BLOOD TISSUE IMAGE TO IDENTIFY MALARIA DISEASE CLASSIFICATION
Abstract - Plasmodium falciparum malaria epidemics are common and often lethal, according to reports. Through the use of meteorological characteristics that are determinants of transmission potential, epidemics havebeenformallyattemptedtobepredicted.Regarding therelativeweightandpredictivepowerofthesecriteria, however,thereislittleagreement.Toidentifypreciseand significant indicators for epidemic prediction we are using ASKalgorithm, it is essential to comprehend the causes of variance. In this study, we extracted several blood cell properties and used convolutional neural network-basedmodelstoidentifymalariainbloodtissue images using structured analysis. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) were used in deep learning to successfully classify malaria blood tissues. It was described as a new technique that offers effective categorization detection.
Key Words: Malaria detection, Plasmodium parasite, Transfer learning, Convolutional neural networks, Computer aided design (CAD), Alex net, Lenet
1. INTRODUCTION
Millionsofpeoplesufferfrommalaria,aparasiteillnessthat is most prevalent in underdeveloped nations. Effective malariatreatmentanddiseasemanagementdependonan early and precise diagnosis. Currently, the most used approachfordiagnosingmalariaismicroscopicanalysisof bloodsmears.Thisstrategy ofdiagnosingmalaria islabor andtime-intensive,henceautomatedandeffectivemethods arerequired.
A branch of artificial intelligence called deep learning has demonstratedpromiseinanumberofpicturecategorization tasks. Deep learning for malaria prediction using blood tissuepictureshasattractedmoreattentioninrecentyears. Researchershavecreatedmachinelearningmodelsthatcan accurately predict the presence of malaria using vast datasets of blood tissue pictures that are both malariapositiveandmalaria-negative.
Inthisproject,wewillexploretheuseofdeeplearningfor malariapredictionusingbloodtissueimages.Wewillbegin byacquiringadatasetofbloodtissueimagesfrommalariapositive and malaria-negative patients, and we will preprocessthedatatoensurequalityandstandardization.
Wewillthendevelopandtraindeeplearningmodels,suchas convolutionalneuralnetworksanddeepbeliefnetworks,on thisdatasettopredictthepresenceofmalaria.Finally,we willevaluatetheperformanceofourmodelsusingavariety of metrics, such as accuracy, precision, and recall, and compare them to traditional approaches for malaria diagnosis.
Theultimateobjectiveofthisresearchistocreateareliable andeffectiveautomatedmethodfordiagnosingmalariathat maybeemployedinenvironmentswithlimitedresources. We can enhance malaria early diagnosis and treatment, loweringthetotalhealthburdenoftheillness,by utilizing deeplearningtoanalyzebloodtissuepictures.

2. PROPOSED SYSTEM
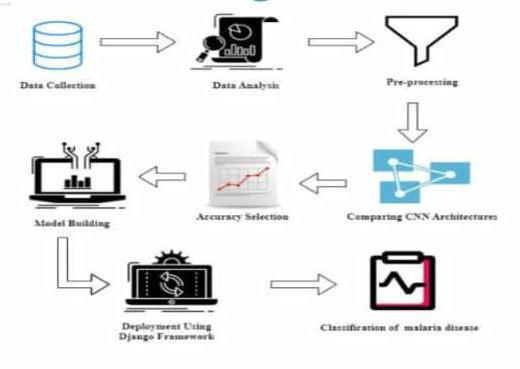
2.1 ARCHITECTURE DIAGRAM
EXPLANATION
Uploadthebloodtissueimagesasdataset.Thedatasetsis preprocessed such as image reshaping, resizing and conversion to the array form. The train dataset is used to traintheCNNmodel.
After the model is trained, the blood tissue image dataset undergo the testing model. The model is deployed using Djangoframework.Atlastthemalariaispredicted.
LIST OF MODULES

2.2 Import the Given Image from the Dataset
We have to import our data set using the Keras preprocessingimagedatageneratorfunction.Wealsocreate size,rescale,range,zoomrange,andhorizontalflip.Thenwe importourimagedatasetfromthefolderthroughthedata generatorfunction.Herewesettotrain,test,andvalidate; wealsosettargetsize,batchsize,andclassmode.Fromthis function,wehavetotrainusingourowncreatednetworkby addinglayersofCNN.
Pooling layers: Thepoolinglayerdownsamplesthefeature mapsandreducesthenumberofparametersneededforthe network. It helps to make the CNN more robust to small variationsintheinputimage.
Fully connected layers: These layers take as input the flattenedoutputoftheearlierlayersandclassifytheimage into malaria-positive or malaria-negative based on the extracted features. These layers are trained using back propagation to adjust the weights of the network and improveitsaccuracy.
To train the CNN algorithm for malaria prediction using bloodtissueimages,alargedatasetofmalaria-positiveand malaria-negative blood tissue images is needed. The CNN model then goes through an iterative process of training, validation and testing to optimize the accuracy of malaria prediction.
Overall, CNNs offer an effective and efficient approach for malaria prediction using blood tissue images, providing a potentialsolutionforaccuratelyandquicklydiagnosingthe disease.
2.5 Alex NET
Convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture called AlexNetismadetoidentifyobjectsinphotos.Itwascreated specificallyfortheImageNetLargeScaleVisualRecognition Challenge(ILSVRC)in2012.There,itearnedatop-5error rateof15.3%,whichwasfarbetterthanthepriorstateof the art. Eight layers make up the architecture, with five convolutional layersatthebottom,twofullylinkedlayers abovethem,andasoftaxoutputlayeratthetop.Thereare over60millionparametersinit.
2.3 To Train the Module from the Given Image Dataset
Weaddtrainingstepsforeachepochwhileutilisingthe classifierandfitgeneratoralgorithmstotrainourdataset, and we then add up the epochs, validation steps, and validation data. We can train our dataset using this informationandthisisbasisprocess.
2.4 Convolutional layers:
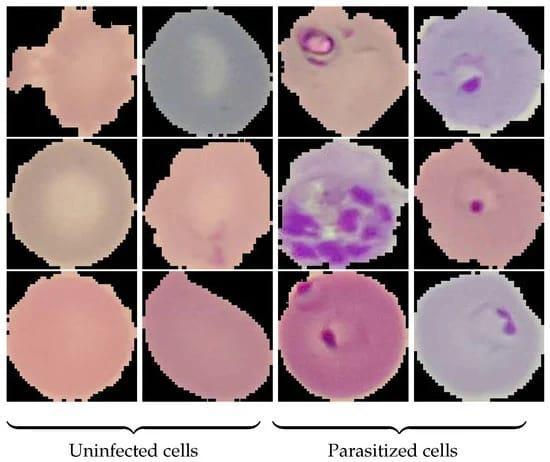
ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(CNNs)areatypeofdeep learning algorithm that is commonly used for image classificationtaskssuchasmalaria predictionusing blood tissueimages.Here'sabriefexplanationofhowCNNswork:
Convolutional layers: Inthislayer,theCNNappliesasetof filterstotheinputimagetoextractrelevantfeatures.Each filterlooksforspecificpatternsintheimage,suchasedges, curves,orshapes.Theoutputofthislayerisasetoffeature mapsthatrepresenttheextractedfeatures.
Becauseofitsarchitecture,AlexNetisabletolearnintricate characteristics directly from unprocessed photos. ConvolutionallayersmakeupthefirstfivelayersofAlexNet, whichareeachfollowedbyamax-poolinglayer.Theimage's characteristicsthatarepertinenttotheclassificationjobare extractedusingconvolutions.Thepictureisdownsampled using max-pooling, which also lowers the amount of parametersinthenetwork.
Linear Rectified Units Instead of the sigmoid, AlexNet employstheReLUactivationfunction.ReLUcomputesmore quicklyandaidsinpreventingthevanishinggradientissue thatmighthappenwhenusingsigmoid.
NormalisationofLocalReactionTonormaliseeachneuron's output basedonits nearby neurons,LRN isutilisedin the firstandsecondconvolutionallayers.Byenhancingcontrast betweenvariousareasoftheimage,thisissupposedtoaid generalisation.Toavoidoverfitting,AlexNetusesdropoutin thefullylinkedlayers.Inordertoforcethenetworktolearn morerobustfeatures,dropoutrandomlyremovespartofthe neuronsduringtraining.
Utilisingstochasticgradientdescent(SGD)withmomentum, thenetwork'sweightsaremodifiedthroughouttraining.To optimise its parameters for the classification task, the network is trained using a sizable dataset of blood tissue pictures of malaria-positive and malaria-negative individuals. After being trained, the AlexNet algorithm is capableofclassifyingphotosofrawbloodtissue.
2.6 LENET
Oneofthefirstpre-trainedmodelswasLenet-5,whichYann LeCun and colleagues developed in the research article Gradient-BasedLearningAppliedtoDocumentRecognition published in 1998. For reading both machine-printed and handwritten characters, they employed this architecture. Thismodel'ssimplisticanduncomplicatedarchitecturewas largely responsible for its success. It is an image categorizationconvolutionneuralnetworkwithmanylayers.
2.5.1 Alexnet Architecture
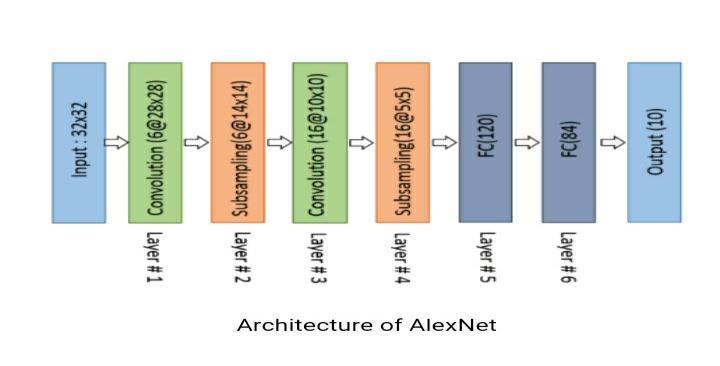
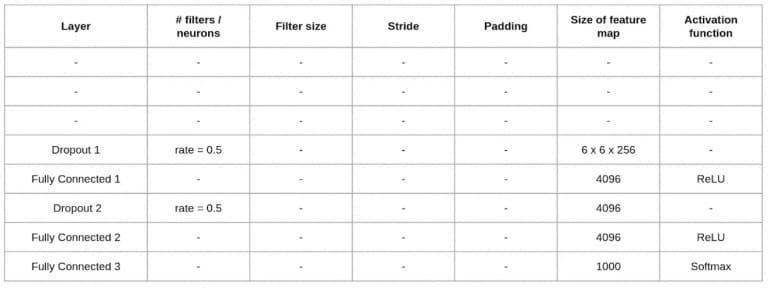
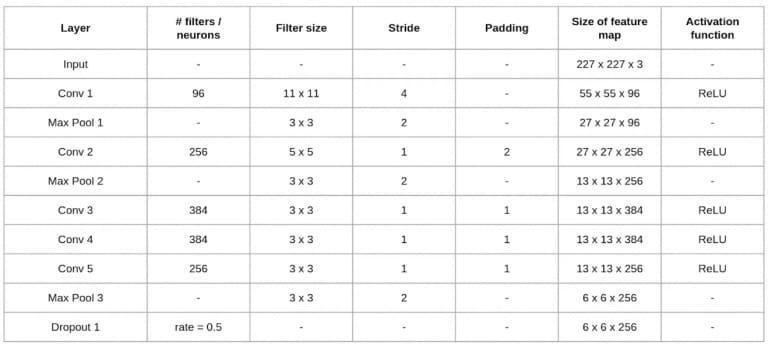
AlexNet is a popular deep convolutional neural network modelthatwasproposedbyKrizhevskyetal.in2012.Itwon the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC)in2012,achievingatop-5errorrateof15.3%.The architectureofAlexNetconsistsof5convolutionallayers,3 max pooling layers, and 3 fully connected layers. Each convolutionallayerisfollowedbyaReLUactivationfunction, and each max pooling layer uses a pool size of 3x3 with a strideof2pixels.
ThefirstconvolutionallayerintheAlexNetarchitecturehas 96filters,eachwiththesizeof11x11pixelsandastrideof4 pixels. This layer is followed by a max pooling layer that reduces the spatial dimensions of the output by half. The secondconvolutionallayerconsistsof256filterswithasize of 5x5 pixels and a stride of 1 pixel. Similarly to the first layer,thislayerisfollowedbyamaxpoolinglayer.Thethird, fourth,andfifthconvolutionallayerseachhave384,384,and 256filters,respectively,withasizeof3x3pixelsandastride of1pixel.
2.6.1 Architecture of Lenet

PublishedonMarch18,2021,andupdatedonMarch30th, 2021byShipraSaxena
DeepLearningandAdvancedComputerVisionVideos
Pre-trainedmodelsareaquickandinexpensivewaytosolve deeplearningissueswithtransferlearning. Recognisethe Lenet-5architectureasdescribedbytheauthors.
Oneofthefirstpre-trainedmodelswasLenet-5,whichYann LeCun and colleagues developed in the research article Gradient-BasedLearningAppliedtoDocumentRecognition published in 1998. For reading both machine-printed and handwrittencharacters,theyemployedthisarchitecture.
Thismodel'ssimplisticanduncomplicatedarchitecturewas largely responsible for its success. It is an image categorizationconvolutionneuralnetworkwithmanylayers.
Lenet-5 is among the early pre-trained models that Yann LeCun and colleagues suggested in the research article Gradient-BasedLearningAppliedtoDocumentRecognition published in 1998. This design was used to identify both machine-printedandhandwrittencharacters.
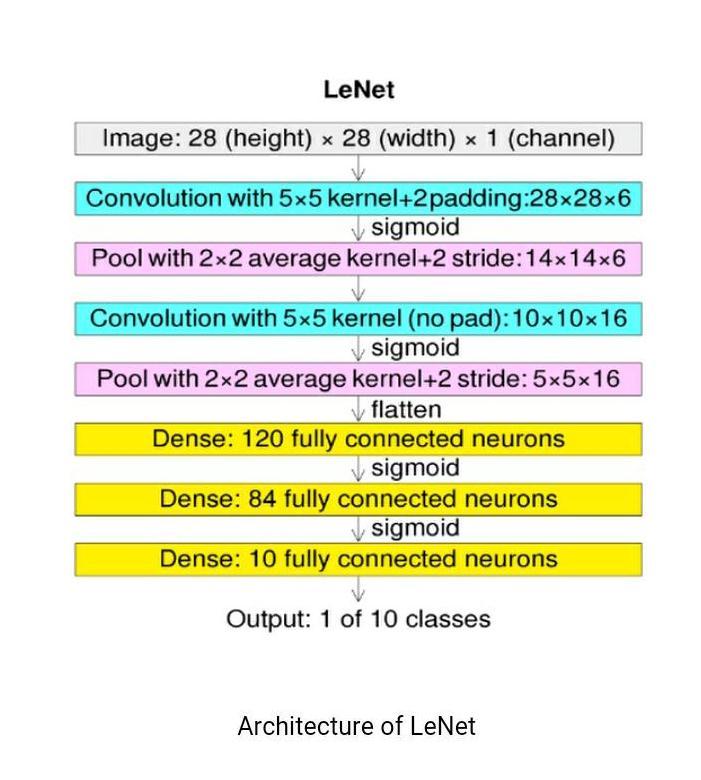

This model's uncomplicated construction was primarily responsibleforitssuccess.Amulti-layerconvolutionneural networkisusedtoclassifyimages.
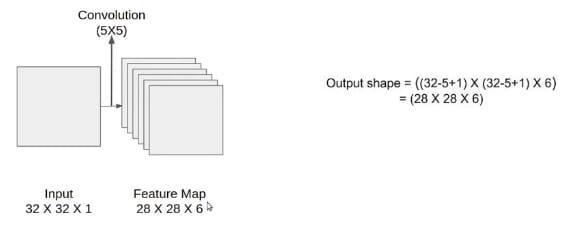
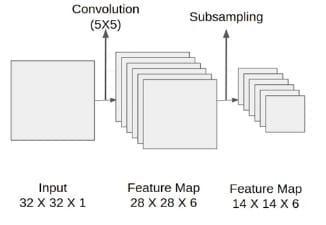
Let'sexamineLenet-5'sarchitecture.Thenetworkisknown as Lenet-5 since it contains five layers with learnable parameters.Itcombinesaveragepoolingwiththreesetsof convolutionallayers.Wehavetwocompletelylinkedlayers following the convolution and average pooling layers. Finally, a Softmax classifier places the photos in the appropriateclass.Thismodel'sinputisa32by32grayscale picture,thereforethereisjustonechannel.
3. ASK ALGORITHM
Step 1: The input image is first processed to remove unwantednoisefromtheRGBcellimage.
Step2:Thepreprocessedimageisthengivenasaninputto thesegmentationstage.
Step 3: The image is segmented to extract the region of interestfromtheimage,andwegetthesegmentationimage.
Step4:Wethenfeedtheimagesasan inputtothefeature extraction stage, where the output will be the feature vectors.
Step5:Thenextstageistheclassificationstage,wherethe inputwillbethefeaturevectors,andoutputistheclassified labelasparasiticandnon-parasitic.
4. CONCLUSION
Itfocusedhowimagefromgivendataset(traineddataset) and past data set used to predict the pattern of malaria diseasesusingCNNmodel.Thisbringssomeofthefollowing insightsaboutmalariadiseaseprediction.Themajorbenefit oftheCNNclassificationframeworkistheabilitytoclassify images automatically. Malariadisease is a blood tissue disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and often can’t be remedied because the patients are diagnosedtoolatewiththediseases.Inthisstudy,wehave discussedtheoverviewofmethodologiesfordetectingthe abnormalities in blood tissue images which includes collection of blood tissue image data set, pre-processing techniques,featureextractiontechniquesandclassification schemes.
2.7 DEPLOYMENT
DeployingthemodelinDjangoFrameworkandpredicting output In this module the trained deep learning model is convertedintohierarchicaldataformatfile(.h5file)whichis thendeployedinourdjangoframeworkforprovidingbetter userinterfaceandpredictingtheoutputwhetherthegiven materialimageisFabric,Glass,Plastic.
MODELACCURACYOFLENET
5. FUTURE WORK
Medical department wants to automate the detecting of malaria disease from eligibility process (real time).To optimize the work to implement in Artificial Intelligence environment.
REFERENCES
[1] WearablesDetectMalariaEarlyinaControlledHumanInfection Study. Sidhartha Chaudhury, Chenggang Yu, RuifengLiu(2022)
[2] TowardsanEfficientPredictionModelofMalariaCases in Senegal.Ousseynou Mbaye, Mouhamadou Lamine Ba1.June,(2019)
[3] Malaria outbreak detection with machine learning methods,july21(2020)
[4] Malaria Epidemic Prediction Model by Using Twitter Data and Precipitation Volume in Nigeria Nduwayezu Maurice,SatyabrataAicha,HanSukYoung,KimJungEon, KimHoon,ParkJunseok,HwangWon-Joo,may(2019)
[5] World Health Organization, World Malaria Report, Geneva,Switzerland:WHO,2018.
[6] M.Spring,M.Polhemus,andC.Ockenhouse,“Controlled human malaria infection,” J. Infect. Dis., vol. 209, no. Suppl2,pp.S40
S45,2014.
[7] M. C. Langenberg et al., “Controlled human malaria infection with graded numbers of Plasmodium falciparum NF135.C10- or NF166.C8-infected mosquitoes,” Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg.,vol.99, no. 3, pp. 709–712,2018.
[8] M.B.Laurensetal.,“Aconsultationontheoptimization ofcontrolledhumanmalariainfectionbymosquitobite forevaluationofcandidatemalariavaccines,”Vaccine, vol.30,no.36,pp.5302–5304,2012.
[9] J. E. Epstein et al., “Safety and clinical outcome of experimental challenge of human volunteers with Plasmodium falciparum-infected mosquitoes: An update,”J.Infect.Dis.,vol.196,no.1,pp.145–154,Jul. 2007.
[10] United States Food and Drug Administration, “Guidance for industry tox- icity grading scale for healthy adult and adolescent volunteers enrolled in preventivevaccineclinicaltrials,”2007.Accessed:Oct.3, 2021, [Online].

Available: http://www.fda.gov/cber/guidelines.htm
[11] B.Mordmülleretal.,“Directvenousinoculationof Plasmodium falci- parum sporozoites for controlled human malaria infection: A dose-finding trial in two centres,”Malar.J.,vol.14,pp.117,Mar.2015.
[12] M. Sklar et al., “A three-antigen Plasmodium falciparum DNA prime Adenovirus boost malaria vaccine regimen is superior to a two-antigen regimen andprotectsagainstcontrolledhumanmalariainfection inhealthymalaria-naïveadults,”PLoSOne,vol.16,no.9, Sep.2021,Art.no.e0256980.
[13] J.E.Sasaki,D.John,andP.S.Freedson,“Validation andcomparisonofActigraphactivitymonitors,” J.Sci. Med.Sport.,vol.14,no.5,pp.411–416,Sep.2011.
[14] J.KarjalainenandM.Viitasalo,“Feverandcardiac rhythm,” Arch. Intern. Med., vol. 146, no. 6, pp. 1169–1171,Jun.1986.
[15] J. Radin et al., “Assessment of prolonged physiological and behavioral changes associated with COVID-19infection,”JAMANetw.Open,vol.4,no.7,Jul. 2021,Art.no.e2115959.
