An Effect of Compressive Sensing on Image Steganalysis
 I.Swathi1 , K.Sravani2
M.Seshagirirao3
T.S.R.Krishnaprasad4
I.Swathi1 , K.Sravani2
M.Seshagirirao3
T.S.R.Krishnaprasad4
Abstract - As from several obtained measurements which are suggested from the Nyquist sampling theory, the compressive sensing theory states that the signal can be regained with a high nature ofprospectwhenitshowssparsity in some domain. In this project, a new frame work is proposed to that compressive sensing is used to recover the signal by adapting the known sparsifyingbasisviaL0 minimization. The natural image of the intrinsic sparsity fis mainly effected by the overlapped sparsely represented image, which is to be patched with the help of adapted sparsifying basis in the form of L0 norm to reduce the blocking artifacts and conveying the CS solution space. To exhibit the executed scheme tractable and robust a split Bregman iteration based technique is generated to solve the non convex L0 minimzation problem efficiently. The experimental results should be taken in to account on CS recovery execution which leads to give the proposed algorithm with a compelled performance for the growth of current state of the art schemes which leads to produce best convergence property.
Key Words: Compressive sensing, image recovery, sparsifyingbasisoptimization.
1. INTRODUCTION
Steganalysiswasextensivelystudiedoverthelastdecadeto detect the secret signal presence (including payloads) embeddedinhostimagesobtainedfromknownsources.In steganography, the medium used to embed the message stated as cover and can be text or an image. Covers with embeddedsecretmessagesarealsodefinedasStegoobjects. In many cases, the objective of steg analysis can be formulated as a binary classification problem that distinguishesbetweencoverandstegoobjects.Inthiscase, we are interested in recovering secret messages. Existing approaches to web analytics generally involve two major steps.H.Featureextractionandclassification-baseddecision making.asacompressionmethod.Thereisa mainproblem with CS is its weak robustness. Conventional CS reconstructionreliesonmatricestogainthefeatureofsignal alongwiththeprocessingofsignals.Thegoalistocaptureas muchinformationaspossibleinasfewsamplesaspossible withoutintroducingaliasing.Reconstructionalsopresentsa special challenge because it solves systems of underdeterminedlinearequations.
1.1 Framework
Withtheincreasingexchangeofdigitaldataovernetworks, datasecurityhasbecomeamajorconcernaroundtheworld. Theproliferationofdigitaldataraisesconcernsaboutdata beingattackedortamperedwithbyunauthorizedpersons. SincetheInternetprovidesameansofcommunicationfor disseminating information, the technique of hiding secret messagesinvariousmultimedia contentisanimprovedand more effective technique. Steganography is a data hiding techniqueaimedatsendingmessagesoverchannelswhere otherinformationisalreadybeingsent.Themainobjective of web analytics is to detect messages hidden in cover objects,suchasdigitalmedia,anddeducewhetherthemedia isembeddedwithsensitivedata.
1.2 Method of Approach
TorecoverthesecretsignalMATLABTool(R2019A)isused fortheexecution.Thenominalimagesteganalysiscanonly usedtoknowthepresenceofdetectionoftheimagebutit can’t focus on secret signal recovery of original messages whichareembeddedinahostimage..Toexecutethisissue theimagesteganalysiscanbetakenintoaccountwiththe help of compressive sensing cs domain, where block CS measurementsmatrixproducethe thetransformcoefficient of stego- image which reflects the statistical differences betweenthecoverandstego–images.Thereconstruction image by using compressive sensing is used to find the suitable values of model parameters in order to gain the mostexecutedone.
1.3 Execution of the work
The execution of CS- based criterion on stego images to recoverthesecretsignalsfromthe extractedfeatures,the stegnographicalgorithmsarecombinedwiththeapplication ofmosteffectivefeaturessensedbytheBCSmeasurement matrixandtorecoverthehiddensignalsbymulti-hypothesis predictionswithaTikhonovregularizationintheCSdomain. Theoutputshowsthereconstructedfingerprintimageswith 40 features were detected by BCS as compared to other embedding algorithms, and JPHS is the weakest among embeddingalgorithms.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
The spatial domain based image steganography used to transformdomainoneintermsofembeddingcapacity,but the stego-image contains high amount of redundant data Themainusageofcompressivesensingistoconstructthe acquiredsignalefficiently Inthefieldofimagerestoration development,thecompressivesensingtheoryplaysacrucial role,whichhasdrawnquiteanamountofattentionwhichis analternativetothepresentmethodofsamplingwiththe helpofcompression.Toexplodetheredundancyinaexisted signal, the CS used for sampling and compression at the same time. CS theory exhibits the signal can be decoded from the suggested fewer measurements by the Nyquist samplingtheory,whenthesignalissparseinsomedomain, which has substantially changes the way of engineers thinkingofdataacquisition.
2.1 Proposed System
Theproposedalgorithmiscomparedwithfourtypesof cs recovery methods i.e., wavelet method (DWT) , total variation (TV) method , multi-hypothesis (MH) method , collaborativesparsity(CoS)method,whichdealwithimage signals in the wavelet domain, the gradient domain, the randomprojectionresidualdomain,andthehybridspacetransformdomain,respectively.Itisworthemphasizingthat MH and CoS are known as the current state-of-the-art algorithmsforimageCSrecovery.Theproposedalgorithm canbeexecutedindualnaturethattoeliminatetheringing effectsandtopreservemuchshaperedgesandfinerdetails, whichshowsmuchclearerandbettervisualresultsthanthe othercompetingmethodsOurworkalsooffersafreshand successfulinstancetocorroboratetheCStheoryappliedfor naturalimages.

2.2 Existing system
Assteganographymayalsoreasonimagecontentmaterial modified imperceptibly, it's miles anticipated such modificationsmaybedetectedviawayofmeansoftheusage ofremodelareacoefficientsinafirst-classscale,inwhichCS canplayancrucialfunctiontosignifythemodificationsfrom the neighborhood remodel coefficients added via way of means ofthe embeddedmystery messages.Therefore, we purpose to BCS to come across DCT or Discrete Wavelet Transform(DWT)steganographicembeddinginformationin images,speciallytoreconstructtheauthenticmysterysign. Inthesectorofphotographrestoration,possiblythemostup to date subject matter is the latest improvement of CompressiveSensing(CS)principle,whichhasdrawnpretty an quantity of interest as an opportunity to the contemporary method of sampling observed via way of meansofcompression.Byexploitingtheredundancyexisted in a sign, CS conducts sampling and compression on the equaltime.CSprincipleindicatesthatasignmaybedecoded frommanyfewermeasurementsthancautionedviawayof meansoftheNyquistsamplingprinciple,whilstthesignis
sparseinafewarea,thatresultsinsupposeforinformation acquisition.
3. CS APPLICATION SECURITY
3.1 Image Encryption
TheCStogetherwithchaostheoryisusedforhybridimage compression-encryptionalgorithms.Whenanimageisinthe process of CS it has executed with a block of Arnold transformation which is followed by XOR operation to permute the measurement positions then dissipate the Gaussiandistribution.
3.2. Image Watermarking
A robust image watermarking scheme for image tamping identificationandlocalizationbasedonCSanddistributed source coding principles was described earlier. The basic idea is to form a hash, which is robustly embedded as a watermarkintheimageTheamountofextracted dataisnot largeenough,thenthe CSisusedtoretrievethecoefficients bydevelopingthesparsenessintheDCTdomain
3.3 Image Hiding
AdatahidingisbasedonsubsamplingandCSwasscheduled totherelyingonthe CSpropertiesincludingsparsitywith randomprojectionthenthesecretdatacanbeembeddedin the observation domain of the image. The method was further extended to an image steganography algorithm in terms of some details on design procedures and experiments,buttheyareroughlyconsistentinthetrainof thought
3.4 Image Hashing
Kangelal.proposedasecureandrobustimageschemeusing CS and visual information fidelity. The CS makes the hash size keep small while the visual 2510 VOLUME 4,2016 Y. Zhang et al.: Review of CS in Information Security Field informationfidelityhelpstoberobustagainstmostimage manipulations. Thefoundationisthatifthetamperingcan solving a convex optimization problem with constraints forced by the transmitted hash, provided that it is sparse enough CS for a robust image hash sparse which is to be represented for robust image hashing with tampering recovery capability and strong robustness that against contentpreserving
3.5 Image Authentication
AnopticalencryptiontechniquebasedonCSwasemployed to create a cancellable biometric authentication scheme, which encrypts a finger vein image using a compressive imagingsystemwhencapturingimage.Anewpointofview, encryptedsensing,basedonDRPEandCS,wasproposedfor biometric authentication, which further improves the securitytoprotectthebiometrictemplate
3.6 Video and Audio Security
Cossalter al.stated thatforthevideosurveillanceofassured privacytrackingsystemfortheCSdataCreditsystemafixed camerahasinstalledto analyzethevideoframesto detecta possiblemovingobjectinthescenewherethereconstructed unnecessaryoriginalcontentofthevideosequence
3.7. Cloud Security Scenario
Incloudsecurityscenario,privacy-assuredmultimediacloud computing based on CS and sparse representation was investigated,whichdiscussedsomecompressivemultimedia applications,includingmultimediacompression,adaptation, editing/manipulation, enhancement, retrieval, and recognition.Theguaranteedoriginalsignalcanbeinprivacy sinceeachcloudonlyhasasmallamountofinformationin termsofboththemeasurementsandasymmetricsupportset.
the BCS measurement matrix, and recovered the hidden signal by multi-hypothesis prediction using his Tikhonov regularization in the CS domain to a reconstructed fingerprintimagewith40featureswithdifferentalgorithms. Compared with other embedding algorithms, the reconstructed fingerprint image of nsF5 can achieve the closestapproximationtotheoriginalsignalwith40features detected by BCS, and JPHS is the weakest among the embeddingalgorithms..
Since steganography can imperceptibly change image content, it is hoped that such changes can be detected at finerscalesusingtransform-domaincoefficients.HereCScan playanimportant role incharacterizingthechangesfrom the local transform coefficients introduced by the embedding.secretmessage.Therefore,themainaimofBCS istodetecttheDCTorDSTsteganographicembeddeddata inimagesrespectivelytoreconstructtheoriginalsecret
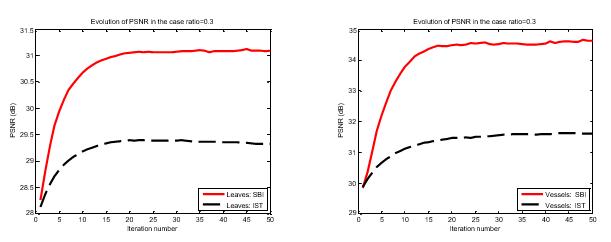
Fig-2: ComparisonbetweenSBIandISTforsolvingour proposedl0minimization Fromlefttoright:progression ofthePSNR(dB)

4.3 Performance Assessment
Inourexperiments,theCSmeasurementsareproduced by applyingaGaussianrandomprojectionmatrixtotheoriginal imagesignalatblocklevel,Thevalueof λ isrelatedtothe overlappedstepsize,whichwillbegiveninthefollowing.All the experiments are performed in Matlab 7.12.0 on a Dell OPTIPLEX computer with Intel(R) Core(TM) 2 Duo CPU E8400processor(3.00GHz),3.25Gmemory,andWindows XPoperatingsystem.
4.4 Algorithm Convergence
4.1 Comparison of the Extracted Features
To conveniently compare the effect of the number of functionsinthestegaanalyzer,weextract2000stegoimages with an embedding rate of 0.15 bpp using the embedding algorithmsF5,PQ,Outguess,andJPHS.Ontheotherhand, wetrainallfunctionsusingsupportvectormachines(SVMs) to derive the best fitness function that performs well in differentapplications.WethenappliedanimprovednatureinspiredCSalgorithmandcompareditwiththeoptimized DPSO algorithm. Each algorithm has 35 iterations and a populationsizeof30
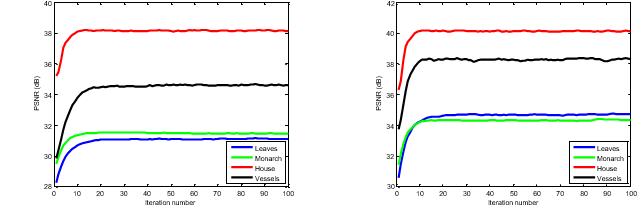
4.2 Quality of Recovered Secret Signal
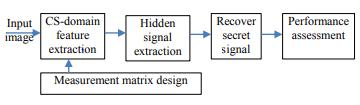
In our approach, wetried to find a CS-based covert signal recovery criterion using features extracted from stego images.Thefinalexperimentcombinedfoursteganography algorithms,appliedthemosteffectivefeaturescapturedby
Here,empiricalevidenceisillustratedthegoodconvergence withaproposedalgorithm,theplotsofevolutionofPSNR versusiterationnumbersforfourtestimageswithvarious subrates (subrate=30% and subrate=40%). As from the observed growthofiterationnumber,allthePSNRcurves increasesmonolithically,stableandflatwhichexhibitsthe goodconvergenceproperty
decibels (dB) results achieved by proposed algorithm for fourtestimagesw.r.t theiterationnumberinthecasesof subrate=30% and subrate=40%
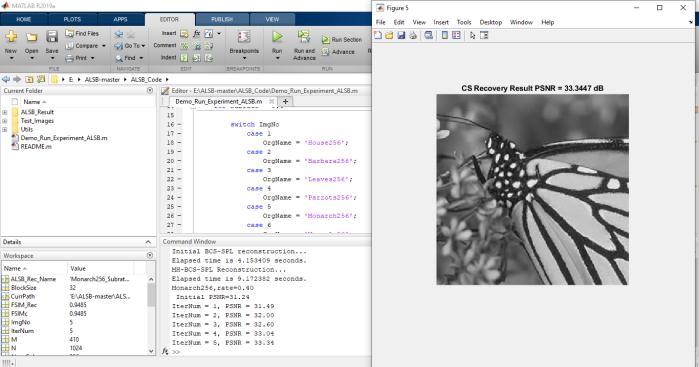
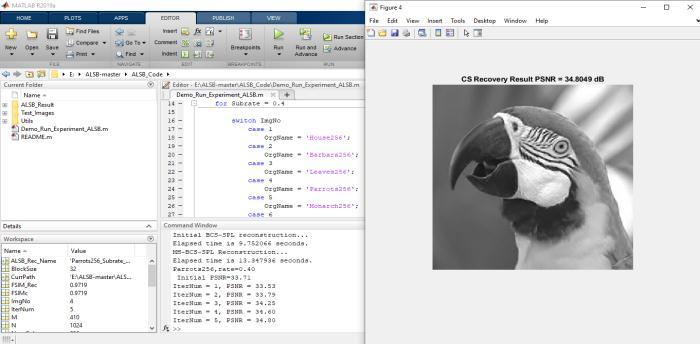
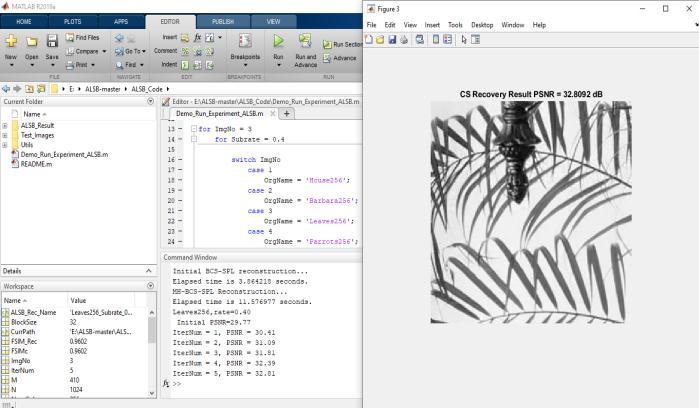
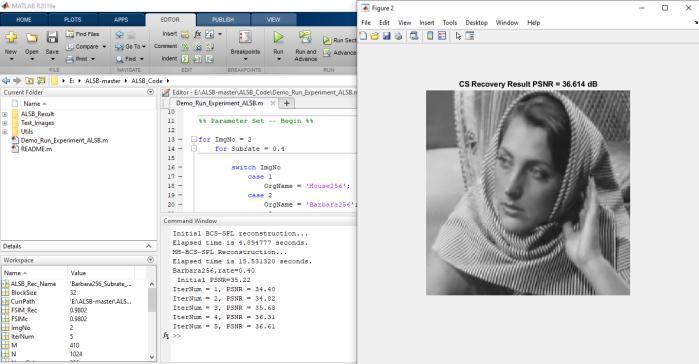
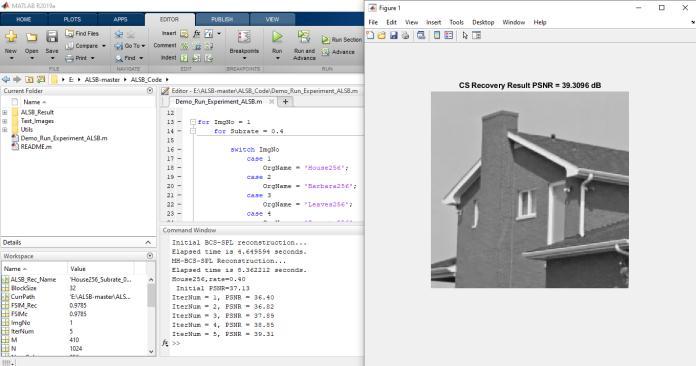
5. RESULT AND ANALYSIS

5.1 Objective or Numerical Measures
Thesemeasuresareusedtocomparethecoverimagesand theircorrespondingstego-imagesbasedonsomenumerical criteria that do not require extensive subjective studies. Hence,inrecenttimes,thesemeasuresaremorecommonly used for image quality assessment .These include Peak Signal-to-Noiseratio,PSNRvaluetotheimperceptibilityof stego-images.Thatis,PSNR-10log10R2MSEdB

6. CONCLUSIONS
In this project, we propose to characterize the inherent sparsity of natural images by a patch-based redundant sparsity representation using adaptively learned sparsification bases. This particular type of surrogate representation is formulated by non-convex minimization for compressed image acquisition recovery. This can be efficiently solved by a developed technique based on split Bregmaniteration.Experimentalresultsonawiderangeof natural images for CS restoration show that the proposed algorithmachievessignificantperformancegainsovermany current state-of-the-art schemes and exhibits superior convergence properties. This project presents a secure cryptographic scheme that combines the strengths of compressedsensingschemes.Thismethodalsoprovidesan effective way to compress data. This combined chemistry meets requirements such as capacity, security, and robustnessforsecuredatatransmissionoveropenchannels. Theproposedmethodcanalsobeappliedtoaudioandvideo dataasafutureimprovement.
REFERENCES
[1] L. Rudin, S. Osher, and E. Fatemi, “Nonlinear total variationbasednoiseremovalalgorithms,” Phys. D.,60 (1992)259–268.
[2] D.GemanandG.Reynolds,“Constrainedrestorationand therecoveryofdiscontinuities,” IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 14 (3) (1992) 367–383
[3] D. Mumford and J. Shah, “Optimal approximation by piecewisesmoothfunctionsandassociatedvariational problems,”Comm. on Pure and Appl. Math., 42 (1989) 577–685
[4] A.A.EfrosandT.K.Leung,“Texturesynthesisbynonparametricsampling,” Proc. of Int.Conf.ComputerVision, Kerkyra,Greece,(1999)1022–1038.

[5] A.Buades,B.Coll,andJ.M.Morel,“Anon-localalgorithm for image denoising,” proc. of Int. Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, (2005)60–65.
[6] H.Takeda,S.Farsiu,andP.Milanfar,“Kernelregression forimageprocessingandreconstruction,” IEEETrans.on Image Process.,16(2)(2007)349–366.
