Volume: 10 Issue: 03 | Mar 2023 www.irjet.net


Volume: 10 Issue: 03 | Mar 2023 www.irjet.net

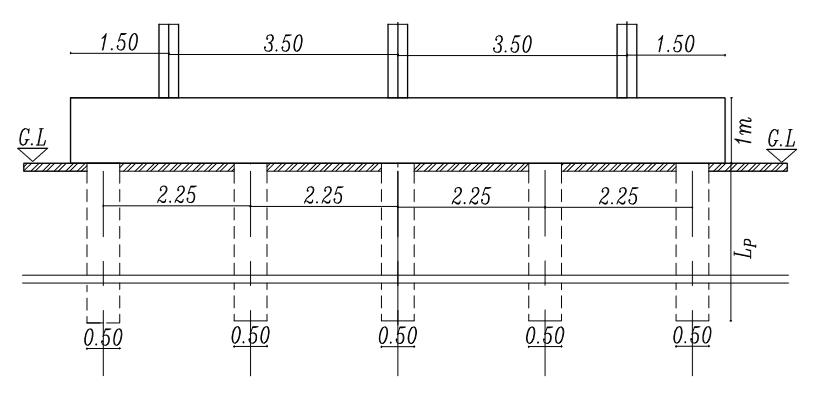
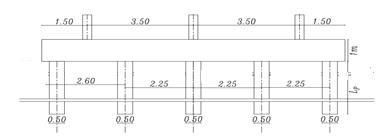
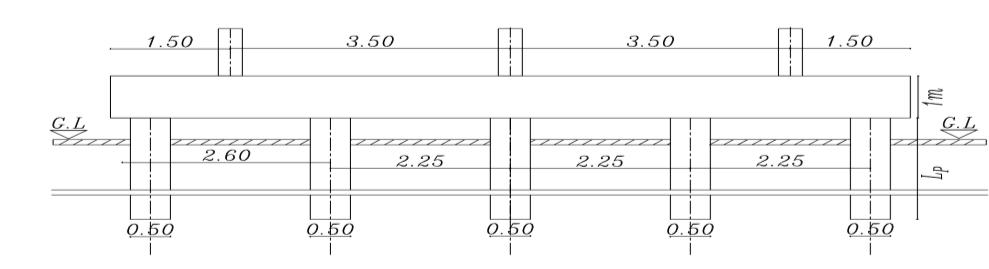
The present study is mainly based on the determination of the effect of pile length on settlement and straining actions in the raft rested on piles and the effect of the contact of the raft to the soil under the effect of static load and dynamic load. The pile diameter is fixed (D = 0.5 m), and spacing between piles are fixed (Sp = 4.5D) with various pile length (Lp = 28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D). The thickness of the raft is 1.00 m and the dimensions of the raft are 10*10 m Theboreholethatwaschosentobe used in the analysis of soil consists of six layers which are Silty sand and traces of clay, Silty sand, medium stiff clay, and dense sand, and is simulated by a semi-infinite element. Finite element package of a PLAXIS 3D version 2013. (a finite element code for soil and rock analysis) has been used to determine the bending moment, the shear force on the raft, and the settlement. Inthecaseofpiledraftrestingonthesoil,itwasfoundthatthebendingmomentintheraftdecreased by29%, the shear force in the raft decreased to 0.5% and the settlement of piled raft decreased 40% by increase the pile length undertheeffectofstaticload,thebendingmomentintheraftdecreasedby29%,theshearforceintheraftdecreasedto 0.5% and the settlement of piled raft decreased 40% under the effect of dynamic load . It found also that the bending momentintheraftinthecaseofaslabconnectedtothepilesisgreaterthanthecaseofpiledraftrestedonthesoilby 7%. In addition, the shear force in the raft as the slab connected the piles is larger than the rested piled raft by 2%. The settlementinthecaseofraftactasaslabconnectedtothepilesishigherthanrestedpiledraftby10%
Keywords:PileLength,PileRaftFoundation
The straining action and the settlement in piled raft foundationareaffectedbymanydifferentfactorssuchas pile length, pile diameter raft thickness, and type of soil buttoavaryingdegree.
Akinmusuru (1980) studiedtheeffectofpilelengthand raft geometry on piled raft load sharing. Experimental results on a single piled raft unit revealed that the raft share increases extensively by enlarging the raft width, whereasthepilelengthhasaninconsiderableimpacton loadsharing.
Clancy and Randolph (1993) determined an approach for the analysis of piled raft foundations based on the transferofaloadofindividualpiles,togetherwithelastic interaction between different piles and with the raft. They presented the effect of raft stiffness and spacing betweenpilesandpilelengthandstiffness.
Bisht, R.S. and Singh, B.(2012) presented a study on the behavior of piled raft foundation with various pile lengths it was found that settlements decrease with the increaseinpilelength.The maximumoverall settlement atthecenterofpiledraftdecreased
Elsamny, M. K. et al. (2018) presented a study on the analysis of pile-raft foundations non-rested and directly rested on the soil. A finite element was used in this study. The vertical displacement for the group of four pile caps rested on the soil. Vertical displacement for a group of four pile caps non-rested on soil It was concluded that the group efficiency of pile groups for piles cap rested on soil is more than that for piles caps non-restedonthesoil.Thegroupefficiencywasfoundto berangingfrom1.43to1.60forfourpilescaprestedon soil and was found to be ranging from 1.13 to 1.25 for four piles cap non-rested on the soil. The settlement of pilegroupsforpilecaprestingonsoilislessthanthatfor pilecapnon-restedonthesoil.
Elsamny, M. K. et .al (2020) Studied the effect of pile length on load sharing of pile raft foundation under differentloadsitwasfoundthatthestressesincreaseby increasing the pile length but at Lp ≥ 38D there is no significant effect. The load increase by increasing the lengthofthepileAlthough,theloaddecreaseafter(65to 70)%lengthofthepile.Theloadstransferredtosoilby friction increase by increasing pile length. The loads transferredtosoilbyendbearingdecreasebyincreasing pilelength

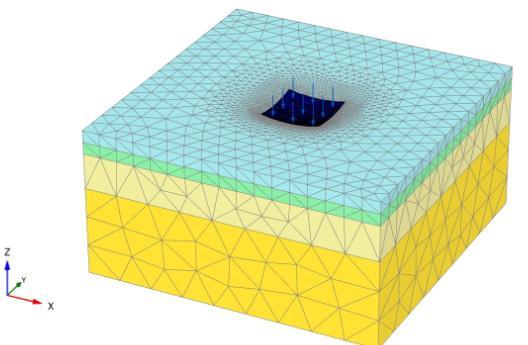
The used computer program was for the proposal of a three-dimensionalfiniteelementpackageofaPLAXIS3D version 2013 model to simulate the theoretical effect of pile lengthinpileraftfoundation
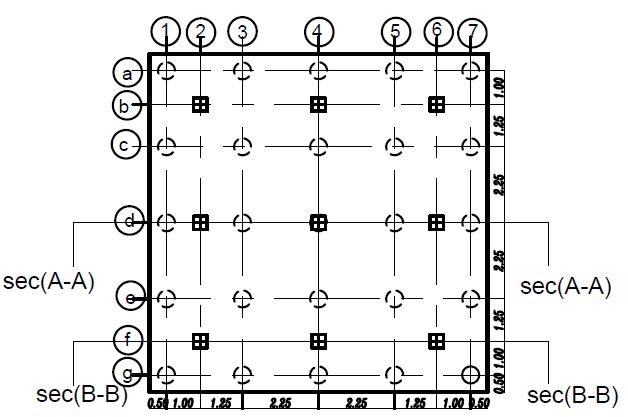
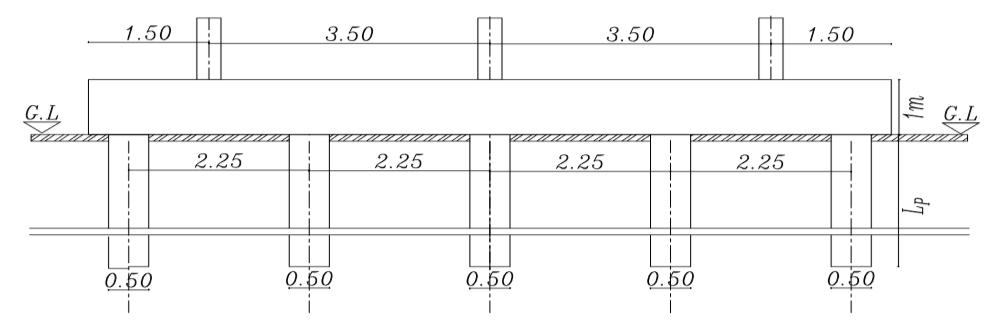
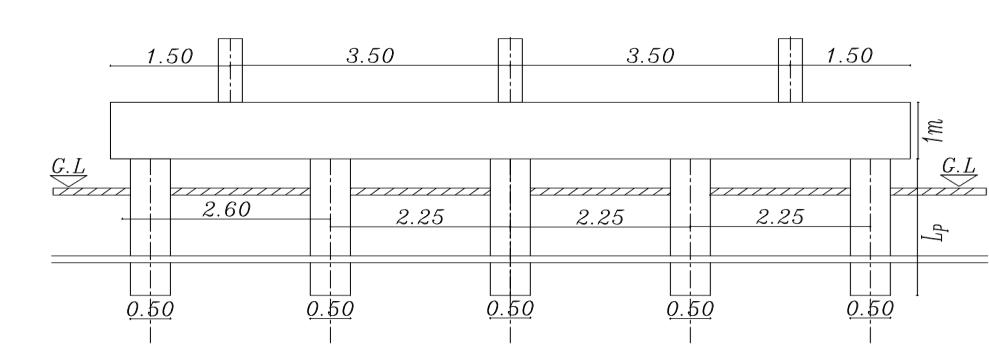
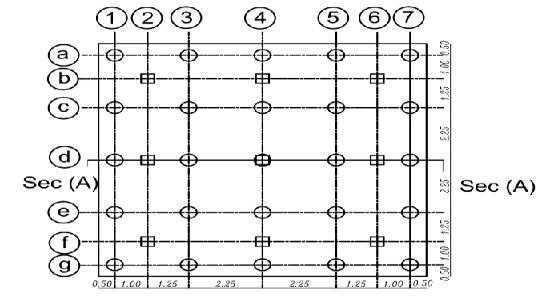
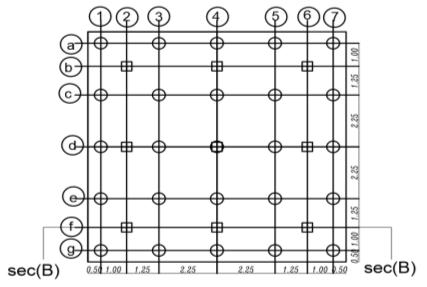
Inthepresentstudy,atheoreticalanalysishasbeendone foraselectedsite(inagovernmentalproject inSemesta city, Beni-suef, Governorate, Egypt).Fig. (1) illustrates a boreholefortheprevioussitethatwaschosentobeused in the analysis. The soil consists of four layers and is simulatedbyasemi-finiteelement
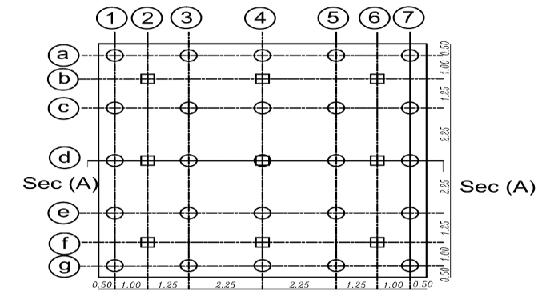
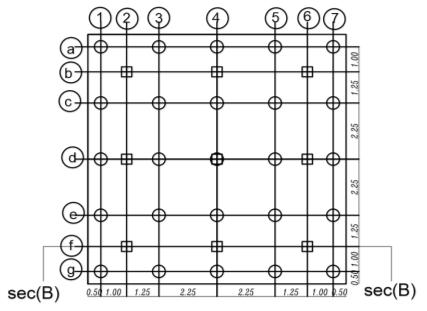
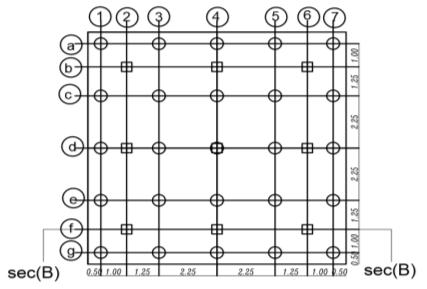
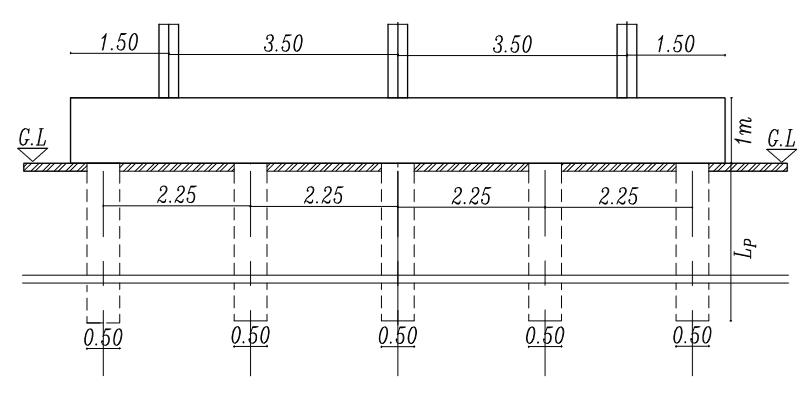
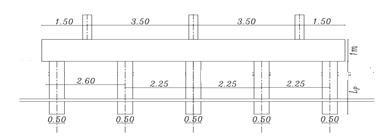
. isotropic homogenous elastic material. The analysis programconsistsofapiled-raft foundation consisting of 25 piles their diameters are fixed (D = 0.5m) and the spacing between piles is fixed (Sp = 4.5D) and they have various pile lengths (Lp= 28D,32D,36D, and 40D). Analysis carried out on two categoriesasfollows
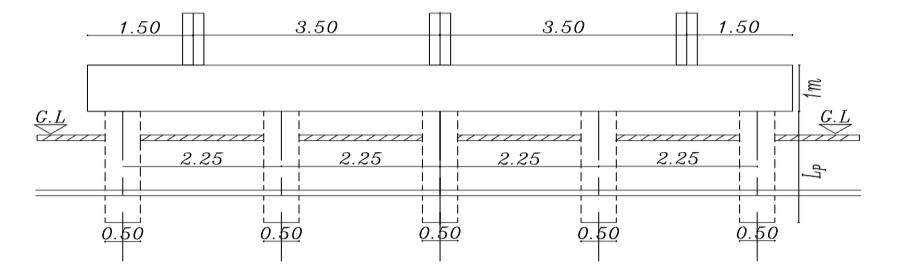
restedpiledraft
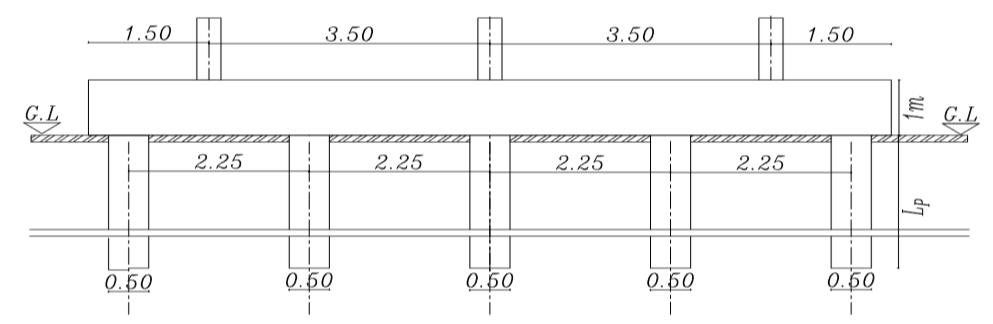
raftactasaslabconnectedthepiles
Thedetailsandvariationsoftheseselected
parameters are listed in tables from (1) to (3). and figures(2)and(3)


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 03 | Mar 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Finite element model:
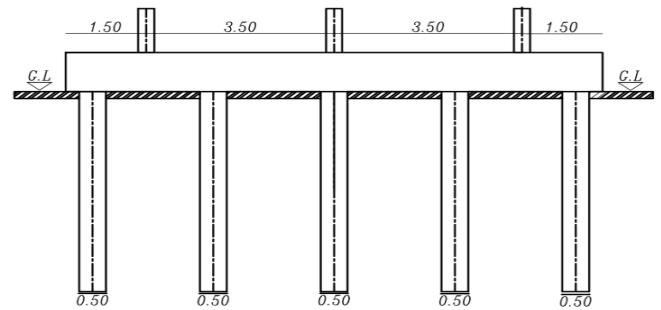
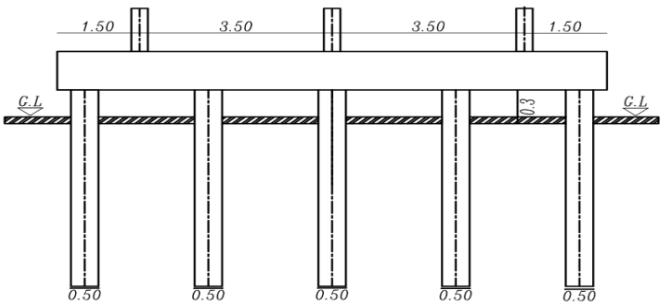
Figures (3) and (4) show the cross sections of the piled raftinthetwocasesrestedonthesoiland theraftactas aslabconnectedthepiles(Lp=32D,D=0.5mSp=4.5D)
3 -Parametric study
Theeffectofpilelengthonthefollowing:
i. Thesettlementofpiledraft
ii. Thebendingmomentontheraft
iii. Theshearforceontheraft
3. 1. Finite Element Results:
The obtained results of selected examples for different
casesareshowninfigures(6to17)asfollows:
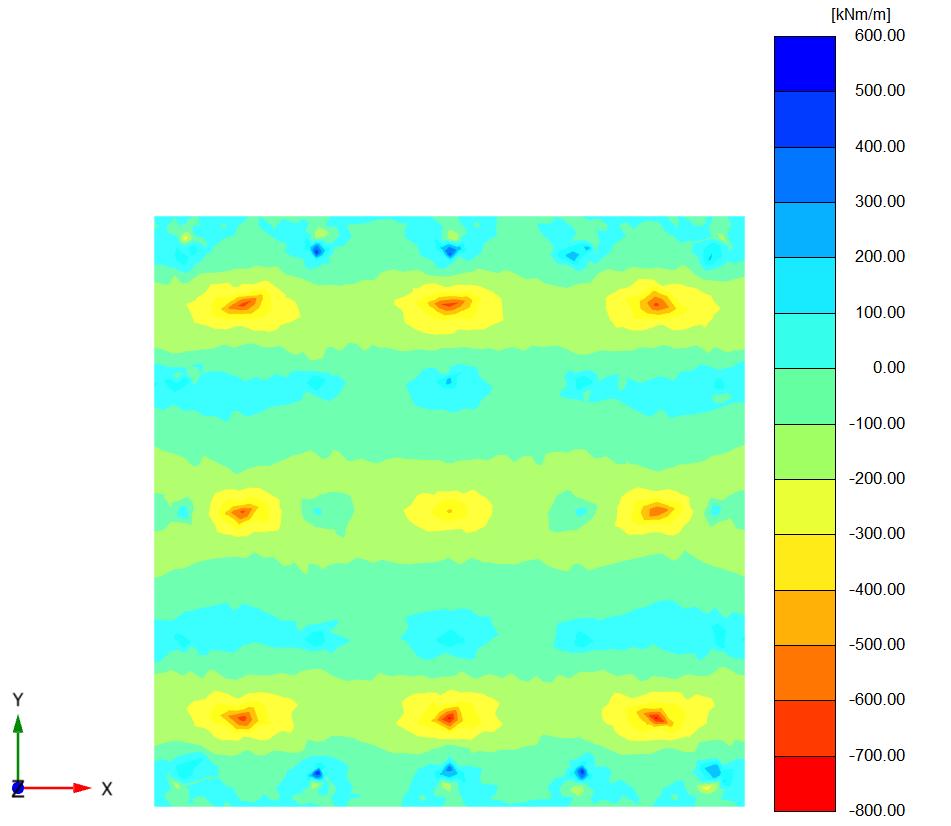
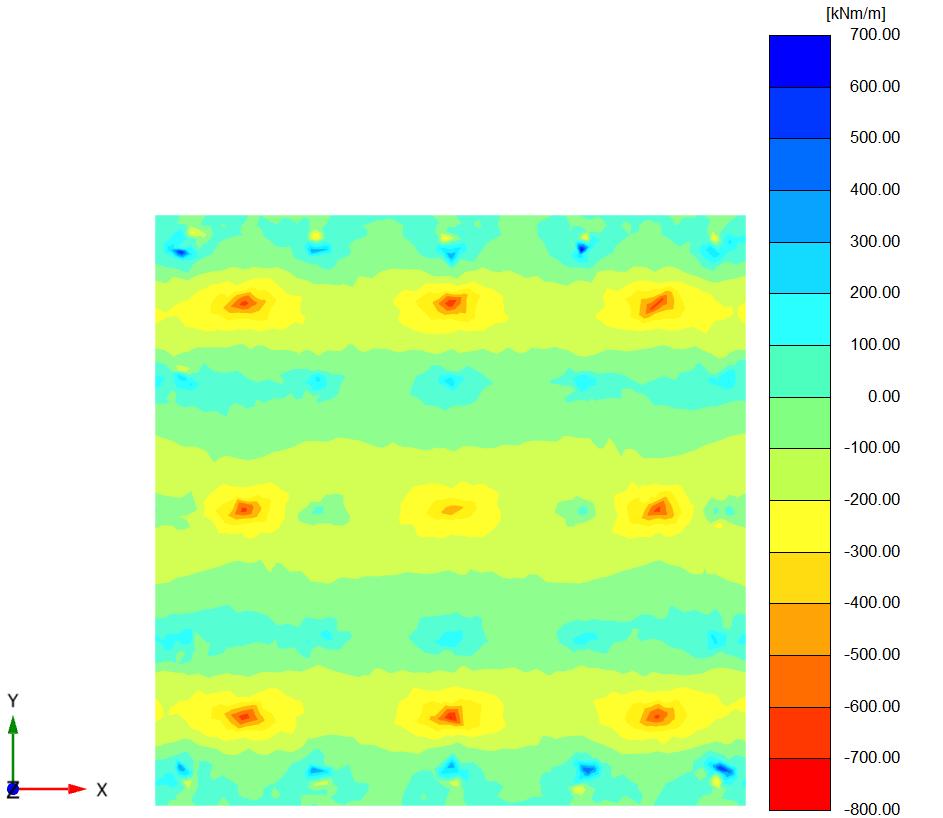
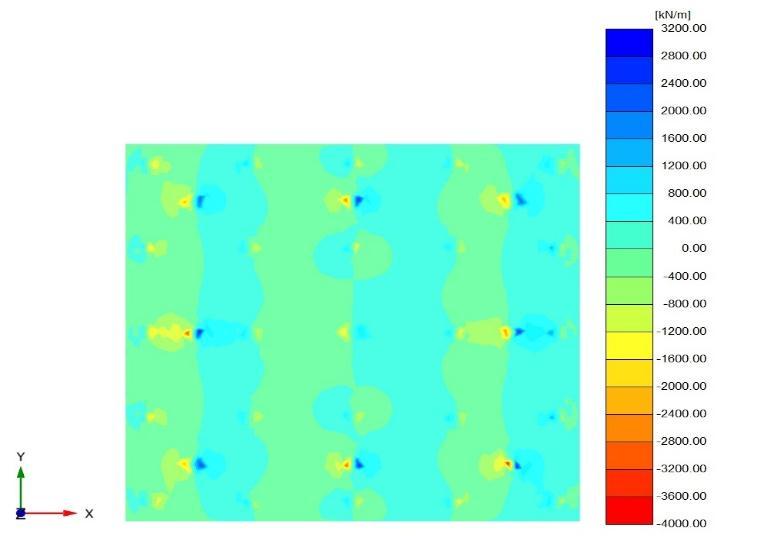
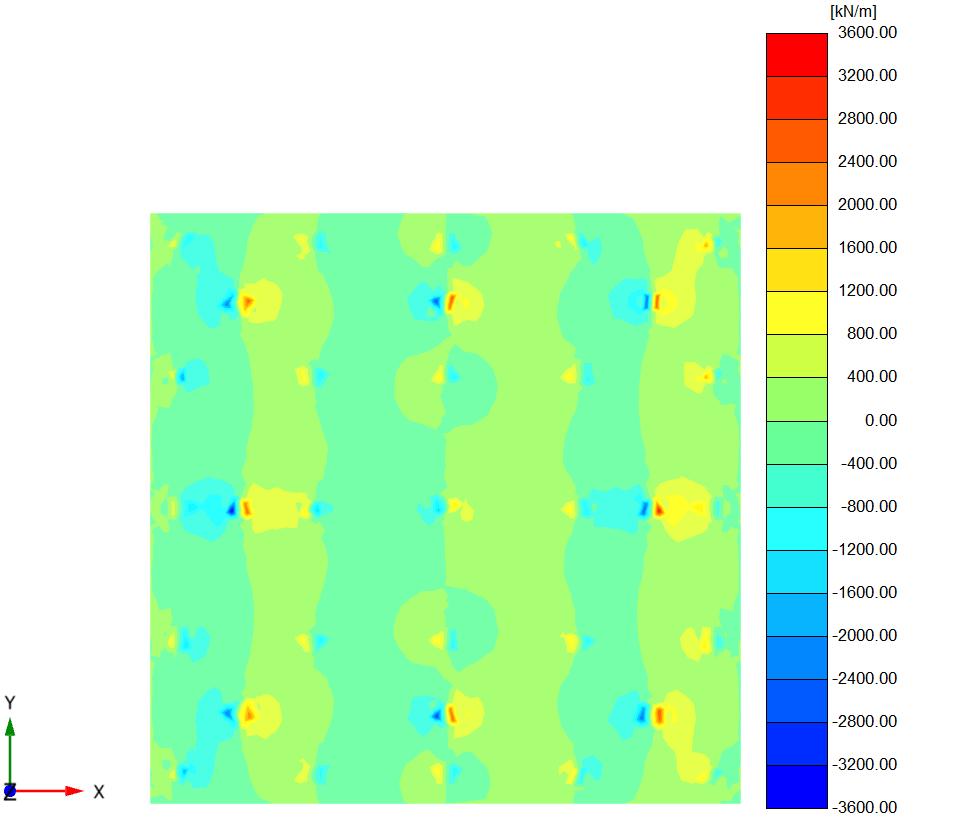
Figure (6) and (7) shows the bending momentontheraftinthetwocasesrestedon thesoilandtheraftactasaslabconnectedto the piles from the soil ( Lp =32D, D = 0.5m, andSp=4.5D).
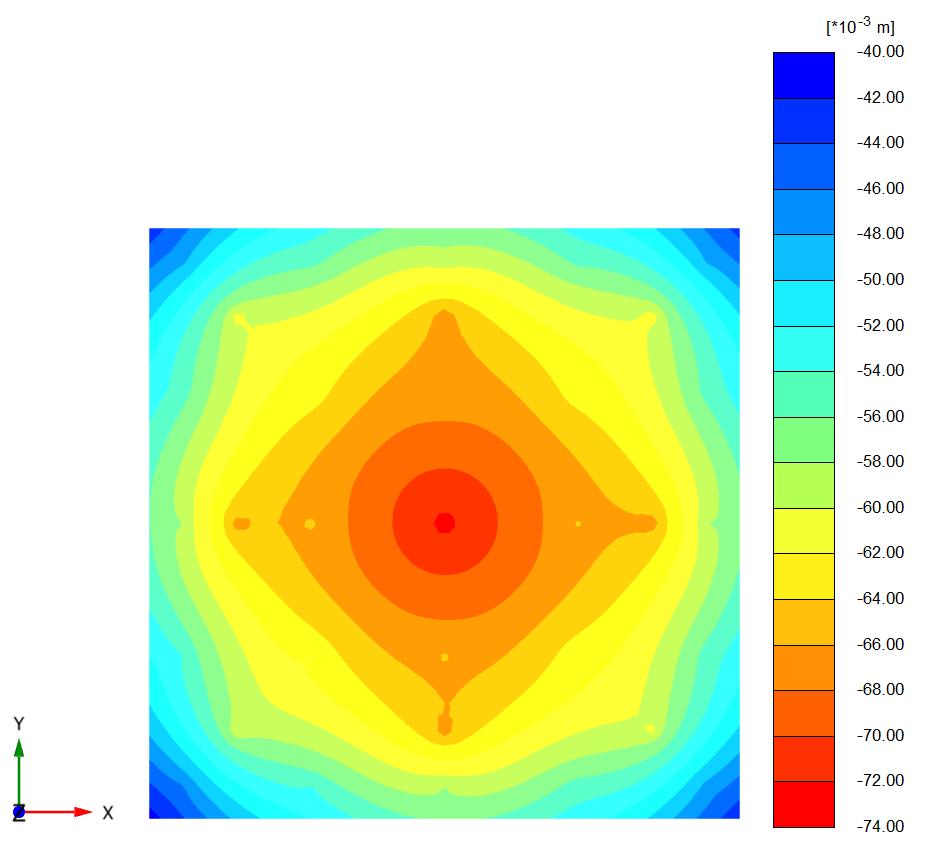
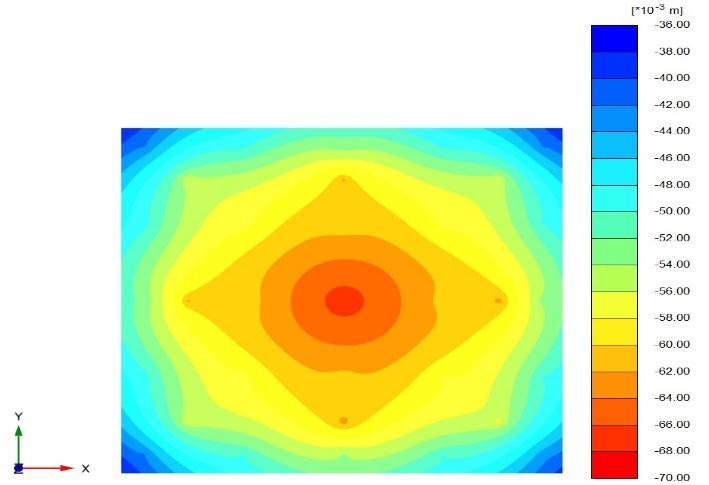
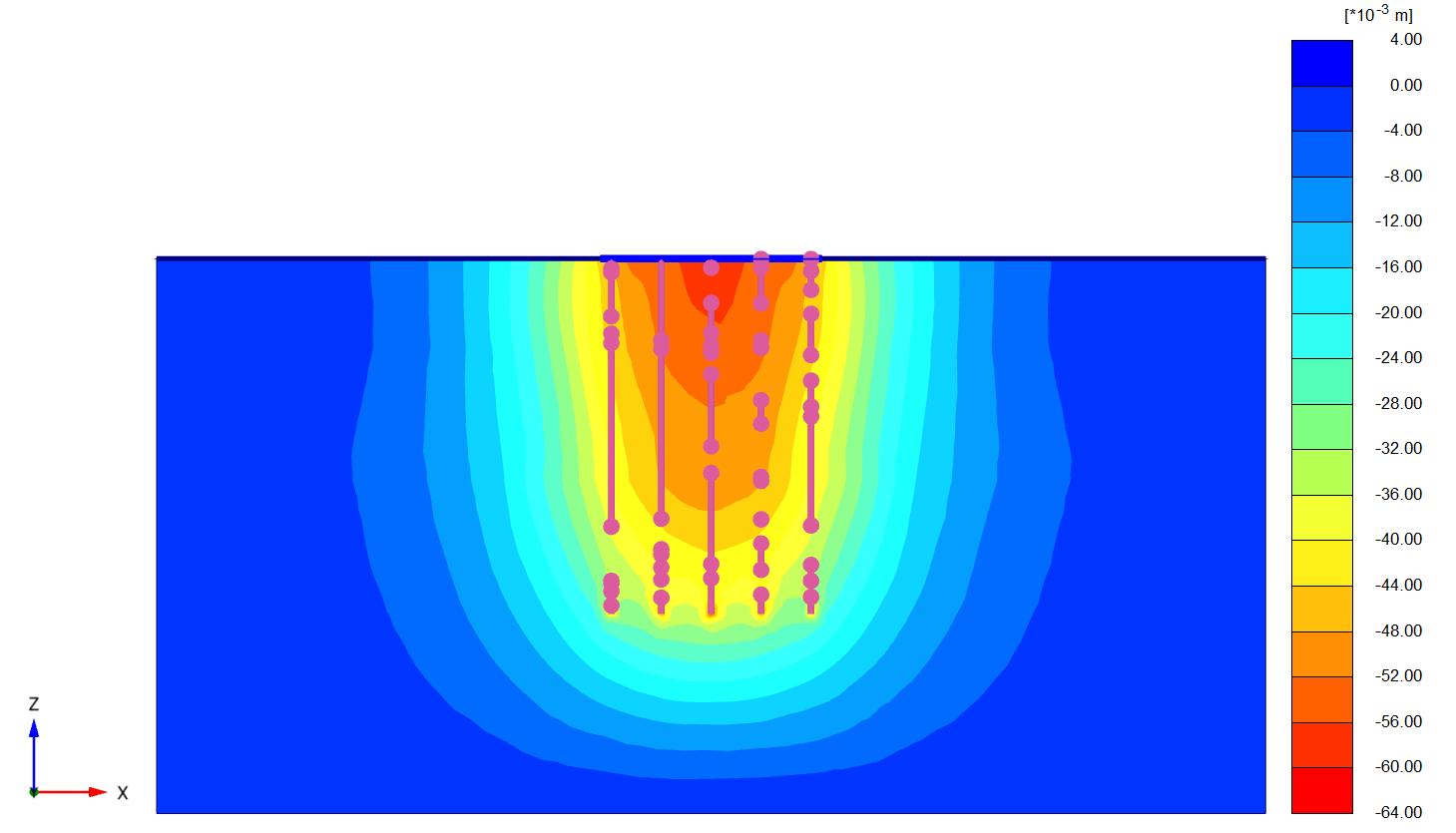
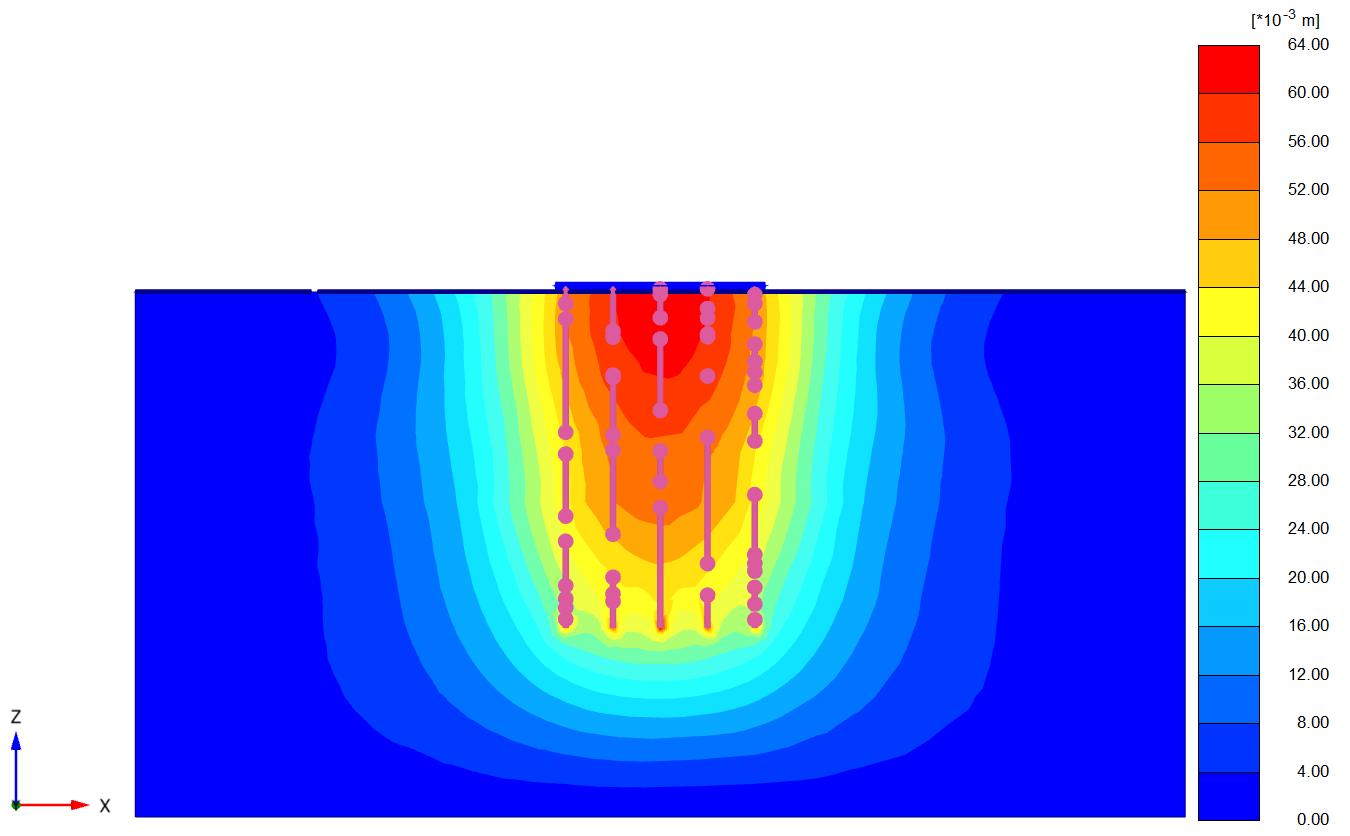
Figures(8)and(9)showtheverticaldisplacementofthe soilundertheraftinthe(x-y)plane(asshading)forthe twocases(Lp=32D,D=0.5m,andSp=4.5D).
Figures (10) and (11) show the verticaldisplacement of soilundertheraftin(x-z)plane(as shading)forthetwo cases(Lp=32D,D=0.5m,andSp=4.5D)
Figures(21)and(23)showtheshearforceon theraft forthetwocases(Lp =32D,D=0.5 m,andSp=4.5D
.




3. 2. Analysis of results:
Figures (14), (15) shows the relation between vertical settlementonthe raft in the two caseswithvarious pile length = where Lp = (28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D) for (D = 0.5 m), with raft thickness 1m in sec A. It can be observed that with increasing pile length from 28D to 40D the settlement decreases 40% in the case of piled raft rested on the soil and settlement decreased 35% in the case of piled raft with raft act as slab connected the pile.

Figures (16), (17) shows the relation between vertical settlementonthe raft in the two caseswithvarious pile length = where Lp = (28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D) for (D = 0.5 m), with raft thickness 1m in sec B. It can be seen that with increasing pile length from 28D to 40D the settlementdecreases38%inthecaseofpiledraftrested onthesoilandthesettlementdecreases35%inthecase ofpiledraftwithraftactasslabconnectedthepile.
Figures (18) and (19) shows the relation between the bendingmomentoftheraftinthetwocaseswithvarious pile length where Lp = (28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D) for (D = 0.5 m),withraftthickness=1minsecA.Itcanbe observed that with increasing pile length from 28D to 40D the bending moment in the raft decrease 29% in the case of piled raft rested on the soil and the bendingmomentintheraftdecreases20%inthecaseof piledraftwithraftactasslabconnectedthepile.
Figures (20) and (21) shows the relation between the bendingmomentoftheraftinthetwocaseswithvarious pilelengthwhereLp=(28D,32D,36D,and40D)for(D= 0.5 m), with raft thickness = 1m in sec B. It can be observed that with increasing pile length from 28D to 40Dthebendingmomentintheraftdecreasesfrom1%t to2%.inthecaseofpiledraftrestedonthesoilandthe bending moment in the raft decreases from 1% to 1.5% in the case of piled raft with raft act as slab connected thepile.
Figures(22), (23)shows therelation betweentheshear forceontheraftinthetwocaseswithvariouspilelength where Lp = (28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D) for (D = 0.5 m), withraftthickness1minsecAfromthesefigures,it canbeshownwithincreasingpilelengthfrom28Dto40 D the shear force on the raft decreased from 1%to0.5% in the case of piled raft rested on the soil and the shear force on the raft decreases from1%to0.5%. in the caseofpiledraftwithraftactasslabconnectedthepile.
Figures(24), (25)shows therelation betweentheshear forceontheraftinthetwocaseswithvariouspilelength
where Lp = (28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D) for (D = 0.5 m), with raft thickness 1m in sec B .it can be observed that with increasing pile length from 28D to 40D the shearforceontheraftdecreasesfrom1%to0.5%. inthe case of piled raft rested on the soil and the shear forceontheraftdecreasesfrom1%to0.5%.inthecaseof piledraftwithraftactasaslabconnectedthepile.
Figures (26), (27) and fig (38) show comparison in the settlement, bending moment and shear force between piled raft foundation rested on the soil and piled raft foundation with raft act as slab connected the piles where lp=28D and raft thickness(1m). it can be concluded that the settlement in the piled raft in the case of raft act as slab connected to the piles is greater than the case of rested piled raft by 10%, the bending moment in the raft in the case of a raft act as a slab connectedtothepilesisgreaterthanthecaseofarested piledraftby7%andtheshearforceina raft inthecase ofa raft actasa slabconnectedthe pilesis greaterthan inthecaseofarestedpiledraftby2%
Figures (29), (30) shows the relation between settlementonthe raft in the two caseswithvarious pile length = where Lp = (28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D) for (D = 0.5 m), with the effect of dynamic load and static load, with raft thickness 1m in sec A. It can be observed that with increasing pile length from 28D to 40D the settlementdecreases40%inthecaseofpiledraftrested on the soil and settlement decreased 35% in the case of piledraftwithraftactasslabconnectedthepile.
Figures (31) and (32) shows the relation between the bending moment of the raft with the effect of dynamic load and static load, in the two cases with various pile lengthwhereLp= (28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D) for (D = 0.5 m), with raft thickness = 1m in sec A. It can be observed that with increasing pile length from 28D to 40D the bending moment in the raft decrease 29% in the case of piled raft rested on the soil and the bending moment in the raft decreases from 20% in the caseofpiledraftwithraftactasslabconnectedthepile. Figures(33), (34)shows therelation betweentheshear forceontheraftinthetwocaseswithvariouspilelength where Lp = (28D, 32D, 36D, and 40D) for (D = 0.5 m),withtheeffectofdynamicloadandstaticload with raft thickness 1m in sec A from these figures, it can be shown with increasing pile length from 28D to 40 D the shear force on the raft decreased 0.5% in the case of piledraftrestedonthesoilandtheshearforceonthe raftdecreases0.5%.inthecaseofpiledraftwithraftact asslabconnectedthepile.



















Piled raft rested on the soil
piled raft with raft act as slab connected the piles
Piled raft rested on the soil
piled raft with raft act as slab connected the piles

Fig(27)showcomparisoninthebendingmomentintheraft betweenpiledraftfoundationrestedonthesoilandpiledraft foundationwithraftactasslabconnectedthepiles.


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 03 | Mar 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
pile length 28D static load
pile length 32D static load
pile length 36D static load




pile length 40D static load
pile length 28D dynamic
pile length 32D dynamic
pile length 36D dynamic
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 03 | Mar 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
pile length 28D static load
pile length 32D static load
pile length 36D static load
pile length 40D static load
pile length 28D dynamic load
pile length 32D dynamic load
pile length 36D dynamic load
pile length 40D dynamic load
pile length 28D static load
pile length 32D static load
pile length 36D static load




pile length 40D static load
pile length 28D dynamic load
pile length 32D dynamic load
pile length 36D dynamic load
pile length 40D dynamic load




International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 03 | Mar 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Fromthepresentstudy,thefollowingsareconcluded:
i.In the case of rested piled raft increasing pile length leadsto
Thebendingmomentintheraftdecreases29%
Thesettlementdecreases40%ofpiledraftfoundation
theshearforceintheraftdecreasesfromto0.5%
ii. In the case of a raft act as a slab connected the piles increasingpilelengthleadsto
Thebendingmomentintheraftdecreases20%
Thesettlementdecreases35%ofpiledraftfoundation
theshearforceintheraftdecreases0.5%
iii. The comparison between the two cases piled raft rested on the soil and piled raft act as a slab connectedthepiles
The bending moment in the raft in the case of a raft actasaslabconnectedtothepilesisgreaterthanthe caseofarestedpiledraftby10%
the settlement in the piled raft in the caseof raft act asslabconnectedtothepilesisgreaterthanthecase ofrestedpiledraftby7%
The shear force in a raft in the case of a raft act asa slabconnectedthepiles isgreaterthaninthecaseof arestedpiledraftby2%
iv. Theeffectofpilelengthwithdynamicforce
In the case of rested piled raft increasing pile lengthleadsto
Thebendingmomentintheraftdecreases29%
Thesettlementdecreases40%ofpiledraftfoundation
v.the shear force in the raft decreases from 0.5% In the case of a raft act as a slab connected the piles increasingpilelengthleadsto

Thebendingmomentintheraftdecreases20%
Thesettlement35%ofpiledraftfoundation
Theshearforceintheraftdecreases0.5%
References:
1. Akinmusuru,J.O.(1980),InteractionofPiles andCap in Piled Footings, ASCE, Vol. 106, No. GT 11, pp. 12631268.

2. Bisht, R.S., and Singh, B. (2012) "Behavior Of Piled Raft Foundation By Numerical Modeling" SAITM Research Symposium On Engineering Advancements (SAITM–RSEA2012).
3. Clancy, P. and Randolph, M. F. (1993) An Approximate Analysis Procedure for Piled Raft
Foundations, International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, Vol.17, No.12, pp.849.869.
4. Elsamny, M. K. and Abd EL Samee W. Nashaat and Essa. Tasneem. A (2018) "Analysis of pile-raft foundations non-rested and directly rested on soil" International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 9, Issue 3, March 2018, pp. 418

439.
5. Elsamny, M. K., Ezz-Eldeen, H. A., Elbatal, S. A. and Kamar, A. M. (2020)" Effect of Pile Length on Load Sharing Of Pile Raft Foundation under Different Loads" NEWYORKSCIENCEJOURNAL·July2020