DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING MACHINE LEARNING TECHNIQUE
1 Ashik Ajan, Anu Mole R S, Greeshma Gireesh, Saranya S, 2 Sivakumar R1UG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering
2Asst. Prof, Department of Computer Science and Engineering

UKF College of Engineering and Technology, Parippally, Kerala, India ***
Abstract - A method for detecting diabetic retinal disease based on integrated shallow convolutional neural networks. Early diabetic retinal disease (DR) detection is crucial for diabetics to lower their risk of going blind. Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based techniques for automatically detecting DR through classification of patient retinal images. Such methods rely on a very big data set made up of retinal photographs with specified category labels to aid in their CNN training. It might occasionally be challenging to compile enough precisely labelled photos to use as model training examples. According t0 the trials on publicly accessible data sets show that, when compared to the most recent typical integrated CNN learning algorithms, the suggested technique can increase classification accuracy by 3% on small data sets. The test shows that although if the suggested approach's classification accuracy, its time cost drops to roughly 30% of the smallest dataset, which is approximately 10% of the original dataset and falls by 6%. A method for detecting diabetic retinal disease based on integrated shallow convolutional neural networks. Early diabetic retinal disease (DR)detection is crucial for diabetics to lower their risk of going blind. Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Deep Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based techniques for automatically detecting DR through classification of patient retinal images. Such methods rely on a very big data set made up of retinal photographs with specified category labels to aid in their CNN training. It might occasionally be challenging to compile enough precisely labelled photos to use as model training examples. According t0 the trials on publicly accessible data sets show that, when compared to the most recent typical integrated CNN learning algorithms, the suggested technique can increase classification accuracy by 3% on small data sets. The test shows that although if the suggested approach's classification accuracy, its time cost drops to roughly 30% of the smallest dataset, which is approximately 10% of the original dataset and falls by 6%.
Key Words: Convolutional neural network, diabetic retinopathy, image classification, integrated learning, performanceintegration.
1. INTRODUCTION
Blindness or vision loss may result from the eye disorder known as diabetic retinopathy. Early identification and treatment for DR patients are crucial to preventing blindness. All agree that early diagnosis and therapy can reduce DR patients' risk of blindness to 5%. Medical personnel have traditionally used 2D colourimages of the eye fundus to manually distinguishDR. In these cases, a doctor's education and expertise areessential to a precise diagnosis. It makes logical to use automatic retinopathy pictureclassificationforDRdiagnosisgiventhesizeofthe DR patient group. Many investigations on the categorizationofretinalorothermedicalimageshavebeen carried out over the course of the last few decades. In traditional machine learning approaches, such as those using Support Vector Machine, K-Nearest Neighbor, Regression, and some other techniques, offline extraction of features is frequently required prior to training. Deep machine learning has been widely utilized in the categorization of photos in response to the most tremendousgrowthofimagedataontheInternet.Inthese cases,a doctor'seducationandexpertise areessential toa precisediagnosis.
To attain high precision, these techniques frequently require massive datasets and incredibly deep networks. However in the actual world, it might be challenging to compile high-quality labelled datasets for model training. Another widely acknowledged fact is that manually labelling a dataset is extremely difficult and timeconsuming. Another widely acknowledged fact is how difficult and error-prone manually labelling a dataset is. operation subject to mistakes. If mistakes are made while labelling, the accuracy of the model that is learning from the dataset will be significantly damaged. A highly deep neural network may demand specialised computing environments or take a long time to train. Additionally, it is believed that the likelihood of the model overfitting increases as a CNN gets deeper and fewer data samples areavailable.Itisthereforeintriguingtofindoutwhether shallow neural networks can also accurately classify medicalimages,evenonasmalllabelledsample.Wewant to investigate how retinal images can be classified using integrated multi-scale shallow CNNs in this paper,
focusing on the case where there aren't enough highqualitylabelledtrainingsamples.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
For diabetic people, diabetic retinopathy continues to be the predominantcause oflegal blindness. More than 90% of visual loss can beavoided with proper medical and ophthalmologic care. There are therapies that can be extremely effective when used at the right time in the disease process. Routine management by an ophthalmologistisessentialinadvancedstagesofdiabetic retinopathy, such as NPDR, PDR, and diabetic macular edema [1]. Among adults aged 20 to 74, diabetic retinopathyisthemostcommonfactorinnewinstancesof blindness. Nearly all type 1 diabetes patients and more than 60% of type 2 diabetic patients develop retinopathy throughout the first two decades of the disease. Legal blindness waspresentin3.6%oftype 1diabetespatients withayoungeronsetand1.6%oftype2diabetespatients with an older start in the Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study ofDiabeticRetinopathy(WESDR).86%ofblindnessinthe group with younger onset was caused by diabetic retinopathy. One-third of the instances of legal blindness in the older-onset group, when other eye disorders were prevalent, were brought on by diabetic retinopathy. Early identification, prompt enrolment into the health care system, patient education, regular lifelong evaluation, appropriate referral, and timely treatmentare critical to avoiding vision loss. Frequent eye examinations are required for people with moderate-to-severe NPDR in order to decide whether to start treatment. The requirement for yearly dilated eye exams is less clear for individualswhodon'thave retinopathyorjusthavea few microaneurysms. Some have proposed a longer gap between examinations because for these patients, the annual rate of progression to either proliferative retinopathy or macular edema is modest. Factors which are considered in this are: 1) Other visual function outcomes, such as visual acuity worse than 20/40, are clinically significant, occur significantly more frequently, andhaveeconomiceffects.Theanalysesinitiallymadethe assumptionthatlegalblindnesswasthesolelevelofvisual losshavingeconomicrepercussions. 2) Theanalysesmade use of NPDR progression data from diabetic individuals whohadjustreceivedtheirdiagnosis.
TheConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(CNN),amodelthat focuses on classifying images based on object recognition, isusedinthisstudyanddetection,issuggestedforuse.The primary goal isto categorize a collection of photos which includes each of the four classes in the development of Diabetic Retinopathy [2]. The Diabetic Retinopathy Detection dataset and the Indian Diabetic Retinopathy Image Dataset were both used. Based on accuracy, loss function,and AUC, statistical analysis is used toassess the suggested CNN's performance. The research results point
to the potential for CNN to classify DR into its various degrees in people with diabetes mellitus, leading to the developmentofaprototypecomputer-aideddiagnosistool.

"ImageNet," a new image database and expansive ontology ofimages,is introduced [3]. Multispectral data is a viable source of data for autonomous nautical ship recognition since it combines information about both visible and infrared objects. In this paper, we convert multispectral ship recognition job into a convolution feature fusion issue and propose a feature fusion architecture called Hybrid Fusion in order to benefit from deep convolution neural network and multispectral data. Via three channels of single-spectral photos and four channelsofmultispectral images,wefine-tunetheVGG-16 model that was previously trained on Image Net. To prevent over-fitting, we apply established regularization approaches.Investigatedarethethreeotherfeaturefusion architectures as well as hybrid fusion. Each fusion architecture has branches for extracting features from visible and infrared images, and the pre-trained and refined VGG-16 models are used in these branches as feature extractors. In every Image Net classifies the many image types into a semantic hierarchy that is densely populated. The firststage inthe developmentofImageNet is the collection of potential photos for each synset. To highlight the variations, the ImageNet database is contrastedwithotherdatasets.Otherdatasetsusedforthe comparisonincludeTinyImage,ESPdataset,LabelMe,and Lotus Hill datasets. The current condition of ImageNet, whichconsistsof12subtrees,5247synsets,and3.2million images, is thoroughly examined in this work. Finally, we present three straightforward applications in automatic object clustering, image classification, and object identificationtodemonstratetheutilityofImageNet.
A support vector machine-based deep learning technique for feature extraction and categorization. The final fully connected layer's high-level properties, which act as the input features for classification using a Support Vector Machine, are created using convolutional neural network transfer learning [4]. The amount of calculation time neededforCNN-tunedclassificationcanbedecreasedwith this technique. Because to the ease of overfitting in deep models, such deep networks frequently exhibit poor performance on small datasets (CIFAR-10). Our findings show that, because to the enhancements we made, the deep CNN can successfully fit small datasets with results that are noticeably better than before. This study tries to boost multi-class DR classification performance. Retinal fundus pictures from four classes of unbalanced and small datasets are used in the proposed model. This study also assesses the accuracy value-based combination performance of CNN SVM and CNN Softmax in order to validate the conclusions.
This study also assesses the accuracy value-based combinationperformanceofCNNSVMandCNNinorderto validatetheconclusions.So,alargeportionoftheimagenet datasetsusedtotraindeepconvolutionalneuralnetworks. The network model is developed on top of such a vast dataset primarily ignores the incorporation of further networklayersandthefactthatthemajorityofapplication data sets are several times bigger than imagenet datasets. With the proper changes, small datasets can be accommodated by Deep Convolutional Neural Network, and the results are usually far more effective than those obtained earlier [5]. The weighted distance between the colourhistogramsoftwoimages,expressedasaquadratic form, may be referred to as a match measure in image retrievalbasedoncolour.Thisdistancemeasurementuses high-dimensional characteristics and is computationally demanding (O(N)). We suggest using low-dimensional, straightforward distance measures to compare the colour distributions, and we demonstrate how these lower bounds on the histogram distance measure. According to results on colour histogram matching in big image databases, prefiltering using the more straightforward distance measures results in a significant reduction in processing time because the quadratic histogram distance isnowperformedonasmallersetofphotos.Indexinginto the database can also be done using the low-dimensional distance metric. Chronic diabetes is a condition that can resultindiabeticretinopathy,whichcanleadtoblindness. Consequently, to avoid the increased severity of diabetic retinopathy, early identification is crucial. In order to determine the appropriate follow-up treatment toprevent furtherretinaldamage,anautomatedmethodcanassistin the rapid detection of diabetic retinopathy. This paper suggests utilising a support vector machine to extract featuresandperformclassificationusingdeeplearning.As inputfeaturesforclassificationutilisingthesupportvector machine,weemploythehigh-levelfeaturesofthelastfully connected layer based on transfer learning from Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) (SVM). By employing this technique, the classification process using CNN with fine-tuning requires less calculation time. Using 77and70retinalpicturesfromtheMessidordatabase,the suggested approach is tested.By adopting Support Vector Machine technique, the calculation time needed for the CNN- tuned classification process can be decreased. Retinal images 77 and 70 from the Messidor database are usedtotestthesuggestedapproachusingbases12and13, respectively.
The various phases of DR are recognized and categorized in color fundus pictures using a Convolutional Neural Network ensemble-based framework. The method is trained and tested using the largest publicly accessible dataset of fundus pictures (the Kaggle dataset). A metaalgorithm that combines different machine learning methodsiscalledtheensemblemethod,isusedtogenerate the prediction model [6]. Data from different prediction
modelsarecombinedusingastackingmodeltobuildanew model.Amatchmeasureforcolourcouldbedefinedasthe weightedseparationbetweenthecolourhistogramsoftwo photographs, which is represented by a quadratic form. These are thelowestlimitations of the histogram distance measure, as demonstrated by a comparison of the colour distributions using low-dimensional, easily calculable distance measurements. With stacking, all of the outputs from the many models are combined to create a single output. This method combines the Resnet50, Inceptionv3, Xception, Dense - 121, and Dense169, which are five deep CNNmodels
Theretrievalofcontent-basedimagesandvideosinthis paper makes extensive use of colors. The issues of colour spaces, illumination invariance, colour quantization, and colour similarity functions have all been the subject of projects [7]. An eye condition known as diabetic retinopathy (DR) harms the retinal blood vessels. If DR is not identified in its early stages, it can cause vision impairment and ultimately result in blindness. Normal, mild, moderate, severe, and PDR are the five phases or grades of DR (Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy For the purpose of identifying this fatal ailment, the coloured fundus photographs are frequently examined by highly qualified doctors. Manually diagnosing this ailment by professionals is time-consuming and error-prone. Thus, several computer vision-based methods have been developed to automatically identify DR and its various stages from retinal pictures. However, because they are unable to encapsulate the underlying complex features, these approaches can only accurately detect DR's numerous stages, especially for the early stages. In this study, we made use of the widelyA few of the suggested algorithms (distance measure) have been created to implementmachinecolourconstancy,althoughtheirusein actual environments is currently being researched. Since images with "similar" feature distributions are frequently seen as having similar appearances without requiring any semantic interpretation of this, the concept of feature similarity also plays a crucial role in content-based retrieval. This method aids in calculating the similarity betweentwophotos'featuresafteracriticalanalysis.
The study demonstrates that current glaucoma screening methods based on intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements are insufficiently sensitive [8]. A persistent eye condition called glaucoma causes vision loss. Early disease detection is crucial because there is no treatment for it. For population-based glaucoma screening, the intraocular pressure (IOP) assays now in use are not sensitive enough. Assessment of the optic nerve head in retinal fundus pictures is superior and more promising. This study suggests utilizing superpixel classification to segment the optic disc and optic cup for glaucoma screening. Histograms and centre surround statistics are employed in optic disc segmentation to categories each

super pixel as a disc or a non-disc. In order toanalyse the effectiveness of the automated optic disc segmentation, a self-assessment reliability score is calculated. Together withhistogramsandcentresurroundstatistics,thefeature space for optic cup segmentation also contains position data.An eye condition known as diabetic retinopathy (DR) harmstheretinalbloodvessels.IfDRisnotidentifiedinits earlystages,itcancausevisionimpairmentandultimately result in blindness. Normal, mild, moderate, severe, and PDR are the five phases or grades of DR (Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy). The coloured fundus photos are oftenexaminedbyhighlyqualifiedprofessionalstoidentify this catastrophic condition. It takes time and is prone to error for clinicians to manually diagnose this illness. Determining DR and its various stages automatically from retinal images has so been proposed using a variety of computer vision-based techniques. Nevertheless, these techniques can only identify DR's many stages with a relatively poor level of accuracy, especially for the early stages, because they are unable to encode the underlying intricate properties. In this study, we made use of the widely According to the study, super pixel classification canbeusedtodistinguishbetweentheopticdiscandoptic cupwhenperformingglaucomascreenings.Toquantifythe efficiencyoftheautomatedopticdiscsegmentation,aselfassessment reliability score is developed. The histograms and centre surround statistics for the optic cup segmentation are also included to the feature space in order to enhance performance. The suggested segmentation techniques have been tested using a database of 650 photographs on which the boundaries of the optic disc and the optic cup have been meticulously delineated by knowledgeable specialists. The average overlapping errors for segmenting the optic disc and cup were9.5%and24.1%,respectively.Themethodprovesthe efficiency of the self-evaluation by showing that overlapping error increases as the reliability score decreases. Segmentation and glaucoma screening are also possibleapplicationsofthetechnology.
Image analysis in the context of medical imaging with computerassistance.Deeplearning,oneofthemostrecent developments in machine learning aids in finding, categorizing, and quantify patterns in medical images. Theyexplainedtheprinciplesofdeep learningtechniques and reviewed their achievements in image registration, tissue segmentation, identification of anatomical and cellular features, computer-aided disease diagnosis and prognosis, and addressed researchchallenges and future possibilities for advancement [9]. Both clinical applications and academic research have been significantly impacted by computational modelling for medical image processing. Deep learning's recent advancements have opened up new perspectives on medical image analysis by making it possible to identify morphologicaland/ortexturalpatternsinimagesentirely based on data. Although deep learning techniques have
attained cutting-edge performance in a variety of medical applications,thereisstillpotentialfordevelopment.

Theidentificationandclassificationofleukocytes,orwhite bloodcells,whicharecrucialforthediagnosisofdiseases, are covered in this article. Skilled workers manually operate the blood cells, which has several limitations includingpooranalysisspeed.Thisstudysuggestsasystem for automatically identifying and categorizing WBCs in peripheral blood pictures. [10] Due to its crucial uses in the diagnosis of diseases, the detection and classification ofwhitebloodcells(WBCs,alsoknownasleukocytes)isa hot topic. The morphological study of blood cells is now performedmanuallybyqualifiedworkers,whichhassome disadvantages like sluggish analysis, non-standard accuracy, and reliance on the operator's abilities. Few articles take both into account, despite the fact that numerouspapershavelookedatthedetectionofWBCsor the classification of WBCs separately. This study suggests a system for automatically identifying and categorising WBCs in peripheral blood pictures. It first suggests an algorithm based on a straightforward relationship between the colours R, B, and morphological operation to identify WBCs in microscope images. Then a pairwise rotationgranularityfeatureTheneutrophil,monocyte,and lymphocyte subtypes of WBCs are identified by random forest using the high-level properties that are automaticallyextractedfromWBCsbyconvolutionneural networks. Pairwise rotation invariant co-occurrence local binary pattern, or PRICoLBP, is used in conjunction with SVM as a granularity feature to discriminate between eosinophil and basophil, is employed as a granularity feature along with SVM. A detection method is more accurate, less expensive, and virtually as effective as an iterativethresholdmethod.
3. PROPOSED SYSTEM
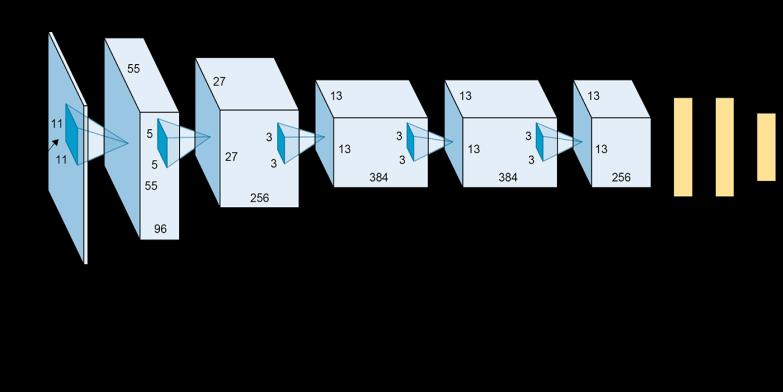
Wesuggestamachinelearning-basedstrategy.Inorderto further increase the classification accuracy, a more effective method of combining shallow CNNs will be investigated. The performance of the integrated shallow CNN model will be enhanced by the transformation of picturesamplesandtherepetitivesamplingofthedataset. Backend of the system is created using VGG 16 image classification algorithm which is a multilayered convolutional neural network. For the front end, a User Interface is created using the tkinter python library, this allows the users to input the images to the algorithm and see the predicted output. Prediction with prediction accuracy and confidence score is shown as result. Multiscale shallow CNNs with performance integration are introduced to the early identification of diabetic retinopathy through the classification of retinal images. When there aren't enough high-quality labelled examples, it can nevertheless perform well at picture classification because multiple base learners are capable of sensing
features under diverse vision-related receptive fields and sampling repeating datasets. The trials indicate that the performance integration model is more accurate than other integration models, such as those based on mean and voting. In addition, the suggested approach outperforms previous approaches when comparing classificationeffectandefficiencyonsmalldatasets.
Conf.Inf.Commun.Technol.Syst.(ICTS),Surabaya,IN, USA,Jul.2019,pp.152–157.
[4] J.Hafner,H.S.Sawhney,W.Equitz,M.Flickner,andW. Niblack, ‘‘Efficient color histogram indexing for quadratic form distance functions,’’ IEEE Trans. PatternAnal.Mach.Intell.,vol.17,no.7,pp.729
736, Jul.1995,doi:10.1109/34.391417
[5] S. Qummar, F. G. Khan, S. Shah, A. Khan, S. Shamshirband, Z. U. Rehman, I. Ahmed Khan, and W. Jadoon, ‘‘A deep learning ensemble approach for diabetic retinopathy detection,’’ IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 150530–150539, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947484e
[6] J.Cheng, J.Liu,Y. Xu,F. Yin, D. W. K. Wong,N.-M.Tan, D. Tao, C.-Y. Cheng, T. Aung, and T. Y. Wong, ‘‘Superpixel classification based optic disc and optic cup segmentation for glaucoma screening,’’ IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 1019–1032, Jun. 2013,doi:10.1109/TMI.2013.2247770
4. CONCLUSIONS
We conclude that the CNN-based image classification method,therearecategoriesforProliferativeDR,MildDR, Moderate DR, Severe DR, and No DR. This is significantly more helpful than the two-class classification techniques thatarecurrentlyinuse,whichclassifyimagesintoyes-ornogroupsaccordingonwhetherthepatienthasDRornot. This does not supply us with any information on the severity and extent of the patient's condition, but our algorithm gives us deeperinsights into the severity and extent of the sickness, enabling the doctors to offer appropriate care. Future research will refine our suggested strategy in the manner described below. To further increase the classification accuracy, a more efficient method of combining shallow CNNs will be investigated. By integrating the modification of picture samples with repetitive dataset sampling, the integrated shallowCNNmodelwouldoperatemoreeffectively.
REFERENCES
[1] J.Deng,W.Dong,R.Socher,L.-J.Li,K.Li,andL.Fei-Fei, ‘‘ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database,’’ in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit.,Miami,FL,USA,Jun.2009,pp.248–255.

[2] S. Zhou, C. Chen, G. Han, and X. Hou, ‘‘Deep convolutional neural network with dilated convolution using small size dataset,’’ in Proc. Chin. Control Conf. (CCC), Guangzhou, China, Jul. 2019, pp. 8568–8572.
[3] D. U. N. Qomariah, H. Tjandrasa, and C. Fatichah, ‘‘Classification of diabetic retinopathy and normal retinal imagesusing CNN andSVM,’’inProc.12th Int.
[7] D. Shen, G. Wu, and H. Suk, ‘‘Deep learning in medical image analysis,’’ Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., vol. 19, pp. 221–248,Jun.2017.
[8] J.Zhao, M. Zhang, Z. Zhou, J. Chu, and F. Cao, ‘‘Automatic detection and classification of leukocytes using convolutional neural networks,’’ Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,vol.55,no.8,pp.1287–1301,Aug.2017,doi: 10.1007/s11517-016-1590-x
