SOIL EXPLORATION AND GEOTECHNICAL DESIGN OF A FOUNDATION
5 Professor Department of Civil Engineering, New Horizon Institute of Technology and Management Thane, Maharashtra, India. ***
Abstract - Before the actual construction process starts, it is important to conduct a site investigation and soil exploration to acquire vital information about the soil and site conditions. In a construction site investigation is the first and crucial step. These are outlined in the project to ensure that the site is appropriate for the proposed construction and to offer recommendations on the design and construction processes.
Following soil investigation based on the soil report, further geotechnical design of a shallow foundation was performed; however, the results indicated that the load coming from the structure was less than the results of the shallow foundation, so we opted for the geotechnical design of a pile foundation, which resulted at an end bearing capacity greater than the load coming from the structure. The geotechnical design of the pile consists of recommending the size of the pile and calculating the safe working load of each pile.
Key Words: Deep Foundation, Pile Foundation, Shallow Foundation, Bore-hole, Site Investigation, Soil Exploration.
1. INTRODUCTION
The geotechnical design of a multi-story commercial building includes a thorough site investigation and soil report analysis. After studying the soil report, the appropriate type of foundation was chosen using calculations and information from the site report such as typeofsoil,depthofboreholeetc.
Thisinvolvesadetailsiteinvestigationstudyandanalysisof soil report our site. After studying the soil report, selected foundation type and site report including site condition, type of soil, and depth of bore-hole and basically, there are twotypesoffoundation:1. Shallow2.Deepfoundation.For selecting the type of foundation following detailed design stepswereinvolved:
– Studyofsoilreport
– Calculationstructuralload
– Bearingcapacitycalculationofshallowfoundation.
i. As per IS 6403, 1981 and IRC 78, 2014 - 1: If the soil typeissuitable(hardstrata)tocarrytheloadandthe bearing capacity exceeds the load resulting from the construction,wemayuseashallowfoundation.
ii. If the foundation's bearing capacity is less than the load from the building, we must use a raft or pile foundation.

Forcondition2:Furtherwehavetocalculateloadcarrying capacityofpilefoundation.
There are different design methods to calculate bearing capacity and End bearing capacity of soil/ Rock based on sitecondition.
1.1 Site investigation
The process of acquiring and analyzing information on a site's surrounds, including the geology, topography, hydrology, and environmental conditions, is known as site investigation.Themainobjectiveofasiteinvestigationisto find any potential issues or hazards that might impact the construction process or the final structure's stability and safety.
Site investigation is the process of studying about a site's physical and environmental characteristics in order to determine whether it is suitable for a particular civil engineering project. It entails a careful analysis of the geology, hydrology, topography, soil properties, and other elements that potentially influence the site's development orusage.
Drilling,sampling,andgeophysicalsurveysarejustafewof the field and lab tasks that site investigations normally involve. The investigation's findings are summarized in a reportthatoffersrecommendationsfortheproject'sdesign and construction as well as any possible mitigation strategiestoaddresssafetyorenvironmentalissues.
1.2 Soil Exploration
A phase of site research called soil exploration focuses primarilyonthesoilcharacteristicsofthelocation.Inorder
to assist the design and construction process, soil exploration aims to give thorough information about the soilconditions.
The following steps are commonly included in the soil explorationprocess:
A) Borehole drilling
Boreholedrillingistheprocessofmakingholesintheearth togathersoilsamplesforanalysis.
B) Sampling
Toascertainthekind,consistency,andstrengthofthesoil,soil samplesaregatheredfromboreholesatvariousdepths.
C) Testing in the lab
The physical and chemical characteristics of the soil samples, such as density, permeability, shear strength, and compressibility,areexaminedinthelab.
D) Analysis
The design and construction processes are made more effective by using the information gathered during the soil explorationphase.Forinstance,itmaybeusedtodecideon thenecessarykindanddepthoffoundations,thesite'sslope stability,andthebestbuildingmethods.
In conclusion, site investigation and soil exploration are crucialstepsinthebuildingprocessthatprovideimportant detailsaboutthesiteconditionsandsoilcharacteristics.The stability and safety of the completed structure are ensured using this information, which is also utilized to guide the designandconstructionprocess.
1.3 Foundation:
Thelowest portionofa building orstructure,knownas the foundation, is where the weight of the structure is transferred to the ground or rock below. The performance andsafetyoftheentirestructurecanbegreatlyimpactedby the design and construction of the foundations, which are essentialpartsofanybuildingorstructure. Theseveraltypesoffoundationsfrequentlyusedinbuilding constructionareasfollows:
Deep Foundation:
Whenthesoilatthesurfaceisunstableorweakandunable tosustaintheweightofthestructure,deepfoundationsare employed.
The following category was explored for deep foundation forthisproject:
• Pile Foundation:
Pile foundations are employed when a structure has to be sustainedata deeperlevel andthesoilclosetothesurface is unstable. They have a long, lean form that might be cylindricalorrectangular.
1.4 Site Details:
NHES Educational Complex near Village Kavesar, Anand NagarCrossingofGhodbunderRoadinThane,Maharashtra, toestablishateachinghospitalandmedicalcollegebuilding. Thegeotechnicalinvestigationreportforallninecompleted boreholesattheThanesiteisincludedinthisreport.

The investigation site is a region of the area known as the "DeccanTraps," a termusedinIndiangeology. The present researches reveal that the geologic occurrences of various rock types, including the deposits of mafic rocks, are separate from those in the remainder of the Deccan Trapcovered area. Amygdaloidal Basalt, Compact Porphyritic Basalt, etc. In boreholes around Thane regions, a few marker horizons (trachytic, Tachylite beds) have been found.Thelevelsofthese,however,donotrelate.Theyhave beendescribedinthecorelogsthatareincluded.According torecentstudies,itisnotpossibletocompletelyruleoutthe possibilityofsub-aqueousvolcaniceruptions.
The geologic environment of this area corresponds to the literature review conducted for the Geology of Mumbai region;itshowsthatthevolcanicactivityinthisareadiffers from that of the rest of Maharashtra's volcanic province in various ways, which include their association with several evolved rock types like Rhyolites and Trachytes with significant amounts of felsic and basictuffs,andtheir being partially or entirely sub-aqueous eruptions as indicated by pillowstructuresandspiliticcompositions
According to the literature research, there are not many defects in the Mumbai region. The area has active earthquakeactivity.
The document contained includes sections on the lithologic descriptions, as well as their geotechnical relevance. These sections are further supported by microscopic data, which areattached.
Shallow Foundation:
When the earth is sturdy enough to sustain the weight of the structure close to the surface, shallow foundations are employed.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2. DESCRIPTION OF PROJECT
FoundationAnalysisand Design
Shallow Foundation Deep Foundation
2.1 Shallow Foundation:
PileFoundation
Bearingcapacity&settlementpressureofsoilat3mdepth forShallowfoundationareaasfollow,
i. Bearing Capacity – Using Standard Penetration Test – N Value
ForSquareandCircularFooting:
qnu= 1/3.0(N2BWγ+3(100+N2)DfWq
qnu= 0.33 N2 BWγ + 1 (100 + N2) Df Wq
Where,
N=StandardPenetrationtestvalue


qnu =Bearingcapacity
Table -1: BearingCapacityvaluesusingN-value
ii. Settlement Analysis- using Teng’s Equation
Qnp = 35 (N – 3) × (B + 0.3 / 2B)2 × Wγ × Rd
Where,Rd=(1+Df/B≤2.0)…...DepthCorrectionFactor

Table -2: SettlementAnalysisusingTeng’sEquation
2.2 Pile Foundation
i. Load Carrying Capacity of Pile foundation
Capacity of Piles in Intermediate Geo-Material and Rock
����=�� +�� f
���� = Kₛₛ ×q
c ×df ×Ab + Aₛ×Cus
=ultimatecapacityofpile
=ultimateendbearing
f=ultimatesidesocketshear
Kₛₛ=Empiricalco-efficient(valuerangesfrom0.3-1.2)
Qc= avgunconfinedcompressivestrengthofrock
f =depthfactor
=1+0.4xlengthofsocket/diaofsocket
Ab=c/sofbasepile
Aₛ =surfaceareaofsocket
Cus=Ultimateshearstrengthofrockalongsocketlength
K=1.03
qc =6118.29t/m2
d =1+0.4x3x1(3d)/1 =2.2=1.2
Ab = π/4x1² =0.785m2
Aₛ =πd=πx1x3 =9.42m2
Formula ���� = 1 x 6118.29 x 1.2 x 0.785 + 9.42 x 17.59 = 5929.12 ton
Cus=0.225x√9c =17.59
ForDiameter=1m
Qallow = (Re/3 ) + (Raf/6) = 5763.42/3 + 165.69/6 = 1948.75 ton
ForDiameter=1.2m
Qallow = (Re/3 ) + (Raf/6) = 8296.40/3 + 198.76/6 = 2798.59 ton
ForDiameter=0.9m
���� = 1 x 6118.29 x 1.2 x 0.64 + 7.63 x 17.59 = 4833.05 ton
Qallow = (Re/3 ) + (Raf/6) = 4698.84/3 + 134.21/6 = 1588.64 ton
2.3 Load coming from Structure:
Heightofbuilding–75m
No.offloors–20floors
Eachfloorht.–75m
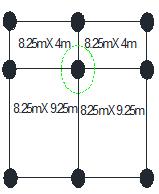
Sizeofeachroom–8.25X9.25m
Corridorsize–8.25X4m
LiveLoad–5kN/
ThicknessofSlab-150mm=.15m
Sizeofbeam–400X450mm
Load Calculation
1. Wall Load:
WallLoad =0.23x3.15x2.5 =1.81t/m
TotalLoad =LoadpermxTotallength =1.81x(9.25+5)
Wall load = 25.75 ton
2. From column:
Volumeofcol. =π\4x12 x3.75 =2.94m3
Volumeofsteel =1%ofconcrete =0.029m3
LoadonColumn=2.94x2.5+0.029x7.8
Column Load = 7.576 ton
���� = 1 x 6118.29 x 1.2 x 1.13 + 11.30 x 17.59 = 8495.16 ton
Volumeofcol. =0.4x0.45x1 =0.18m3
Volumeofsteel=2%ofconcrete =0.0036m3
LoadonBeam =0.18x2.5+0.0036x7.8 =0.48t/m
TotalLoadon beam =0.48x(8.25x2+9.25x2)
Load on Beam = 16.8 ton
4. From Slab:
SlabloadS1 =0.15x8.25x9.25 =11.44m3
Volumeofsteel=2%ofconcrete =0.22m3
TotalLoadon SlabS1 =(11.44x2.5)+(0.22x7.8) =30.31ton
SlabloadS2 =0.15x8.25x5 =6.18ton
TotalLoadon SlabS2 =(6.18X2.5)+(0.12X7.8) =(16.38+30.31)/2
TotalSlabLoad=23.34ton
TotalLoadonColumn =73.45×21 =1542.45ton
Total Load on Column = 1800t
3. OBSERVATIONS
3.1 For Shallow Foundation:
• Based on the subsurface conditions met, competent stratumisnotavailableatshallowerdepth.
• Silty sand is observed from ground level to the depth varyingfrom6.5mto13.5minallboreholes.

• Underlying this layer, completely weathered Basalt is encounteredatdepthfrom6.6mto24.0m.
• Topographyoftheterrainisseennearlyflat.Thesiteis DeccantrapbasicallyconsistingofBasalticrock.
• Basalthereisnotofgoodquality.
3.2 For Pile Foundation:
• Pilediameterconsideredinanalysisis1mand1.2m.
• The strata consist of overburden soil followed by weathered rock and at further depths. The relative depthsvaryfromboretobore.
• For the purpose of assessment of pile capacity, the contribution from weathered rock and overburden is notconsidered.
• All Borehole samples show veins and abnormally low UCSinsomerocksamples.Henceitisnotconsideredas representative.
• Astheoverburdenisobservedfromgroundleveltothe depthvaryingfrom3.00mto9.00mitisnotadvisedto goforshallowfoundation.Theheterogeneousnatureof the strata leads to settlement of unpredictable nature. Instead we recommend to adopt pile foundation to transfer the load to firm strata. With this, settlement willbeconsiderablylow
3.1. Results:
I. Shallow Foundation
The results after calculating the Bearing capacity & settlement pressure of soil at 3m depth for Shallow foundationareaasfollow,
Table -3: Resultsofshallowfoundation
III. Load from Structure on Foundation
Manualcalculationforstructure
• Totalwallload=25.75t
• Loadonbeam=16.8t
• Loadoncolumnfromslab=7.576t
• Totalloadonslab1=30.31t
• Totalloadonslab2=6.18t
• Totalloadoncolumn=1800t
Total Load = 1800t (17651.97 kN)
4. CONCLUSION
At the NHES Educational Complex near the village of Kavesar, Anand Nagar Crossing of Ghodbunder Road in Thane,Maharashtra.
Soil Investigation: The geotechnical investigation reports for all nine completed boreholes were studied and we concludethat,
• Siltysandisvisible fromthesurfacetoa depthranging from6.5mto13.5m.
• Fullyweatheredbasaltisfoundatadepthof6.6meters and24.0metersunderthislayer.
• From the ground, up to a depth ranging from 6.5 m to 13.5m,overburdenisvisible.
• Thelandappearstohavearelativelyleveltopography.
• ThelocationisessentiallyabasalticrockDeccantrap.
• Here,thebasaltisofpoorgrade.
Pileandshallowfoundationwereconsideredforthedesign offoundation
Shallow Foundation
Where,
N=StandardPenetrationtestvalue
Qnu =Bearingcapacity
qns =SafeBearingCapacity
II. Pile Foundation

Table -2: ResultsofPilefoundation
After calculating the bearing capacity of the shallow foundation, it was found to be less than the load coming fromthestructure,whichis1800tonnes(17651.97kN)
Furthermore, based on the subsurface conditions encountered, a competent stratum is not available at a shallower depth. In all boreholes, silty sand was observed fromgroundleveltoadepthrangingfrom6.5mto13.5m, with completely weathered basalt found underlying this layer at a depth ranging from 6.6 m to 24.0 m. The topographyoftheterrainisnearlyflat,andthesiteconsists ofbasalticrock fromtheDeccantrap,butthequalityofthe basalt is not good. Considering the overburden and soil condition,itisnotrecommendedtoproceedwithashallow foundation.
Pile foundation:
Based on soil report and calculation, A pile foundation is advisedsinceexcellentgraderockisnotpresentatshallow depths, according to field and laboratory research. A pile foundationcantransfertheloadofthestructuretoadeeper
and more competent stratum, thus ensuring the stability andsafetyofthestructure.
Thepilediameterswereselectedas0.9m,1.0mand1.2m., asper IRC78, the allowable pilecapacity were observedto be 1588 tonnes (158822 KN), 1948 tonnes (19409 kN) 2798tonnes(27879kN)respectively.
Finally, a single pile with diameter 1m having load caring capacity of 1948 ton was suggested for the proposed structure
As per IRC 78, the material to be used for the construction of pile foundation shall be M30 grade Reinforce cement concrete
5. REFERENCES
Indian Standard, IS: 2720 Part 4 (1995, Reaffirmed 2015).“Grainsizeanalysisofsoil”BIS,NewDelhi.
[1] Indian Standard, IS: 2720 Part 3 (1980, Reaffirmed 2016). “Determination of specific gravity” BIS, New Delhi
[2] Indian Standard, IS 2720 Part 5 (1985, Ref. 2015)). “LiquidLimitandPlasticLimitTest”BIS,NewDelhi
[3] Indian Standard, IS 2720 Part 6 (1972, Ref. 2016). “ShrinkageLimitTest”BIS,NewDelhi
[4] Indian Standard, IS: 12070-1987, code of practice for design and construction of shallow foundations on rocks
[5] Indian Standard, IS: 13365 (Part 1): 1988, Quantitative classificationsystemofrockmass-Guidelines.
[6] Indian Standard, IS: 6403: 1981, Code of practice for determinationofbearingcapacityshallowfoundations.
[7] Indian Road Congress, IRC 78: 2014, Standard Specificationsandcoderofpracticeforroadbridges.

[8] Dr.s.k.tiwari, m.k.kumawat, (2020) “Guidelines for PlanningSoilInvestigationofBuildingProject”
[9] HarryG.Poulos,(2018)“Tallbuildingfoundationdesign methodandapplication”
[10]Vedprakash Maralapalle, Analysis and Design of foundationforG+5residentialbuilding”
[11]A.R.Arora,“SoilMechanicsandFoundationDesign”
[12]MJ Tomlinson, “Foundation Design and Construction”
