A Review on the Integration of Biomimicry Strategies as a Tool for Sustainable Construction Management
Aishwarya Chandrasekaran1 , Mr. A. Sheik Farid 21Postgraduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, B.S Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology Vandalur, Chennai-600048

2Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering,B.S Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology Vandalur, Chennai-600048
Abstract - The irregular climatic conditions caused by the global effects of controversial conservation and preservation applications have placed an unfair pressure on existing and future resources. In the case of the construction industry, the depletion factor has necessitated the strict implementation of sustainability-inducing practices in terms of materials, techniques, and operations, as well as construction project management. The construction industry has a significant economic influence and provides a chance to address climate change and global problems. The connection between management and sustainability allows for the identification of components, structures, and integration methods. This study emphasizes the concept of using biomimicry principles as a framework to promote sustainability in the building industry. Nature is used as a reference, benchmark, and model to influence design decisions and how the built and natural environments are perceived through design, materials, and technology. This study also demonstrates how it can be used to generate profit while protecting future generations' lives and resources, for the adaptation of a better understanding of therisks,costs,andadvantagesoftheapplication.
Key Words: Biomimicry,Sustainability,Construction management,natureasmentor.
1. INTRODUCTION
The study of "imitating life" is known as "biomimicry," which takes its name from the Greek words "bios," which refers to life, and "mimesis," which means "to copy." The practice of copying and modeling human behavior after thatofthenatural worldis knownas"biomimicry".Itisa relatively new field of study that looks at the most successful patterns and processes in nature and bases artificial solutions on them. Because of its 3.85 billion years of evolution, nature is considered to be the best, most significant and most reliable source of invention for designers. This is true because nature is very skilled at finding solutions to issues that affect both the environmentanditsinhabitants.
1.1 GENERAL
In the study of biomimicry, experts examine the natural worldtolearnhowdifferentspeciesoforganisms,millions of years ago, overcame their problems. Researchers can incorporate these organisms' strategies into the design of buildings and other physical structures. This review aims to investigate how introducing biomimicry strategies can provide sustainability to the construction project management function. This study aims to ascertain how biomimicry strategies can provide sustainability within the function given the still exploratory nature of the topic and the need to comprehend how organizations are working on sustainability in project management. In addition, it strives to comprehend how the efforts of sustainability might affect project success while utilizing natureasamentor,model,ormeasure.
1.2 HISTORICAL BACKGROUND OF BIOMIMICRY
The term "bionic" is said to have been coined by Jack E. Steele,whouseditforthefirsttimein1956whileworking intheAeronauticsDivisionHouseatWright-PattersonAir ForceBase.In Ohio,a scientific conferencewasscheduled forSeptember1960.Theyreferredtoitasascientificterm anddescribeditsobjectives asthoseofabrand-newfield. With the release of Janine M. Benyus' book "Biomimicry: Inventions Inspired by Nature" in 1997, the term "biomimicry" gained widespread usage. The phrase's popularizationiscreditedtoJanineM.Benyusinthisbook. The term "biomimicry" or "biomimetic" is preferred by those working in the technological fields because it is similartotheterm"bionics,"whichisusedinthemedical field.
2. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Elghawaby Mahmoud (2010), has attempted to reformulate the research that has previously been investigated by Hassan Fathy and used in traditional constructions.HassanFathy'searlierinvestigationintothe concept inspired Mahmoud's attempt, which is based on that investigation. Hassan Fathy is credited with coming up with the concept for this innovative idea first.
Furthermore,itiswidelyacceptedthathecoinedtheterm "breathing facades" to describe these aspects of architecturaldesign.Heoffersaconceptualmodelthatcan be used as a first step in creating buildings that can naturally breathe and circulate fresh air throughout the entire building's interior in order to achieve this. This model can be applied as a first step in creating structures that naturally breathe and circulate clean air throughout the entire structure. This model may be seen as a development toward the creation of buildings with the ability to naturally circulate clean air throughout the entireinteriorofthestructure.
Nick Taylor Buck (2015) discusses the significance of biomimicry as a design methodology in the context of urban infrastructureplanninganddesign.Theapplication ofbiomimicryprinciplestourbaninfrastructureproblems is investigated through the examination of case studies that used biomimicry-inspired techniques rather than mainstream infrastructure approaches. Biomimicry is a city ontology that fosters innovative and collaborative urban infrastructure design and management, supplements dominant future city paradigms such as the smartcity,andmeritsfurtherin-depthinvestigation.
Abubakar Usman Karofi (2015), developedstrategiesto improve energy efficiency through passive cooling, solar efficiency, and aerodynamics. This was accomplished by analyzing the various ventilation means of the buildings, analyzing the various types of roofing on the buildings, assessing the lighting means used within the buildings, identifying the sources of power generation for the selected buildings, and proposing an architectural design for an energy-efficient mixed-use building in Abuja's central business district. The paper concluded on the importance of building energy efficiency and recommended principles for achieving building energy efficiency.
Mauro Luiz Martens, et al (2015), investigated the impactofsustainabilityonprojectsuccess.Amultiple-case studyapproachwasusedinfourdifferentcompaniesfrom Brazil and the United States. Data was collected from a variety of sources, including semi-structured interviews with project and sustainability managers and online questionnaires distributed to project team members. The findings indicate that firms are concerned about sustainability in project management; however, there is a disconnect between perceived importance and actual use in practice. Finally, public-sector firms are more concerned with the social dimension than the private sector.

Liene Kancane (2016), discusses how the biomimicry approach uses natural processes to solve human problems, which can lead to conceptually novel solutions. Northern mammals can serve as an example: fatty tissue
acts as a thermal insulator for the body, but the phasechange properties of the lipids are also used to store and releaseheat.TheamountoflatentheatstoredinPCMscan reduce the energy demand for heating the building and thusCO2emissions.VariousconceptsforPCMintegration inthebuildingenvelopehaverecentlyemerged,including built-in walls, ceilings, and floors, as a thin layer, and in largestoragetanks.ThispaperdiscussesPCMselectionin themeltingtemperaturerangeof21-22°C.
Vincent Blok (2016), discussestheconceptofnatureasit is assumed in biomimetic approaches to technology and innovation. Because current biomimicry practices presuppose a technological model of nature, its claim of being a more ecosystem-friendly approach to technology and innovation is debatable. To preserve the potential of biomimicry as an ecological innovation, he has investigated an alternative to nature's technological model. To that end, he has conducted research on the materiality of natural systems and explored a natural model of nature based on the responsive connectivity of matter. This natural model allows the data to be conceptualized as conative responsiveness to biosphere connectivity.
Shivi Pathak (2019), demonstrates in his research how drawinginspirationfromnaturecanresultinasignificant increase in the efficiency with which available resources are utilized. Biomimicry is all about taking cues from nature to decide how to proceed with the design process when it comes to the construction of eco-friendly buildings. This includes the effectiveness of the building's thermal environment, zero-waste systems, efficient water use, structural design efficiency, and water utilization efficiency,aswellastheeffectivenessofitsenergyuse.
Mahesh Bankar (2019), discusses the use of biomimicry strategies in building to make it more environmentally sustainable in his research. Biomimicry is a novel approach that takes the design principles of Flora and Fauna as its inspiration. The approach is investigated in thecontextofgreenbuildingobjectivessuchasindoorair quality, water efficiency, energy efficiency, and an ecofriendlyHVACsystem.Thestudylooksintothepossibility of using the biomimicry approach in green building technology. This paper discusses how the biomimicry approach solves the purpose of green building in an innovative way, namely resource efficiency and reducing theenvironmentalimpactofthebuilding.
Henrique Sala Benites (2021), proposes that bioconnectivity, or "bio-connections," a nature-focused approach based on biophilic design, biomimetics, and ecosystem services, may be an important enabler for the regeneration of the planetary boundaries' ecological and social boundaries, as well as doughnut economic models. Helooksthroughtheliteraturetoseehowbio-connections
can help circular and regenerative processes at the local scaleofthebuiltenvironmentdomain.Healsoaddssome real-world examples from selected urban communities in existing urban areas around the world that claim a green approachtothediscussion.
Ankush Kumar Meena, et al (2021), conducted a bibliometric analysis of biomimicry-related literature to determine the recent growth of biomimicry as an architectural method. This survey considers the period between 1990 and 2020. The Scopus database is used as theprimarysourceforbibliometricanalysisinthispaper. External software such as iMapBuilder and VOS Viewer are used for data visualization. The study's goal is to demonstrate the importance of biomimicry in today's world. The study's findings highlight the scarcity of biomimicry research and the need for additional research on the subject. A new research approach for comprehensivebiomimicryresearchpavesthewayforthe findingsofthisanalysis.
Niloufar Varshabi (2022), investigates the evolution of biomimicry as an architectural approach by conducting a bibliometricreviewofresearchonbiomimicryandenergy efficiency. Another goal of this research is to emphasize the importance of biomimicry in modern design. This study examined articles published in the Web of Science database between 2010 and 2021. The analysis results were graphically represented using VOS viewer and SankeyMATICsoftware.Thisstudy'sfindingsrevealedthe needforadditionalresearch,inadditiontotheinadequacy of biomimicry research. This review can be used as a startingpointforfutureresearchintotransferringnatural phenomena to architecture to solve the problem of efficientenergyconsumption.
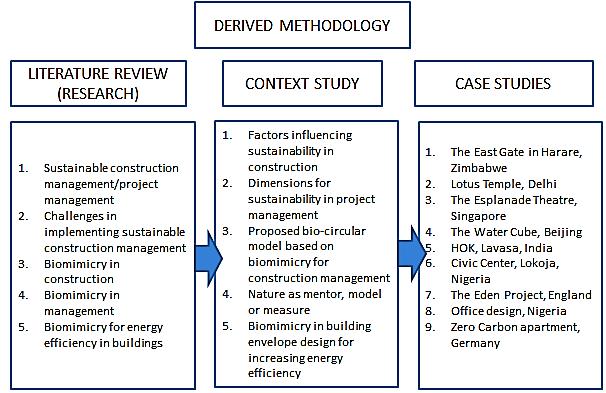
3. DERIVED METHODOLOGY
Themethodologydevelopedfromthereviewofliterature focuses on problem-solving approaches based on biomimicry that are capable of addressing issues at the envelope,structure,execution,ormanagementlevels.This is based on the assumption that naturealready addresses the majority of the problems associated with indoor environments,problemsforwhichsolutionsmaybefound in one or a combination of Pinnacles' strategies and principles. For the purpose of defining the case study for the theoretical framework, climate-related concerns were chosenandexaminedinacontextstudyofsimilarapplied cases in building and energy management. This methodology serves as a foundation for a better understandingofhowtoapplythebiomimicryframework toachievesustainableconstructionmanagement.
3. CONCLUSIONS
DerivedMethodology
The earth's natural resources, particularly its energy sources, are being used up quickly due to urbanization. The mechanical system of the building was used to its fullest extent for active cooling, which increased greenhousegasemissionsandhadagreaterimpactonour delicate ecosystem. This occurrence gave people from all over the world new perspectives and stimulated the creation of methods to increase the energy efficiency of buildings. This review of the relevant journal articles yieldsanumberofmethodsandtoolsthatmaybeusedto investigate the energy efficiency of an existing structure and lessen that structure's reliance on the building's mechanicalsystembyemployingbiomimicrytactics.
The objective of this literature review is to better understand the role of building elements in reducing energy consumption using a biomimetic approach. A framework is created to aid in the analytical study of variousexamplesinordertocomprehendandanalysethe various biomimicry techniques and strategies that can be applied to various building elements in order to achieve efficiency in building construction and management. Theseexampleshavebeenconsideredintermsofbuilding typology, inspiration from nature, application in design, and how problems were solved through their use as a solution.

REFERENCES
[1] Benyus, J.M. (1997).Biomimicry:Innovation inspired bynature.
[2] KAROFI, ABUBAKAR USMAN. "INTEGRATION OF BIOMIMICRY PRINCIPLES AS A MEANS TO ENERGY EFFICIENCYINOFFICEDESIGN,ABUJA,NIGERIA."
[3] Martens, M. L., & Carvalho, M. M. (2016). “The challenge of introducing sustainability into project
management function: multiple-case studies”. Journal ofCleanerProduction, 117,29-40.
[4] Taylor Buck, N. (2017). “The art of imitating life: The potential contribution of biomimicry in shaping the future of our cities”. Environment and Planning B: UrbanAnalyticsandCityScience, 44(1),120-140.
[5] Blok, V. (2016). “Biomimicry and the materiality of ecological technology and innovation: Toward a naturalmodelofnature”. EnvironmentalPhilosophy.
[6] Benites,H.S.,&Osmond,P.(2021).“Bioconnectionsas enablers of regenerative circularity for the built environment”. UrbanPlanning, 6(4),25-39.
[7] Kancane, L., Vanaga, R., & Blumberga, A. (2016). “Modeling of Building Envelope's Thermal Properties by Applying Phase Change Materials”. Energy Procedia, 95,175-180.
[8] Pathak, S. (2019). “Biomimicry:(innovation inspired by nature)”. International Journal of New Technology andResearch, 5(6),34-38.
[9] Mahmoud, E. L. G. H. A. W. A. B. Y. (2010). “Biomimicry: a New Approach to Enhance the Efficiency of Natural Ventilation Systems in Hot Climate”. In International seminar arquitectonics network,Architectureandresearch,Barcelona
[10] Varshabi, N., Arslan Selçuk, S., & Mutlu Avinç, G. (2022). “Biomimicry for Energy-Efficient Building Design:ABibliometricAnalysis”. Biomimetics, 7(1),21.
[11] Bankar,M., & Jogdand,V. (2020).“FeasibilityStudyof Adaptation of Biomimicry Approach in Green Building”. In E3S Web of Conferences (Vol. 170, p. 06010).EDPSciences.
[12] Imani, N., & Vale, B. (2022). “Developing a Method to Connect Thermal Physiology in Animals and Plants to the Design of Energy Efficient Buildings”. Biomimetics, 7(2),67.

