FUTURE OF SHOPPING WITH METAVERSE
SHRISHTY JAIN1 , VIPLOV SINGH2 , SHIVANGI MISHRA3 , DR. POOJA GUPTA4 , MS. RUCHI GOEL5
1Student, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Delhi, India

2Student, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Delhi, India
3Student, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Delhi, India
4Professor, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Delhi, India
5Professor, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Delhi, India ***
Abstract The use of metaverse shopping applications has the potential to enhance the customer experience and drive increased sales and customer satisfaction. A metaverse shopping application is a 3D program that allows users to browse and purchase products in a virtual world. These applications can be created using technologies such as Mozilla Hubs, Three.js, and A-Frame, which offer powerful tools for creating immersive and interactive shopping experiences. The concept of a metaverse has been popularized in science fictionliteratureandhasbeenusedtodescribeacollective virtual shared space, created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical reality and physically persistent virtual space, including the sum of all virtual worlds, augmented realities, and the internet. These technologies can be used to create virtual storefronts, animate and interact with products, and integrate ecommerce systems for making purchases within the virtual environment. This research paper aims to explore the possibility of online shopping using a metaverse shopping application, a collective virtual shared space where users caninteract with each other andwith virtual objectsandenvironments.
Keywords Metaverse, Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality, 3 Dimensional modeling, online shopping, virtual environment, Non Fungible Tokens, Blockchain, ecommerceplatform
I. INTRODUCTION
The term "metaverse" refers to the shared virtual space created by the convergence of virtual augmented physical reality and physically persistent virtual space, including the sum of all virtual worlds, augmented reality, and the Internet. The concept of the Metaverse has become commonplace in science fiction literature and refers to the convergence of virtually augmented physical reality and physically persistent virtual space, including all virtual worlds, augmented reality, and the sum of augmented reality. is used to describe the collective virtual shared space created by and the internet. The term was coined by science fiction writer
Neal Stephenson in his 1992 novel Snow Crash. In the context of virtual reality, the metaverse is often used to represent a shared virtual space that users can access and interact with in real time using their avatars or digital representations. This space can be used for a variety of purposes including socializing, entertaining, teaching, and working. The metaverse is sometimes called a "virtual world," "virtual reality," or "virtual space." The concept of the metaverse has received a great deal of attention in recent years due to rapid technological advances and the growing popularity of virtual and augmented reality. Many companies and organizations are exploring the potential of the Metaverse as a platform for new forms of communication, collaboration, and entertainment, and areinvestinginresearchanddevelopmenttoexpandthe possibilities of virtual and augmented reality technologies.
A blockchain is a decentralized decentralized database that maintains an ever-growing list of records called blocks.Eachblockcontainsatimestampandalinktothe previous block, forming a chain of blocks. The database is managed by a peer-to-peer network that collectively adheres to protocols for validating new blocks. Once recorded, the data in a block cannot be retroactively changed without changing all subsequent blocks and obtaining approval from the network. This makes it a safeandtransparentwayto store andtransfer data and ensures that data stored on the blockchain is tamperproof. The first and most famous application of blockchain technology is the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, createdin2009.
However, the possible uses of blockchain technology extend far beyond cryptocurrencies and financial transactions.Otherpotentialapplicationsincludesupply he chain management, voting systems, and the creation of virtual worlds and avatars in the metaverse. Blockchain technology is based on the use of cryptography to secure transactions and verify the authenticityofdata.Itreliesonadecentralizednetwork ofcomputersratherthanacentralauthoritytomaintain
the integrity of data stored on the blockchain. This decentralized structure makes it difficult for individuals or groups to manipulate data on the blockchain and ensuresthattheinformationstoredontheblockchainis accurateandup-to-date.
Anon-fungibletoken(NFT)isatypeofdigitalassetthat represents ownership of a unique item or asset. NFTs areuniqueinthattheyarestoredontheblockchainand are not 1:1 exchangeable with other tokens or assets. This is in contrast to "fungible" tokens, such as cash or cryptocurrencies, which can be exchanged one-for-one withothertokensofthesametype.NFTsarecommonly used to represent ownership of digital art, collectibles, and other virtual items. It can also be used to represent physical assets such as real estate or rare collectibles. NFT uniqueness is verified on the blockchain, providing apermanentrecordofownershipandauthenticity.NFTs havegainedalotofattentioninrecentyearsastheyare used to sell digital art and collectibles for large sums of money. They are also used in various other applications such as creating virtual properties and representing ingame items in online games. The use of NFTs has the potential to revolutionize the way digital and physical assets are bought and sold, creating new opportunities forcreatorstomonetizetheirwork.
II. Related Work

Janna Anderson and Lee Rainie in their research [8] discussthepotentialfutureofthemetaverseasavirtual world where users can interact in real-time. The research explores the potential impact of the metaverse onvariousindustriesandsocietyasa whole. Itsuggests that the metaverse has the potential to revolutionize these industries and provide benefits such as enhanced social interactions, improved education, and increased accessibility. However, it also highlights the potential negative impacts such as addiction and breakdown of socialcohesion.
Overall, the paper suggests that the metaverse has the potentialtobeamajorcomputingplatforminthefuture and will likely have a significant impact on society and variousindustries.
Vitalik Buterin[9] introduces Ethereum, a decentralized platform for smart contracts built on blockchain technology. It allows developers to create and deploy decentralized applications (DApps) on a global, decentralizednetwork.Ethereumisdesignedtobemore general-purpose than Bitcoin and features smart contracts, and self-executing agreements that automate business processes and reduce intermediaries, making transactions faster and more efficient. The paper presents Ethereum as a decentralized platform for building and running DApps and smart contracts, enablingnewformsofcollaborationandvaluecreation
Another author explains[10] that Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are unique digital assets that cannot be exchanged like-for-like, making them ideal for use in fields such as virtual events, digital collectibles, play-toearn games, and metaverses. Focuses specifically on the gaming industry, including play-to-earn games and metaverses, which are immersive and shared virtual worlds that allow users to engage in various activities and trade items using their own economy and currencies.The authors use a combination of traditional financial analysis and network analysis to study the play-to-earnandmetaversetokenmarket,findingthatit exhibits high volatility and strong correlations between different tokens. They also find that the market is influenced by both external factors, such as the overall cryptocurrency market, and internal factors specific to thegamingindustry.
Sir Burke discusses the potential of virtual shopping, also known as online shopping, and its potential to revolutionize the retail industry[7]. He explores the benefits of virtual shopping for both consumers and retailers, including convenience, lower costs, and the ability to offer a wider range of products. Burke also discusses the challenges that virtual shopping poses, includingissuesofsecurityandprivacy,andtheneedfor retailers to adapt their marketing strategies to the virtual environment. Overall, the paper presents a detailedanalysisofthepotentialofvirtualshoppingand itsimpactontheretailindustry.
DavisetalandCagnina [2,6] examinedtherelationship betweenonlinestoreatmospherics(i.e.,thesensoryand psychological cues in an online shopping environment) and shopper responses. The authors developed a model to test this relationship and conducted a study to test their model using an online survey. The results of the study indicated that online store atmospherics had a significant impact on shopper responses, including affectiveresponses(e.g.,feelingsofpleasureorarousal), behavioral intentions (e.g., intention to purchase), and actual purchasing behavior. The study also found that different types of online store atmospherics (e.g., visual, auditory, and tactile) had different effects on shopper responses. Overall, this study suggests that online retailers should consider the impact of online store atmospherics on shopper behavior and carefully design their online shopping environments to optimize the shoppingexperiencefortheircustomers.
The evolution of e-business models and the emergence of virtual worlds as a new platform for online business. The authors argue that virtual worlds offer unique opportunities for businesses to create immersive and interactiveexperiencesfortheircustomersandthatthey representthenextstageintheevolutionofe-business.
The article also discusses the challenges and limitations of virtual worlds as a business platform, including security, privacy, and intellectual property issues. The authors conclude by discussing the potential future developments of virtual worlds as a platform for ebusiness and the potential impact on businesses and consumers.
From the study of available literature on Metaverse, blockchain,andNFTs,ithasbeenconcludedthata wide range of items, including virtual real estate, art, and collectibles, can be used in a metaverse, which is a virtual world where users can interact and engage with eachother.TheuseofNFTsinametaverseallowsforthe creation of unique, scarce, and tradable digital assets that can be used for various purposes, including shopping. Moreover, it has been identified that existing techniques or methods are not collaborative enough to provideagreatexperienceandeaseofuse.Thisincludes audio and video best practices for creating immersive and engaging shopping environments, as well as strategies for leveraging the unique features and capabilities of a metaverse to create a seamless and enjoyableshoppingexperienceforusers.
Theintroduction(sectionI)providesanoverviewofthe main topic of the paper and introduces some of the key concepts or terms that will be discussed in the paper.
Section II discusses previous research in the field, including research on blockchain, NFTs, and the metaverse,andhowitrelatestothetopicofshoppingin themetaverse.
Theprocessflowdiagram(sectionIII)likelyoutlinesthe steps or stages involved in the project or research describedinthepaper.
The implementation (section IV) likely describes how the project or research was carried out, including any methodsortechniquesused.
The results (section V) likely present the findings or outcomesoftheprojectorresearch.
Thereferences(sectionVI)likelylistthesourcescitedin the paper, including any previous research or resources used.

III. Process Flow Diagrams
Theoverallapproachisbroadlydividedintotwomodels as
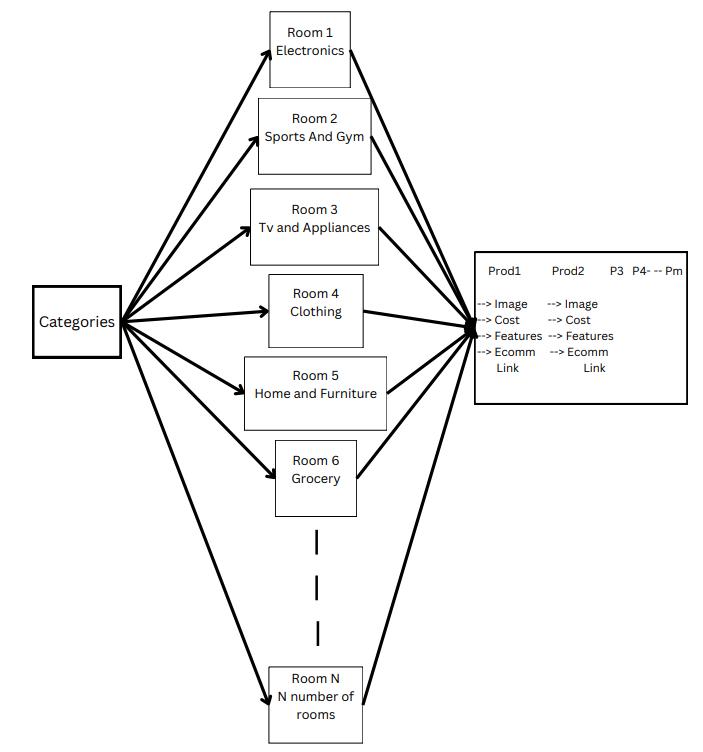
A.CollaborativeecommercewebsiteasshowninFig1.1
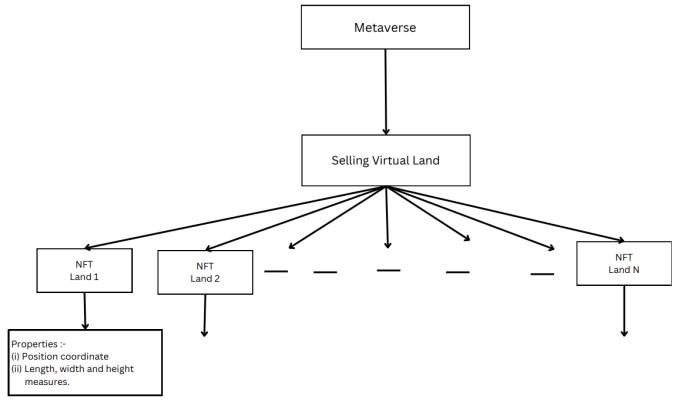
B.MetaverseforbusinessmenasshowninFig1.2
Both of these models combined solve a lot of crucial problemswhichwillbediscussedinthefurthersections. Thestructureofthesemodelsareasfollows.
Model A is how the various users will see our portal as. The platformis broadlydivided intomultiplecategories whichconnecttoaroom,whichcontainsalltheproducts of that particular category, where users can talk, view each other and select an avatar while roaming around theroom.
For example in Fig. 1.1, Rooms 1,2,3…n represent Electronics, Sports and Gym, …, Grocery respectively. Thetotalnumberofroomscanbetakenasn,whereeach n is a collection of ‘m’ products and the detail of each product.
Model B explains how the portal will work for businessmen who want to buy a piece of land in our metaverse. They will be able to buy /purchase a land areawiththehelpofsmartcontractsbyconnectingtheir e-wallet to the portal. Now that that area is theirs, they can customize it however they want with the help of a developer and can customize their shop in multiple possible ways. The process has been shown in Fig. 1.2, where each NFT represents a piece of land. The no. of NFTscanbetakenas‘n’whereeachnhaspropertieslike positionandmeasurementsstoredatthebackend.
IV. Implementation

To implement collaborative ecommerce website - study aimstoexplorethepotentialuseofthemetaverseinthe fieldsofvirtualshoppingandcollaborativeshopping.To doso,wedevelopedavirtualreality(VR)simulationofa trainingscenarioinaspecificpartofanalreadyexisting shoppingwebportal,flipkartonlineshoppingwebsite.
ThesimulationwasdevelopedusingthelibraryThree.js with javascript, Mozilla Hubs and Spoke. The simulation consisted of a series of actions and portals which were mostintuitiveinorderfortheelderlypeopletonavigate through the shopping website instinctively. It is designed to be least intimidating. The tasks were designedtomimicreal-worldscenariosandweremeant to cooperate with the users’ knowledge and skills along withtheirinstincts.
The mentioned simulation aims to develop a projectbasedlearningto explorethepotential ofthemetaverse as a platform for creating a collaborative online shopping experience, which the current portals clearly lack, an approach that emphasizes the improvement of the whole experience through the completion of authenticandmeaningfulvirtualroomscreatedwiththe help of Mozilla Hubs Spoke. To conduct the study, we implemented a project-based learning approach in a virtualrealityenvironmentwithinthemetaverse.
It has been tested with a diverse student population. A total of 20 users tested the demo, where the group includedpeoplefromvaryingagesandbackgrounds.The demo was designed to be interdisciplinary and focused onproblem-basedlearning.
To implement metaverse for businessmen - a land was created and a smart contract, written in solidity, was developed on mix.ethereum.org to set up buildings and configure their properties, such as dimensions and positioncoordinates,ontheland.Thecontractwasthen deployed on the Polygon Mumbai test network and connected to a portal, allowing the NFTs representing
the land to be displayed in a metaverse and purchased bybusinessownerswhocanmintthem.
V. Result
The result analysis has been done by comparing the existing scenario to the proposed scenario with respect tofewpropertiesasshowninTable1.1.
Table1.1Comparingexistingandproposedscenariofor modelA
Domain Existing Scenario Proposed Scenario
User Preferences poorly designed or difficult to navigate a cluttered or confusinglayout can make it difficult for users to find what they are looking for and can contribute to this frustration.
Collaborative Environment difficult for multiple people toshoptogether and make decisions about purchases in real-time.
Make shopping more interactive, appealing to younger consumers and providing a sense of community and social interaction.
real-world setting. Collaborative environments have the potential to enhance the future of online shopping by addressing all issues.
Differently abledFriendly Offline shopping can be difficult for differentlyabled individuals due to physical barriers, a lack of accessibility features, limited product selection, and socialisolation.
in the future could provide accessibility features, convenience for individuals with mobility impairments or those in rural areas, socialization opportunities, and customization options.
InferencesfromthemodelA:
1. User preferences:
Incurrentscenarios,poorlydesignedordifficult tonavigatee-commercewebsitescanfrustrateusersand discourage purchases. This canbecaused by a cluttered orconfusinglayout.
Ane-commercesitewithaclutteredorconfusinglayout can be difficult for users to navigate and find what they are looking for. This can lead to frustration and users leavingyoursitewithoutmakingapurchase.
In future scenarios, the proposed interface can make shopping more interactive and enjoyable. This is especiallyappealingtoyoungerconsumerswhoareused tointeractiveandimmersiveexperiences.
Many gamified shopping experiences include elements ofcompetitionandcollaboration,sonewuserinterfaces canprovideasenseofcommunityandsocialinteraction. This could make shopping less isolated and more appealingtoconsumers.
Many gamified shopping experiences include tailored recommendations and offers based on consumer preferencesandbehavior,allowingplatformstoprovide asenseofpersonalizedattentionandcustomization.
2. Collaborative Environment:
In the current scenario, online shopping lacks a supportiveenvironmentinseveralrespects

. It can be difficult for multiple people to shop together and make real-time purchasing decisions. In brick-andmortar stores, it's easy for friends and family to discuss and decide together what to buy. However, in an online environment,thiskindofconversationandcollaboration canbemoredifficult.
Another reason online shopping lacks a collaborative environment is the lack of social interaction. When shopping in brick-and-mortar stores, it's common to have conversations with store clerks and other customers who can assist in decision-making and add a socialelementtotheshoppingexperience.
In addition, online shopping lacks a collaborative environmentasitisdifficulttogetasenseofhowitems will look or fit in the physical environment. There is a possibility. It's easy to try on clothes and see how furniture fits in a physical store, but not in an online environment. This allows people to make informed decisionsandItcanbedifficulttocollaboratewithother userswhenmakingpurchases.
Overall,onlineshoppingoffersmanybenefitsintermsof convenience and efficiency, but may lack the collaborativeandsocialelementsofshoppinginstores.
Collaborativeenvironmentshavethepotentialtogreatly improve the future of online shopping. Here are some potential benefits of a collaborative environment for futureonlineshopping:Improveddecision-making:
In a collaborative environment, shoppers make more informed purchasing decisions by sharing opinions and reviews, comparing prices and features, and seeking advice.Ican.fromothers.
EnhancedSocialExperience:Collaborativeenvironments are more social by allowing users to browse and shop with friends and others, and receive recommendations and advice from others. Give your users an interactive shoppingexperience.
Increased accessibility: Collaborative environments make online shopping more accessible for people with disabilitiesandmobilityissues,aspeoplecanshopfrom thecomfortoftheirhomesinsteadofgoingtoaphysical store.
Increased Convenience: Collaborative environments allow shoppers to shop anytime, anywhere, providing greater convenience than traditional brick-and-mortar stores. Personalized Recommendations: Collaborative environmentsallowonlineshoppingplatformstocollect data about shopper preferences and behavior and use that information to provide personalized recommendations to personalize the shopping experience.Adjustable.
Overall, collaborative environments shape the future of online shopping by improving decision-making, providing a more social and interactive shopping experience, improving accessibility, and providing more convenient and personalized recommendations. It has thepotentialtobegreatlyimproved.
The result analysis for Model B has also been done by comparing the existing scenario to the proposed scenario with respect to few properties as shown in Table1.2.
Domain Existing Scenario Proposed Scenario
Reach and abilitytoscale Offline marketplaces have limited
Online marketplaces have a wider
Ability to customize or personalize the shopping experience
customer reach due to physical location.
Do not offer the same level of customization or personalization as online marketplaces, which can make it more difficult for sellers to tailor their products to the specific needs and preferences of their customers.
customer reach due to internet accessibility.

Online marketplaces offer more customization options than offline, allowing sellers to better meet specific customer needs andpreferences.
One of the main limitations of offline marketplaces is that they may not offer the same level of customization and personalization as online marketplaces. This can make it difficult for sellers to tailor their products and services to the specific needs and preferences of their customers.
For example, online marketplaces often offer sellers a widerangeofcustomization.Wecanprovideheroptions foryourproduct.B.Differentsize,colorormaterial.This allows sellers to better serve the specific needs and preferences of their customers. In contrast, offline marketplaces may offer fewer customization options, making it difficult for sellers to meet their customers' specificneedsandpreferences.
3. Ability to offer a wide range of payment options
Abilityto offera wide range of payment options
Offline marketplaces are not very friendly regarding varied payment options.
An online metaverse shopping portal can include all the possible payment options.
Thedetaileddiscussionhasbeendoneinfurthersection.
InferencesfromthemodelB:
1. Reach and ability to scale
In the current scenario, one of the main limitations of offline marketplaces is that they are limited to the physical location of the marketplace. This means that sellers can only reach customers who are physicallypresentatthemarketlocation.
This is in contrast to online marketplaces, which can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows sellers to reach a much wider audience, expandtheirbusiness,orreachnewmarketswithease.
2. Ability to customize or personalize the shopping experience
An offline marketplace is a physical location where sellers can sell their products and services directlytocustomers.It'saconvenientandeffectiveway forsellerstoreachcustomers,butitcanalsohavesome limitations when it comes to customization and personalizationcomparedtoonlinemarketplaces.
One of the main limitations of offline marketplacesisthattheycannotofferasmanypayment options as online marketplaces. This can limit seller flexibilityandmakeitdifficulttoaccommodatecustomer preferences.
For example, online marketplaces often allow sellers to offer a wide range of payment options, including: B. Credit cards, debit cards, e-wallets, mobile payments. This allows sellers to better meet their customers' specific payment preferences. In contrast, offline marketplaces may not offer as many payment options, limiting the flexibility of sellers and making it harder to accommodatecustomerpreferences.
Additionally, online marketplaces often allow sellers to process payments more quickly and efficiently. This is more convenient for both sellers and customers. In contrast,offlinemarketplacescanrequiremoretimeand effort to process payments, which can be an inconvenience for both sellers and customers. Marketplaces can be a convenient and effective way for sellers to reach customers, but they can limit a seller's flexibility and make it difficult to accommodate preferences when it comes to payment options. It also presents some challenges and limitations that it has. of theircustomers.
VI. Future Scope
The work discussed here can be incorporated with more collaborative shopping experiences into the metaverse and work towards customizable avatars and storing them with a user's ID. The NFT-based Virtual Space can be improved by creating profiles for sellers/businessmen and making the process of buying andsellingvirtual landsaccessibletothem.Thissection canalsobeworkeduponbymakingitscalable,requiring a good world building around it and having an endless
scope of creativity. The collaborative shopping experience can be made better by focusing on finding a way to execute collaborations that is more suitable for scalability and can handle a large audience at once. The current method of creating rooms with Mozilla Hubs (Spoke)isseenasconvenientbutnotidealforscalability asitcan'thandlelargeaudiencesatonce.
VII. Conclusion
The limitations of current online shopping experiences and the potential benefits of incorporating collaborative environments in the future of online shopping has been discussed in this work. The current onlineshoppingexperiencescanbefrustratingforusers due to cluttered or confusing layouts and lack of social interactions.The proposedinterfacecanmakeshopping more interactive and fun, providing a sense of community and social interaction, and a sense of personalized attention and customization. Collaborative environments in online shopping can improve decisionmaking by allowing shoppers to work together and share opinions and reviews, enhance social experience by providing more social and interactive shopping experience, increase accessibility for people with disabilities or mobility issues, provide greater convenience, and tailor the shopping experience to individual users through personalized recommendations. Overall, it has been inferred that collaborativeenvironmentshavethepotentialtogreatly enhancethefutureofonlineshopping.
VIII. References
[1] Vineet, S., Swetha, S.V., & Rani, M.N. (2021). The advent of virtual reality in the future of e-commerce. BusinessStudiesJournal,13(S3),1-8.
[2]. Cagnina, M. R., & Poian, M. (2009). “Beyond EbusinessModels:TheRoadtoVirtualWorlds.”Electronic CommerceResearch,9(1),49-75.
[3]. Bourkalis, M., Papagiannidis, S., & Li, F. (2009). Retail spatial evolution: paving the way from the traditional to metaverse retailing. Electronic Commerce Research9(1):135-148.
[4]. Lee, Lik-Hang & Braud, Tristan & Zhou, Pengyuan & Wang, Lin & Xu, Dianlei & Lin, Zijun & Kumar, Abhishek & Bermejo, Carlos & Hui, Pan. (2021). “All One Needs to Know about Metaverse: A Complete Survey on Technological Singularity, Virtual Ecosystem, and Research Agenda”, JOURNAL OF LATEX CLASS FILES, VOL.14,NO.8,SEPTEMBER2021
[5]. M. Buffa & J.C. Lafon. (2000) 3D virtual warehouse on the Web. In Information Visualization, 2000.
Proceedings. IEEE International Conference on. 479–484.

[6]. Eroglu, S. A., Machleit, K. A., & Davis, L. M. (2003). “Empirical Testing of a Model of Online Store Atmospherics and Shopper Responses.” Psychology & Marketing,20(2),139-150.
[7]. Burke, R. R. (1997). “Do you see what I see? The Future of Virtual Shopping.” Journal of the Academy of MarketingScience,25(4),352-360.
[8]. "The Metaverse in 2040" authored by Janna AndersonandLeeRainie.
[9]. “Ethereum: A Next-Generation Smart Contract and DecentralizedApplicationPlatform"byVitalikButerin
[10] “The new crypto niche: NFTs, play-to-earn, and metaversetokens”DavidVidal-Tom´
[11] Sparkes, Matthew. "What is a metaverse." (2021): 18.
[12] Wang, Yuntao, et al. "A survey on metaverse: Fundamentals, security, and privacy." IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials (2022).
[13] Wang, Yuntao, et al. "A survey on metaverse: Fundamentals, security, and privacy." IEEE CommunicationsSurveys&Tutorials(2022).
[14]. Agarwal, Udit, Kuldeep Singh, and Rajesh Verma. "An Overview of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFT)."
[15] Wang, Yuntao, et al. "A survey on metaverse: Fundamentals, security, and privacy." IEEE CommunicationsSurveys&Tutorials(2022).
