Application of Augmented Reality for Engineering Graphics
Raj Sanghrajka1 , Aditya Hendre2 , Sanjay Lohar31Student, rajsanghrajka17@gmail.com
2Student, adityahendre22@gmail.com
3Assistant Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, VCET, Maharashtra, India

Abstract - Learning how to transfer information from 2D sketch or design to manufacture is the main idea behind the Engineering Graphics (EG) subject. It plays an important role for an engineering student to learn how to study 2D sketches and turn them into engineering structures. Thus, its crucial role for engineering college to teach and train the students who can communicate in and understand the Graphical representation language. As the lecture timings are limited in the classroom, it might be difficult and challenging for the faculty to relate the 3D geometry and its 2D projections and also it will be difficult for the students to understand the relations effectively. In this paper, we have discussed the advantages and difficulties in adopting Augmented Reality (AR) in engineering graphics. We studied and created an AR based solution specially for engineeringgraphics training. The approach aims in creating awareness and built interest in learners. Our main aim is to use AR system for teaching engineering graphics and provide personalised training experience to students. The AR application simplifies complex relationship and make it easier for the learners to understand which will be extremely helpful. Faculties have found this AR based approach to be a good and useful teaching technique. Using AR technology for learning different venture may prove popular in upcoming time.
Key Words: Engineering Drawing; Augmented Reality; Teaching tool
1.INTRODUCTION
Technologyknownasaugmentedreality(AR)canincrease thesenseoforiginalityandgiveadditionaldetailsaboutthe outsideenvironment.Manyindustries,includinghealthcare, business,andeducationuseaugmentedrealitytechnology. Thisprojectintroducesaugmentedrealitytotheengineering drawingcourse.Engineeringsketchingisaknowledgethat students rarely encounter, making it challenging to learn The research suggests a practical augmented reality (AR) application (AR app) to maintain close contact with the models and views. Real views and virtual models are effectivelymergedwiththeaidofanARsoftware.Touching the screen will allow you to move and rotate the models. Thus, using a mobile phone for excellent engineering drawing study is advantageous for students. Students' spatialthinkingisimprovedandtheirspiritofinventionis fosteredbytheinteractivelearningenvironment.
This project's goal is to find the application of augmented realityinengineeringgraphics.Severalelectronicdatabases wereusedtodiscoverarticlespublishedbetween2000and 2016inordertoaccomplishthegoalofthiswork.Alimited number of keyword combinations, including augmented reality, engineering drawings, engineering education, and teaching methodology, were utilised to search for related articles. The review's conclusions demonstrate that the application of augmented reality can improve educational opportunities for students and their ability to deal with challengingengineeringdrawingconcepts.Tofigureoutthe challengesintheengineeringdrawing,severalresearchers havecreatedaugmentedrealityteachingaids.Whenaresult, asmorestudyisdoneontheaugmentedrealitytechnology, theresultswillundoubtedlyimproveengineeringdrawing classes.Asaresult,theteachingaidscreatedasaresultof theresearchwillraisethebarforinstructionandlearning, whichwillbeadvantageousforbothteachersandpupils.
2. RELATED WORK
Institutions of higher education (HE) and business are concernedaboutthelossintechnicaldrawing(TD)standards that results from a lack of knowledge of the fundamental ideasandcustomsthatguideoptimalpractises.Nowadaysits seenthatanimatedeffectandvisualizationandaugmented reality can improve the understanding of students and increasestudents’interestandfunoflearningcomparedto the theoretical and traditional methods of teaching. The purposeofthisstudyistodevelopandevaluatetechniques andtoolsbasedonvirtualandaugmentedreality,aswellas theiroveralleffectsontechnicaldrawingideaseducationin higher education settings. Based on the past finding of internationalstudythatexaminedtheneedofknowledgeand understandingofTDandabilityevaluation,andviewsofTD education,newtoolsandprocedureshavebeendeveloped. For the growthof unique designersand engineers, TDhas proven as essential requirement. They play a key role in transitionofthetechnicalproductspecifications(TPS)(form, size,tolerances,materials, etc.)formanufacturingprocess anddevelopnewproduct.ForHEinstitutionsandtraditional trainingmethods,thedeclineinstandardsbroughtonbya lackofunderstandingofkeyconceptsandtheprotocolsof draftingprocessesthatsupportthesepractisesisanissue. Themajorityintheteachingoftechnicaldrawingskills,itis fact that students studying engineering and product designing requires practical approach (sensing the design,
visualising) more that of theoretical sequence of teaching styles(abstract,auditorypractices).
ThetheoryonARanditsuseinthedifferentindustrieslike automotive,constructionarchitecturehasbeenexaminedby anumberofscholars.
Researchershaveidentifiednewapplicationsforaugmented reality in the classroom. Amir H. Behzadan showed the outputs & observations of a project that attempted to revolutionise the current environment of learning in construction field by creating and using an interactive augmented reality tool that would surely enhance the understanding of student about the construction process, equipment’sused,andoperationalsafety.TheARbookwas madewithtrackerphotosbyjoiningallofthepiecesofpaper. UsingtheARtoolkit,headmounteddisplayswereusedasa platformfordisplayingaugmentedinformationovermarkers (HMD).Thestudyfoundthatwhenusedsuccessfully,ARhas an important action on student achievement, promotes teacher-studentunderstanding,andaidsinthedevelopment ofstudents'problem-solvingskills.
In previous study,Behzadanand Shirazicreated the CAMART ("context-aware mobile augmented reality tool") AR tool. An instructional tool for the civil engineering and constructionindustriesiscalledaCAM-ART.ThecreatedAR tool was tested and evaluated for its effects on and advantages to student learning in a course at the undergraduate level. Students were instructed to access virtual information from the textbook on the subject deliveredinanormalwayusingtheirmobiledevices(suchas iPads,iPhones,tablets,orsmartphones).Tomaketheprocess moreengagingandcollaborative,theyorganisedintogroups. Results showed that AR can aid improve learning environmentsandlowertechnologicalbarriersforstudents intheclassroom.Additionally,byoccupyingparticipantsina AV(Audio-Video)enabledlearningenvironment,CAM-ART provided an interactive atmosphere that fostered engagement and cooperation between students and coursework.
Another research project looked on urban landscape interventionsinBarcelona.In2013,ErnestRedondomade thecaseforaugmentedrealityasa potentialnewteaching tool.ThestudyinvolvedtheS1andS2groups.WhileS2used AR,S1usedmoreconventionaltechniquesbasedonslides. The findings showed that AR is undoubtedly helpful in comprehending architectural proposals. Additionally, AR promotes spatial relationships by accurately and instantly displayingtruescaleandposition.
David Fonseca examined the viability of using augmented reality on mobile devices for architecture education in a similar study. The study concentrated on the tool's convenience, how well students performedafterusingAR, andhowmuchmorestudentsparticipated.Intheacademic year 2011–2012,thestudywasconducted with third-year
Civil Engineering students. A course was made that was thoughtinclassandassessedaftereachsession.Thefindings suggest that while AR was effective for visualising straightforwardmodels,itwouldbemoredifficulttoemploy withcomplexmodels.Studentswereinspiredbytheiruseof ARtechnologyandwelcomedothercomparableinnovations if they helped them achieve better academically. In the classroom,studentswerereportedtobemoreengaged.With the use of 3D virtual content, they were better able to comprehendandcommunicate.ARmaximiseslearningasa result.
Chen et al. conducted similar studies to improve students' spatialabilityusingAR(Chenetal.2011).Theproject-built trainingmethodsthatcanimprovestudents'spatialabilities inordertohelpthemlearnengineeringgraphicsprinciplesas effectivelyaspossibleusingaugmentedreality(AR)models andtangible(3D)model approaches.Thestudy concluded that AR piqued students' interests. Augmented reality and physicalmodelsworkingtogethercanresultinbetterresults

Thesameresearch,whichsoughttodeterminetheusefulness ofAR asa teachingtechniqueforpupils,wasconductedin 2015. (Shirazi and Behzadan 2015). To create a model buildingoutofbasicbuildingcomponents,theprojectuseda web-based programming environment viz Junaio. The mission was finished by two teams: Team 1 employed the conventionalliterature-basedmethod,whileTeam2made useofanARtool.Theoutcomeswiththesecondgroupwere successful. While performing the job, they appeared more independentandneededtheteacherlessfrequently.Itgave theassurancethatARcouldbeappliedwithcomplexsubjects andcurricula.
In2016,StevenK.Ayertriedusedaugmentedreality(AR)in sustainabledesigninstructionbyremodellingaportionofan existingstructure.Inthatexperiment,thelearnersdeveloped, imagined,andassessedexternal wall drawingstoimprove the sustainability of an existing structure. An application calledEcoCampusandanaugmentedreality(AR)simulation interfaceweredeveloped.UsersofEcoCampuswereableto seepotentialbuildingdesignsinrelationtocurrentbuilding space. In choosing the best design for the building, it also considered several factors. According to the findings, studentswhoutilisedEcoCampuswereabletogetadeeper knowledgeandperformbetteroverallacrossallsubjectareas than those who used paper-based forms. Internal dependenciesbetweenARandsimulationgametechnology wereoneresearchrestriction.Theycouldnotbeevaluated impartially.
3. DESIGNING EDUCATIONAL AR APPLICATION
Based on our study and research, we must take two important strategies for implementing an AR-based EngineeringGraphicseducationsystem.Theyare1.Realtime tracking and alignment strategy in which computer can provide and place a practical object in real environment
accurately. 2. Communal strategy in which user can communicatewiththecomputerandrelocatetheobjectto different place easily. There are libraries and software specially for AR applications. For our objective which is renderingtheobjecttherearemanywaysbutOpenGListhe bestformechanicalstructuresasgeometricalcharacterslike chamfer, rib, cylinder, cone can be identified and put up quicklyandeasily.
The content of an AR application should be carefully and precisely added and for that proper procedure must be selected as graphical education is very important in developing a student’s thinking and understanding skills. Graphics problem solving process involves some logical reference and to build user interface, educational requirementsandmechanicalstandardsareconsidered.
4. OVERVIEW OF AR BASED ENGINEERING GRAPHICS SYSTEM
TheARbasedEngineeringGraphicsSystemconsistsofFive Modules viz; Track and register module, gesture identificationmodule,actiondirections/instructionmodule 3Dmodeldatabaseandrendering/displayengine.Foreasier understandingofthismodulesfollowingflowchartcanbe usedwhichisalsothealgorithmofourapplication.
smartphone. Theutilization ofthe QRcodeforgettingthe modelsisbasedonvision-basedtrackingsystem.Laterwhen therequireddataiscollectedtherenderingenginewhichis the AR core engine is started. Lastly the operation data providedbytheuserarecollectedandinteractionsaremade due to which the users can zoom, rotate or cut the object basedontheirrequirements.


The 3D models were made on SolidWorks and Fusion360 software.Thismodelsfromthedatabasecanbeaccessedor retrievedbyusingascannercodeasshowninfigure2.
Fig1.ArchitectureorAlgorithm
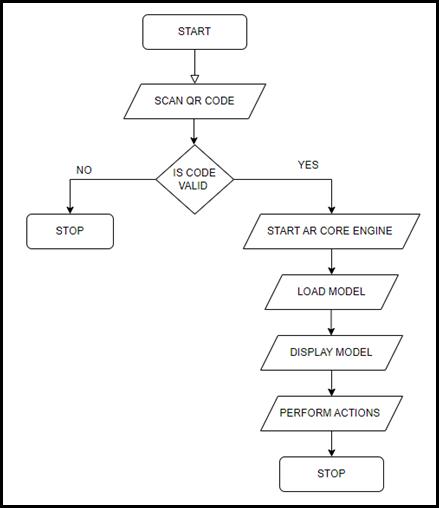
Out of which the first two modules the track and register moduleandgestureidentificationmoduleplaysavitalrole inARsystem.Theworkofthismoduleistocollectthevideo captured/traced by camera which in all is responsible for evaluatingthepositionofthecamera.Thesystempicksup the3Dmodelfromthedatabaseorbackendanddisplaysit accurately with respect to the camera position of the
5. IMPLEMENTATION

Ourappusesanormalbookasaninterfacewhichwillhave the2Dsketchofmodelsandthescanningcodeof3Dmodel forrespectivesketch.Studentsorlearnerscansimplylook theSketchesimagineandscanthecodefromtheirmobile phone application and complete their assignments and understand the relation between sketches as easy as they writetheirotherassignments.Whentheyfocustheircamera onthevalidscanningcodefromtheapp,the3Dmodelcomes on the mobile screen with the help of that they can understandtherelationbetweenthe2Dand3Dprojections. Theycanalsousedifferentfeatureslike360ᵒrotation,zoom inandoutandSectioncutinanydirection.
Thehardwarerequirementsforourapptoworkonmobiles phones are 4GB of RAM and 1GB of ROM and the android versionofthemobilephoneshouldbeAndroid5ormore. Thehardwarerequirementsrequiredforappdevelopment are 8GB of RAM or more and 16GB of ROM or more and operatingsystemisWindows10,11.TheSoftwareweused areGoogleARcore,UNITY,andAndroidStudio.Learnerscan installtheappbyscanningthecodefromtheirphonecamera andtheywillberedirectedtothedrivelinkwheretheywill find the APK file for the app which will be used for app installation.
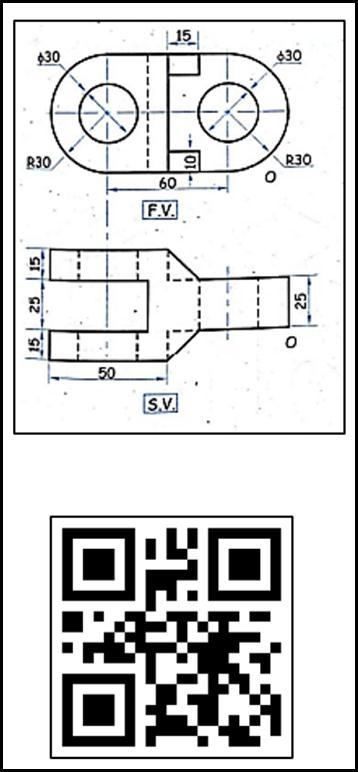
Fig3representstheeyeoftheknucklejoint.Whenstudents faceproblemsinimaginingthesketch,theycanstarttheAR appandseethe3Dviewofit.Thevirtual3Dobjectwillget on their screen from the database and can create an environmentofself-learningasARapplicationprovidesselflearningtutorials.Theycanalsorotatetheobjectandcansee thesectionalviewbyusingthesectionfeature.
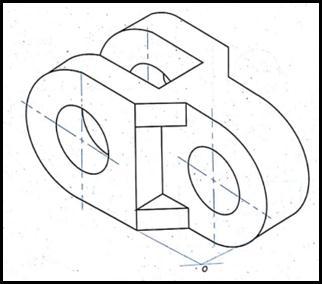
Students can access the 3D model and some important information from the AR-based learning Approach which alsoreducestheamountofthetimewhichteachersspendin theclassroomteachingusingatraditionaltechnique.Using AR-basedlearningissignificantlybeneficialwhencompared totraditionaltechniquewhichusesaxonometricdrawingfor explanationasshowninfig4.Thesedrawingaredisplayed only in single plane projection and since they are fixed, it concealstherearviewofthe3Dmodelduetowhichanew comerorstudentsfacedifficultiestounderstandthemodel whereasARapproachshowsalloftheexternalfeaturesfrom all sides.The students cankeep busythemselveswiththe modelinarealenvironmentalsotheycancommunicatewith themodelsbyrotatingorzoomingittovisualizetheminute details in space. They can also identify between the fixed construction and hidden constructions in the drawing by having sections at any distance in any directions. For learners planning their future in Design background, requiresalotofpracticeotherthanclassroompractice,so this self-spaced, AR-based application provides flexibility andconveniencetothem.Thiscanalsohelptostudentswho are unable to focus or concentrate due to classroom environmentorsettings.
6. CONCLUSIONS
The possibility for using mobile augmented reality to educate and learn orthographic projection to engineering studentshasbeenidentifiedbythisstudy.Theusageofthis technology has been viewed as most promising learning strategies to provoke students' interests and improve learning outcomes. Due to the promising potential of this technology'suseamong21st-centurycitizens,thisstrategy, which made use of Mobile Augmented Reality (MAR) technology,waschosen.Itencouragesself-directedlearning andcangivepupilsaflexiblelearningenvironment.Students learn more quickly and efficiently thanks to its simplicity, andtheyaremoreinterestedinlearningoverallthanksto this technology's novelty. In order to understand how respondents, feel about and accept the use of MAR in teachingandlearning,thisstudyevaluateshowrespondents use apps. Results show that respondents strongly agreed that it could satisfy all of the characteristics, including usability, concept comprehension, visualization help, and usageaim.Inordertoraisethestandardofeducationand deepen students' understandings, it is hoped that these findings would inspire additional researchers to continue integratingMARinteachingandlearning.
REFERENCES
[1] Behzadan, A. H., Iqbal, A., and Kamat, V. R. (2011). "A collaborative augmented reality-based modelling environmentforconstructionengineeringandmanagement education." Proceedings of the 2011 Winter Simulation Conference(WSC),IEEE,3568-3576.

[2] Shirazi, A., and Behzadan, A. H. (2014). "Design and assessmentofamobileaugmentedreality-basedinformation delivery tool for construction and civil engineering curriculum." J. Prof.Issues Eng.Educ.Pract., 141(3), 04014012.
[3] Redondo, E., Fonseca, D., Sánchez, A., and Navarro, I. (2013)."Newstrategiesusinghandheldaugmentedreality and mobile learning-teaching methodologies, in civil engineeringdegrees."ProcediaComputerScience,2552-61.
[4] Fonseca, D., Martí, N., Redondo, E., Navarro, I., and Sánchez,A.(2014)."Relationshipbetweenstudentprofile, tooluse,participation,andacademicperformancewiththe use of Augmented Reality technology for visualized architecturemodels."Comput.Hum.Behav.,31434-445.
[5]Chen,Y.,Chi,H.,Hung,W.,andKang,S.(2011)."Useof tangible and augmented reality models in engineering graphics courses." Journal of Professional Issues in EngineeringEducation&Practice,137(4),267-276.
[6]Shirazi,A.,andBehzadan,A.H.(2015)."ContentDelivery Using Augmented Reality to Enhance Students’ Performance in a Building Design and Assembly Project." AdvancesinEngineeringEducation,4(3).
[7] Ayer, S. K., Messner, J. I., and Anumba, C. J. (2016). "Augmented Reality Gaming in Sustainable Design Education."J.Archit.Eng.,22(1),04015012.

