Pet Care Application
Ratnangsu Chatterjee, Apoorvi SinghApoorvi Singh, Student SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Tamil Nadu, India
Ratnangsu Chatterjee, Student & SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Tamil Nadu, India

Mrs. Saveetha D, Professor, Dept. of Networking and Communications, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Tamil Nadu, India ***
Abstract - Recently there has been a major uptick in the number of pet owners in India. In the past few years, the number of pet owners has increased. Thus, it has become increasingly important for proper pet care applications and personnel. Knowing the correct breed of a pet is crucial for providing adequate care. The pet’s age, height, and weight all have a significant impact on how well they respond to a healthy diet, regular exercise, and other measures of wellness. These considerations determine dietary choices. Having more pets increases the risk of their deaths, as it is difficult to properly care for any animal. As a result, it is crucial to know the correct disease in the early stages as it can save the lives of many pets. The ability to predict breed more effectively is a strength made possible by deep learning, a model of algorithms capable of tackling informational challenges. It is possible to categories and forecast based just on the occurrence of raw data as a source of information. An example, Convolution Neural Networks (CNNs) provide a common framework for picture Sorting and spotting. In this effort, we use a convolution neural network (CNN) for detecting canines in randomly generated photos thereby demonstrating carelessness with regard to attribution of a rare and unique canine breed. The analysis was validated using commonly used metrics; hence the diagram display verifies that the algorithm (CNN) produces accurate evaluation precision across all data- sets. One area where machine learning has found use is in disease prediction. More cutting-edge medical technology is needed to give patients the best care possible. Decision Tree Classifier in Na¨ıve Bayes algorithm were chosen and applied to the data to achieve the best possible outcomes. Machine learning’s potential in healthcare has been demonstrated, and it has the potential to significantly improve patients’ health. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to investigate the feasibility of integrating machine learning into an existing veterinary healthcare infrastructure for pets. The entire therapy procedure can be optimised if the disease is forecast-ed in advance using specific machine learning algorithms rather than being performed directly on the patient. The failure to perform or carry out early diagnosis of an illness may also occur. As a result, anticipating the course of a disease is crucial. As the old adage goes, ”Prevention is better than cure,” so accurate disease forecasting would undoubtedly result in earlydisease prevention.
Key Words: Convolution Neural Network(CNN), Decision Tree, Machine Learning, Deep learning, Breed Prediction, Dis-easePrediction
1.INTRODUCTION
In India, over 19.5 million dogs were maintained as companionanimalsin2018,accordingtorecentestimates,itis anticipatedthattherewillbemorethan31millionpeople living with their pets in the India by 2023. Thus, it is important for pet owners to properly understand their pets’ breedanditsparticularneeds.
1.1 Breed Prediction using CNN
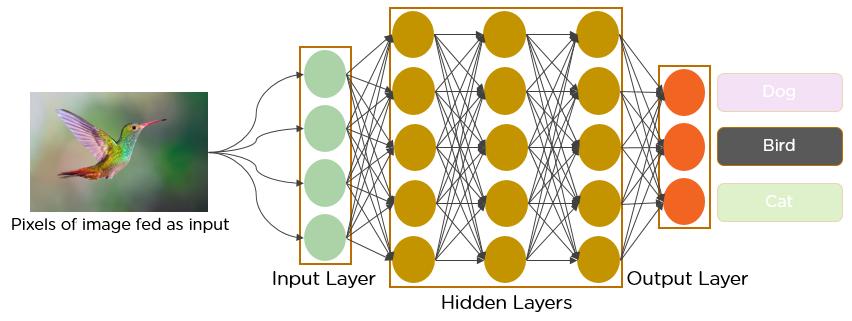
Images of dogs will be analysed in an effort to determine their breed. Since all dog breeds are similar in terms of their physical traits and overall structure, distinguishingbetweenthemisachallengingproblem,making this a fine-grained classification problem. Furthermore,thereisminimalinter-breedandhighintra-breed variation;thatis,therearerelativelyfewdifferences between breeds and there are quite substantial changes within breeds, including size, shape, and colour. The caninespeciesisthemostgeneticallyandphysicallyvaried on Earth. Photographs showing dogs of the same breed in differ- ent lighting and poses add to the challenges of breedidentifica-tionbroughtonbythedataset’sdiversity. This problem is not only difficult, but the solution is alsoapplicabletootherfine-grainedclassificationproblems.Themethodsusedtosolvethisproblem,forexample, would aid in the identification of cat and horse breeds, as well as bird and plant species - and even car models. As a fine-grained classification problem, any set of classes with relatively little variation within it can be solved.Intherealworld,suchanidentifiercouldbeused in biodiversity studies, saving scientists time and resources when conducting research on the health and abundanceofspecificspeciespopulations.Thesestudies are critical for assessing the state of ecosystems, and their accuracy is especially important because of their influence on policy changes. Breed prediction may also aid veterinarians in treating breed-specific ailments in stray,unidentifieddogsinneedofmedicalattention.We eventually decided that dogs were the most interesting
class to experiment with because of their enormous diversity, loving nature, and abundance in photographs, but we also hope to broaden our understanding of the fine-grained classification problem and provide a useful toolforscientistsacrossdisciplines.
1.2 Disease Prediction Using Decision Tree Classifier

Early and accurate disease prediction is also a necessary factor in helping new pet owners. The healthcare industry generates and uses a large amount of data that canbeusedtoextractinformationaboutaspecificdisease inapet.Thishealthcareinformationisbeusedtoprovide the most effective and best treatment for the health of your pet. This area also requires some improvement throughtheuseofinformativedatainhealthcaresciences. However, because there is so much data, extracting informationfromitcanbedifficult,sodataminingandmachinelearningtechniquesareused.Theexpectedoutcome ofthis projectis topredictthediseaseinadvancesothat the risk of death can be avoided at an early stage, saving the lives of pets and reducing the cost of treatment to a certain extent. The main goal is to improve pet care by incorporating the concept of machine learning into healthcare. Machine learning has already made identifying and forecasting various diseases much easier. Predictive disease analysis using many machine learning algorithms allows us to predict the disease andtreatthe pets effectively.Diseasepredictionusingmachinelearningalso makesuseofthepet’shistoryandhealthdatabyemploying various concepts such as data mining and machine learning techniques, as well as some algorithms. Deep learning research in disparate areas of machine learning hasledtoashifttowardmachinelearningmodelsthatcan learnandunderstandhierarchicalrepresentations of raw datawithsomepre-processing.
2. OBJECTIVE
Our missionis to provide assistanceto pet owners so that they can better understand and care for their animals.
• Theability toaccurately identify the early stages of anydisease can save the lives of a great number of pets.
• Deepening our understanding of AI and machine learningacrossarangeoffieldsandputtingthatunderstandingtouse.Utilizing knowledgeofavariety ofmachinelearningalgorithms and artificial intelligence designs.
3. RELATED WORKS
Deep learning has been a part of the machine learning world for quite some time. According to the authors
Foote, 2017, the origins of deep learning can be traced back to 1943, when Walter Pitts and Warren McCulloch attempted to design a computer based on the neural network of the human intellect. Foote, 2017 states that ”the earliest efforts in developing Deep Learning algorithms came from Alexey Grigoryevich Ivakhnenko (developed the Group Method of Data Handling) and Valentin Grigoryevich Lapa (author of Cybernetics and Forecasting Techniques) in 1965.” Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that employs multi-layer neural networks tocarry out operations. Each layer of the neural network ismadeupofseveralneuronsthatarealllinkedinsucha way that they can communicate with one another. This neuron was created in the hope that it would function similarlytotheneuroninhumanintelligence.Inthiscase, theneuronwouldattempttocalculatetheweightedaverageofthevalues,i.e.theinputsignalandtheoutputsignal transmitted by the connected neuron. Arora et al., 2015. In Nokwon Jeong and Soosun Cho’s 2017 paper, the authors attempt image classification on Instagram images, withthegoalofevaluatingthecompetitivepowerofdeep learning for classification of real-time social networking images. In their study, the authors Nokwon Jeong and Soosun Cho (2017) look at the performance of preexistingCNNframeworkssuchasAlexNetandResNetand how well they perform on the ImageNet dataset, which demonstratedoutstandingcapabilities.
4. SYSTEM DESIGN
Fig-1 Block Diagram Breed Prediction
4.1.1 Breed Prediction
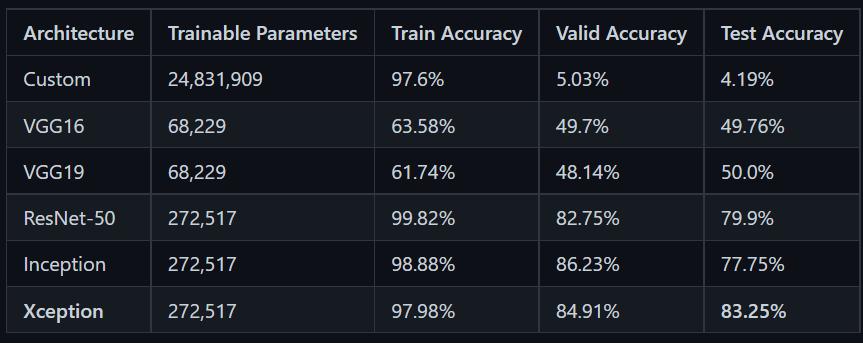
Forbreedpredictionweuseimagerecognition. Wecreate a Simple image recognition agent that uses a pre-trained CNN to accurately recognise the breed of a dog using imageprocessing. Weuseaaccuracymetrictotesttheaccuracy of 5 different pre- trained CNN namely, VGG16, VGG19,RESNET50,InceptionandXception.Outofthese5 Exception was found out to be the most accurate at 83.78% accuracy. A data-set of 133 dog breed was taken fromKaggletotraintheseCNNsanda pre-trainedhuman
and dog face detector was taken from the github link of OpenCV.
4.1.2 Disease Prediction
Disease prediction was done by using Decision Tree Classifier and Naive Bayes algo- rithm. A data-set of dog diseasewastakenfromkaggle.Thedata-setwasdividedinto threecolumnsbasedondiseasename,frequencyofoccurrenceandsymptoms.Usingthesedataadecisiontreewas created by cleaning and arranging the data.This decision tree was then used to train the agent using Naive Bayes algorithm. Naive Bayes algorithm was used as it is a slow yet accurate method of predicting in conditions where probabilityispresent.
5. METHODOLOGY

Fig-2 Block Diagram Disease Prediction
5.1 Breed Prediction using CNN
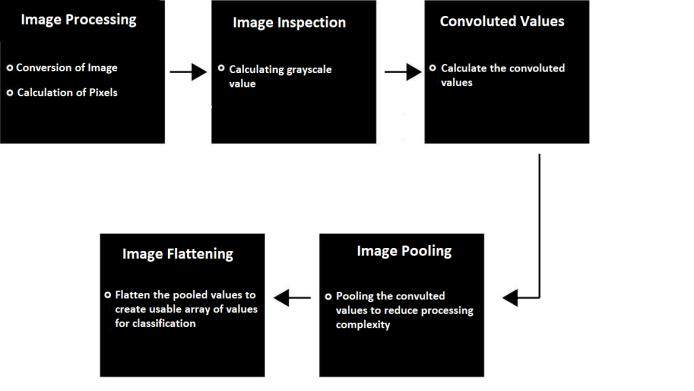
A convolution network consumes such images as three distinct colour strata stacked one on top of the other. A standard colour image is viewed as a rectangular box whosewidthandheightaredeterminedbythenumberof pixels in those dimensions. Channels are the depth layers in the three layers of colours (RGB) interpreted by CNNs.Such images are consumed by a convolution network as three colour layers, one on top of the other. A standard colour image is perceived as a box, with width and height determined by the amount of pixels used. Channels refer to the depth levels in the three layers of colours (RGB) used by CNNs for their interpretation. The CONVOLUTIONLAYERis thecorebuildingblockofaCNN networkanddoesthemajorityofthecomputationalheavy lifting. Filters or kernels are used to convolve data or images.Filtersaresmallunitsthatweapplytodataviaasliding window. The depth of the image is the same as the depth of the input; for a colour image with an RGB depth of4, a depth 4 filter would also be applied to it. This procedure entails taking the element-wise product of the image’s filters and then summing those specific values for
each sliding action. A 2d matrix would be the output of a convolution with a 3d filter and colour.Now, imagine a flashlight shining over the top left corner of the image to explain a convolution layer. To understand how this works, imagine a flashlight shining its light over a 5 x 5 area.Nowimaginethis flashlightmoving acrossallofthe areasoftheinputimage.Thisflashlightisknownasafilter (also known as a neuron or a kernel), and the region it illuminates is known as the receptive field. This filter is also a number array (the numbers are called weights or parameters).The second layer is the ACTIVATION LAYER, whichusestheReLu(RectifiedLinearUnit).Inthisphase, we use the rectifier function to increase non-linearity in the CNN. Images are made up of various objects that are not linearly related to one another. The third layer is the POOLING LAYER, which incorporates feature down- sampling.Itisappliedtoeachlayerofthe3Dvolume.Thislayer typically contains the following hyper- parameters. A typical POOLING LAYER employs a non-overlapping 2 cross2maxfilterwithastrideofAmaxfilterwouldreturn themaximumvaluein theregion’sfeatures.Whenthereis avolumeof26across 32,thevolumecanbedecreasedto 13 crosses, 32 feature map by utilising a max pool layer with 2 cross 2 filters and an astride of 2. Finally, then comes the FULLY CONNECTED LAYER, which requires flattening.Theentire poolingfeaturemapmatrixis transformedintoasinglecolumn,whichisthensuppliedtothe neural network for pro- messing. We created a model by combining these features using fully connected layers. Finally,toclassifytheoutput,wehaveanactivationfunction suchassoft-maxorsigmoid.
5.2 Disease Prediction using Naive Bayes Algorithm
The Naive Bayes method is a supervised learning technique that uses the Bayes theorem to solve classification issues. It is mostly utilised in text classification with a largetrainingdata-set.TheNaveBayesClassifier isasimpleandeffectiveClassificationmethodthataidsinthedevelopment of fast machine learning models capable of making quick predictions. It is a probabilistic classifier, whichmeansitpredictsbasedonanobject’slikelihood.

Fig-3 Formula Used

6. MATERIALS AND METHOD
6.1 Breed Prediction
6.1.1 Statistics and Datasets
Thedatasetusedtotraintheimagerecognitionsoft-ware was taken from kaggle. It includes 3 folders of labelled pictures of different dog breeds divided into three sets train,test and valid. The train folder contains pictures of 133 dog breed along with its name and are well-labelled. The pictures for the dog breed was sorted in alphabetical order for ease of reading and access. Another dataset of human faces was also used that was required to train the human/dog face detectors to distinguish between human dogfaces.
6.1.2 Data Preprocessing and Visualization
6.1.3 Model and Approach
The dataset was imported and the data in it was read, sortedandvisualised.Apre-trainedfacerecognitionagent was download from OpenCV github and trained using the human dataset and dog dataset to detect humans and dogs. after the agents were trained some random images where imported and the face detector was tested. After a satisfying level of accuracy was reached the face detector was imported in CNN and 5 different pre-trained CNNs were tested using an ac- curacy matrix and the one with highest accuracy was finally used as our CNN.the CNNs used where VGG16, VGG19, RESNET50, Inception and Xception.
6.1.3.1 VGG16
VGG16isaconvolutionalneuralnetworkmodelproposed inthepublication”VeryDeep ConvolutionalNetworksfor Large-Scale Image Recognition” by K. Simonyan and A. Zisserman of the University of Oxford. In ImageNet, a datasetofover14millionimagesclassifiedinto1000classes, the model achieves 92.7% top-5 test accuracy. It was one ofthewell-knownmodelssubmittedtotheILSVRC-2014.

ForourtestCGG16achievedanaccuracyof49.76%.
6.1.3.2 VGG19
VGG-19isa19-layerdeepconvolutionalneuralnetwork.A pretrainedversionofthenet-worktrainedonoveramillion photos from the Im- ageNet database can be loaded [1]. The pretrained network can categorise photos into 1000 different object categories, including keyboards, mice, pen- cils, and various animals. As a result, the network has learned detailed feature representations for a diversesetofimages.
ForourtestCGG16achievedanaccuracyof50.00%.
6.1.3.3 RESNET50
Fig-4 Distribution of Data in Dataset
The acquired dataset was put into the system, where it was transformed and read.Itis dividedintothreecategories: test, train, and valid datasets. Each image was measured and added to a list based on its size. The size was then plotted along a graph, followed by a feature pixel. Pixels from all three datasets were combined and plotted together.Finally,thedatasetwaspartitionedintoavailable data. Following the division of the dataset, the animals’ breedswereenumeratedandplottedonagraph.
Residual Networks, or ResNets, learn residual functions with reference to the layer inputs rather than learning unreferenced functions. Instead of hoping that each few stacked layers directly fit a desired underlying mapping, residual nets allow these layers to fit a residual mapping. They stack residual blocks on top of each other to form networks,suchasaResNet-50,whichhasfiftylayers.
ForourtestCGG16achievedanaccuracyof79.98%.
6.1.3.4 Inception
An inception network is a deep neural network with an architectural design made up of re- peating components knownasInceptionmodules.ForourtestCGG16achieved anaccuracyof77.75%.
6.1.3.5 Xceptionn
An inception network is a deep neural network with an architectural design made up of re- peating components knownasInceptionmodules.ForourtestCGG16achieved anaccuracyof77.75%..
ForourtestCGG16achievedanaccuracyof83.25%.
Thus,Xcpetionhasthebestaccuracyinidentifyingthedog breed through imageandhenceit was used to design our agent.

ensures that patients receive the care they require as quickly as possible. The accuracy score on the test and train dataset was compared with the X-axis and Y-axis to gettheaccuracynumber.Additionallyfortraindatasetwe use gradient boosting classifier. By cross- validating the meanwascalculatedtobe100%.Wecheckedthediscrepanciesbetweentheactualvaluesandthepredictedvalues soastopreventwrong predictionresults.thenk-foldwas imported and multiple different algorithms were tested with different values of k-fold. The best outcome was gained when the k-value was set to 2. so the model was buildonthebasisofk-valuebeing2.
8. RESULTS AND CONCLUSION
8.1.
Result
Fig-5 Evaluation Metrics

7. DISEASE PREDICTION
7.1. Statics and Data
The dataset used to analyse dog diseases came from the website kaggle. The dataset includes a variety of human diseases, each of which was broken down into it's own columnandlabelled withthedisease’s name,thecount of diseaseoccurrences,andthesymptoms
7.2. Data Preprocessing and Visualisation
Adatasetthathadnotbeencleanedupwasobtainedfrom Kaggle. The raw dataset was brought into the pro- gram whereitwasreadafterbeingimportedthere.Thedataset was cleaned up by first removing all of the values that were NaN. After that, the tables were rearranged so that the disease occurrences were listed in descending order. Following that, the table was partitioned using lambda in accordance with the symptoms. After that, this dataset was input into an AI system that employs decision trees basedontheNaiveBayesalgorithm.
7.3. Model and Approach
We used a number of different analytical data mining techniques in order to estimate the most accurate illness thatcouldbeassociatedonlywiththepatient’scondi-tion. Additionally, we use an algorithm called Naive Bayes in ordertomapthesymptoms withpotentialdiseasesbased on a database that contains multiple disease symptoms records. Patients not only benefit from this system becauseitmakes thedoctors’ jobs easier butalsobecause it
Withtheincreaseinthenumberofpetownerinthecountryitisveryessentialtogetproperattentionandcarefor the pets. hence our project aims at streamlining the processofgettingabetterunderstandingofourpetsandtaking better care of there health by using image prediction softwaretounderstandtheirbreedanddiseaseprediction to get an idea of what they might be suffering from the conclusion regarding the prediction accuracies gained through theapplicationoftheCNNproceduretoavariety ofstandarddatasets.Theresultshavenotchangedthanks totheestimateaccuracyinproportionthatwascalculated separately for test data and inside train information. In addition to the prediction accuracy percentage values, a graph displaying the MSE, or mean squared error, is also provided. The graphs display the variation of MSE as a function of regard along the path to the training epochs. TheMSEmetricisthesimplestandmostwidelyutilisedof all the quality metrics. Thus, a very accurate method of identifyingthebreed ofadogwas reachedbyusingXception neural Network, which helped us in getting a high percentage of accuracy in determining the breed of the dog.
Ourprimarypurposeofwastocomprehendandenhance themethodofdisease prediction,as well as tocarry out a comparative analysis of algorithms in order to locate
thealgorithmthatwasmostideallysuited.Theaccuracy scoresofthealgorithmswerecompared,andinaddition to that, data visualisation was done in order to gain a morein-depth understanding ofthe data and the trends within it. In the end, when all of the results obtained by the various algorithms used for disease prediction from hospital data were compared to one another, it was found that the CART model, also known as a decision tree,gavethehighestperformance.
9. FUTURE WORKS
Fig-7 Disease Prediction Result

8.2. Conclusions
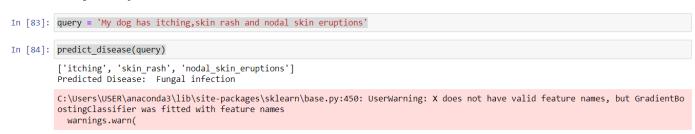
In addition to its use as a method for data analysis and prediction, convolutional neural networks have recently seen a surge in popularity as a solution for problems involving the classification of images. The goal of this deep learningmethodforpredictingdogbreeds,whichwasdevelopedwiththehelpofaconvolutionalneuralnetwork,is todetermineofonehundredimagesbyusingtheirimages asinput.Utilizetransferlearningasameanstowardbuildingamodelthatcanproduceoutputandaroundhundreds of different dog breeds. The results for the images that were shown to the model were satisfactory overall. The algorithm wasveryaccuratewhenitcametodetermining thebreedsofdogs.Transferlearningrequiresagreatdeal offlexibilityinthefutureintermsofcombiningaprebuilt model with the model that we developed. It is possible to achievecomparativelyhigherlevelsofac-curacyusingthe system that we have proposed. After that, researchers, doctors, and other medical professionals will use this in order to provide patients with the most effective treatmentandmedicalcarepossible.Therefore,theapplication of machine learning in the medical field can result in an effective treatment, while also ensuring that the patient receives adequate care. In this section, we make an attempt to incorporate some of the machine learning in healthcare functions that are available into our system. When a disease is predicted for a patient, machine learning is implemented instead of direct diagnosis. Certain machinelearningalgorithmsareusedduringthisprocess, and as a result, healthcare can be made more intelligent and effective. The Logistic Regression algorithm and the KNNalgorithmhavethehighestaccuracywhencompared to the other algorithms used for disease prediction based on our dataset and the output we anticipate. This is the case when we analyse both the input data and the expectedoutput.
Future research should look into the potential of convolutional neural networks in predicting dog breeds. Given the success of our keypoint detection network, this techniquelookspromisingforfutureprojects.However,neural networks take a long time to train, and due to time constraints, we were unable to perform many iterations on our technique. We recommend further research into neural networks for keypoint detection, specifically training networks with a different architecture and batch iterator to see which approaches may be more suc- cessful. Furthermore, given our success with neural networks and keypointdetection,werecommendimplementinganeural network for breed classification as well, as this has not been done previously. Finally, neural networks take time totrainanditerateon,whichshouldbetakenintoaccount for future efforts; however, neural networks are formidable classifiers that will improve prediction accuracy over moretraditionaltechniques.
Aswecanclearlyseetoday,computersandtechnologyare beingusedtoconsideramassiveamountofdata,computers are beingused to performvarious complex tasks with commendable accuracy rates. Machine learning (ML) is a collection of techniques and algorithms that allow computerstoperformsuchcomplextasksinasimplifiedmanner. We can say that we have grown in the fields of big data, machine learning, and data sciences, among other things,andthatwehavebeenapartofoneofthoseindustries that have been able to collect such data and staff to transformtheirgoodsandservicesinthedesiredmanner. The learning methods developed for these industries and researcheshavetremendouspotentialtoimprovemedical researchandclinicalcareforpatientsinthebestwaypossible. Machine learning employs mathematical algorithms and procedures to describe the relationship between model variables and others. Our paper will describe the processoftrainingthemodelandlearninganappropriate algorithm to predict the presence of a specific disease from a tissue sample based on its features. Though these algorithms work in different and distinct ways depending on how they are developed and used by the researchers. Oneapproachistoconsidertheirultimategoals.Thepurpose of our paper and statistical methods is to reach a conclusion about the data collected from a wide range of samplesdrawnfromourpopulation.Althoughmanytechniques, such as linear and logistic regression, can predict diseases.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
WeexpressourhumblegratitudetoDrC.Muthamizhchelvan, Vice-Chancellor, SRM Institute of Science and Technology,forthefacilitiesextendedfortheprojectworkand his continued support. We extend our sincere thanks to
Dean-CET, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Dr T.V.Gopal,forhisvaluablesupport.

WewishtothankDrRevathiVenkataraman,Professorand Chairperson, School of Computing, SRM Institute of ScienceandTechnology,forhersupportthroughouttheproject work. We are incredibly grateful to our Head of the Department, Dr. Annapurani Panaiyappan.K Professor, Department of Net- working and Communications, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, for her suggestions andencouragementatallthestagesoftheprojectwork.
We want to convey our thanks to our Panel Head, Vinoth Kumar S, Associate Profess, Department of Networking and Communications, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, for their inputs during the project reviews and support. We register our immeasurable thanks to our Faculty Advisor, Dr.P Supraja, Associate professor, Department of Networking and Communication, SRM InstituteofScienceandTechnology,forleadingandhelpingus tocompleteourcourse.
Our inexpressible respect and thanks to my guide, Mrs. Eliza- beth Jesi, Associate professor, Department of Networking and Communication, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, for providing us with an opportunity to pursue our project under her mentorship. She provided us with the freedom and support to explore the research topicsofourinterest.
WesincerelythanktheNetworkingandCommunications Department staff and students, SRM Institute of Science andTechnology,fortheirhelpduringourproject.
REFERENCES
1. Kaitlyn Mulligan and Pablo Rivas- Dog Breed IdentificationwithaNeuralNetworkoverLearnedRepresentationsfromTheXceptionCNN
2. JSreenand Manoj,Rakshith S,Kanchana V- Identification of Cattle Breed using the Convolutional Neural Network
3. Bickey Kumar shah ,Aman Kumar,Amrit Kumar-Dog Breed ClassifierforFacial RecognitionusingConvolutionalNeuralNetworks
4. Dr.D.DurgaBhavani,MirHabeebullahShahQuadri,Y. Ram Reddy- Dog Breed Identification Using ConvolutionalNeuralNetworksonAndroid
5. YuHanLIU-FeatureExtractionandImageRecognition withConvolu-tionalNeuralNetworks
6. Brankica Bratic,Vladimir Kurbalija, Mirjana Ivanovic,IztokOder,ZoranBosnic,MachineLearningforPre-
dictingCognitiveDiseases:Methods,DataSourcesand RiskFactors,2018
7. K. Gomathi, D. Shanmuga Priya-Multi Disease PredictionusingDataMining
8. S.Vijiyarani,S.Sudha-DiseasePredictioninDataMining Technique,January2013
9. Emily Jones , JohnAlawneh ,Mary Thompson,Chiara Palmieri , Karen Jackson and Rachel AllavenaPredicting Diagnosis of Australian Canine and Feline Urinary Bladder Disease Based on Histologic Features,November2020
10. SnehaI.Kadari,ShubhadaS.Kulkarni,SharadaG.Kulkarni-Dog Breed Prediction using Convolutional NeuralNetwork,June2020
11. Kriti Gandhi1, Mansi Mittal2, Neha Gupta3, Shafali Dhall-DiseasePredictionusingMachineLearning,June 2020
12. Kriti Gandhi1, Mansi Mittal2, Neha Gupta3, Shafali Dhall-DiseasePredictionusingMachineLearning,June 2020
13. KeithD.Foote, (2017).A BriefHistory ofDeepLearning-DATAVER-SITY.
14. Arora,A.,Candel,A.,Lanford,J.,LeDell,E.andParmar, V.(2015).DeepLearningwithH2O.3rded.
15. NokwonJeong, Soosun Cho (2017)’ Instagram image classificationwithDeepLearning
