Dewatering Flocculated Dredged Soil Slurry with Application of Overburden Pressure
Varsha V. S1, Ms. Jaseena A. Rasheed21PG Student, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sarabhai Institute of Science & Technology, Kerala, India
2Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sarabhai Institute of Science & Technology, Kerala, India ***

Abstract - Dewatering of dredged soil slurry is the most important part in land reclamation projects. Since over the years, due to urbanization, there is a rapid growth of population and development of the economy. Hence, land scarcity is one of the major problems faced by people in the world. To solve such problems, the inoperable region must be converted to land for a useful purpose. Such regions include water-logged areas that have high water content, which need to be transformed into useful lands for human needs. The soil slurry collected from these lands is characterized to have low permeability and high compressibility and has nearly or no shear strength. These limitations can be overcome by providing proper dewatering methods. One of the methods used in the dewatering or consolidation process is by using vertical drains in that area. Even though dewatering can be achieved by a natural draining process with the help of vertical drains under an application of an overburden pressure but this may take a bit longer duration than expected. In order to make dewatering more efficient and quicker, flocculants can be added to the soil slurry. With the use of these flocculants, that is., ferric chloride (FeCl3) in varyingpercentages,dewateringcanbeeffectivelyachieved. A model test is conducted by applying an overburden pressure on the surface to study the effect of flocculant in the dredged soil slurry under a surcharge preloading. An improved settlement rate and water discharge were obtained with the flocculant-aided soil slurry as 14.12 mm and 809 mL respectively under a surcharge loading when it is compared to the sand drain. This shows that the flocculant at its optimum percentage content can be providedforbetterdewateringresults.
Key Words: Dredged soil slurry, Flocculant, Model test, Settlementrate,Waterdischarged,Overburdenpressure
1.INTRODUCTION
Due to urbanization, one of the major problems faced by people around the world is land scarcity. Hence, to overcome such a problem, the available unusable lands need to be reclaimed by the dredging process and converted into usable lands. In some localities which are located near the coastal areas, the dredged soil collected from suchareas has a largeamountof water present init. And hence they have very low or no strength at all. They are also said to be highly compressible and have low
permeability, which later upon surface disturbance, may cause settlement due to high water content and thus lead to damage to the adjacent structures or to the structure constructed above the ground level. Some may also experience differential settlement due to improper dewateringprocesses.Thisismainlyobservedinsoftsoils such as clayey soil and silt where they have low permeability due to its finess nature. Since they are fine particles, it takes a large period for the dewatering or consolidation process. And hence the settlement rate will besmaller.So,beforeusingthesetypesofsoilsfortheland reclamationprocess,thesoilslurryneedstobedewatered properly. Hence the main important part of the land reclamation process is to reduce the water content of the collecteddredgedslurrybytheeffectiveprocess.Thereare various techniques for dewatering such as sump wells, simplepumping,gravitydrainage,etc.Onesuchmethodis by applying an overburden pressure on the surface of the ground.
In order to improve the dewatering efficiency, some chemicals can be added to the soil slurry. This helps the individual soil particles to aggregate together and form flocs, which makes dewatering more efficient. In wastewatertreatmentorganicandinorganicchemicalsare added, this can also be applied to this dredged soil slurry. Some of the applications ofusing flocculant are that itcan beusedfortailinginmixingoilsandandfordewatering.
In this study, model tests are conducted for the collected dredged soil in combination with the flocculant under an overburdenpressure.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
Someofthecollectedliteraturesarediscussedbelow;
Varghese.Get.al.(2012):Thestudymainlyfocuses on dewatering lateritic-lithomarge (L-S) soil with vertical sand drains under a pressure of 50 kg to 200 kg load. It explains the consolidation process using vertical drains which can be used in the construction of roads and railways. The coir fibers used as a reinforcement in the vertical drains improved the consolidation process when they are subjected to an overburden pressure. With the use of 50 % L and 50 % S soil, the settlement rate increased up to 24.8% due to the addition of coir fibers randomly in the vertical drain when it was
comparedtothesamesoilcombinationwithnocoir reinforcement vertical drain. An increment in settlement rate of 16.1 % was obtained with the addition of randomly placed coir fiber reinforcementintheverticaldrainwith25%Land 75%Ssoilcombinationwhencomparedtothatsoil mix combination when coir reinforcement was not introducedtotheverticalunderloadvariationfrom 50kgto200kg.For0%Land100%Scombination, asettlementof32.6%increasewasobservedunder a load ranging from 50 kg to 200 kg when it was comparedtothesoilmixwithverticaldrainalone.
Chen.Set.al.(2016):Thispaperconcludesthatthe use of cationic polyacrylamide (CPAM) shows a better result than other flocculants used. The optimum dosage for CPAM was obtained as 2 kg/t. With the use of jute fiber, sludge dewatering improved by introducing several numbers of pores in the sludge cake along with CPAM and thus offering various numbers of channels for draining but the settlement rate was diminished due to increment in sludge content. It was also observed that with use of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), it could improve the dewateringcapacity due to the release of water-bound particles. But, using more than 100 kg/t hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) led to negative results. It is said that with the help of CPAM, the settlingtimeanddewateringperformanceofsludge improved due to a decrease in the binding of particles,neutralizingcharges,andbyincreasingthe permeability.
Absari. F et. al. (2018) : This study shows the comparative study of prefabricated vertical drains under vacuum preloading and surcharge loading. The degree of consolidation achieved at 90% consolidation under vacuum preloading was obtained as 74% which is more effective compared to that under surcharge preloading using Asaoka Method. In both preloading methods, the consolidation settlement linearly increases with time. But it was shown that the settlement that occurred from consolidation under surcharge preloading was more compared to vacuum preloading.By usingAsaoka Method,thecoefficient of consolidation ratio was obtained as 5.90 in the case of vacuum preloading while the coefficient of consolidation ratio obtained under surcharge preloadingwasintherangeof2.21to4.25.Byusing PLAXIS 2D, the consolidation time that is required by surcharge preloading was found to be more effectivewhencomparedtovacuumpreloadingwith thesameloadingintensity.
Fu. H et. al. (2018) : This paper includes the consolidation of dredged slurry under a combination of vacuum preloading and electroosmosis consolidation using different flocculants. Under the settling column test, the inorganic ferric chloride flocculant showed a better result when
compared with aluminum sulphate as a flocculant when used with dredged slurry. But, with the addition of flocculant, an increase in the water discharge quantity was obtained and an increase in the size of soil particles when it was compared to conventional electro-osmosis and vacuum preloadingtechniques.Italsogivesahigheraverage shear strength of the soil. This increases the permeability of the soil and increased the shear strength of the soil. Even though the addition of a flocculantcanimprovethedewateringperformance andtheconsolidationprocessofsoil,theelectrodes used in the electro-osmosis get corroded quickly duetothepresenceofsaltcontentintheflocculant.
Cai. Y et. al. (2019) : This study includes the application of flocculants in the dredged sludge under vacuum preloading various conclusions. The optimumflocculantpercentagewasobtainedas0.08 % for anionic polyacrylamide (APAM) which is an organic flocculant and 0.8 % for ferric chloride (FeCl3) which is an inorganic compound under vacuum preloading by using settling column test. Water discharge was found to be increased to 46.5 %and56.8%forAPAMandFeCl3 respectively.The heavymetalspresentinthesoilflowoutalongwith waterdrainageundervacuumpreloading.Butwhen flocculantisaddedtothesoilslurry,itgetssolidifies by about 80 %. Here, one-tenth of APAM is only required for advanced dewatering compared to FeCl3 whenconsideringthedrainageeffect.
Chenhui. L et. al. (2019) : This paper explains the effect of the consolidation process which is conducted in both laboratory and field tests under the influence of vacuum pressure. In soils near the ground surface, the PVD having longer lengths showed much higher vacuum pressure when compared to PVD having shorter lengths. In the laboratory model test, the degree of consolidation and vane shear strength was obtained as 51 % and 18.2 kPa whereas, in the practical test, it was obtainedas72.1%and26kPabelowadepthof6m fromthesurface.
Lu. Y et. al. (2020) : This paper describes the dewatering of the stored landfill sludge using FeCl3 andaFentonreagentwithvaryingadditivecontents. It showed that both the reagents had an improving effect consolidation process as well as the permeability of the landfill sludge. The 4 % of Fenton reagent with Fe2+ showed better performance than with 8 % content. The permeability coefficient drops below a load of 50 kPa. After the addition of Fenton, it was noted that the initial coefficient of consolidation was higher when compared with that of FeCl3.And it was observed that as the pressure increases the coefficient values also increase until it reaches 100 kPa. The greater influence was observed for the Fenton has a coefficient of consolidation until it

reaches 50 kPa. The FeCl3 provides a coagulation effect and oxidation whereas the Fenton reagent providesdepolymerizationandoxidation.
3. OBJECTIVES
The main objectives of the study conducted are listed as follows;

To find the effectives of flocculant when it is introducedtothesoilslurryundertheapplicationof anoverburdenpressure.
To know the optimum percentage of the flocculant which can be added in the soil slurry with the help ofverticaldrainsduringdewateringprocess.
Todeterminetherateofsettlementwhenthesoilis treatedwithvariouspercentagesofflocculantunder anoverburdenpressure.
To determine the quantity of water which is discharged during the dewatering process of flocculated soil slurry under a uniform surcharge preloading.
To compare the settlement rate and the amount of water discharged from the dewatering process under same intensity of continuous application of overburden pressure of both normal soil with vertical drain (NVD) and flocculated soil with verticaldrains.
4. SCOPE
The scope for the study can be concluded and they are givenbelowasfollows;
Thesizeoftheverticaldrainusedinthedewatering process can be varied according to the site conditions.
By providing with a greater number of vertical drainsmayormaynotimprovetheefficiencyofthe dewateringperformance.
Thematerialsusedtomakethedewateringprocess quicker can be varied according to the cheap availability.
5. MATERIALS USED
The materials used in this study are obtained from various regions and are tested according to the Indian Standardspecifications.
5.1 Dredged slurry
The dredged slurry was obtained from Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, and was found to have a high-watercontentof87.36%.Itwasdarkishgreyincolor and was found 1.5 m depth below the ground level. Table 2 shows the properties obtained for the dredge slurry in
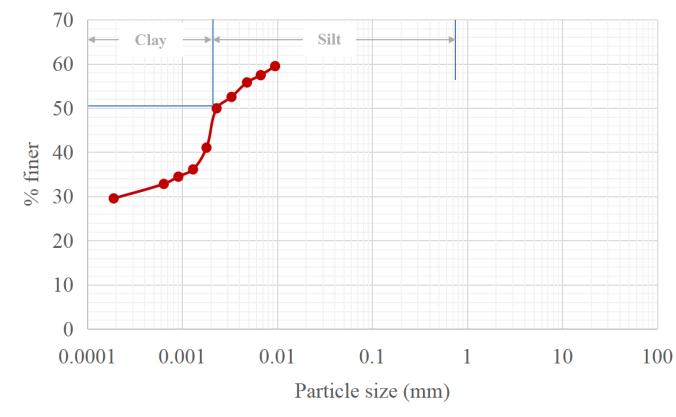
accordancewiththeIndian Standard.Theliquidlimitwas obtainedas29.00%andtheplasticlimitwas20.20%.Fig. 1showsthegradationcurveaccordingtotheIS2720(Part 4)-1985,wherethepercentageofclaywasfoundas50.05 %andclassifiedaslowplasticityclay(CL).Thepercentage ofclaywasobtainedas50.05%accordingtotheIScode.
5.2 Flocculant
Flocculantusedinthisstudyisferricchloride(FeCl3), which is collected from a local market in Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala. These compounds are commonly used in process of waste water treatment during dewatering. It is an inorganic compound used for assisting in dewatering during the consolidation process inthesoilslurry.Itwasobtainedinadry powderedform. Table 2 shows the properties of FeCl3 from the manufacturer.
5.3
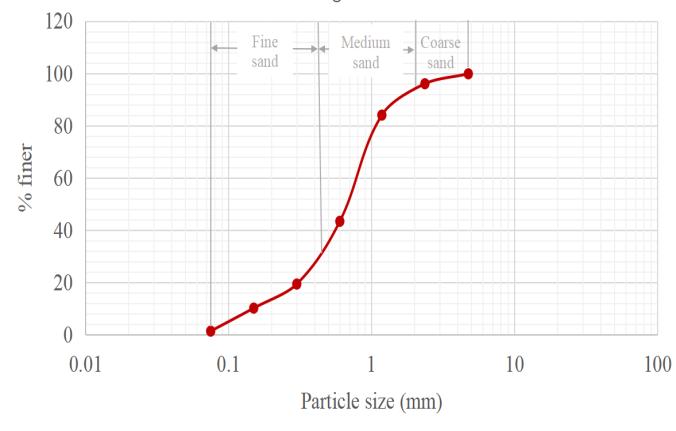
River sand was collected from Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala and it was used as a draining material in the vertical drain. It was collected and dried for it to be used asthedrainingmaterialintheverticaldrain.Itsproperties as shown in table 3. From the soil gradation curve by IndianStandardshowninFig2,theuniformitycoefficient andthecoefficientofcurvaturewereobtainedas6.15and 1.86andthesoilwasclassifiedaswell-gradedsand(SW).
6. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Theresultsofthesettlementrateandwaterdischargeare obtainedundersurchargepreloadingonthemodeltestand theyareasfollows;

6.1 Settlement rate
The settlement obtained from the model test under a period of 14-day were obtained for both NVD and flocculant-aidedsoilslurry.
Chart 1 shows a graphical representation of the settlement rate with respect to the duration for normal soil with vertical drain (NVD) where sand is kept as the draining materials. From the graphical representation (chart 1) it is shown that as the duration of surcharge loading increases the settlement rate also get increased. The settlement occurred at the first day was obtained as 3.06 mm for NVD under surcharge preloading and its corresponding settlement occurred at the end of 14-day consolidation process were obtained as 13.49 mm under thesameintensityofsurchargeloading.
Thesamesetofthemodeltestwasconductedwiththe soil when flocculant is added to the soil slurry. The settlement rate corresponding to flocculant-aided soil slurry is represented at Chart 2 as shown. The same incrementtrendinNVDwasalsoobservedforflocculated soil slurry, that is., as the duration increases the rate of settlement get also increased. But with the use of flocculantinsoilslurry,thesettlementrateincreased.The rate of settlement occurred from flocculant-aided soil slurrywas7.03mmatthefirstdayand14.12attheendof 14-day consolidation process after the continuous applicationofsurchargeloadatitssurface.
Chart 4 shows a graphical representation of water dischargedforadurationof14daysforNVD.Itwasshown that as time increases the water discharged from the consolidationmodelwillalsogetincreased.Thedischarge obtained for NVD at the first day were obtained as 49mL and at the end of 14-day consolidation were obtained as 701mLundersurchargeloadingofcontinuousapplication ofloadtilltheendof14-dayconsolidationprocess.
The rate of settlement obtained at 14-day consolidation with the application of surcharge loading of same intensity throughout the period for both NVD and flocculant-aided soil slurry are shown in chart 3. It was observedthat,withtheuse offlocculantinsoilslurry,the settlementrateincreasedfrom13.49mmforNVDto14.12 mmforflocculatedsoilslurry.
6.2 Water
The results for water discharge obtained under the application of surcharge loading till 14-day consolidation process were obtained for both NVD and flocculant-aided soilslurry.
The water discharged with respect to duration is represented in Chart 5 as shown for flocculant-aided soil slurry. The water discharge was also increased in case of flocculant-aided soil slurry when the time increases. The water discharge at 1st day were obtained as 119 mL and 801 mL at the end of 14-day when flocculant is added to the soil slurry. With the use of flocculant at its optimum content, the water discharge was found to increase when comparedtootherpercentagesofflocculant.

The variation of the quantity of water discharged are shown in Chart 6 for both NVD and flocculant-aided soil slurry under continuous surcharge loading for 14 days. It isseenthat701mLwaterwasdischargedattheendof14 days for NVD and the water discharged at the end of 14 days for flocculated soil slurry was obtained as 801 mL, that is., 100 mL was increment were found when flocculant is added to the soil slurry at its optimum content.
7. CONCLUSIONS
In this study, laboratory tests are conducted on a largescaleconsolidationmodelofflocculant-aidedsoilslurryin combination with the surcharge preloading methods. It canbeconcludedasfollows;
The flocculant-aided soil slurry showed an improved result compared to the NVD both in the settlementrateaswellasinthewaterdischargefor a period of 14-day consolidation process under an overburden pressure in the consolidation model test.
Itisshownthatthesettlementrateincreasedasthe duration of loading increased for both NVD and flocculant-aided soil slurry. But the rate of settlement improved when it comes to the flocculatedsoilslurryat14.12mmcomparedtothe NVDat13.49mmattheendof14-dayconsolidation.
Theamountofdewateredwaterwasalsoincreased as the duration for both NVD and flocculated soil slurry.Inflocculatedsoilslurry,theamountofwater discharged was obtained as 809 mL whereas, for NVD,itwasobtainedas701mL.Thisshowsthatthe amount of water discharged is more in flocculated
soilslurrythaninNVD.
Inbothrateofsettlementaswellasintheamountof
water discharged, flocculated soil slurry showed an
improvementindewateringperformanceunderthe consolidationmodeltestbyapplyinganoverburden pressure.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Itookeffortstocompletethisthesispaper,however,it wouldhavebeenimpossiblewithoutthehelpandsupport of many people. I would greatly like to thank the Lord Almightyforprovidingmewiththisopportunity.Ialsolike togivemyspecialthankstomyguide,Jaseena.A.Rasheed, and express my gratitude to the Head of the Department, Prof. R. Jayachandran Nair for their guidance and support in this thesis. I would like to give my thanks and appreciation also to my colleagues and the people who willingly helped me with their utmost ability during the thesis.
REFERENCES
[1] Absari. F, Juliastuti, Putra. R. P & Suhendra. A, “Effectiveness study of prefabricated vertical drain using vacuum preloading and surcharge preloading”, EarthandEnvironmentalScience,Vol.195,2018.
[2] Alias.S,Ayob.A,Bashar.N.A.M&Zubir.Z.H,“Water treatment sludge as an alternative liner for Landfill Site: FTIR and XRD analysis”, Advances in Civil Engineering,October2016.
[3] Antony. J, Krishnapriya. P. B & Sandeep. M. N (2016), “Efficiency of Vacuum Preloading on Consolidation Behaviour of Cochin Marine Clay”, International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering ScienceandTechnology,Vol.24,pp:256-262.
[4] Artidteang. S, Bergado. D. T, Kumar. A, Saowapakpiboon. J & Teerachaikulpanich. N (2011), “Enhancement of efficiency of prefabricated vertical drainsusingsurcharge,vacuumandheat preloading”, GeosyntheticsInternational,part-18.

[5] Cai.Y,Fu.H,Hai.J,Hu.X,Liu.F,Lou.X,Wang.J &Wu. W), “Application of flocculation combined with vacuum preloading to reduce river-dredged sludge”, MarineGeoresources&Geotechnology, February 2019.
[6] Chen. G, Deng. Q, Lu. Y, Wu. Y, Xu. Y, Ye. P & Zhang. X (2021), “Influence of prefabricated vertical drains spacing on FeCl3-vacuum consolidation of a landfill sludge”,ElsevierSoilsandFoundations61(2021),pp: 1630–1644.
[7] Chen.S,Li.H&Yang.J,“Dewateringsewagesludgeby acombinationofhydrogenperoxide,jutefiberwastes andcationicpolyacrylamide”,Elsevier,March2018.
[8] Chenhui. L, Junfeng. N, Jingchun. ,Hongtao. F, Xiuqing. H,Donghai.X,Youchang.L,Zhi.G,Zhengde.X&Qiang. Y, “Consolidation Effect of Prefabricated Vertical Drains with Different Lengths for Soft Subsoil under Vacuum Preloading”, Advance in Civil Engineering, Vol.2019,12pages.
[9] Fu. H, Hu. X, Li. X, Wang. J, Yuanqiang. C & Zhao. R, “Vacuum preloading and electro-osmosis consolidation of dredged slurry pre-treated with flocculants”, Engineering Geology, Vol. 9, September 2018.
[10] Lu. Y, Tran. C. Q, Vu. V. Q, Wu. Y, Yao. J & Zhang. X, “Insight into conditioning landfill sludge with ferric chloride and a Fenton reagent: Effects on the consolidation properties and advanced dewatering”, Chemosphere252,pg:126-528,August2020
[11] Hu. Z (2021), “Experimental study on flocculationVacuum-Electroosmosis method for strengthing soth soil foundation in coastal area”, Earth and EnvironmentalScience,Vol.643,pp:012167.
[12] Jia.H,Jian.C,Keat.T.S,Pang.L.K&Trang.V.T(2017), “Sedimentaation behaviour of flocculant-treated soil slurry”, Marine Geosources & Geotechnology,Vol. 35 (5),pp:593-602.
[13] John. J & Thomas. U (2016), “Improvement of Coir Reinforced Clay Soil by Natural and Synthetic PrefabricatedVerticalDrains”,InternationalJournalof Engineering Research & Technology, Vol. 5, Issue 03, ISSN:2278-0181.

[14] Khoteja. D, Pan. Y, Pu. H & Zhou.Y (2021), “Rapid treatmentofhigh-water-contentdredgedslurryusing composite flocculant and PHD facilitated vacuum”, MarineGeoresources&Geotechnology.
[15] Kiran. N. M. B, Prasad. V. S. D & Shivanarayana. C (2016), “Stabilization of Marine Clay Using Ferric Chloride and Quarry Dust”, International Journal of Engineering Research and Development, Volume 12, Issue3(2016),pg:01-09.
[16] Varghese. G, Ramakrishna. H, Kumar. H. G. N, Prashanth. L. D & Santosh. G, “A Model Study on AcceleratedConsolidation ofCoirReinforcedLateritic Lithomarge Soil Blends with Vertical Sand Drains for Pavement Foundations”, Open Journal of Soil Science, Vol.2,Issue3,September2012.
