1,2,3
International

1,2,3
International

***
Abstract: Braintumorsareamongthemostfrequentandseveretypesofcancer,withalifeexpectancyofa fewmonthsin the advance stages, due to which a fast, automated, efficient and reliable technique to detect tumor is required. Various modelsincludingCTScans,MRIandultrasoundimagesareusedtodetecttumor indifferentpartsofbody,butsuchmethods pose difficultyin identifying andanalyzingthe true picture. Currently,doctors locatethe position and the area oftumor by lookingatthescansandimagesmanually, whichresultsininaccuratedetectionandisoftentimeconsuming.
DeepLearninghasbeenarguedtohavepotentialtoovercomethechallengesassociatedwithdetectingbrain tumorsinwhich earlydiseasedetectioncanbedoneusingA.I.andNeuralNetworkAlgorithms.
InCNNacompletelyautomatedcomputerizedsystememploysoptimaldeepfeaturesandabstractionlevel fortestingandin VGG-16fewdropoutlayersareaddedsoprovidebetteridentification.Ontestingthetechnique providesexcellentandreliable results. Inception-v3is a convolutional neural network thatis48layersdeep. ResNet-50is a convolutional neural network thatis50layersdeep.
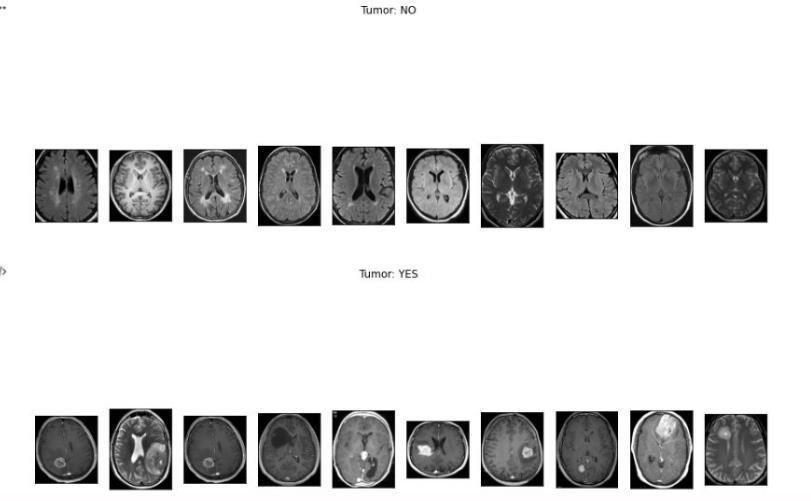
InourworkwehaveusedConvolutionalNeuralNetwork,VGG-16,ResNet-50andInceptionv3tosegment MRIimages(JPEG) into twocategories, those that havetumorand those thatdo not. The datasetconsists of 253 images, with 155 with tumor and98withouttumor.
Keywords: DeepLearning,ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork,ArtificialIntelligence,VGG-16,ResNet-50, Inceptionv3
Introduction: Brain tumor can be classified into cancerous and non-cancerous tumor, the cancerous tumor can quickly spreadtoothertissuesin brainandleadtoworseningthepatient’scondition.Whenmostofthe cellsgetdamaged,theyare replaced by new cells. if damaged cells are not eliminated with the new cells, it can cause serious consequences. The productionofthenewcellscellsoftenresultsintheformationofa masstissue,whichthenleadstotheformationoftumor. Brain tumor detection is highly tedious and complex due to the size, shape, location and type of tumor in the brain. Identification of tumors in the early stage is strenuous as it cannot accurately measure the size, shape and location of the tumor
However,ifthetumoristreatedearlyintheformationprocess,thechanceofpatient’streatmentisvery high.Therefore, the treatment of tumor depends on the timely identification of the tumor. In this regard, in the field of medical imaging, AI and digital image processing has made a huge impact by using convolutional neural network (CNN). Tumor segmentation is a process of separating better and healthier tissues from the affected areas. As a result, segmentation is the most challenging taskinidentificationtechniques.Insteadof beingexpertinthebraintumordetection,manyofthemoderntechniquesdepend on general edge detection methods. Due to their efficiency in detecting features of images, deep learning algorithms are largelyused fortumorsegmentationtasks,theyhaveshowedsignificantconsistencyandaccuracy indetecting cases
For visual identification and detection, the CNN architecture is the most popular and extensively used machine learning approach. In this project, we use a convolutional neural network (CNN) technique combined with Data Augmentation and Image Processing to analyses MRI images(JPEG) to determine which images have and which do not have brain tumors. Medicalimage segmentationtakesalongtimeothermedicalexperts.Hence,preciselyidentifyingabraintumormanually is next to impossible task also one can find that there is a lot of difference among doctors opinion. To overcome these constraints,computerassistedtechnologyistheneedofthehour,asthemedicalfield requiresquickandreliableprocedures to identify life threatening diseases such as cancer, which is the top cause of death for patients worldwide. Hence, utilizing
BrainMRIImages(JPEG),wepresentamethodforclassifying MRIimages(JPEG)intothosewithandwithoutthepresenceofa braintumorsutilizingadataaugmentationstrategy andaconvolutionalneuralnetworkmodelinourstudy.

Proposed System: Edgedetectionisa processoffindingandexaminingcertaindisruptionsinan image.Thedisruptionsare sudden changes in the information stored in image which identifies boundaries of objects in a scene. Currently, there are many edge detection techniques available which are used to identify specific types of edges. The aim is to reduce the informationstoredintheimagewhileconservingthe requiredproperties
Efficientedgedetectionmechanismisusedintheproject
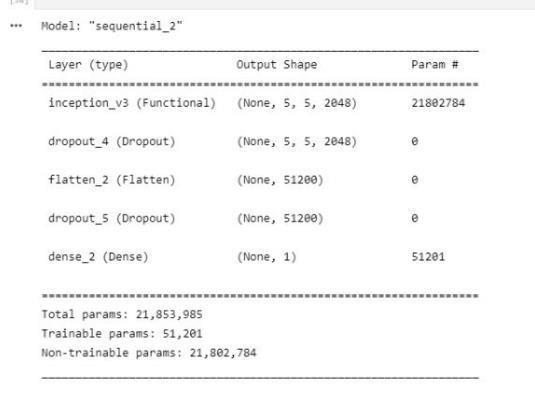
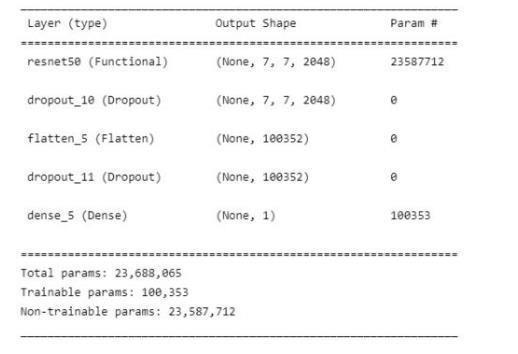
We propose a method that is sequential in its operation. It uses techniques such as convolutional neural network, max pooling,flatteninganda dropoutlayertoavoidover-fitting.Weusetransferlearningto assign weightstoourfeatures.The MRI image(JPEG) sequentially goes through the above stated layers and feature extraction is performed.DICOM images is large in size when we use to it to train model parameter increase so to decrease parameter we use dicom converted jpeg imagesfrom Kaggle. The MRIimages(JPEG)havebeen dividedintotrainingandtestingpartswherethefirstpartisused for furthertrainingofa VGG-16CNN,ResNet-50,Inceptionv3.
Algorithm demonstratesthestep-by-stepworkingprocessoftheproposedsystem.
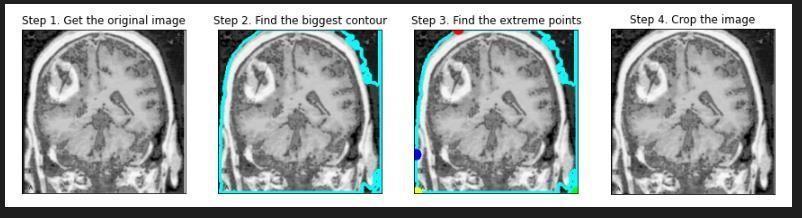
Literature Review: The lump in the brain tumor can be present at different locations and shapes, during the time of segmentation . Brain tumors are segmented using the MRF system. Generative models successfully generalize hidden data with some constraints in the training step. Without the use of a specific model, these strategies can be employed to comprehend the pattern of a brain tumor. The distribution of identical and independent voxels on the ground of context factors is constantly taken into account in these styles. As a result, some small or isolated clusters of voxels may be distributed incorrectly into the wrong class, generally in anatomically and physiologically incongruent places. To avoid these issues, numerous experimenters used probabilistic predictions to fit neighborhood information into a Conditional RandomField(CRF) classifier.DeepCNNmodelsareusedtoautomaticallylearnscalesofcomplexdataattributes.
Inthisworkwehaveenforcedapre-trainedandadvancedinterpretationofVGG-16ConvolutionalNeural Network(CNN)to categorizebraintumorimagestakenwithcameraintotwotypesthatis cancerous andnormalimages.Althoughthenetwork model does not need feature extraction to apply a small quantum, training CNN architecture is tough and tedious since it needs a dataset for testing and training before the structure is ready for classification, which is not always available. In addition, hardware is required for computing the massive factor for large images. . Since DL Algorithms can effectively expresscritical relationswithoutdemandinga widevarietyof equipment,theyarearemarkabledevelopmentinML . Asa result,theyevolvedfleetlytoserveasablessinginseveralhealthinformaticsfields,suchas informatics,healthcareanalytics, andpatternidentification.
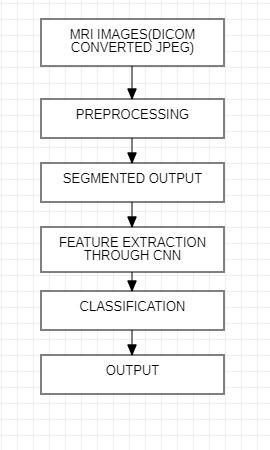
Methodology Result and Discussion: The dataset used in the design is Brain MRI Images(JPEG) for Brain Tumor
Identification , which is easily available on Kaggle. The dataset includes 253 images of brain MRI ,out of which 155 have tumourand98imagesdonothavetumour.Ourdatasetwasdividedinto threepartsfortraining,validation,andtesting.The

trainingdataisusedtolearnthemodelandgetusedto thefeatures,whilethevalidationdataisusedtoestimatethemodel andinterpretitsparameters.
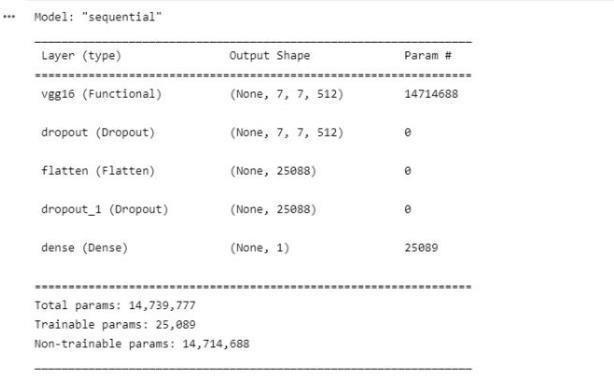

ThevalidationisimplementedusingCross-Validation.Ourmodel’sfinalevaluationwillbeonthegroundof testdata.
Insomecases,theareasoffatintheimagesareincorrectlyidentifiedastumor,orthetumorsmaynotbe seenbythedoctor; themostexacttreatmentiscompletelydependedonthedoctor’sskill.Inthispaper, theCNNhasbeenusedforBraintumor detection using some images. There were some margins of the images gathered from the imaging centers, which were removed to provide a high resolution view of the image One of the main reasons for using the feature extraction technique wastoincreasetheaccuracyofthenetwork.

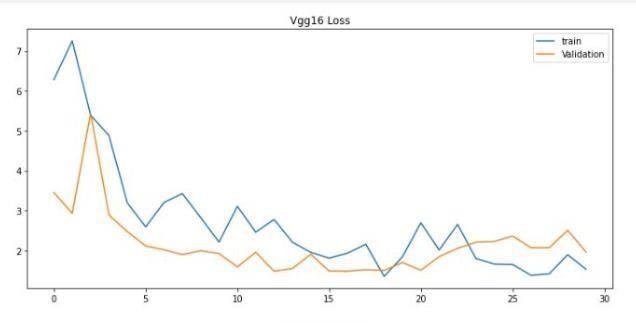
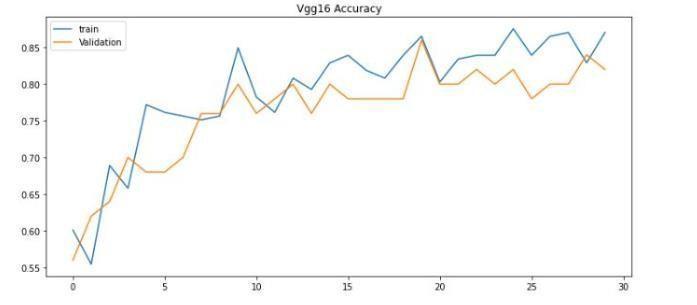

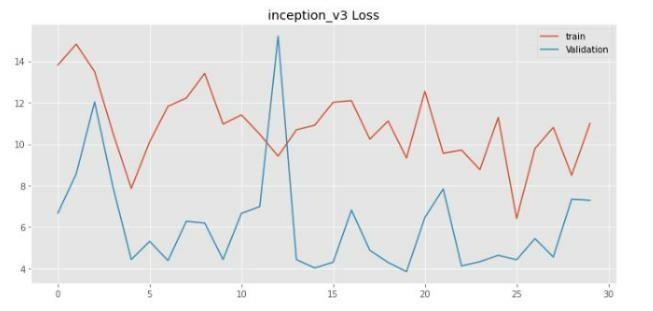
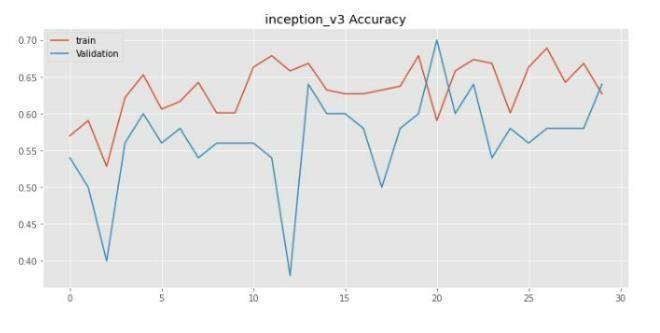
Imageswerereshapedinto244×244sizeandpassedthroughaconvolutionallayerwiththreefilters.Subsequently,theoutput passesthroughmaxpoolandflatteninglayers.Themodelhasbeentrainedwith30,120epochs.
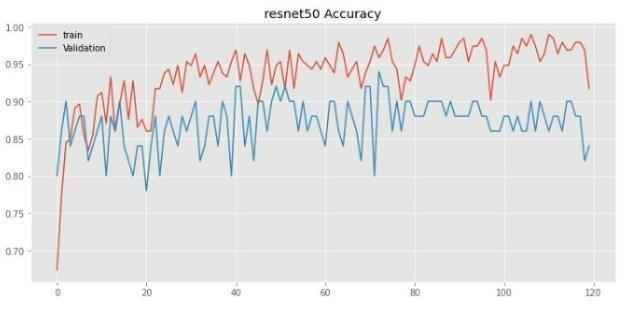
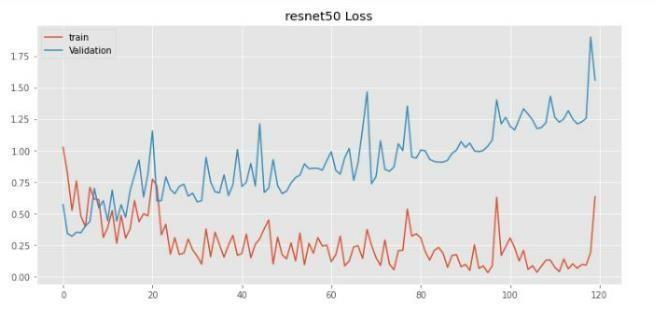
Theessentialvariablesstatedforthegivenmodelshowedthatitwaseffectiveinfindingoriginaltumorareas,whileavoiding false ones. Most current techniques focus on the entire tumor region, resulting in incorrect measurements for core and augmentregions.The methodsproposedinthedocumentshouldincludestatisticalanddeeplearningbasedtechnology,with CNNdealingwithtaskcomplexity.Duetotheclinicalsignificanceofthetumordetectionproblem,timeconstraints,sensitivity, and accuracy are essential. The results validated the efficiency and efficacy of the proposed models, especially in terms of fundamentalandaugmentingregionsofsomevalues,whereitoutperformedpreviousmethodsbyawidemargin.

Conclusion and Future Scope: Inthisproject,weusedMRIimages(JPEG)ofthebraintodivideintotwotypes,onehaving tumor and the other nothaving tumor. We executed a sequential model where the images were reshaped to 244x 244 then theconvolutional layer, max-pooling layer, flatteningis performed on thoseimages toconvert it to a vector form.Hence, we used ImageNet dataset which contains a large number of medical pictures, which helps in feature enhancement. The architectureusedisVGG-16,ResNet-50,Inceptionv3whichisfurtherimprovedbyusingadropoutlayer.Whencomparedto manual detection done by doctors or clinical physicians, the results of the experiments on different pictures show that the analysisforbraintumourdetectionisquickandefficient.Ourresearchshowthatthedescribedwaycanhelpintheaccurate and timely detection of brain tumours, as well as it can locate the exact region of tumor. As a result, the given method is essentialforidentifyingtumoursfromimages. Accordingtoourresearch,thegivenmethodisessentialfortakingthecorrect decisionbymedicalexperts
Thegivenmethodcanbeexpandedforbetterclassificationinfutureresearch.Thesemethodscanefficientlytreat othertypes of tumors and disorders. This model can be used during operations for searching and locating the exact region of tumor. Detectingtumoursintheoperationtheatrecouldbedoneinrealtimesituations.Futureresearchcanmakeuseofmethodsto acquirethenearestlocationofinfectedareainthebraintoisolatethem fromunaffectedparts,testingtheefficiencyofneural network,improvedmodelscouldbedoneinthenearfuture.
References:
[1] NileshBhaskarraoBahadure, ArunKumarRay, andHarPalThethi, “ImageAnalysisforMRIBasedBrainTumorDetection andFeatureExtractionUsingBiologicallyInspiredBWTandSVM”, 2017
[2] LuxitKapoor, SanjeevThakur “ASurveyonBrainTumorDetectionUsingImageProcessing Techniques”, 2017
[3] PraveenGamage “IdentificationofBrainTumorusingImageProcessing Techniques”,2017
[4] Deepa, AkanshaSingh “ReviewofBrainTumorDetectionfromMRIImages”, 2016
[5] Devendra Somwanshi , Ashutosh Kumar, Pratima Sharma, Deepika Joshi “An efficient Brain Tumor Detection from MRI ImagesusingEntropyMeasures ”, 2016
[6] A.Demirhan, M.Toru, andI.Guler, “Segmentationoftumorandedemaalongwithhealthytissuesofbrainusingwavelets andneuralnetworks”, 2015
[7] Yaqub, M.; Feng, J.; Zia, M.S.; Arshid,K.; Jia, K.; Rehman, Z.U.; Mehmood, A “State-of-the-artCNNoptimizerforbraintumor segmentationinmagneticresonanceimages”, 2020
[8] Amin, J.; Sharif, M.; Yasmin, M.; Fernandes, S.L. “A distinctive approach in brain tumor detection and classification using M.R.I.PatternRecognit.Lett.”, 2020
