SECURE E-BANKING APPLICATION BASED ON VISUAL CRYPTOGRAPHY
Yogesh Kore1, A. G. Patil , Aishwarya Hasbe3 ,Anuja Chougule4, Ajinkya Sakale51B.Tech IV, E&TC, Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology, Budhgaon, Maharashtra, India.
2Assistant Professor,E&TC, Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology, Budhgaon, Maharashtra, India.

3 B.Tech IV, E&TC, Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology, Budhgaon, Maharashtra, India.
4 B.Tech IV, E&TC, Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology, Budhgaon, Maharashtra, India.
5 B.Tech IV, E&TC, Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology, Budhgaon, Maharashtra, India. ***
Abstract - There are numerous securityissues as a result of the sharp rise in computer use. As a result, security has taken the top spot in today's internet operations. To prevent such security risks, numerous verification and certification algorithms are used today. The visual encryption is one of them. The phishing attack is one of the significant dangers. In our initiative, we've demonstrated how visual encryption can protect online shoppers from phishing attacks. A securityproviding program that uses images is called visual encryption. The initial picture is secured or kept in visual cryptography by being divided into n shares.
Key Words: Phishing, Visual Cryptography Scheme, Shares, RSA, Encryption, Decryption.
1. INTRODUCTION

Nowadays, everyone in the globe does business online. Online crimes of all kinds are as prevalent as online interactionsareintoday'sworld.Thethreemaincategories ofverificationmethodsareknowledge-based,token-based, andfingerprint.Knowledge-basedsecurityrequirestheuser torecallanytext-basedorgraphicpasscode.Techniquesthat rely on knowledge can also be categorized as memory or identificationbased.Inrecall-basedmethods,theusermust rememberthepreviouslyestablishedprivatepassword.The user must be able to determine or recognize the private password in recognition-based systems. The use of recognition-basedmethodsisincreasingprotection.
person'sprivateinformation,suchasapasswordorcredit cardinformation,anddoesnotcorrespondtocybercrime.In thesamewaythatweattempttocatchfishwhenwegolake orseafishing,phisherstrytograbpeople'scredentialswhen theysendoutphishingemails.Itisa"gamethatscammers use to steal personal information from unwary users," accordingtoonedefinition.Oneencryptedcommunication canonlybedecodedusingthehumanvisionsystemwhen using visual cryptography. It is possible to use a visual cryptographic method by thresholding, blurring, and then encrypting a picture. We used a method that is based on recognition.
We have thoroughly examined and discussed visual cryptographyinthisproject.Thispaperdemonstratesour projectdesignandtheuseofimagesaspasswordsforonline transactions. The procedures used to create shares of the pictureandprocesstheimagearecoveredindepthinthe partsbelow.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
Forthisapproach wehavestudieddifferentbooksand IEEEpapers.
One significant security risk that everyone is currently exposed to is phishing attacks. Phishing is the theft of a
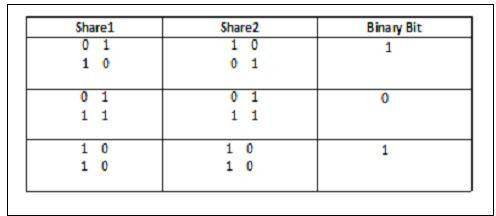
The encoding method suggested by Naor and Shamir [1] dividesabinarypictureintotwoshares,Share1andShare2. Fig.2 top two rows are selected to produce Share1 and Share2ifpixeliswhite.Similartothis,Share1andShare2 aregeneratedifapixelinthebottomtworowsofFig.2is dark.Sinceeachsharepixelpissplitintotwowhiteandtwo black pixels, neither share by itself can reveal whether a pixel p is white or black. Only when both files are superimposed will the secret picture be visible. Stacking sharesillustratesanORprocedure.ORisalossyrestoration procedure. We can get a lossless restore of the original picture if the XOR operation is used in place of the OR operation. However, XOR operation requires calculation. The OR procedure can only be simulated by the actual stackingprocess.
Thismethodhasthefollowingshortcomings:
Itonlyworkswithblackandwhitepictures.
Shares are four times larger than the original picture,requiringmorestoragespace.
As each cycle requires the encoding of a single image,ittakestime.
2.2 Color Visual Cryptography Schemes
Chang and Tsai anticipated color visual encryption strategy for sharing a secret color picture and also for generating the meaningful share to send a secret color image.Forasecretcolorimage,twoimportantcolorimages are chosen as cover imagesthat are the same size as the secret color image. The secret color picture is then concealedintotwocamouflageimagesusingapresetColor Index Table. One disadvantage of this strategy is that additionalspaceisneededtobuildtheColorIndexTable.
SimilartotheVerheul,VanTilborg,Yang,andLaih[3] schemes, the number of sub-pixels in this scheme is proportionaltothenumberofcolorsinthehiddenpicture. The size of shares will increase as the secret picture containsmorecolors.Chin-ChenChangetal[4]createda private color picture sharing system based on modified visual encryption to overcome this restriction. This plan offers a more effective method to conceal a gray picture acrossvariousshares.Inthissystem,thesizeoftheshares isset;itdoesnotchangedependingonhowmanycolorsare visibleinthehiddenpicture.Thereisnoneedforapreset ColorIndexTablewithScheme.
3. VISUAL CRYPTOGRAPHY
Visual cryptography is a safe method for spotting fake websitesandthephishingattacksthatarebroughtonbyit. Onlythesenderandrecipientcandecodethemessagesusing the method of transmitting as well as receiving messages. ThismethodwasdevelopedbyNaorandShamirasaquick andsafemeanstoshareapassword-protectedsecretimage.
Thismethodconsistsoftwosteps:picturesharecreationand encryption decryption. Messages are encrypted and decryptedusingastraightforwardmathematicalformula.The creation of the picture shares is the second crucial componentofthisscheme.
VCSisacryptographic methodthatencodesvisual data so thatonlyahumanbeingisabletoperformthedecryption. Applying one of the following methods, we can use this technique:
A.(2,2)ThresholdVCSscheme itthesimplestschemethat generatestwosharesofoneimage.Userneedtohavethese bothsharesforwhileobtainingoriginalimage.
B.(n,n)ThresholdVCSschemeHerewegeneratensharesof the image. When all this n shares are combined then only secretimagewillgetrevealed.Onemissingcanletusobtain secretimage.
C.(K,N)ThresholdVCSschemeHerewe generatensharesof theimage.Butthesecretimageisrevealedonlywhenweget groupofatleastkshares.
4. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY

-3: ArchitectureofE-bankingSystem
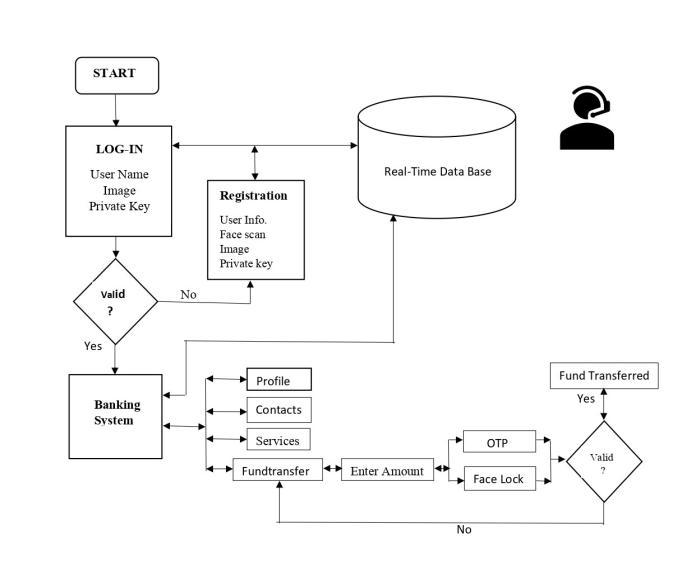
In this section we will study the block diagram of the system. We have divided the entire transaction into two phases,whichwehavelabeled:
4.1 Registration Phase:
Foronlinetransactionsandpurchases,youmustfirstopen abankaccount.Atthisstage,youprovideyourbankwith youridentityinformation.WeareusingtheRSAalgorithm andalsosetthepublicandprivatekeysforyouraccount.
Alsoweneedtoscanthumbandfacewhichwillbeused during login as extra authentication option. Above Fig.3 shows thestep-by-step execution of this phase. Itshows how a user registers with a bank. In it, the public key belongstotheuserandtheprivatekeyiskeptinthebank
4.2 Transaction Phase:
Actual interaction between the customer, the merchant server, and the trusted server occurs during this stage. Heretheimageprocessingisdone.Theactionsarecarried outintheorderdepictedinFig.3.above InthisVCversion, wehaveimplementedafewminorchanges.Afterentering amountuserwillreceiveOTP,andiftheoptiscorrectthen thumb scanning will be done. All this steps are authenticatedandiftheyarevalidthentransactionwillbe done. Trusted servers have their own databases where they keep records of both vendor and customer information. Bank is able to determine any problematic vendorwebsite.Phishingcanbeavoidedandhaltedasa result.
5. RSA Fig -4: AuthenticationinRSA
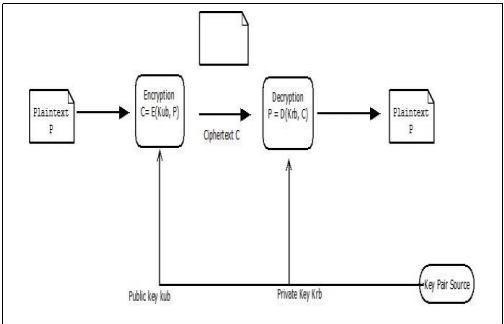
Rivest, Shamir, and Adleman is referred to as RSA. The mostpopularpublic-keycryptography method isRSA. It mainlyconsistsoftwoblocksoftext,theplaintextandthe ciphertext.Inourproject,weusedtheRSAalgorithmfor thetwomainactivities:imageencryptionanddecryption. Figure4illustratestheprocess.Thisoffersthenecessary verificationforthetransaction.

PlaintextandencryptiontextsintheRSAblockarenothing morethannumbersintherangeof0ton-1,wherenisa certain number. Key generation, encryption, and decryptionarethethreeconsecutivestagesinRSA.Inthis method,onepartyencryptsdatausingapublickey,andthe otherpartydecryptsitusingaprivatekey.Thesearethe stagesofthealgorithm:
5.1 Key Generation:
1)Selectanytwodistinctprimenumberspandq,p≠q.
2)Computen=p*q,wherenismodulus.
3)Thencomputeφ(n)=(p-1)(q-1),whereφis Euler’stotientfunction.
4)Chooseintegeresuchthat1<e<φ(n) and gcd(φ(n),e)=1.WhereeisreleasedasPublickey.
5)Computed=e(modφ(n)),wheredis releasedasPrivateKey
6)GetpublickeyasKU={e,n}.
7)GetprivatekeyasKr={d,n}.
5 2 Encryption:
Toobtainciphertext,plaintextblocksP<nisusedas: C=Pemodn.
5.3 Decryption:
Toobtainplaintext,ciphertextblockCisusedas: P=Cdmodn.
Becauseitischallengingtocalculatelargenumbers,RSAis safer. Due to this, obtaining φ(n) is also challenging. It is challenging to take a user's data or credentials without getting φ (n). The fact that RSA can be used for both cryptography and digital signatures is a benefit. There are manyattacksthataimtobreaktheRSAsecuritycode.Oneof themis theBruteforceattack.Butittakeseffort.Usercan alterthepicturenumeroustimesuntil phisherattemptsat breakingoursecurityareuseless.Thegreatestfeatureofour design is that it can change the image numerous times as needed.
6. IMAGE THRESHOLDING
Ourapproachusesimagesaspasswords.Splittheimageinto nsharestouseasasecretpassword.Animageisacollection of pixels. Images can be 2D arrays. Again, pixels are the smallestvisualelements,asshowninFig.5.Pixelsarestored inintegerformat.Formatsare8b,24,and32bits.
Themostcommoncolorcodeisthe24bitRGBformat,which contains 8 bits of each red,green, and blue color. An 8-bit

imageisjustamonochromeimage. Themajorityofpicture analysisusesgrayscaleimages.Theyaredistinctfromblack and white photos. In our method, color images are first transformedtomonochrome,whichisthenchangedtoblack andwhite.Thisblackandwhitepictureproducesthenshares asapasscode,also.
6.1 Conversion of color imageintogray scaleimage:
ConvertinganRGB24-bitpicturetoagrayscale8-bitimage is the first stage in the image processing procedure. The methodsbelowdemonstratehowtodone:
a)Gothroughtheentirecolorpictureandeachpixel'svalue. Thispixelnumberhasa24bitwidth.
b) Next, divide the red, green, and blue colors by right shiftingthepixelvalueby8bits.
Finally, use hexadecimal 15 to execute the logical AND operationasshownbelow.
B=pix&0ff
G=(pix>>8)&0ff
R=(pix>>16)&0ff
c) Next, compute the gray scale component of each red, green, and blue pixel value. This is done by averaging Gs=(r+g+b)/3
d)Reconstruct24-bitvaluesfrom8-bitgrayscaleandsave tonewlocation.
6.2 Conversion of gray scale into black and white:
Thismethodofpicturesegmentationisalsoreferredtoas imagethresholding.Here,wechangetheessentialaspectsof thepicturetowhitepixelsandtheremainingportionsto blackpixels.Asiscommonknowledge,binaryimagescome inblackandwhite.Thefollowingalgorithmicmethodswill beusedforthis:
1.Determinethethresholdvalue,T.
2.MakeaduplicateoftheoriginalImageArray(let'scallit “binary")withthesamenumberofrowsandcolumnsbut withallcomponentssetto0.(zero).
3.Ifthegraylevelpixelat(i,j)ishigherthanorequaltothe threshold value, T, then give 1 to binary(i, j); otherwise, assign0tobinary.(i,j).

Foreachgrayscalepoint,repeattheprocess.
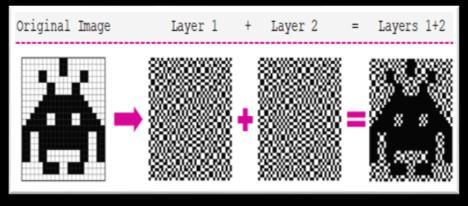
6.3 Share generation from binary image:
Fig
(2,2)Sharegenerationscheme
Thismethodinvolvesdividingthepictureintonparts.We have generated 2 shares in this example. For the binary inputpicture,whichisformattedas1and0?Here,one2*2 grid is generated for each pixel. Shares are generated as indicated above. Here, a single random 2x2 matrix is producedandissubsequentlyreferredtoasshare1.
Fig
PictorialrepresentationofSharegeneration
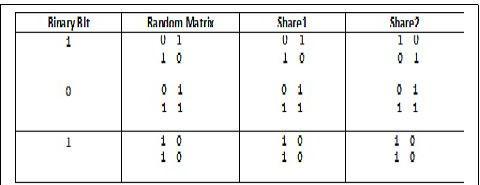
Ifthebinarypixelisblack,theshare2iscreatedbyswapping thecolumnsofthematrix,asshowninfig.6above.Whena binary pixel is white, share 2 is equal to share 1. Next, we createabinarypicturebymatchingtwoshares.Iftheshares are identical, white pixels are produced. If different, black pixels are produced again. The user must verify the authenticityofthevendorwhenthepurchaseiscomplete.To acquiretheoriginalpictureatthismoment,hemustoverlay theshares.Thisispossibleasillustratedinfig.8.
Thus, we have seen each image processing method in this manner.
3. CONCLUSIONS
This system is created using Java technology as a web application.

Thismethodemploys ColorImageVisual Cryptographyto securepasswords,anditiscurrentlytechnologicallyhardto defeat this security. The Core Banking Application will benefit greatly from this system, and bank clients will no longerexperiencepasswordtheftissues.Oncethissystemis installed on a web server, every device connected to the network can view it using a browser without needing to installanysoftware.
REFERENCES
[1] Moni Naor and Adi Shamir, “Visual Cryptography”, advancesincryptology–Eurocrypt,pp1-12,1995
[2] Ateniese,G.,Blundo,C.,DeSantis,A.,andStinson,D.R. (1996),” Constructions and bounds for visual cryptography”, in 23rd International Colloquium on Automata,LanguagesandProgramming''(ICALP'96).
[3] E.Verheuland H. V. Tilburg, “Constructions and PropertiesofKOutOfNVisualSecretSharingSchemes.” Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 11(2), pp.179–196, 1997.
[4] C.C.Wu,L.H.Chen,“AStudy OnVisual Cryptography”, Master Thesis, Institute of Computer and Information Science,NationalChiaoTungUniversity,Taiwan,R.O.C., 1998.S.J.Shyu,S.
[5] Y.Huanga,Y.K.Lee,R.Z.Wang,andK.Chen,“Sharing multiple secrets in visual cryptography”, Pattern Recognition,Vol.40,Issue12,pp.3633-3651,2007.
[6] Tao Li, Baoxiang Du, and Xiaowen Liang, “Image Encryption Algorithm Based on Logistic and TwoDimensionalLorenz”,2019IEEE.
[7] Chandrasekhara & Jagadisha, “Secure banking application using visual Cryptography against fake websiteauthenticity”,IJACECT,Vol.02,Issue02,2022.M. Young, The Technical Writer’s Handbook. Mill Valley, CA:UniversityScience,1989.
