Understanding Social Engineering and it’s impact on Merchant basedUPI frauds.
Simran JainUniversity of Mumbai Institute of Distance & Open Learning (IDOL) Information Technology, University of Mumbai

Abstract - Social engineering cyberattacks are becoming an increasing concern in the field of cybersecurity. This attack uses psychological techniques to trick people into disclosing sensitive information or performing actions that could compromise the integrity of the system. In recent decades, social engineering attacks have become more sophisticated, making it harder for individuals and organizations to detect and prevent them. With the increase in UPI based payment usage, there is an exponential growth in UPI based frauds primarily by using SocialEngineeringTechniques.Considering this, our research was conducted to understand how these social engineering attacks are executed by malicious party by keeping merchant users of UPI as a prime target. This was conducted by taking real examples of OR code manipulation using watering hole concept of Social Engineering. We also discuss how these social engineering attacks could be prevented and UPI based payments could be made safer. This is one of the studies in India to comprehensively understand fraud and scams in UPI based payment models focusing majorly on social engineering-based attacks on merchant users of UPI-based payment apps and empirically investigate factors driving the increasing frauds in this adopted model of payment.
Key Words: Social Engineering, UPI, UPI Frauds, UPI mechanism
1.INTRODUCTION
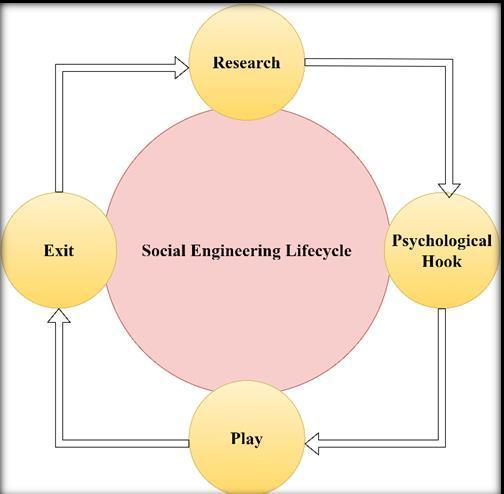
Social engineering is a type of attack that involves manipulating people to obtain information orresources.It is a kind of psychological tampering used to gain unauthorized access to private data such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other personally identifiable information.Social engineeringattacksarebecoming more frequent since they’re simple to carry out and can be difficult to detect. Refer Fig-1 to understand the Social EngineeringLifecycle.
UPIatermthatstandsforUnifiedPaymentsinterface.UPI is a real-time online payments system developed and maintainedbytheNationalPaymentsCorporationofIndia. Its primary working protocol is that it allowsusers to transfer funds between bank accounts instantly using an active mobile device through a payment’s application.
According to Yash Madwanna et.[1],Dominant working
features of UPI is that it is a simple and secure method of transferring money without the need for entering bank details or IFSC codes. Users are assigned a virtual ID (called UPI ID) which is linked to their bank account and canbeusedtomaketransactions.
1.1 Banking based social engineering tactics.
ThisUPIscammingtechniqueusingsmartsocialengineering skillsinvolvesanemailortextmessagethatappearstobe fromalegitimatebank,askingtherecipienttoclickonalink tologin,leadstoafakewebsitewherecybercriminalscan usethisinformationtoaccessthevictim'srealbankaccount and steal money or sensitive information, is a common exampleofbanking-basedphishing.[2]
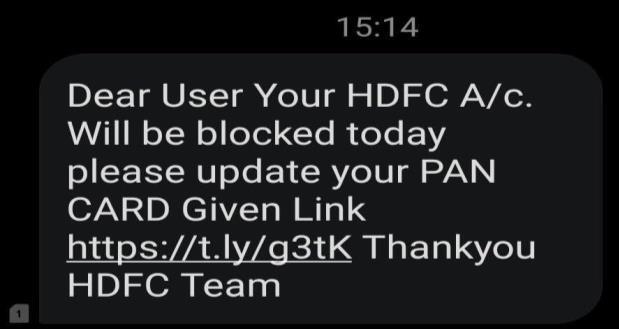
1.2 Phishing of Bank Websites & Emails
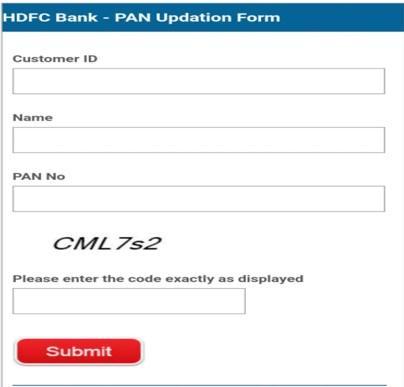
Cybercriminalsfrequentlyusetacticssuchascreatingfake email addresses that closely resemble the bank's official email address, websites or including the bank's logo and brandinginthemessagetomakethephishingmessageor webpageappearmorelegitimate.
links ordownload attachments fromunsolicited emails or textmessagesandshouldalwaysverifytheauthenticityof any requests for personal or financial information to avoid falling victimtobanking-basedphishingattacks.Individuals shouldalso use strong, unique passwords for their online accountsand enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
2. UPI & IT’S WORKING MECHANISM

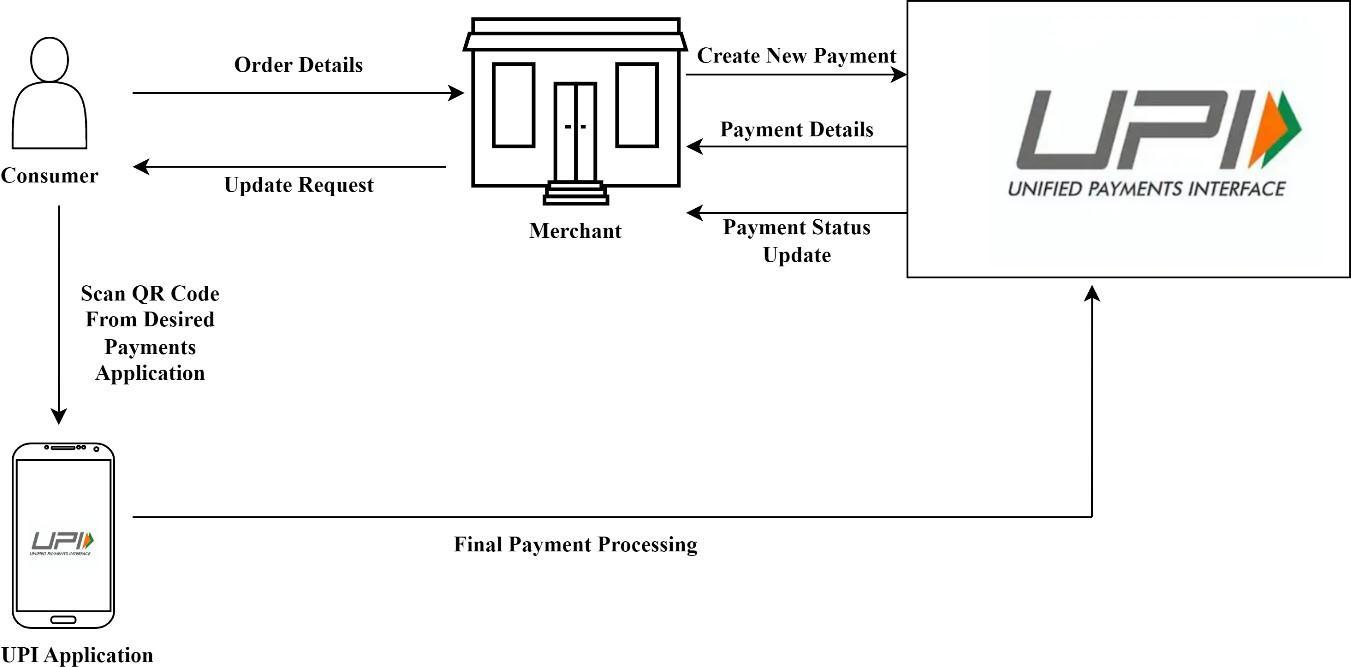
The low-level working of Unified Payments Interface paymentsinvolvesvariouscomponentsandprotocolssuchas HTTP, SSL, TLS, and 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication) that workinunisontoensurethesecureanderrorfreetransferof fundsbetweenbanks.AnoverviewofstepsinvolvedisUser Registration where the user is registered and the bank account is securely verified and linked to the user’s UPI account, setting up a UPI pin for enabling transactions. Similar process is followed for a merchant account willing to setup their UPI account via QR code scanner. Further, a Virtual Payment Address (VPA) is generated by a user’s or merchant’sbankwhichisauniqueidentifierlinkedtotheir bank account. Payment Initiation takes place from a consumersideviatheirUPIapplicationbyenteringmerchant VPA or by scanning their QR code which further queries a requestwithorderandpaymentdetailstotheUPIinterface. A payment process is initiated withgeneration of payment details. Upon these processes, the QR code scan process is initiated. This enables direct payment service generation from user UPI application to the UPI interface via PSP (Payment service provider). Upon further verification of paymentfrom user.TheNPCIswitchreceivesthe payment request and opts to check for user account balance to ensure sufficient funds, if sufficient funds are verified, the switch forwards the user request to the bank for authentication. Authentication step enables the bank account to send an authentication request to the user’s mobile device and promptsthemtoinputtheirUPIpin.Furtheranauthorization check takes place where in the linked bank account authorizes the payment and relays the process back to the NPCI switch[3]. Further, the UPI initiates a status update thread via webhook and provides it directly to the merchant. Final step is generation of update query on the user side whichmarksthe endof a UPIpayment cyclebetweenuser and merchant. Low level working of the payment transaction canbereferredinFig-5.
Individualsmust bevigilant andcautious when receiving unsolicited emails or communications from banks or financial institutions. Individuals should never click on
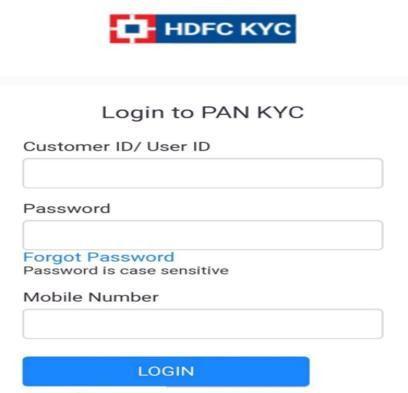
2.1
UPI (Unified Payments Interface) frauds using social engineering are becoming a common trend now due to increase in UPI users in the country. Frauds typically involvea fraudster tricking a victim or merchant using UPI QRcodesintoprovidingtheirUPIcredentials,suchastheir UPI PIN or UPI ID, through some form of social manipulation. The socialengineering-based attack to give risetoUPIfraudsinonhigh increasedaybyday.Anormal workingofaUPIbasedsocialengineeringfraudincludesan attacker to lure the victims into visiting the fake site or downloadingthefakeappbysendingthemphishingemails or social media messages. Once the victims access the fake UPI payment app or website, the attackerscansteal theirUPIPIN,password,orothersensitiveinformation. The attackers can also use the fake app or website to initiate fraudulent transactions from the victims' bank accounts.

One trend in UPI frauds using social engineering is targeted towards merchant accounts opting for UPI paymentsusingQRcodewhichiswhatourresearchpaper focuses on. A simple working of this technique is that a user scans the QR code implanted by a merchant and instantly gets account details of the user after which the user can opt to enter the amount on their respective UPI application and proceed to pay the merchant. As the number of merchants opting for UPI based payments is increasing, so is the commensurate amount of UPI based fraudswiththesemerchants.
2.2 Watering Hole Social Engineering Attack
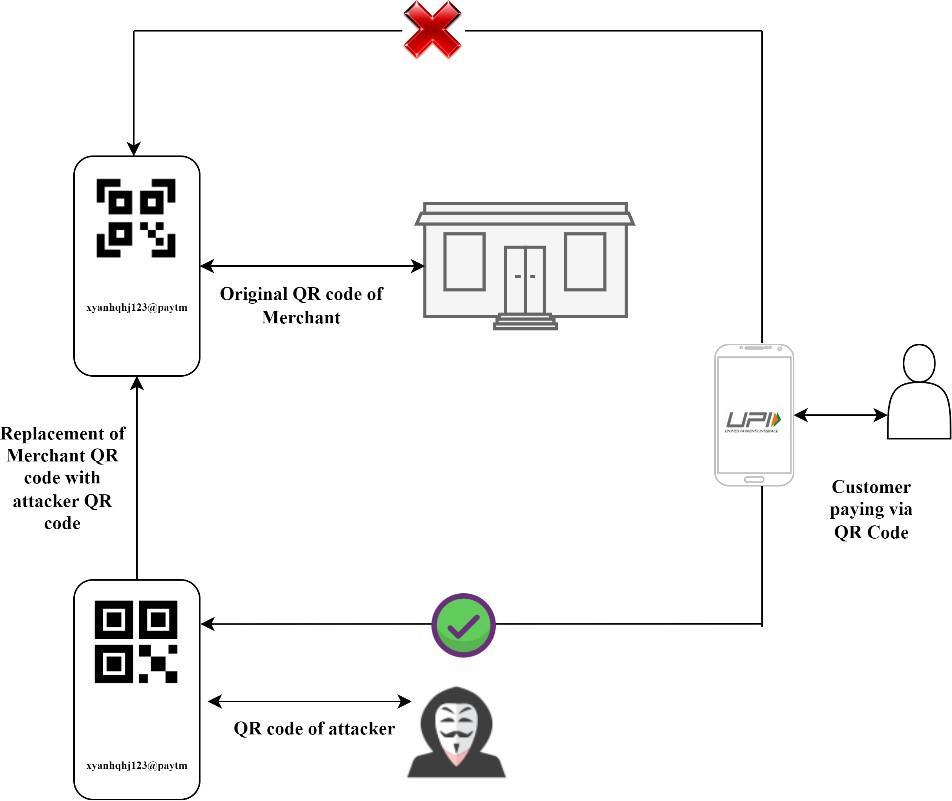
Our primary focus is to analyze the trending social engineering attack called Watering hole attack where the primarytargetsaremerchants.Thissocialengineering-based attackworksasfollows:
1. Theattackerlocatesthemerchantshopandfiguresout theUPIScannerthatthemerchantisusing.
2. Next,throughaseriesofmanipulation,oftenpretending tobeatechnicianfromUPIpaymentscompany,theyget holdoftheQRscanner.
3. TheattackerthenoptstoreplicatetheQRcodescanner exactly as the shop owner’s scanner, only difference wouldbethattheattackerwouldreplacethemerchant’s QRcodewiththeirownQRcode.
4. This shall enable the payments directed for the merchant to be redirected to the attackers account instead.
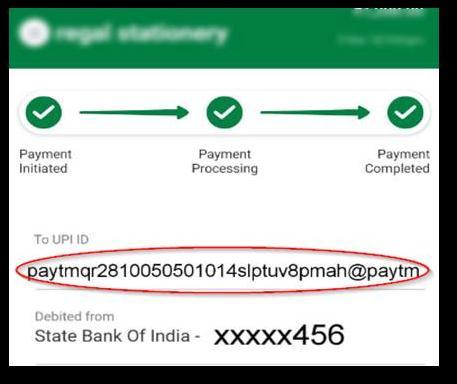
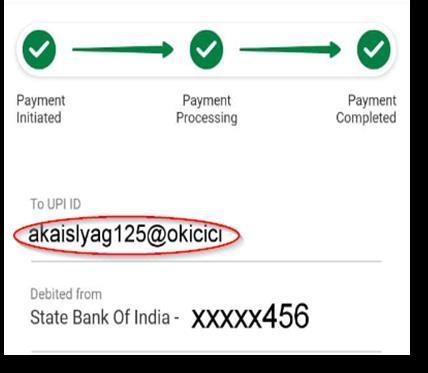
5. One of the points to be noted for why this scam is not easily detected by Merchants is the UPI name that the merchant gets. It is a series of random character set which is usually never readable and can’tbe memorised by anaïve user. Refer fig 7 for the UPI id that has random characters generated to maintainuniqueness.
6. The attacker takes advantage of this loophole to successfullyimplementthesocialengineering attack and thereby scamming the merchant optingfor UPI basedpayments.

2.3 Defense against such social engineering attacks
Tocombatsocialengineering-basedUPIfraud,afusionof education, awareness, and technological solutions is a mandatory.Afewmethodologiesthatcouldbefollowed are:
1. Educationandawareness:Aformofcombatingcouldbe conducting educational seminars, awareness camps, and educational camps for merchants for safer usage of UPI application daily. This would enable the merchants to be vigilant and aware users of UPI based payment applications.
2. Two-factorauthentication:Anaddedlayerofsecurityin theformof2FAcanbeimpliedbytheuserwhichwillgive anextrastepofsecurityinformofauthenticationandwill ensure thattheaddedlayer workstoprovide securityto the merchant account and prevent any fraudulent transfers.
3. ManualVerification:Oneoftheloopholesthatahacker takesadvantageofusingsocialengineeringistherandom character generation upon payment, this could be fraudulent transfer and can take advantage of the merchant’s naivety. To ensure this doesn’t happen, themerchant must ensure manual verification of the payment received from the consumer, if any suspicious activity isdetectedtheyshouldimmediately raiseanissue attheUPIhelpcenter.
4. Collaboration & Use of technology: Collaboration between individuals, merchant organizations, and law enforcementagenciescanhelppreventanddetectsocial engineering-based UPI frauds. This includes sharing information about new threats and collaborating on strategiestoidentifyandpreventthesetypesoffrauds. Merchantscanopttousevarioustechnologicalsolutions such as Paytm soundbox, which upon successful transaction, recites a full audio message of the amount receivedtherebymakingthemerchantawareandverify thetransactionthattookplace.
Individuals and organizations can reduce their risk of falling victim to social engineering-based UPI frauds andprotectthemselvesfromfinanciallossesand other negative consequences by implementing these defensestrategies.
3. CONCLUSION
In recent decades, UPI-based social engineering fraud has becomeagrowingconcern.AsmorepeopledependonUPIbased payment systems for financial transactions, cybercriminals are developing new methods to exploit vulnerabilitiesinthesesystemstocommitfraud.
Additionally,UPI-basedsocialengineeringfraudscanhave serious financial and personal consequences for victims. Private citizens must be aware of the risks and take precautions,suchasverifyingtheauthenticityofpayment requests and keeping their personal information secure. Organizationsandfinancialinstitutionsshouldalsotakean immediatemeasuretopreventanddetectsocialengineering fraud, such as monitoring for suspicious activity and providing employees and customers with education and training.
UPI-based social engineering cases of fraud are likely to remain a severe risk as the digital economy continues to grow.Individualsandorganizations,ontheotherhand,can minimize the likelihood of falling victim to these types of scams by remaining vigilant and taking proactive measures.
REFERENCES
[1] Yash Madwanna, Mayur Khadse, B R Chandavarkar, "Security Issues of Unified Payments Interface and Challenges: Case Study", 2021 2nd International Conference on Secure Cyber Computing and Communications (ICSCCC),pp.150-154,2021.
[2] IANS. Attention! UPI, payments frauds soar high in eastern Indian states: Report. https://www.indiatvnews.com/business/news-upipaymentsfrauds-soar-high-in-eastern-indian-statesreport-701790,May2021.
[3] NPCI. UPI live members. https://www.npci.org.in/ what-we-do/upi/live-members,2022.
[4] NPCI. UPI third party apps. https://www.npci.org.in/ what-we-do/upi/3rd-party-apps,2022.
[5] Aburrous, M., Hossain, M., Dahal, K., & Thabtah, F. (2010). Intelligent phishing detection system for ebanking using fuzzy data mining. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(12), 7913-7921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.04.044
[6] Gupta, Nakul , Jhamb, Dharmender, “How India can develop it’s fraud prevention model Journal of Payments Strategy & Systems, Volume 14/Number3 /Autumn/Fall2020,pp.237-255(19)
[7] https://www.npci.org.in/
[8] Kumar, A., Choudhary, R. K., Mishra, S. K., Kar, S. K., & Bansal,R.(2022).THEGROWTHTRAJECTORYOFUPIBASEDMOBILEPAYMENTSININDIA:ENABLERSAND INHIBITORS. Indian Journal of Finance and Banking, 11(1), 45-59. https://doi.org/10.46281/ijfb.v11i1.1855.

[9] Zulkurnain,A.U.;Hamidy,A.K.B.;Husain,A.B.;Chizari,H. Socialengineeringattackmitigation. Int.J.Math.Comput. Sci. 2015, 1,188
198.
[10] Parekh,S.;Parikh,D.;Kotak,S.;Sankhe,S.Anewmethod for detection of phishing websites: Url detection. In Proceedings of the Second IEEE International Conference on Inventive Communication and ComputationalTechnologies,Coimbatore,India,20–21 April2018;pp.949–952.
[11] CharviVij,ShrutiKeshari,"StudyonLexicalAnalysisof Malicious URLs using Machine Learning", 2022 Fifth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Technologies (CCICT),pp.120-127, 2022.

