STUDY OF COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO ATRIUM BUILDINGS IN VARIOUS SEISMIC ZONES WITH AND WITHOUT SHEAR WALLS
Tanushyama Banerjee1, Shayan Das2, Prasun Chakraborty3, Suchandra Das4 , Sudip Saha5, Mansur Alam6, Paramita Dutta7, Mainak Ghosh8
1 Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, C.I.E.M., Kolkata, West Bengal, India

2,3,4,5,6,7,8 B. Tech Student, Department of Civil Engineering, C.I.E.M., Kolkata, West Bengal, India ***
Abstract - This work is concerned withtheanalysisofatrium building structure to determine the importance of shear wall in high-rise building Shear walls provide large strength and stiffness to buildings in the direction of their orientation, which reduces lateral sway of the building and thereby reduces damage to the structure andits contents. The present paper considered two atrium buildings (G+9) with and without shear walls having the same plan area. Each building is subjectedto differentseismiczones.Theparametersselected for the comparison are nodal displacement and bending moment. Results were traced in tabular format for all parameters value and observed against selected zone like V, IV, III and II.
Key Words: Atrium Building, High-Rise Building, Shear Wall, Wind Load Analysis, Seismic Analysis, Nodal Displacement, Bending Moment
1. INTRODUCTION
Humans are always fascinated with uniquely designed buildings.Inarchitecture,anatriumisalargeopen-airorskylightcoveredspacesurroundedbyabuilding.Atriawerea common feature inAncient Roman dwellings, providinglightandventilationtotheinterior.Modernatria, asdevelopedinthelate19thand20thcenturies,areoften severalstorieshigh,withaglazedrooforlargewindows,and oftenlocatedimmediatelybeyondabuilding'smainentrance doors.
Toanalyzethehigh-risebuildingsomeusefulsoftware’s likeSTAADPro,ETABSetc.arewidelyusedbythedesigners and researchers in this field. In traditional calculation of modelofhigh-risebuilding,thefollowingfactorsaffectingthe earthquakedesignofstructuresaredifferentseismiczones, dampingfactorofthestructure,importanceofthebuilding, type of soil, natural frequency of the building, different seismiczones,etc.
Any sudden shaking of the ground caused by the movement of tectonic plates is called earthquake. This shaking may cause building damage. When the ground shakes, the building foundation vibrate in a manner that’s
similartothesurroundingground.TheIndiansubcontinent hasahistoryofdevastatingearthquakes.
Shear walls provide large strength and stiffness to buildingsinthedirectionoftheirorientation,whichreduces lateralswayofthebuildingandtherebyreducesdamageto the structure and its contents. Shear wall is a vertical structuralelementthatresistslateralforcesintheplaneof thewallthroughshearandbending.Thebehaviorofshear wallsdependsonthematerialused,thewallthickness,length &positionofthewallinthebuildingframe.Theirthickness canbeabove150mmorbelow400mmintallbuildings;they are like vertical-oriented wide beams that carry the earthquakeloadtowardsthefoundation.Thiswallresiststhe lateralloadsthatareimposedonthestructureduetowind, earthquake,orsometimesduetohydrostaticorlateralearth pressure.Shearwallbuildingsareacommonchoiceinmany earthquake prone countries. They reduces earthquake damage in structural and nonstructural elements such as glass windows and construction materials. Buildings with shear walls have shown very good performance during earthquakesinhighseismicareas.Shearwallsdesignedto resist gravity/vertical loads and earthquake/wind lateral loads.Thesetypesofwallsarestructurallycombinedwiththe rooforfloor.Thesewallsresisttheshearforcesthattryto pushthewallsupandthelateralforcesofairthatpushthe wallsinandoutofthestructure
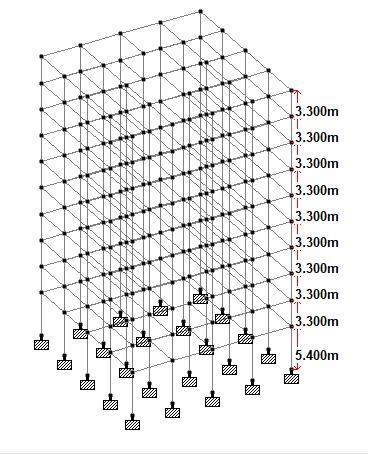
Inthispaper,analysisoftwoG+9storey atriumbuildings againstseismicloadandwind loadas per IS:875 part(III) and IS 1893 part(I)-2016 using STAAD Pro has been conductedtocomparethemaximumnodaldisplacementand maximum bending moment of the structures. The plan dimensionremainssameforallthemodelsi.e.,20mX20m. Seismiczonewasvariedforeachmodel.Intheseismiczoning mapgivenintheearthquakeresistantdesigncodeIS1893 (Part 1) 2016 assigns four levels of seismicity for India in terms of zone factors. According to that, here we consider four cities Visakhapatnam (Zone II), Kolkata (Zone- III), DehraDun(Zone-IV),Shillong(Zone-V)withaconstantwind speedof50m/s.Themodelsaresubjectedtodeadloads,live load, seismic load and wind load. The member forces are calculatedusingloadcombinationsasperIS456:2000.
2. PRELIMINARY DATA OF THE STRUCTURE CONSIDERED FOR ANALYSIS OF MODELS USED BY STAAD PRO
VariousISCodeslikeIS1893:2016(Part1)andIS456:2000, IS875PART(I),IS875PART(II),IS875PART(III) were usedfordesignpurpose.Therequiredsizesof beamsand columnsforanalysisanddesignpurposeiscalculated.
Table -1: DescriptionofStructuralItemsRequiredforthe DesignModels
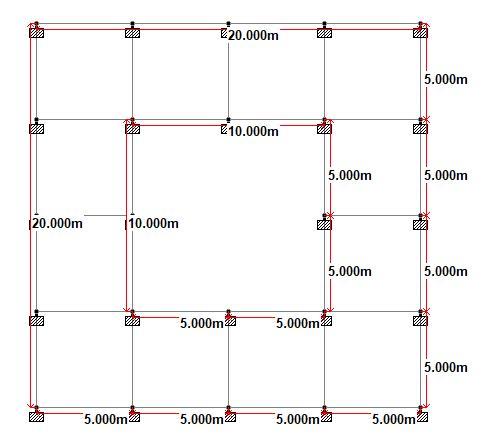
Table -2: Descriptionofvariouscombinationofloads assignedinthemembersofthemodels


4. RESULT & DISCUSSION
4.1 Check for maximum nodal deflection under different seismic zones
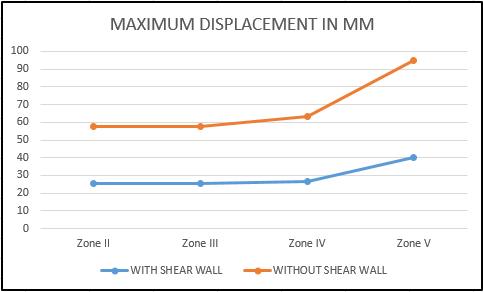
The details of the variation of nodal deflection in with and without shear wall Atrium building for different load conditions and for different seismic zones has been tabulatedinTable6andChart1respectively
Table 6 -: Variationofmaximumnodaldisplacement underdifferentseismiczonesforAtriumwithandwithout shearWall
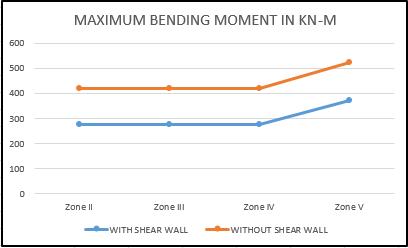
Table 7 -: Variationofmaximumbendingmomentunder differentseismiczonesforAtriumwithandwithoutshear wall MAXIMUM BENDING MOMENT IN KN-M SEISMIC ZONES ATRIUMWITH
Chart -1 -: MaximumDisplacement
4.2 Check for maximum bending moment under different seismic zones
Thedetailsofthevariationofbendingmomentinwithand without shear wall Atrium building for different load conditions and for different seismic zones has been tabulatedinTable7andChart2respectively
5. CONCLUSIONS
In this study, analysis of G+9 storey Atrium buildingswithandwithoutshearwallsagainstseismicload andwindloadasperIS:875part(III)andIS1893part(I)2016usingSTAADProhasbeenconductedtocomparethe nodaldisplacementandbendingmomentofthestructures.
TheconclusiondrawnfromthestudyofG+9Atrium buildingthatprovidingshearwallssubstantiallyreducesthe lateraldisplacementandbendingmomentduetoearthquake and wind loading. Also the stability and stiffness of the structurewillincreasewiththeoptimumplacementofshear walls.
REFERENCES
[1] Ankit Purohit (2017): "Seismic Analysis of G+12 Multistory Building Varying Zone and Soil Type" Volume-4,Issue-6.
[2] Vishal v. Gupta, ashwin soosan pillai, akash bharmal, prof.Jaydeep.B.Chougale,“studyofeffectoforientation

ofcolumnandpositionofshearwallong+13storeyed earthquakeresistantstructure”.
[3] RaghavSinghShekhawat,AnshulSud,PoonamDhiman, “Economical placement of shear walls in a moment resistingframeforearthquakeprotection”
[4] “Analysis of Atrium Design for Improved Building Performance in Public Building”- Sweta Waiba a , SanjayaUpretyb,PrativaLamsal

[5] Suchita Tuppad, R.J.Fernandes, “Optimum location of shearwallinamultistoreybuildingbuildingsubjected toseismicbehaviourusinggeneticalgorithm.”
[6] “Seismic performance of multi-story building with differentlocationsofshearwallanddiagrid”authoreds. P.Sharma,j.P.Bhandri.
[7] IS:456-2000:Indianstandardcodeofpracticeforplain andreinforcedconcrete
[8] IS:875(part1)1987:codeofpracticeforDesignloads (other than earthquake) For buildings and structures Part 1 dead loads - unit weights of building materials andStoredmaterials(secondrevision).
[9] IS: 875 (part 2)-1987: Code of practice (other than earthquake)part2:imposedloads(Secondrevision)
[10] IS:875(part3)-2015:CodeofpracticeforDesignloads (other than earthquake) For buildings and structures Part3Windloads(Thirdrevision)
