Plant Leaf Disease Detection Using Machine Learning
V.Balu, K.Jayasree, N.Sirisha Reddy***
Abstract - The situation of any country in the world depends on its agrarian product. Especially India is depending on husbandry. The product gets affectedbyconditionsofthecrop. The yield of a crop is always dependent upon the base of the crop’sdisease. However, the yield will probably increase, Ifthe complaint can be removed. Thecomplaintthatcausedthecrop to decline could be flashed back by the splint of the plant. The system uses Artificial Intelligence grounded on an algorithm we call machine literacy to estimate the superiority of the splint. The factory splint provides us with the most important data to distinguish the complaint of the factory. The development of the Android app gives growers the capability to do this. Identify factory splint conditions grounded on the image of factory splint taken from the Android app camera source. Detecting conditions of the splint of the factory at an early stage gives it the strength to overcome and treat accordingly by furnishing details to the planter, on what preventative measures should be taken. Android mobile operation which can automatically identify the factory’s conditions grounded on their splint appearance with some computer vision and machine literacy ways..
Key Words: CNN, Deep Learning, Disease Detection, MachineLearning,NeuralNetwork,Tensorflow.
1.INTRODUCTION
Tensorflowandmachinevisionhave beenwidelyused in monitoring plants, harvesting, and other stages of plant growth. Tensor flow is usually combined with artificial intelligencelikeneuralnetworkstodetectmaturefruitsin these cases, the accuracy ranges between 60% and 100% depending on the type of fruit and other conditions. Crop monitoring is another domain where machine vision has beenadopted(e.g.,forproductionmonitoring,thedetection ofdiseases,orinsectinvasion)..
The original discoveryofa complaintcan begrounded on machinevisionandtensorflowthatwillinduceanalertifits symptoms are recognized. Molecular analyses have a advanced cost but may be carried out later if a factory complaint has to be formally verified. The factory disease opinioncanbegroundedoncolorfulsymptomsasdescribed Symptomscanfrequentlybegroupedasunderdevelopment ofapkinsororgans(shortinternodes,underdevelopedroots, deformedleaves,lackofchlorophyll,fruits,andflowersthat don't develop), overdevelopment of factory corridor like apkinsororgans,necrosisoffactorycorridor(wilts,shootor splint scars, splint spots, fruit rots) and alternations like mosaic patterns and altered achromatism in leaves and flowers.Theprogressionofthediseasesymptomscanvary
significantly. Biotic agents the speed of the symptom progression.Thereareprimaryandsecondarysymptomsof adisease.
Forillustration,therootdecaycanbeprimarysymptomofa treewhilethesecondarysymptomcanbethetreetripping over. Secondary raiders that attack the tree in the after stages of the disease may obscure the original disease symptomsmakingtheopinionmorecomplicated.Otherdata like indecorous pesticide operation can beget analogous symptoms to spots that are present as a result of any contagious agent. Nonetheless, the symptoms caused by pesticide injury appear suddenly and no progression is observed.Thespotsmayalsofollowthespraypatterns of the pesticide. Dressings can also beget splint deformation whichmaybeconfusedwithviralconditions.still,thenew leavesarefreeof symptoms,indicatingalackofsymptom progression.furtherthanoneproblemorpathogeninfecting thefactorycanbepresent.Inthiscase,thesymptomsmay significantly dicer from that of the individual pathogens whentheyactalone.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY

Factory complaint identification is critical for a comprehensive knowledge of their growth and health. A deep literacy armature model known as CapsNet is suggestedinthisstudythatusesfactoryprintstodetermine ifit'shealthyorhasacomplaint.Thesuggestedarmatureis puttothetestusingthePlantVillagedataset,whichincludes over 60,000 images of sick and healthy shops. Capsules outperform CNN models because they integrate exposure andrelativespatialconnectionsbetweendistinctfactorsin an reality. When compared to former factory complaint bracketmodels,theCapsNetmodelhasshowntobemuch moreaccurateintermsofvaticinationdelicacy
For splint complaint identification in plants, the authors suggestedanenhancedpointcalculationfashiongrounded onSqueezeandExcitation(SE)Networksbeforeprocessing bytheoriginalCapsulenetworks.Witha64X64picturesize, SE- Alex- CapsNet obtains the maximum delicacy of92.1, compared to85.53 for Capsule Network. The suggested approachmaybeusedtodevelopamobileoperationwith lowprocessingconditionsthatcanbeputonlow-costsmart phones and used by farmers. For comparison, the bracket accuracies of six cutting-edge CNN models are presented AlexNet,SqueezeNet,ResNet50,VGG16,VGG19,andInception V3.Deep convolutional neural network (CNN) models are employedinthisstudytoidentifyanddiagnoseproblemsin plantsbylookingattheir leaves.CNN modelsbeara huge
number of parameters and a high cost of calculation. The typical CNN model is substituted in this study by four distinct deep literacy models InceptionV3, InceptionResnetV2,MobileNetV2, and EfficientNetB0. The models are trained and tested using a factory dataset of 53,407 prints. When compared to a standard CNN model, thesemodelsaremoreaccurateandtakelowertimetotrain.
3.PROBLEM STATEMENT
Plantdiseaseshaveturnedintoachallengeastheycancause a significant reduction in both the quality and quantity of agricultural products. The automatic detection of plant diseases is an essential research topic. It may prove beneficial in monitoring large fields of crops and thus automaticallydetectingthesymptomsofdiseasesassoonas they appear on plant leaves. The proposed system is a software solution for detecting and classifying plant leaf diseases.
4.PROPOSED METHOD
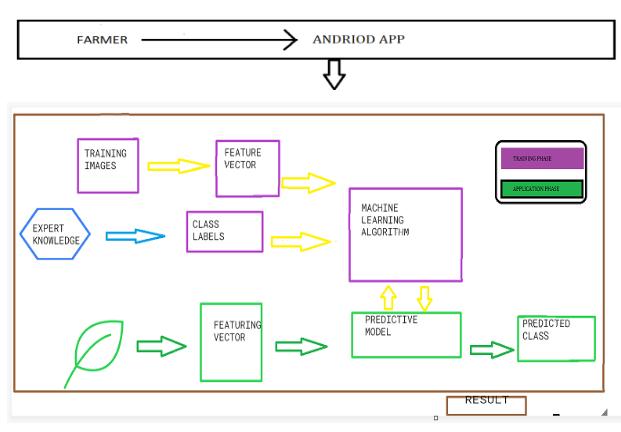
To reduce the loss chance of the crops, we present one Androidappwhichdistinguishesandidentifythesymptoms of the disease on a plant splint. Our app work on similar plants which are infected by numerous conditions that as fungi, contagions. To describe &classify factory disease by usingmachineliteracyways.Itidentifiesthefactualtypeof disease and gives its preventative measures and related recoverymemosaredisplayedbyusingtheCNNalgorithm. Andeventually,wegetallinformationregardingthedisease, its symptoms, its preventative medium, and recovery suggestionattheveritablyleasttimeandlowcost

5.ALGORITHM
CONVOLUTION NEURAL NETWORK(CNN)
STEP1:CONVOLUTIONOPERATION:The first step is convolutionoperation.Inthisstep,wewilltouchonfeature detectors, which serve as the neural network's filters. We will also discuss featuremaps, learning the parameters of suchmaps,howpatternsaredetected,thelayersofdetection and how the findings are mapped out.
STEP1(B):RELULAYER
The nextpartofthisstep will involvetheRectifiedLinear Unitor ReLU.Inthisstep,ReLUandexplorehowlinearity functions in the environment of Convolutional Neural Networks.Inthis,wewillhavethe5layerstodisplaybetter results.
STEP2:POOLING
Inthispart,we'llunderstandpoolingandwillgettoknow exactlyhowitgenerallyworks.Ournexuswillbeaspecific typeofpooling;maxpooling.We'llcovervariousapproaches havingmean(orsum)pooling.
STEP3:FLATTENING
Itisabriefbreakdownoftheflatteningprocessandhowwe move from pooled to flattened layers while working with ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(CNN).
6.ARCHITECTURE
Farmer can capture the particular leaf acquired using an android camera after successfully installation of this app, thenmachinelearningtechniqueisappliedtotheacquired image to extract useful results that are necessary for the analysis.basicprocedureoftheproposedplantleafdisease experiments and evaluations on different segmentations, featureextractionsandclassificationmethodsweredoneto find the most effective approach and identification based detection algorithm is used in this model. Farmer can get result is which disease infected by the plant like fungus, viruses
7.PROJECT DESCRIPTION
Thisprojectistodevelopa completesystemcomprisinga trained model on the server, as well as an application for mobile phones that display recognized diseases in fruits, vegetables, and other plants based on photographs taken fromthephonecamera.Thisapplicationwillaidfarmersby facilitatingtherecognitionandtreatmentofplantdiseasesin a timely manner and help them make informed decisions when utilizing chemical pesticides. Also, future work will involvespreadingtheuseofthemodelacrossawiderland area by training it to detect plant diseases onaerialphotosfromorchardsandvineyardscapturedwith drones,inadditiontoconvolutionneuralnetworksforobject detection.
9.CONCLUSION
Thisprojectproposedtofindoutthediseaseintheleafwith a union of shape, texture and color feature withdrawal. Firstly,thefarmershavetosendthediseasedleafimageofa plantandtheseimagesarereadandprocessedautomatically andtheresultsweredisplayed.Theoutputofthisprojectis togetholdofrelevantresultsthatcanspotoutdiseasedleaf of certain commonly caused disease to plants. Initially, healthy and diseased images are composed and preprocessed.Later,attributeslikeshape,colorandtextureare graspoutfromtheseimages.Basedontheclassificationand typeofdiseaseatextisshowedtotheuserbythisproject.
10.REFERENCES
1.StreyS,StreyR,BurkertS,KnakeP,RaetzK,SeyarthK,et al.Plant Doctorapp. Available online:https://plantix.net/




2.LukeE,BeckermanJ,SadofC,RichmondD,McClureD,Hill M,LuY.PurduePlantDoctorAppSuite.PurdueUniversity. Available online: https://www.purdueplantdoctor.com/
3. Petrellis N. A Review of Image Processing Techniques CommoninHumanandPlantDiseaseDiagnosis.Symmetry 2018,10,270.
4. Johannes A, Picon A, Alvarez-Gila A, Echazarra J, Rodriguez-Vaamonde S, Navajas A.D, Ortiz-Barredo A. Automatic plant disease diagnosis using mobile capture devices,appliedonawheatusecase.Comput.Electron.Agric. 2017,138,200–209.
5.MohantyS.P,HughesD.P,SalathéM.UsingDeepLearning for Image-Based Plant Disease Detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2016,7,346.
6. Prasad S, Peddoju S, Ghosh D. Multi-resolution mobile visionsystemforplantleafdiseasediagnosis.SignalImage VideoProcess.2016,10,379–388.
7. Liu T, Wu W, Chen W, Sun C, Zhu X, Guo W. Automated image-processing for counting seedlings in a wheat field. Precis.Agric.2016,17,392
406.
8.BehmannJ,MahleinA.K,RumpfT,RomerC,PlumerL.A review of advanced machine learning methods for the detectionofbioticstressinprecisioncropprotection.Precis. Agric.2015,16,239–260
9.DengX.-L,LiZ,HongT.-S.Citrusdiseaserecognitionbased onweightedscalablevocabularytree.Precis.Agric.2014,16, 321–330
10.Appl.Sci.2019,9,195221of229.CalderónR,MontesBorrego M,Landa B.B, Navas-Cortés J.A, Zarco-Tejada P.J. Detection of downy mildew of opium poppy using highresolutionmulti-spectralandthermalimageryacquiredwith anunmannedaerialvehicle.Precis.Agric.2014,15,639–661
11. Ballesteros R, Ortega J.F, Hernández D, Moreno M.A. Applications of georeferenced high-resolution images obtainedwithunmannedaerialvehicles.PartI:Description ofimageacquisitionandprocessing.Precis.Agric.2014,15, 579–592.
12. Qureshi W.S, Payne A, Walsh K.B, Linker R, Cohen O, DaileyM.N.Machinevisionforcountingfruitonmangotree canopies.Precis.Agric.2014,18,224–244.
13.BarbedoG.C.A.Digitalimageprocessingtechniquesfor detectingquantifyingandclassifyingplantdiseases.Springer Plus2013,2,660.
14.KulkarniA,PatilA.ApplyingImageProcessingTechnique toDetectPlantDiseases.Int.J.Mod.Eng.Res.2012,2,3361–3364.
15. PatilJ,Kumar R. Advances in image processing for detectionofplantdiseases.J.Adv.Bioinform.Appl.Res.2011, 2,135–141.

16.Sankaran S, Mishra A, Ehsani R, Davis C. A review of advancedtechniquesfordetectingplantdiseases.Comput. Electron.Agric.2010,72,1–13.
17. Lai J.-C, Ming B, Li S.-K, Wang K.-R, Xie R.Z, Gao S.-J. An Image-Based Diagnostic Expert System for Corn Diseases. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 1221– 1229. [CrossRef]
