Cauchy’s Inequality based study of the Differential Equations and the Simple Transformation Techniques for Algebra
Sainath Bhargav1School of Computer Science and Engineering, VIT-AP University, G-30, Inavolu, Beside AP Secretariat Amaravati, Andhra Pradesh 522237

Abstract – This paper instigates the multivariate generalization of the widely used Cauchy inequality 1 + x ≤ ex where x can be any non-negative real number. The results of this study can be the solution for the Cauchy’s problem for particular Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE). This is also related to study of the complete monotone function and the divided differences theory. The proof is based on the empty product convention notion and the Beppo Levi theorem of Monotone convergence. This study is also extended to multivariate generalization of the simultaneous inequalities.
Key Words: ODEs, Inequalities, Population Dynamics, SimultaneousInequalities,Divideddifferences
1.INTRODUCTION
The elemental inequality that is being used for various applicationsinPlantBiology,OlympiadInequalityProblems, ImageProcessing,Signal processingandvariouscomputer applicationisgivenin(1).
Wherexcanbeanynon-negativerealnumber,generallyx is considered as smaller values in real time applications. However, multivariate generalization of (1) is not established.Thisisthemainfocusofthispaperistoprove(2) specifically.
***
FromtheanalogueofspecificODECauchyproblem,the generalizedinequalityform(2)isdefined.ThisODECauchy problems are widely used in the plant biology for chromosomeanalysis,populationdynamics,topredictthe virusmutationsandmanyotherproblems.Adirectwayof solutionisrequiredtohandlethesereal-lifeinequality-based problems. However, this cannot be analysed using the elementary methods since the problems are complex in nature.The monotonic studyoffunctionsand meanvalue theoremofdivideddifferenceoffunctionsareessentialfor complex problems. In next section of this paper ODE approach of solving i.e., the study of Cauchy problem is shown the with the aforementioned solutions. The straightforward approach of preliminary analysis of the giveninequalityispresentedinthesection3ofthepaper. The conclusion along with future scope of the work is generalizedinthesection4.
2. ODE Approach of solving
2.1 Primary Analysis
In this paper, autonomous ODE Cauchy problem is consideredasgivenin(3).
Wherex1,x2…….,xnarethepairwisenon-negativedistinct realnumbers.Here
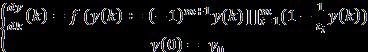
Theemptyproductconventionismade,sothat(2)canbe changedas(1)whenthenvalueis1.Inthispaper,wealso showthattheinequalityin(2)isonlycorrectwhenthevalue of is0.(1),(2)areextendedintowholeEuclideanspace whennvalueis2,and(2)isindeterminateforintherangeof (2,-2),(0,-1)and(1,-1/2)orcanalsobeconsideredas(-1/4, -1/2).
Wheret1,t2…….,tnarethedistinctpositiverealnumbers (pairwise) in the increasing order. The convential representationsof(3)whennis1andnis2arethestandard logisticmodelandthestandardlogisticmodelwiththeAlle effect.Theeccentricmaximalsmoothsolutioncanbeeasily deduced by the concerning classic theory of the Cauchy problems of ODEs from the problems data as (4) and the phaselineisdepictedinFig.-1.
where
TheyintheFig1is,
Fortheuniquenessofthetimeinvariantsetsareutilized,
Here y is the maximal and the inequalities are as follows
>0and0< <1wherex< (6)
Theboundisachievedby (7)
The value of y increases significantly and becomes theproblemofexplodinggradientarises.
b. If the value of n is , then y(k) <0 and f(y(k)) > 0 when t , y is increasing monotonicallythenthekis
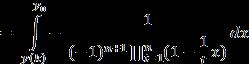
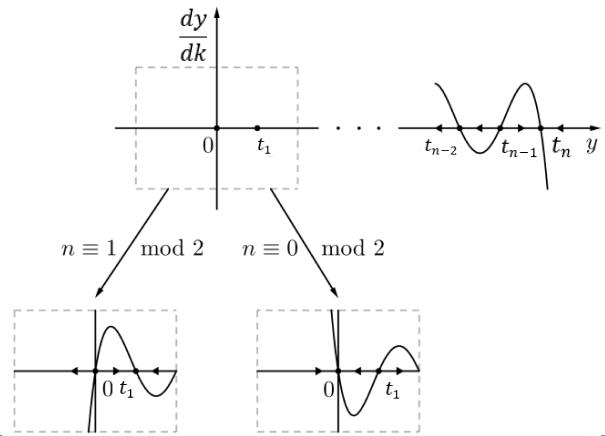
Thebehaviorofyatvariousnvaluesisasfollows
1.
2.
toconcludethequalitativeanalysis.
Now,thereexiststwocasesif
Case(1):
a. If the value of n is , then y(k) <0 and f(y(k)) <0 when t , y is decreasing monotonicallythenthekis
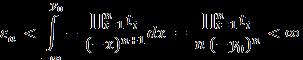
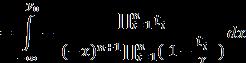
Hence, (8)
Here y is the maximal and the inequalities are as follows (9)
The value of y increases significantly and becomes theproblemofexplodinggradientarises.
Case(2):
Ifthevalueof ,theny(k)> ,givingf(y(t))<0 where t . And the value of y is decreasing monotonically.
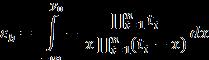

Hence, Hereyisthemaximalandtheinequalitiesareasfollows
>0and0< < wherex>
Theboundisachievedby (10)
The value of y increases significantly and becomes the problemofexplodinggradientarises.
2.2 Final result derivation
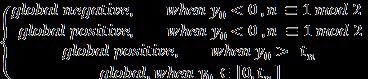
Fromtheequations(5),(7),(9),(10),thefurthercalculations is computed to get the blow up time exactly of extreme solutionwhere
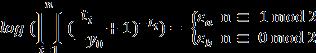
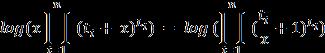

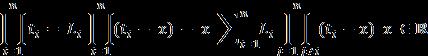
Theaforementionedrelationsofthefunctionsinsidethe areanalyzedfurther:
1. Decompositionofthepartialfractionsisadopted
2. Theanalogousmattercanbemodifiedas: Itsconsequentequalityisdefinedas:
Thecoefficients arecalculatedas: (11)
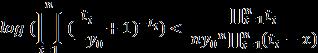
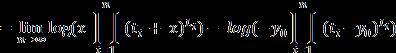
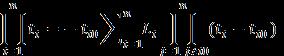

Whenx=0wegetL=1in(11).Thecoefficientof intheRHS of(11)iseliminatedtoget:
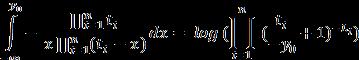
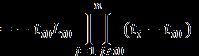
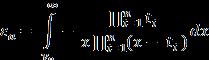
Thevaluesof respectively:
1. If ,then
Herethevalueof
3. When the value is positive, desired result is achieved.
Theequalityin(2)onlyholdswhenthexvaluesiszero.
3. Direct Approach
Firstly,thedefinitionofthemonotonefunctionsisgiven
3.1 Definition: Thefunction f intherangeof(0,∞)is monotonic if and only if the following the condition is satisfied
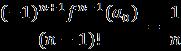
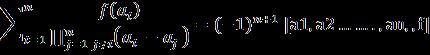
Fromthe(2),weadopttheclassicBeppoLevitheoremand dominated convergence is noted from the Lebesgue theorem,deriving
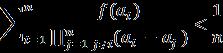
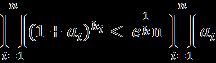
Here,thefisstrictlyincreasingmonotonethenthe function ,impliesthat
3.2 Allowed Repetitions
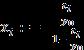
Thenumbersa1,a2…….,anarepositiveanddistinctinthis sectionofthepapertheprobablerepetitionsareshown.For thenaturalnumbersN1,N2…….,Nnthisapproachisdeduced asshownin(13).
REFERENCES
Thegeneralizationoftheresulttothehigherderivativesis thedivideddifferencesofthemeanvaluetheorem,
Hypothesis 1: Iftherearepairwisedistinctrealnumbera1, a2…….,an,followingthecondition and ,then
3.1 Proof of the result
Assumingthata1,a2…….,anarepairwisedistinctpositive realnumbersandbydeducing,
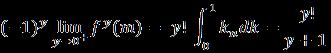
[1] Major,P.(1981)MultipleWiener–Itˆointegrals.Lecture Notes in Mathematics 849, Springer Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg,NewYork.
[2] U.Abel,M.IvanandT.Riedel,Themeanvaluetheorem ofFlettanddivideddifferences,JournalofMathematical AnalysisandApplications,295,1(2004),1–9

[3] Borell, C. (1979) On the integrability of Banach space valued Walsh polynomials. Seminaire de Probabilites XIII,LectureNotesinMath.7211–3.Springer,Berlin.
[4] J. K.Hale, Ordinary Differential Equations, 2nd ed., Krieger,1980.
[5] Dudley,R.M.(1998)UniformCentralLimitTheorems. CambridgeUniversityPress,CambridgeU.K.
[6] M. Iannelli and A. Pugliese, An Introduction to MathematicalPopulationDynamics:AlongtheTrailof VolterraandLotka,Springer,2014.
Similarly, Thiscanbefurtheranalyzedas
