AN XGBOOST-BASED REGRESSION MODEL FOR WILDFIRE IMPACT PREDICTION
Mrs. Priyadharshini M1 , Chrisolus Timonsingh J2 , Insuvai V3, Jenvin Shirly R41 Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering

2 UG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering
3 UG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering
4 UG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering
SRM Valliammai Engineering College, Chengalpattu, Tamil Nadu, India ***
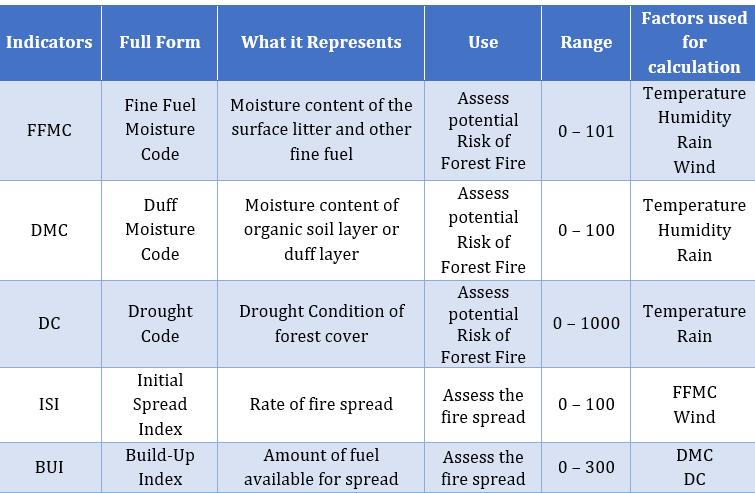
Abstract - AI is a powerful decision-makingtoolthatmakes use of decision makers to do intensive prediction and association tasks. The forest fire predictor plays a vital role in forest fire management. Timelypredictionreducesthenumber of areas affected by this fire, lowering the cost of fire extinguishment and forest damage. This project presents a forest fire prediction mechanism based on artificial intelligence. Prediction can be done with the help of a supervised learning algorithm that entails a set of inputs with an expected output result being fed into the model, enabling it to be trained to identify trends and patterns. The machine learning algorithm works based on previous weather conditions in order to predict the fire hazard level for the day. Given that forest fires are rare, there exists only a few dataset instances, prompting us to devise a method for producing a reasonable prediction using a small and frequently skewed dataset. The easily measurable features are chosen in order to make the prediction, thus effectively reducing the cost of the system. In the past, meteorological datahasbeenincorporated into numerical indices, which can be used for prevention and fire management The Canadian Forest Fire Weather Index (FWI) system, in particular, was designed in the 1970s when computers were scarce, necessitating only simple calculations using look-up tables with readings from four meteorological observations (temperature, relative humidity, rain, andwind) that could be manually collected in weather stations.
Key Words: Impact Prediction, Risk Prediction, Logistic Regression, XGBoost, Wild Fire, Forest Fire, Initial Spread Index,BuildUpIndex
1.INTRODUCTION
[11] Predictionofeventshasalwaysbeenachallengingtask especially when it comes to natural events. Nature has alwaysbeentoughtopredict,whichkickedoffthecuriosity toexplorethepredictabilityofwild-fires.[6]Wildfiresarenot common events, but unfortunatelylead to costlydamages anddeathwhentheyoccur.Meteorologicaldataandnational fire records show that the prime factor for wildfires is climate driven. [12] Prediction of occurrence of wild fire is proved feasible using the meteorological factors like temperature,humidity,windspeedandrain.Occurrenceof
wild-firesinIndianforestsisnotuncommon. [13]Mostofthe firesisoflesserintensityandgenerallyputoutbyrain.But whenthereislessornorainduetodryweather(summer), thefirespreadswithease.Mostnotablewild-fireeventsin India takes place in Uttarakhand, Karnataka and Odissa duringthemonthsofJanuarytoMay.
Thesimplestpracticeistokeeptrackonthemeteorological factorsthatheavilyaffectstheignitionoffire.Thesefactors includetemperature,humidity,rainandwindspeed.With thehelpofthesefactors,itisproposedthatthepredictionof wildfire is feasible. [14] Wildfire could be caused due to variousfactors.Mostofthefireiscausedbyhumansbecause of their carelessness. But during dry seasons, the fire is initiatedbynatureandwhenoccurreditcouldcauseserious damage.InIndia,forestfirefrequentlytakesplacebutare mostlyconsideredharmless.Mostsignificantwildfiretakes place in the place of Uttarakhand, Karnataka and Odissa whichaffectedmorethan10,000acresofforestcoverand caused damage to wildlife and vegetation in India. These firesaresuspectedtobecausedduetodryweather.These firescouldhavebeenpreventedorthedamagecausedcould have been subsided if the occurrence of the fire and its impact was known before. From the research papers, we concluded that prediction of forest fire and its scale is possible using the meteorological factors. We consider 3 moisturecodesasFFMC,DMCandDCwhichcanbeusedto predicttheoccurrenceoffire.Inadditiontothis,thereexist 2moreindicesnamelyInitialSpreadIndex(ISI)andBuildUpindex(BUI)thatcouldinfluencethespreadoffire.With thehelpofthese2indices,itispossibletopredictthearea thatcouldbeaffectedbythefireevenbeforeitoccurs.
1.1 System Overview
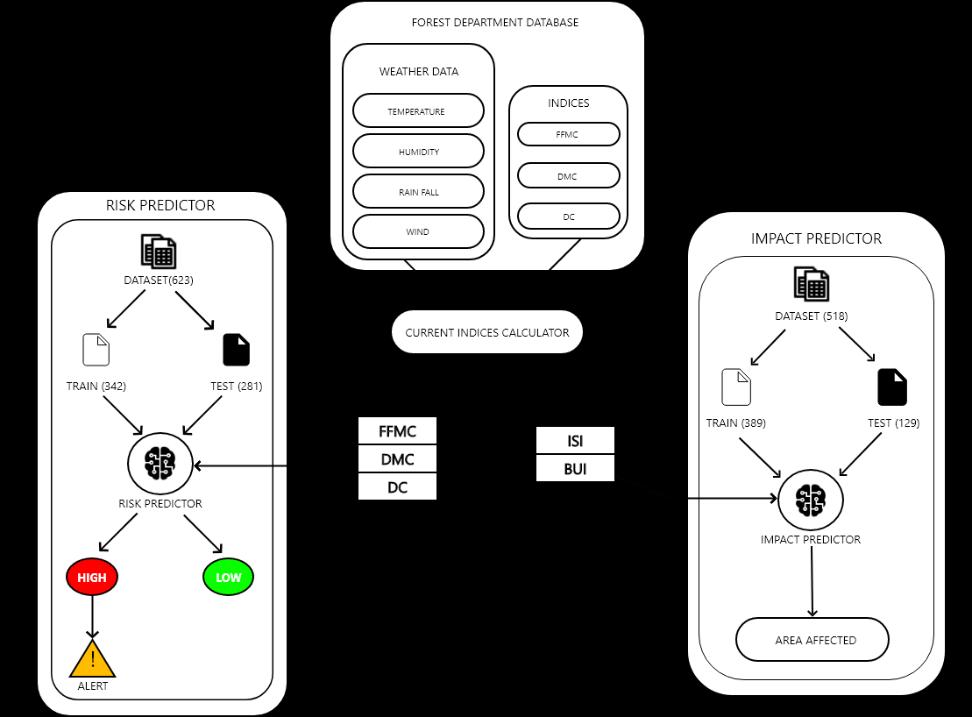
Wild-fire risk and impact prediction system consist of 4 components:ForestDepartmentDatabase,IndicesCalculator, RiskPredictorandImpactPredictor.TheForestDepartment Databaseactsastherepositoryformeteorologicaldataofthe forestcover.Itshouldcontaintemperature,humidity,wind speedandraininvariouspartoftheforest.Italsocontains thepreviousday’smoisturecodessuchasFineFuelMoisture Code(FFMC),DuffMoistureCode(DMC)andDroughtCode
(DC), which plays a major role in calculating the current moisture codes which is carried out by the second component:Indicescalculator.Itnotonlycontainsthelogic forcalculationofmoisturecodes,butalsocancalculatethe indices like Initial Spread Index (ISI) and Build-Up Index (BUI)whichplaysamajorroleinpredictionoftheimpactof forestfire.TheRiskPredictorandImpactPredictoraretwo maincomponentsofthesystemthatworksbasedonMachine LearningModels.TheRiskPredictorisasimpleclassification model calledaslogistic regressionmodel thatpredictsthe likelihoodoftheignitionoffireusingthemoisturecodesina particulararea.Theoutputofthismodelisaprobabilityof theoccurrenceofthefire.Iftheprobabilityvalueisgreater than 70-80 %, an alert is sent to the department through mail.Thismailcarriestheinformationabouttheprobability andtheareathatcouldbeaffectedbythefireifiteveroccurs. TheImpactPredictorisalsoamachinelearningmodelbased oneXtremeGradientBoosting(XGB)algorithmthatfollows ensemble technique of sequential learning which fits distributed gradient boosted decision trees. This model is responsibleforthepredictionoftheareacoveredbythefire. This is possible by considering the ISI and BUI which are calculated from the moisture codes and meteorological dataFordemonstratingtheworkingofthepredictionmodel, anuserinterfaceisdesignedthatcouldaccepttheweather dataasuserinputsaswecurrentlydoesn’thavetheactual databaseoftheforestdepartment.Thefigure–1represents thearchitectureoftheproposedsystem.
in performance and time with respect to other related works.
[2]AstheresultofaresearchconductedinIberianPeninsula during the period of 2010-2014, proposed that a raise in temperature and increase in the duration and intensity of drought leads to larger wildfires, which threatened the environmentaswellashumanlives.Uponfurtheranalysing, theymanagedtodevelopamodelthatperformsprediction basedonthesurfacetemperatureandsoilmoistureyielding accuracyof83.3%.
[3]Firedetectionsystemshavebeenpromotedimmenselyin thepastfewyearsandhavehelpedinthesafetyofpeople and property against fire hazards. The detection of fire hazards on the other hand can lead to unnecessary false alarmsthatcanbeveryexpensiveiftheoccurrencehappens inacommercialbuilding.Aswell,falsefirealarmshavebeen a nuisance to the fire department and cause tie ups in resourcesandneedlesscommotionthatleadstopanic.The problemthatwasaddressedbythisworkwastodetectfires and reduce the occurrence of false positives in a kitchen environment.
[4]Experimentsareconcludedforthreepartitionshavinga different number of training set instances and testing set instances for forest fire Prediction. Results that best accuracy achieved from model trained with sigmoid activation function is for dataset having5 40 training instancesand540testinginstances,withSinCfunctionitis 85.42%,withradialbasisfunctionitis84.95.
[5]Predictionofwild-fireusingthemeteorologicalfactorshas been proved feasible through a study that revealed the relationship between them. It will be helpful for forest departmenttopreventandrescuewildlifeandresourcesby takingeffectiveandappropriatemeasuresinaccordanceto thescaleoffireaspredictedatitsinitialstage.
[6] Part-1 of a two-part paper is intended to review and categorise research in different fields of science and industrialprojectsthatattempttoaddresswildfireissues. The topics include prediction and prevention means, detectionmethods,monitoringandsurveillancetechniques, suppressionmethods,allocationandmappingalgorithms.
Fig – 1: SystemArchitecture
1.2 Related Work
[1] Research on Event Detection for Forest Fire uses a DistributedFixedPartitioningSVMatbasestationstodetect theevents.Themethodpresentedaboveusesthecompact representation model for categorization, which leads to energy efficiency in a distributed environment. The WSN constructedincombinationofCluStreamandSVMisefficient
[7] In a decision tree-based system, they exposed an HLS basedhardwareimplementationofadecisiontreeclassifier as an IP core for forest fire prediction purposes. The designed DT_IP includes an AXI interface that allows its integration into several architectures based on various processorse.g.,theARMandMicroBlazeprocessorsandalso OpenSourcesprocessors,suchastheOpenRISCandNEO (bymeansofthewishbonetoAXI4protocol).Thedeveloped DT_IP has been integrated into the MicroBlaze based FFP SoC. The hardware implementation results show that the decisiontreeclassifierissuitableforourpurpose,sincethe

hardwareimplementationoftheDTclassifierrequiresfew resources.Intheotherhanditgivessignificantperformance.
[8] ProposalofeffectivedetectionofforestfireusingNeural Network, analysed three algorithms U-Net, U2-Net and EfficientSeg.Modelsweretrainedusingdataaugmentation techniques and two loss functions. Using Corsican Fire Dataset,EfficientSeg,U-NetandU2-NetshowedF1scoreof 0.95,0.94and0.92respectively.Uponanalysingtheresult, theresearchconcludedwith proposingEfficientSegasthe bestperformingmodelforforestfiredetection.

[9]AI-based6layereddeeparchitecturemodelwasevaluated by the RMSE score. The experimental works showed that LSTMbaseddeeplearningapproachhaspotentialintheuse of the prediction of forest fires. Besides, the experiments showedthattheproposedapproachoutperformedtheother machinelearningpredictors.
[10] Either the classical or more recent machine learning approaches could be used for fire occurrence detection of peatlands. These approaches in general can be used in various types of fires, including bush fires, forest fires or peatlandfires.Whenthedataisunbalancedbetweenclasses, the accuracy of the prediction can be improved by preprocessing the data using SMOTE approach, to obtain a balanced sample, together with the application of the ensembleclassificationapproach.
1.3 Existing System
Early research papers analysed the relation between meteorologicalfactorsliketemperature,relativehumidity, windspeedandrainandtheoccurrence,growthandspread of wild-fire. Upon analysing the event, it is found that the above-mentionedfactorshighlyinfluencethefire.Theyalso provedthatthepredictionofwildfireusingsuchfactorsis feasible. Most of the existing systems were focused on detecting the fire after it is ignited and already started destroyingtheresources.Itisdonebycollectingtheforest fire images and applying various machine learning algorithms like Neural Network, Decision Trees etc. Some researcheswerefocusedoncreatingacurated,large-scale datasetusinghistoricalwild-fireaggregatingnearlyadecade of remote sensing data using which they analysed the performanceofvariousmachinelearningmodels.
1.4 Proposed System
Webelievethatdetectionandpredictionoftheimpactofthe fire after its occurrence is not of great use, as most of the resources might already be damaged. So, we propose a predictionsystembasedonmachinelearningtechniqueto predicttheriskofwild-fireevenbeforetheoccurrenceand computestheprobabilityoffireusingmeteorologicaldata. Thishelpstheforestdepartmenttotakenecessaryactionsto controlthefireifiteveroccurs.Inadditiontothis,wealso proposeanimpactpredictionsystemthatcouldestimatethe
area that could be affected by the fire if the probability is higher.Thisdescribestheimpactofthewild-fireevenbefore itoccurs.Itisobservedfromthehistoricaldata,thatnotall wild-fire causes serious damage, as most of them covers lesserarea. Bypredictingtheimpact, wecan estimate the seriousnessofthefire.
2. Implementation
Theuserisprovidedwithaportaltopredictthewildfireinan area.Itcanbedonebyinputtingthemeteorologicalfactors like temperature, humidity, rain and wind speed. These meteorologicalfactorscanbeusedtocalculatethe3moisture codes(FFMC-FineFuelMoistureCode,DMC–DuffMoisture Code and DC – Drought Code) and 2 indices (ISI – Initial SpreadIndexandBUI–BuildUpIndex).
Themoisturecodesaffecttheignitionintheforestcoversand the indices help predicting the spread area of the fire. PredictioncanbedoneusingmanyMachineLearningModels. Butbeforethatwemustprocessthedatathatweobtained fromtheinternet. Usingtheprocesseddataset,wemusttrain theMachineLearningmodel.Wecoulduselogisticregression and linear regression model for simple classification and regressionrespectively.Afterpredictionisdone,theresultis displayedtotheusersonthesameportal.Toachievethis,we consider 6 modules: Data Collection and pre-processing, IndicesCalculation,BuildingRiskPredictionModel,Building ImpactPredictionModel,BuildingUserInterfaceandEmail Alert.
2.1 Data Collection and Pre-processing
Sinceourpredictionsystemconsistsoftwomachinelearning models,wehavetocollectsuitabledatasetsforbothofthem, in-ordertotrainthem.Theriskpredictionmodelmustbea binary classifier which means the result of the prediction shouldbe0or1;0representingnoand1representingyes. The impact prediction model must be a regressor that predictstheareathatcouldbeaffectedbythefire.Sincethese
twomodelshighlydifferfromeachother,thedatasetsthat areusedtotrainthemhastobeprocessedandtransformed to make them suitable for each model. For training the classifier, we use a combination of two datasets that were found on Kaggle and UCI Machine learning repository. A suitabledatasetshouldcontainthefollowingfeatures.FFMC, DMC,DCandclass.
First dataset which is obtained from KaggleisMontesinho NaturalParkDatasetthatcontains337recordsofhistorical wild-fire happened in 2007and 13 features. However, the datasetcannotbedirectlyusedtotraintheclassifierasthe targetfeatureisnotofbinary.Instead,itrepresentsthearea coveredbythefire.Wecanconcludethat,whenthevalueis0, thereisnofireoccurred.Whenthearea>0,wecaninferthat thefireoccurred.So,duringpre-processing,weconvertthe values in the feature from numerical to binary. Also, we remove the irrelevant and unwanted features like xcoordinate,y-coordinate,day,month,temperature,humidity, rain, wind speed and ISI. Now we are left with 4 features: FFMC,DMC,DCandclass.
SeconddatasetwhichisobtainedfromUCImachinelearning repositoryisTheAlgerianForestFireDatasetthatcontains 246 records. This dataset is obtained from two regions: Bejaia and Sidi-Bel Abbes during 2012. It contains 14 features.Afterremovingtheirrelevantfeatures,wewouldbe leftwith4features:FFMC,DMC,DCandclass.Nowwecan combine these two datasets to create the suitable dataset which contains 623 record that can be used to train the classifier. For training the regressor, we make use of previouslyobtaineddatasetfromKaggle.Sincethedatasetis heavily skewed, the regression becomes difficult. Also, the datasetlacksanimportantfeature,BUI,thathighlyaffectsthe spread of wild-fire. It has to be included along the other features.ThiscanbedonebycalculatingBUIforeveryrecord in the dataset and appending the value to a new column named as BUI. Now after processing the dataset, we must remove the irrelevant features which results in the new datasetwith6features:FFMC,DMC,DC,ISI,BUIandarea.

2.2 Indices Calculation
The indices under consideration are based on Canadian forestfireweatherindexwhichincludethe3moisturecodes and2indices.Thecalculationoftheseindicesisprovidedby Canadian Forestry Services in 1984. The formulated equationsmakeuseofthemeteorologicaldatatocompute theindices.
2.3 Building Risk Prediction Model
Since risk prediction is a simple classification problem, logisticregressionmodelisused.Thedecidingfactorofthis classifierworksbasedontheprobabilityoftheevent.When theprobabilitycrossesthethreshold,theresultwouldbe1. If the probability stays behind the threshold, the result
would be 0. Generally, for logistic regression model the thresholdvalueis0.5.
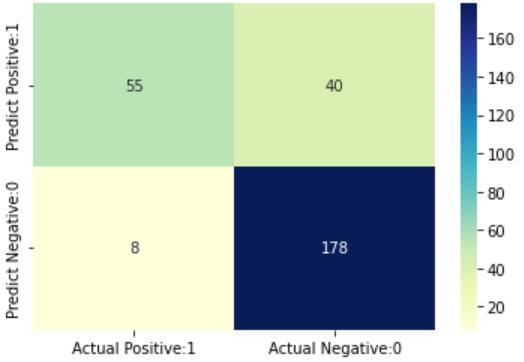
The dataset is divided into training and testing sets, containing 342 and 281 records respectively. After the model is trained, it is fed with the testing set and the predictioniscomparedwiththeactualresult.
Fig-2: ConfusionMatrixofPredictionModel
Theabovefigureshowstheconfusionmatrixofthemodel whichcanbeusedtodeducetheperformanceofthetrained model. Using this confusion matrix, the accuracy of the model can be calculated as Accuracy = (TP+TN)/(TP+TN+FP+FN). The accuracy of the risk predictionmodelisfoundtobe82.92%
2.4 Building Impact Prediction Model
During risk prediction, the model produces a result that contains the probability of occurrence of the fire. If the probabilityishigherthan85%,thenthefireismostlikelyto take place. So, we design an impact prediction model that couldestimatetheareathatcouldbeaffectedbythefire,ifit everoccurs.
Asmentionedbefore,thedatasetobtainedisheavilyskewed; Outof6features,4wereskewed.Toreducetheskewness, weappliedvarioustransformationalgorithmsandobserved theresult.Boxcoxtransformationisfoundtobeaneffective transformationalgorithm whenIcometonormalizingthe leftskeweddata:FFMCandDC.ISIisslightlyskewedtothe rightwhichcanbehandledbysquareroottransformation. Area,a featureofchiefimportancewhichisconsideredas the target feature for the regressor, is heavily skewed to right.Itishandledbylogarithmictransformation.
Impact prediction is considered to be a simple regression problem,soweuselinearregressionwithXGBframework, asXGBisprovedtoout-performvariousotheralgorithms. Aftertestingthemodel,itisfoundthattheRMSE=0.321307
2.5 Building User Interface
User has to be provided with an UI with which theycould interactandperformprediction.Tobuildaninterface,weuse webdevelopmenttoolssuchasHTML,CSSandJavaScript.It consists of 7 input fields: Temperature, Relative humidity, Wind Speed, Rain, FFMC, DMC and DC. The request and responsetotheserverishandledbythepythonFlasklibrary which is a web framework used for backend of the application.Thevaluesfromtheinputareprocessedandfed tothemodeltomakepredictionsandtheresultisreflected ontheUIfortheusertoobserve.
2.6 Email Alert
Afterprediction,iftheprobabilityoffireisfoundtobehigh, analertissenttothedepartmentthroughemailcontaining theinformationabouttheimpactandprobabilityofthefire. ThisisachievedbyintegratingtheMail-GunAPIintheFlask application.Withafreesubscriptionof$0permonth,mail gunallowstheusertosend5000mails/monthwithafixed domainnamethatcannotbechangedunlessweupgradethe plan.Forademo,thereisnoneedforaperfectdomainname. So,wecontinuedwiththefreeplan.
3. CONCLUSION
The proposed system uses logistic regression model to predicttheriskoffireusingthemeteorologicalfactorslike temperature,humidity, rainfall andwindspeed whichare gathered from a particular area. Using the four collected meteorologicalfactors,FireweatherIndex(FFMC,DMCand DC)iscalculatedwhichrepresentsthemoisturecontentof variouslayersoftheforestcover.Usingthisdata,themodel couldpredicttheprobabilityofignitionwithanaccuracyof 82.9%. If the risk is high an alert is sent to the provided email. It is observed that the probability of ignition is directlyproportionaltothetemperatureandwindspeedand inverselyproportionaltothehumidityandrainfall.
When the obtained probability from the risk prediction model isgreaterthan 85%, thefireismostlikelytooccur andthustheimpactpredictionmodelthatisbasedonlinear regression, trained using XG-Boost algorithm, is used to predictthescaleofthefireifiteveroccurs.TheRMSEvalue ofthetrainedregressionmodelisfoundtobe0.382.
The result of the proposed system is helpful in forest fire prevention and rescue. Fire Fighters will be able to take effectiveandappropriatemeasuresiftheriskofwildfirein anareaispredicted.Thus,theproposedsystemmakesuseof the available meteorological factors collected from two differentpartsoftheworldtopredicttheimpactofthewildfire.
3.1 Future Scope
Inadditiontopredictingtheimpactoftheforestfire,wecan also detect if there is any wildlife present in the possible spreadareaofthewildfire.Thiscanbedonebyusingremote sensingimagesinthepredictedareaalongwiththeNeural Networktodetectanywildlifeinthatarea.Ifpresent,they canberescuedordrovetosaferplace.Thishelpsreducing lossoflifeevenbeforethefireoccurs.
REFERENCES
[1] Yashwant Singh & et.al.,(2013), Distributed Event DetectioninWirelessSensorNetworksforForestFires
[2]DavidChaparro&et.al.,(2016).PredictingtheExtentof Wildfires Using Remotely Sensed Soil Moisture and TemperatureTrends
[3]KBDeve&et.al.,(2016),Designofasmartfiredetection system
[4] B. K. Singh & et.al.,(2019).Extreme Learning Machine ApproachforPredictionofForestFiresusingTopographical andMeteorologicalDataofVietnam.
[5]HaoLiang&et.al.,(2019),ANeuralNetworkModelfor WildfireScalePredictionUsingMeteorologicalFactors
[6] Saeed Jazebi & et.al.,(2020).Review of Wildfire Management Techniques Part I: Causes, Prevention, Detection,Suppression,andDataAnalytics
[7] Faroudja ABID & et.al.,(2020), Decision Tree based SystemonChipforForestFiresPrediction.
[8] Rafik Ghali1 & et.al.,(2021).Forest Fires Segmentation usingDeepConvolutionalNeuralNetworks.
[9]NaamanOmar&et.al.,(2021),DeepLearningApproachto PredictForestFiresUsingMeteorologicalMeasurement
[10]DediRosadi&et.al.,(2021).ImprovingMachineLearning PredictionofPeatlandsFireOccurrenceforUnbalancedData UsingSMOTEApproach
[11]MauroCastelli&et.al.,(2015)PredictingBurnedAreas ofForestFires:anArtificialIntelligenceApproach
[12]MutasimMahmoudAl-Kahlout(2020)NeuralNetwork ApproachtoPredictForestFiresusingMeteorologicalData
[13] Krishna Chandra, Atul Kumar Bhardwaj (2015) IncidenceofForestFireinIndiaandItsEffectonTerrestrial EcosystemDynamics,NutrientandMicrobialStatusofSoil
[14]JosepPiñol&et.al.,(1998)ClimateWarming,Wildfire Hazard,andWildfireOccurrenceinCoastalEasternSpain

