“Review On Technological Solution For Rural Sanitation Structure A Case Study Of Village.”
Supriya Patil1, Prof. B.V. Birajdar21Student, Civil Dept. of TKIET Engineering, Maharashtra, India

2Professor, Civil Dept. of TKIET Engineering, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - population living in pastoral area. Since independence, there's a growth of population and presently stands at 125 Cr. The sanitation wasn't at each given any precedence of theliving. Whereas health, husbandry and industrialization entered precedences in 5 time plan by government of India. On completion of 3 times of Swacch Bharat charge, Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation ( MoDWS) organized SWACCHATHON1.0 a Swacch Bharat hackathon which was blazoned on 1st August 2017. Environment sustainability is directly linked to sanitation ( subburaman). Public health conditions relate by Sanitation whichareamortalexcretadisposalandacceptabletreatment ofcleandrinkingwaterandsewage.Sanitationisabecedarian for sustainable development, laying a critical work in promotingmortalhealth,goodandlivelihoodguardingecho systemfrom declination.(sarahdickin,2017).
Key Words: sanitation, groundwater,surfacewater,air, soil, and environment.
1. INTRODUCTION
Sanitationisabroadtermwhichincludessafedisposalof human wastes, waste water management, solid wastes management,watersupply,controlofvectorsofdiseases, domestic and personal hygiene, food, housing, etc. Sanitation and environmental sanitation have the convergenceinmanyaspects,environmentalsanitationis largelyviewedas“thecontrolofallthosefactorsinman’s physicalterrain,health,easing poverty,,enhancingquality oflifeandraisingproductivity-whichareall essentialfor sustainabledevelopment’’(WHO1992).
Fiche et al. (1983) gave a rough guide to the relative importance of different aspects of sanitation as follows: Excretadisposal-25;Excretatreatment-15;Personaland domestic cleanliness-18; Water quality- 11; Water availability-18;Drainageandsilagedisposal-6and
Food hygiene - 17 points. Sanitary household toilet is the mostimportantaspectofsanitation.Besides,restorationof dignity, privacy, safety and social status, sanitation has strongbearingsonchildmortality,maternalhealth,water quality, primary education, gender equity, reduction of
hunger and food security, environmental sustainability, globalpartnershipsandultimatelypovertyalleviation& Improvement of overallqualityof life.Opendefecationis still inpracticein numerous pastoral areas performing in serious social, health, profitable and environmental problems.Openlyleftmortalwastehelpsinpercentageand transmission of pathogens, which carry diseases and infections.Theproblemismostacuteforchildren,women and youthful girls. Children, especially those under 5 are mostpronetodiarrheaandoccasionallyindeed losetheir lives.Lossofnumberofschooldaysisanotherproblemin times of illness. In case of women, lack of sanitation installation frequently forces them to circumscribe themselves by reducing and controlling their diet, which leads to nutritive and health impacts. Women, especially adolescentgirls,faceadvancedpitfallssexualassaultdueto lackofménagetoilets Impactsofgoodsanitation:
Good sanitation has the following impacts on individuals andoncommunity:
•Improveshealth
•Decreaseinmorbidityandmortality
•Improvesman-days
•Improvesproductivity
•Povertyalleviation
•Improveswaterquality
•Minimizesprevalenceofdrop-outinschoolparticularly girlstudents
It is an accepted fact that poor pays directly an laterally more due to bad sanitation. Utmost diurnal stipend base lose out in case of illness due to bad sanitation. Further, othermembersofthefamilywholookafterthesickmember also lose their diurnal earning or training (in the case of children).Inmostoftheruralareashealthfacilityisrarely availableforcingpeopletotaketheadviceofprivatedoctor orquackswhochargeveryhighleadingtomoreeconomic loss. Open defecation has been a deep-confirmed age old sociallyinheritedbehaviorinruralIndia.
Provision of acceptable sanitation content in patrol India hasbeenamajorchallengeduetoitsmiscellaneoussocioprofitableconditions.Hence,evenwithadventoftechnology inruralIndia,substantiveproportionoftheruralpoorstill prefer to purchase a “mobile phone”, rather than on investingforsanitarytoilets,sincesanitationisneitherafelt need nor open defecation is a artistic taboo. The most important challenge for effective implementation of sanitation program in rural areas is that most rural populationbeingpoorlyinformedornotovertly
Consciousof thelinkagebetweensanitationandhealth.Due toinadequateknowledgeandlackof,awarenesstheymostly believe that good or bad health lies due to reasons other thanimprovedorbadsanitation.Anotherimportantbarrier forsanitationisthatthereisnoconceptof
Communityhealthandhygieneinpastoralareas.Wherever, thereisawareness,itislimitedonlytopersonalsanitation andhygiene,notatcommunitylevel.Effectofsanitationcan begauzedonlywhenfacilityandpracticesareadoptedat communitylevel.Bestoptionforimprovedsanitationisby constructionandproperuseofalatrinebythehousehold, whichisownedandmaintainedforitsownuseandbenefit. Such individual toilets can be built through various technologicaloptionstosuitthehousehold’saffordability.
1.1 TOTAL SANITATION CAMPAIGN AND ITS KEY PROVISIONS

Sin 1986, the Rural Development Department initiated India’sfirstpublicprogrammeonpastoralsanitation,the Central Rural Sanitation Program me (CRSP). The CRSP interpretedsanitationasconstructionofmenagetoilets,and concentratedonthecreationofpour-flushtoiletsthrough Tacklesubventionstoinducedemand.Thecrucialissueof motivatinggestechangetoendopendefecationanduseof toiletswasn’taddressed.Asaresulttheprogrammeinthe force driven mode had limited intervention in perfecting pastoralsanitationcontent.Asaresulttherewasonlyjust1 percentannuallygrowthofsanitationcontentthroughout the1990s.
In light of the fairly limited intervention of the CRSP in perfectingthepastoralsanitationcontent,theGovernment ofIndiarestructuredtheprogramme,leadingtothelaunch of the Total Sanitation Campaign (TSC) in the year 1999. TotalSanitationCampaign(TSC)isa
Flagshipschemeof theGovernmentofIndiaadministered by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation. TSC supportsvillcommunitiestoendopendefecationintheir areas and achieve total sanitation, to ameliorate social quality,sequestrationandinsureasepticandhealthyliving terrain. Creation of demand for sanitation from people through Behavior Change Communication (BCC) and supporting them with information on a menu of
technological optionstoconstructandusesafesanitation installation is high ideal of the TSC. Under the TSC, fiscal supportintheformofanincitementisgiventohomesliving BelowthePovertyLine(BPL)forconstructionanduse of toilets.However,themainfocusoftheprogramistocreate sustainable awareness and behavior change among the people,throughcapacitybuildingandmotivationtobuild individualhouseholdlatrines(IHHLs)toownandmaintain. Thekeychallengeinachievingtotalsanitationinvillagesis toprovidesustainabletechnologyaffordableevenforpoor familiesindifferentgeographicalconditionsandalsobring about a change in the knowledge, stations and age–old practicesofthevillagerstowardsopen defecation.Toend this state, furnishing easy access to a restroom and motivatingpeopletousethem
2. BIO DIGESTOR TOILETS:
Bio-digester toilets are constructed to convert human waste into gases and manure. The zero-waste bio digester technology uses psychotropic bacterial like ClostridiumandMethanosarcina(thesemicrobescanlivein coldorhotclimateandfeedonwastetosurvive)tobreak downhumanintousablewaterandgas.
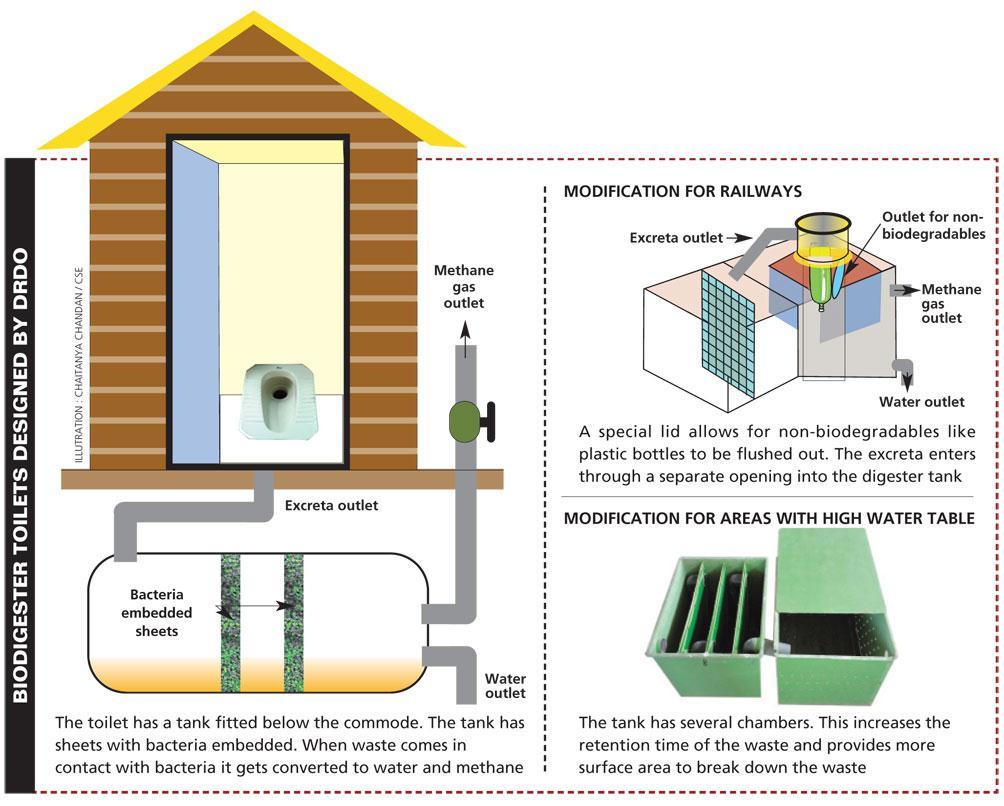
2.1 NUTRIENT CONTENT:
Human faces considered a valuable nutrientsourceinno.ofcountries.Annualamountoftoilet waste is about 520 kg per person. This amount includes altogether7.5kg.ofnitrogen,phosphorus,andpotassium, andsomemicronutrientintheformofusefulplants.Ifthe
nutrients in the faces of one person were used for grain cultivation, it would enable the production of the annual amountofgrainconsumedbyoneperson.Compostingand separatingtoiletshaveenabledthereclamationofhuman excreta and the use of the nutrients contained in it as fertilizer and soil conditioner. In Sweden organic farmers haveinterestinusingliquidmanurelikeurinereasonofthe contentofmacronutrientsandthelowheavymetalcontent.
Itthecirculationofhumanfacesbetweentheurban and rural areas will increase, it must be insured that the qualityandfertilityofsoilsarenotnegativelyaffectedinthe longtermperspective.Thismeansinthepracticethatthere is a need for research on efficiency and environmental impactsofthisorganicfertilizer.
Nutrientssuchasnitrogen,phosphorousandpotassium play an important role in the growthofplants.Ingeneral, nitrogen and potassium make up about 80 percent of the total mineral nutrients in plants; phosphorous, sulphur, calcium and magnesium together constitute 19 percent, whileallthemicronutrientstogetherconstitutelessthan1 percentNitrogen is responsiblefor the dark greencolour ofstem andleaves,vigorousgrowth, branching/ tillering, leaf production, size enlargement, and yield formation. Phosphorousisusedforgrowth.celldivision,seedand fruit development..Resistance of plants todiseaseincreaseby Potassium also creates winter hardiness and drought resistance Italsoincreasesgrainplumpnessand growth of fruit androotvegetables.
Nutrients present in soils are consumed by crops to produce food and other products forthebenefitofhuman beings andanimals.Cropproductsareoften consumed far awayfromtheproductionsites,sometimes thousands of kilometresawayinanothercountry
2.2.PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
As per MoDWS report there are lots villages are facing sanitationproblems.Becauseofthegeographicalconditions thenumbersofguttersarelessinsomeofthevillages.There aresomanypoorvillageswhicharefacingtheproblemslike poor maintenance, and division of toilet wastewater to plants designed for domestic waste. Due to lack of awarenessandbackwardmentalitypeoplepracticesopen defecation.Itcauseslotsofserioushealthissues.Duetolack of information people don’t know the importance of degradation of fecal matter. Improper planning causes illiteracyaboutsanitationstructuresanditscleaning.
2.3 USE OF SEWAGE SLUDGE
IntheNordiccountriesbetween30to48%ofsludgeisused inagriculture.Richinorganicmatterandnutrients,mostly nitrogen and phosphorus, stabilized sludge is used as a fertilizerandsoilconditionerinagriculture.Sludgeisrather
poor in other macro-nutrients, although lime-stabilized sludge contains significant amounts of calcium and magnesium. About a half of the micro-nutrients, copper, zinc,andmanganese,areusableforplants.Thefertilizing value of sludge is weakened by the fact that its nutrient balancedoesnotcorrespondtothenutrientneedsofplants; sludge is poor in nitrogen and rich in phosphorus. The amountofnitrogeninsludgewillincreaseinthefuture,if the removal of nitrogen from wastewater becomes more efficient.Thefertilizingeffectofthenitrogencontainedin thesludgeisslowbutlong-lasting,andthesameappliesto phosphorus,whichtakesyearstobereleasedintothesoilto be used by plants. Organic matter usually constitutes 5060%ofthedrymatterofmechanicallydriedsludge,whichis whytheuseofsludgeinagricultureincreasestheamount organic substances in cultivated land. Above all, sludge is most beneficial in mineral soils. An increase in organic matter in the soil improves the structure and water economy of the soil and stimulates microbe activity. It improvesthestructureandwatereconomyofthesoiland stimulatesmicrobeactivity.Italsoeffectivelybindsvarious harmfulsubstances,suchasheavymetals,preventingtheir actiononthesoil.

3.
We created a survey form it includes annual income,gov.schemes,hometype,privettoilets,ornotoilets etc. After the completion of survey it gives lots of informationandusingthisdataweanalyzetheproblemsof thatvillage.
4.LINKAGES BETWEEN SANITATION, HEALTHAND TOILETS
beforeeatingmeals,andafterdefecation.Sanitation hasa directimpactsonhealth Lackofawarenessofthelinkages betweensanitationandhealth,andhealthandproductivity makesitdifficulttoeffectivelyimplementmostsanitation programmesinruralIndia.Often,theybelievepoorhealth and poor productivity is borne of factors other than sanitation. The SBM (G) programme highlights social and health benefits of sanitation leading to demand driven approach,makingitsuccessfulinruralarea
1) Human waste and disease transmission.
Humanexcretacontainsafullspectrumofpathogensthat transfer from diseased to healthy individuals through several direct and indirect routes, causing infections and superimposedinfections.Inruralareasitisestimatedthat about80%diseasesarewaterbornediseases directlyor indirectly linked with human waste. Infections enters humanbodythroughfluids,fingers,flies,food,andfields
2) Pathogen in human excreta
There are several bacterial pathogens in human waste. Some common bacterial and helminth pathogens are describedbelow
Table 1 Bacterial Pathogens in Human Excreta
Bacteria Diseases Reservoir
Escherichia coli Diarrhoea Human
Salmonella typhii Typhoidfever
S. paratyphii Paratyphoidfever
Table 2: Helminth pathogens in human excreta
Helminths Common name Diseases Transmissi on
Ancyclostoma duodenale
Ascaris lumbricoides
Hookworm Hookworm Human-soilhuman
Roundworm Ascariasis HumanHuman-soil
Taenia saginata Beefworm Taeniasis HumanCow-Human
T. solium Pork
Tapeworm Taeniasis Human-Pigs Human
Trichuris trichura Whipworm Trichuriasis Human–Soil-Human
4. CONCLUSIONS
Villageishavinglesssanitationfacilitiesandhaving lessnumberoftoilets.Villageisfacingsanitationproblem duetogeographical conditions,poormaintenance,due to lack of awareness and backward mentality of people. By monitoringtheusageoftoilet,itisseenthatthosepeople havingtoiletfacilityarenotusingtoiletsregularlyandalso maintenance is poor. It is observed that human excreta contain nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium and these gases have wide applications in various field like agriculturaletc.
5. REFERENCES
1. Avvannava S.M. & Mani M., (2008), “A conceptual modelofpeople’s approach to sanitation”,Scienceof theTotalEnvironmentvol.no.390pageno.1-12.
Human
Human
Other salmonellae Food poisoning and othersalmoellioses
Shigella spp, Bacilliarydysentry
Vibrio cholera Cholera
Other vibrions Diarrhoea
Human
Human
Human
Human
2. Booklet of Asian Development Bank, (2016), “Water for All Series 18: India’s sanitation solutions for All: How to make it happen smart Sanitation Solutions” , Booklet published at 4th World Water ForumheldatMexico.
3. Chi-Chung T., Brill E.D.,Pfeffer J.T.(1987), “Comprehensive Model Of Activated Sludge Wastewater Treatment System” , Journal of Environmentalengineering,vol.113,no.5,.ASCE,ISSN 0733-9372/87/0005-0952/$01.00.paper no.21841.113(5):pageno.952-969.
4. Chi-Chung T., Brill E.D.,Pfeffer J.T.(1987), “Optimization Techniques for Se c"ondary Wastewater Treatment System” , Journal of EnvironmentalEngineering,vol.113,no.5,.ASCE,ISSN 0733-9372/87/.paper no.21840.113(5):page no .935-951.

5. Crocker J., Saywell D., Bartram J. (2017), “Sustainability of Community –LedTotal sanitation Outcomes :Evidences from Ethiopia And Ghana, Elsevier” International Journal of Hygiene and EnvironmentalHealth,pageno.551-557

6. Environmental & Urbanization (2003), “Water sanitation and drainage: ensuring better provision with limited resources” environmental & urbanization,pageno.03-10.
7. Harada H. (2012), “Urine-Diverting system for securing sanitation in Disaster and Emergency Situation, Leadership and Management in Engineering” 12(4):pageno309-314.
8. Huang X.,(2016),“Electrochemical disinfection of toiletwastewaterusingwastewaterelectrolysiscell”, WaterResearch92(2016)pageno.164-172.
9. Kaminsky J. & Javernick A., (2014),“Theorizing the internal social sustainability of sanitation organization” ,ASCE,vol.no.141(2).
10. Kavita Wankhade (2015). “Urban Sanitation in India: Key shift in the national policy frame”, International Institute for Environment and Development,pageno.555-5
11. Mark Sanders MEng (Hons) (2018),“Sustainable Sanitation:fertilizerfromhumanwaste”,Wasteand Resources Management vol.no.168, page no.144151.
12. Reilly K., Elizabeth L. (2014), “The toilet tripod; UnderstandingsuccessfulsanitationinruralIndia,” Elsevier-Health&Place2943-51.
13. Sahoo K.C., Hulland K.R.S.,Caruso B.A.,swalin R.,Freeman M.C.,Panigrahi P., Dreibelbis R.,(2015),“Sanitationrelatedpsychologicalstress:A grounded theory study of women across the lifecourse in Odisa, India”, Social science & medicine, vol.no.139,pageno80-89.
