasonforthedrop swell is eventually because of chemical reaction . The quantum of soil mass drop which is equal to the weight ofplasticaddedasthedropmassofsoilwasreplacedby swellingmaterialthelumpshowsomeenhancementthis soil plastic mixture might also have and effect in reductioninfreeswelling
The strength parameters like cohesion and angle of friction can be obtained using this method. Other arrangement will ameliorate the shear capacity of the soil,itis delicated to the arrangement of the largersize stripsinonthedirectshearmachineasthefaceareawas closed to shear box . The shear capacity from the test is presentedin terms ofstrengthparameterscohesionand angleofinternal friction.Boththe enhancementchange inshearcapacitywererecordedfromcohesionandangle
of internal friction the small value of frictional angle is assigned to the cohesiveness of the soil . The largest value of cohesion and angle of friction. For the collaborated soil was attained independently. This resultsweregiven for the stripsize. Table 7 gives the c andQresultsattainedforeachtreatmentpositionandits sizeaddingtheplasticcontentforthesameplasticstrips sizeisincreasedboththecohesionandfrictionalangle.
The CBR is the most utilized parameter for giving dimensions to the flexible pavement the analysis was carriedwiththehelpofsamecontentofplastic(0,0.2,0.3 and 0.4%). The sample were compacted and their test was conducted till 12.9mm penetration Table 9 shows thepenetrationofplasticvstheCBRloadvalue
Table 9. WC(%)withcorrespondingplasticcontent. Plastic 0% 0.2% 0.3% 0.4% WC(%) 20.11% 22.31% 18.80% 18.1%
TheUnconfinedcompressiveStrengthisdonetofind compressive strength ,for this purpose four samples were compacted and their MDD and OWC with 0,0.2,0.3 and 0.4 percent of plastic bag addition .The height and diameter of the sampler were 120.7 and 102mm respectively.ThesamplewerethenplacedinUCStesting machine and readings were obtain until cracks were observedinthesample Table 8.
Aftergettingtheresultsitisnoticedthatthestrength ofsoilisincreasedasplasticbagpercentageisincreased. Therefore at 0.4% addition of plastic bags unconfined compressive strength was reached. We loses our maximum dry density at 0.4%. So UCS at 0.3% can be accepted as the optimum amount of stabilizer addition. So on the basis of it can be concluded that the plastic bags and bottels increases the cohesion of clay soil sample.
As it can be seen from Table 10. the increase in resistance to penetration is increased as percentage of plastic is increased which also cause increase in CBR ratio.at0.4%thesoilsamplerequiredmoreloadwhich is 2.415KN to penetrate the soil specimen . The CBR valueisachievedmoreat0.4%plasticcontentbutweare losingmaximumdrydensity.hencetherecommendedis soil sample with 0.3% plastic content because it has better soil packing capacity with good CBR value . The CBRvalueforclayshouldbefrom(3-10%).
The following conclusions are drawn grounded on theanalysisandcalculations oftheresultsobtained.Any further a significant and borderline reduction was recordedintheoptimummoisturecontent(OMC)andin themaximumdrydensity(ODD)resultsrespectively.The angle of internal friction and the cohesion increased gradually as the reinforcement percentages and sizes increased. The swelling and the lumps of the soil was reduced significantly at high posibilities of strip content because of replacement in an equal mass of extensive soil by non-extensive plastic. Physical anchor has also some effect in reduction of the free swell. The swelling

reduction similar for different sizes at the same percentage which shows that the dominant factor or constant that contributes to reduction in swelling is percentbyweightofplasticcontent.Thelimitedamount of plastic content and plastic size which results in optimumresultcanbeselectedbasedontheimportance of the selection criterion for a specified engineering work.
In many erection works , stabilizing extensive clay with waste plastic bottles and bags strips is a good alternative as it enhance the volume variation problems of the soil. The strips were acting as reinforcements playing a role of capturing volume changes with change in water content. Incorporating waste plastic bottles in theconstructionindustryalsoisabetterwaytosolvethe issue of insufficient plastic waste disposal which is a majorproblem.
The study advantageous suggest the possibility of utilizing these plastic material as tensile inclusions in extensive soil to increase the resistance to shear, CBR value and reduction in swelling. Many nations are now focussing on the useofthese plasticwaste. According to this paper observed that using the waste in soil stabilization provides better engineering properties to the soil. Indian has started using it in construction and buildingofroadandpavement.
References :-
[1] Arora, K.R. (2004) Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Standard Publishers Distributors, New York.
[2] Gandhi, K.S. (2012) The Expansive Soil Stabilization Using Bagasse Ash. The International Journal of EngineeringResearch&Technology,1,2278.
[3] Fauzi, A., Djauhari, Z. and Fauzi, U.J. (2016) Soil Engineering Properties Improvement and enhancement by Utilization of Cut Waste Plastic and Crushed Waste Glass as Additive. International Journal of Engineering and Technology, 8, 15-18. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJET.2016.V6.851

[4]Saini,K.,Chaudhary,V.,Bisnohi,A.,Agarwal,H.,Ram, M.andSaraswat, S.(2016) EffectonStrength Properties of the Concrete by Using Waste Wood Powder as Partial Replacement of Cement. SSRG International Journal of CivilEngineering,3,172-176...
[5] Chebet, F. C. and Kalumba, D. (2014). Laboratory investigation on re-using polyethylene (plastic) bag waste material for soil reinforcement in geotechnical engineering. Civil Engineering and Urban Planning: An InternationalJournal,1(1),67-82.
[6] Chen, F. H. (2012). Foundations on expansive soils . Elsevier
[7]ASTMD6913M-17(2017)StandardTestMethodsfor Particle-SizedDistribution(Gradation)ofSoilsUsing the Sieve Analysis. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA.
[8] ASTM D4318-17 (2017) Standard Test Methods for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit, and Plasticity Index of Soils. ASTMInternational,WestConshohocken,PA
[9] ASTM D854-14 (2014) Standard Test Methods for Specific Gravity of Soil Solids by Water Pycnometer. ASTMInternational,WestConshohocken,PA.
[10] ASTM D698-12 (2012) Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Compaction of Soil Standard Effort. ASTM International,WestConshohocken,PA.
[11] ASTM D3080-11 (2011) Standard Test Method for Direct Shear Test of Soils Under Consolidated Drained Conditions.ASTMInternational,WestConshohocken,PA.
[12] ASTM D1883-16 (2016) Standard Test Method for CaliforniaBearingRatio(CBR)ofLaboratory-Compacted Soils.ASTMInternational,WestConshohocken.
[13]ASTM D2166-16 (2016) Standard Test Method for UnconfinedCompressiveStrengthofCohesiveSoil.ASTM International,WestConshohocken.
[14] Choudhary, A.K., Jha, J.N. and Gill, K.S. (2010). A study on CBR behavior of waste plastic strip reinforced soil. Emirates journal for engineering research, 15(1), 51-57.
[15] Dalvi, A., Patil, A., Jadhav, Y., Jadhav, K., Nehatrao, P., Gawali, S. and Mantri, S. (2018). Efficacy of Sustainable Soil Stabiliser on Compaction Properties of Expansive Soil. In International Congress and Exhibition" Sustainable Civil Infrastructures: Innovative Infrastructure Geotechnology" (PP77-84). Springer, Cham