BOILER TUBE FAILURE ANALYSIS IN 210MW POWER PLANT STEAM BOILER
Dr. A P Sivasubramaniam1, Sabarinathan G2 , Saran M3, Sridharprasad R K4 , Subash U5Abstract- This study is aimed at analyzing the reasons associated with boiler tube failure. Inspection anddata collectedfromMTPS - I serve as the basis for this analysis. Three samples (damaged LTSH tube, failed Economizer tube and failed RH tube) were collected from MTPS. Metallographic investigations were carried out in the samples collected to understand, interpret and substantiate the probable reasons that led to tube failure which occur when the effective strength falls below a critical level. Apart from visual inspection, optical microscopy, microhardness tests, SEM investigations, chemical analysis and EDS tests were carried out on various regions of the failed tubes and the results have been elaborately discussed. Upon visual inspection, formation of oxide layers on the inner side of the tube has been noticed which indicated that the inner side of the tube is subjected to corrosion. Formation ofoxide layers has led to inhomogeneous overheating which has thereby affected the homogeneity of the tube. The main reason for rupture (hole formation) in the failed region can be attributed to steam erosion either from an adjacent failed tube or from soot blower. Besides steam erosion, flue gas erosion has also occurred due tounevenvelocity of flue gas which could be catalyzed by the presence of unburnt coal particles. Graphitization leading to formation of elongated as well as spherical graphite nodules and spheroidization over a period of time were identified as the major failure mechanisms involved from a microscopic perspective which could be related with overheating accompanied by creep leading to softening of the tube at the failed region thereby causing ductile fracture from a mechanical perspective. SEM micrographs showed the formation of graphite nodules, micro-cracks and void coalescence. Though occurrences of tube failures in boiler couldn’t be completely eradicated, they can be considerably reduced by adopting certain remedial measuressuggestedattheend.
Keywords: Tube failure, metallographic examination, graphitization, spheroidization, overheating, creep, erosion, corrosion, ferrite –pearlitemicro structure.
1. INTRODUCTION
As could be observed from the report of Central ElectricityAuthority,leakagein water wall tubes, super heater tubes, re-heater tubes and economizer tubes accounts for 2.2 % of loss of maximum power generation. While investigating the root cause of these leakages,ittranspiresthattheboilertubesaresubjected to a variety of failures involving one or more of several mechanismslikeerosion,corrosion,stressruptureetc.A detailed study is warranted for understanding the variousmechanismsleadingtofailureofboilertubes.
2. BOILER TUBE FAILURE
The accurate prediction of life of boiler tubes is difficult because of uncertainties associated with operating conditions, material properties, erosion/corrosion rate, geometry of eroded/corroded areas etc. It is very difficult to identify and locate gradual degradation of tubes like thinning, crack formation, deformation till it leads to puncture causing leakages. The only time interval when the tube can be accessed is during the plannedmaintenanceaspertheschedulebesidesforced outages.Thesymptomsofleakageintubearefeedwater consumption higher than normal leading to more make up water, low water level in the boiler drum, pressure drop in steam, hissing sound emitted by leaking steam, white smoke from chimney, fluctuations in furnace pressure.
2.1 VARIOUS NOMENCLATURES INVOLVED IN

2. 2 INVESTIGATION WORK
The investigation was carried out on the following scrapped tubes reportedly discardedand disposed as scrapfromMTPS.
procedures. The sectioned samples are mounted using hot mounting process which uses thermosetting plastic compound bakelite to encapsulate the specimen. The mounting undergoes grinding, polishing using series of emery paper containing successively finer abrasive followed by etching. 2% Nital is used as etchant. The mounted samples are investigated using a Leica DMi8 metallurgicalmicroscope.
Material specifications, design and operating parameters of the LTSH tube as obtainedfrom the thermalpowerplantareasfollows:


Micro indentation hardness measurement on the mounted sample was conducted using Vickers digital micro hardness tester (model: MMT – X7 No:MM5250X, ManufacturerMATSUZAWACO.LTD.,Japan).
3.BOILER TUBE FAILURE ANALYSIS
Failureanalysismainlyconsistof:
Visualinspection
Metallographicexamination
Microhardnesstest
Seminvestigation
3.1VISUAL INSPECTION
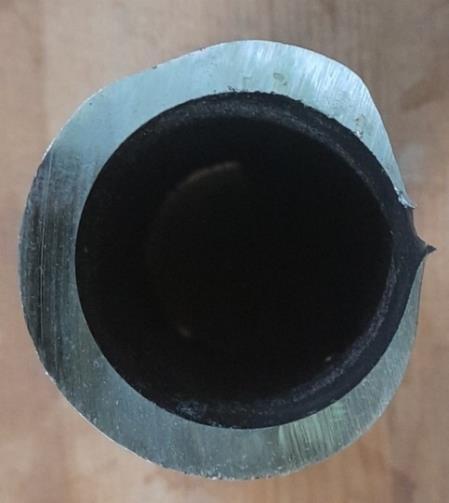
The failed section of the economizer and RH tube was visuallyinspected.Figure3.1(a)presentsanimageofasreceivedsampleofthefailedeconomizertubeandFigure (b) presents an imageof as-receivedsample of thefailed RH tube. The circularity of the tube cross section is varying.
By observing cross section of the economizer and RH tube,itcouldbenotedthathalfofthecrosssection ofthe tube segment was thinner than the other. Figure 3.1 (a) & (b) presents image after making a single cut along transverse plane of failed economizer and RH tube respectively
To analyze the failure of these tubes, visual examination wasperformed by naked eyeand images have been taken by digital camera. The failed economizer tube and failed RH tube suffered significant damage while LTSH tube has not suffered anykindofsignificantdamage.
In order to investigate the potential causes for failure due to microstructural anomalies or degradations, specimens of economizer and RH tube were cut transversely along the cross section of the tube in the failed region, and randomly chosen region in case of LTSHtube.Thesmallringiscutlongitudinallytomake smallspecimensandmarkedasdetailedbelow.
The method of optical microscopy has been used for microstructural examinations. Metallographic sample preparation has been carried out using standard
The measured thicknesses of tube walls at different segmentsareasfollows:


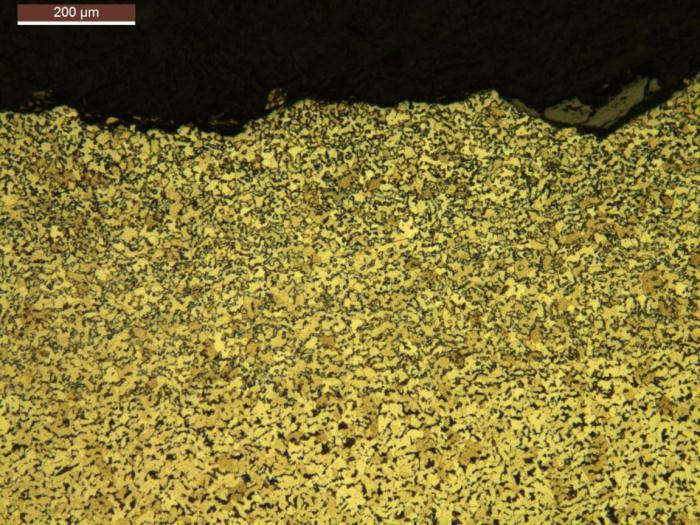
3.2 METALLOGRAPHIC EXAMINATION
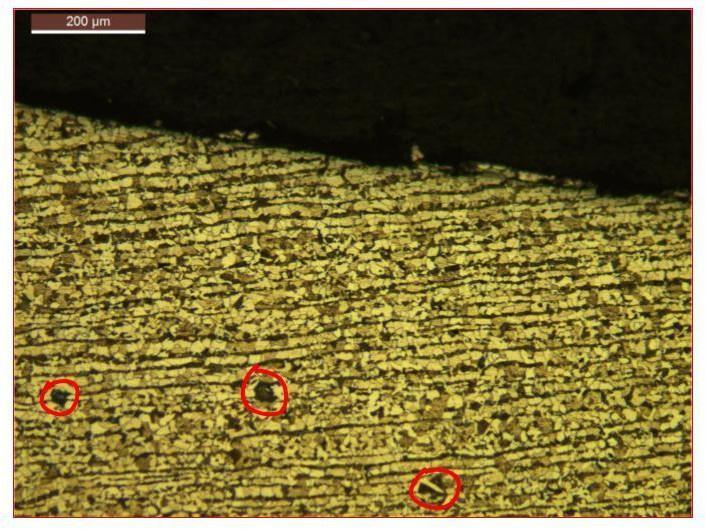
Long term overheating brings about microstructural changes like grain growth, disintegration of pearlite, spheroidization of carbides, graphitization and decarburization leading to loss of strength of the tube material, eventually resulting in stress rupture or creep rupture through grain boundary void formation. The first stage in the transformation is in situ break down of the pearlitecolonies remaining intactbuttheplateletsofiron carbide become spheroids. The next stage is the disappearance of pearlite colonies and dispersion of spherical carbide particles throughout the matrix and then finally the formation of graphite particles and their growth.
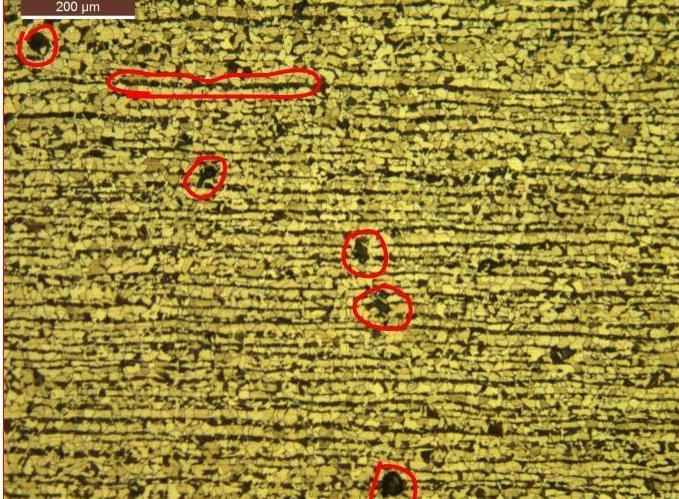

Uponthinning,thetubecouldhavefailedduetofollowing tworeasons:
1. The reduced thickness could not withstand the circumferentialhoopstressandcausedstressrupture.
2. Thinning might have caused over heating which has led the metal temperatures to exceed their creep temperaturelimit.

3.3 MICRO HARDNESS TEST
3.4 SEM INVESTIGATION
In order to investigate the fracture mechanisms involved, SEM investigations were conducted through Scanning Electron Microscope Apreo SEM – Thermo Scientific funded by SRM IST and micro-fractographs were taken at various magnifications for un- etched samples.

By referring the above table, it could be noted that the hardnessinthethinnedportionislesserthanthatofthe thick portion. Softening has occurred in the thinned portion due to overheating. Since yielding / plastic deformation has occurred in the failed region, the inference that could be drawn is that the fracture mechanisminvolvedhereisductilefracture.
2023, IRJET

Impact Factor value: 8.226
By referring the SEM micrographs, we could observe the formation of graphite nodules which confirms the occurrence of elongated as well as spherical graphitization. We could also observe the formation of micro-voids and void coalescence along with microcracksandtheirgrowth.Sincethemainpurposeofdoing SEM in our project is to ascertain the formation of graphite nodules, micro-cracks and void coalescence which occurs due to diffusion of carbon as a result of overheatingaccompaniedbycreep,wehavedoneSEMon un-etched specimens. There is a huge scope for researchers to extend our SEM investigation with specimens after applying various etchants so that the formation of new grains with different microstructures canbeobservedandappreciated.

Apartfrom optical microscopy,micro-hardnesstestand SEM investigation, we have also done chemical analysis and EDS tests on various specimens and the results are attachedasannexures.
4 CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
1. When we refer to the standards being followed in industrial thermal power plants mostly in India, we can find that spheroidal graphitization has been taken into consideration while designing the boiler operation but elongatedgraphitizationhasnotbeentakeninto
2. Regular thickness measurement consideration sincewecouldrarelyfindelongatedgraphitizationbeing discussedinavailableliteratures.
3. Since,“chromiumformsmorestable carbidesthan that of iron and molybdenum”, usage of boiler tube materials with high chromium content can withstand graphitization which is one of the most predominant failure mechanisms identified via microscopic examination.
4. Since yielding / plastic deformation has occurred in the failed region, the inference that could be drawn from the micro-hardness test is that the fracture mechanisminvolvedhereisductilefracture.
5. Standard operating procedure in maintenance should be adhered to reduce maintenance related failuressuchasweldfailures.
6. The quality of coal should be ensured to reduce failuresduetoerosion.
7. The quality of water treatment with robust technologies in Demineralization watertreatment plant (DM plant) should be ensured to avoid failures due to formationofoxidescalesandcorrosion.
8. Reduction of fly ash generation which increases erosion related failures in the design phase naturally increases the generation of wet ash which causes detrimental environmental impacts during its disposal intheashpondviaslurrytransportation.Hence,atrade off must be given between these two while designing newboilers.
9. By usage of tube materials resistant to high temperature, we can reduce failures due to creep mechanism.
10. By usage of tube materials resistant to high internal pressure (Hoop stress), we can reduce failuresduetostressrupture.
11. Usage of supercritical boilers in an emerging technology where we could eliminate the latent heat required for converting water to steam which thereby reduces coal consumption. However, this technology is profitable as far as boiler tube failures are concerned only upon usage of tube materials that couldwithstand

hightemperaturesandpressures.
5ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We express our sincere gratitude to our principal Dr. M. Prem Kumar of Paavai Engineering College, Namakkal. We also express our sincere gratitude to the head of the Mechanical department Dr. A.P. Sivasubramaniam for his constructive suggestions and encouragement during our project for his valuable Support,helpandguidancethroughoutthisproject.
6 REFERENCES
1. Jutaporn Chaichalerm, Chaiyawat Peeratatsuwan, Thee Chowwanonthapunya, ‘A metallurgical investigation on a failed superheater tube used in a thermal biomass power plant’.
2. S.W. Liu, W.Z. Wang, C.J. Liu, ‘Failure analysis of the boiler water-wall tube’, Case Studies in Engineering FailureAnalysis9(2017)35-39.
3.P.Sakthivel,S.Kalaimani,Dr.R.Sasikumar,‘Analysisof TubeFailureinWaterTubeboiler’.
4. Rajat Gupta, S.N. Singh, V. Sehadri, ‘Prediction of uneven wear in a slurry pipeline on the basis of measurementsinapottester’.
5.Xue,S.,Guo,R.,Hu,F.,Ding,K.,Liu,L.,Zheng,L.,Yang,T., ‘Analysis of the causes of leakages and preventive strategies of boiler water- wall tubes in a thermal power plant’, Engineering Failure Analysis (2020), doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104381.
6. Vahid Javaheri, David Porter, Veli- Tapani Kuokkala, ‘Slurry erosion of steel- Review of tests, mechanisms and materials’,Wear408-409(2018)248-273.
7. AHMED ELKHOLY, ‘PREDICTION OF ABRASION WEAR FOR SLURRY PUMP MATERIALS’, Wear, 84 (1983) 39 –49.
8.F.Dehnavi,A.Eslami,F.Ashrafizadeh, ‘Acasestudy on failureofsuperheatertubesinanindustrialpowerplant’, Engineering Failure Analysis (2017), doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.07.007.
9. Babak Hagahighat-Shishavan, Hossein Firouzi-Nerbin, Massoud Nazarian-Samani, Pooria Ashtari, Farzad Nasirpouri, ‘Failure analysis of a superheater tube ruptured in a power plant boiler: Main causes and preventive strategies’, Engineering Failure Analysis 98 (2019)131-140.
10. Rajat K. Roy, Swapan K. Das, Ashis K. Panda and Amitava Mitra, ‘Analysis of Superheater Boiler Tubes FailedthroughNon-linearHeating’,ProcediaEngineering 86(2014)926-932.

