Abstract:
Fake Video Creation and Detection: A Review
Chaitali Jadhav1, Dr. Varsha Ratnaparkhe21Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering, Government College of Engineering Aurangabad, Maharashtra.
2Associate Professor, Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering, Government College of Engineering Aurangabad, Maharashtra ***
The improvement in fake video creation and manipulation has been accelerated by deep learning techniques. The line separating real and fake video has shrunk dramatically due to advancements in deep learning methods especially in the field of Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). This provides access to a number of intriguing applications in various industries for example VFX creation, advertising, video games, etc. On the other hand, there is numerous disadvantages of this technique which create significant security risks such as privacy threat, Nation security, etc. Nowadays Social mediaplatformisalsothekeyfactorinspreading these fake videos. The rapid growth of deepfake videos has an effect on people's personal, social, and political lives. Deepfakesare frequentlyusedto produceobscene videos, harming people's reputations. Thus, there is a critical need for automated solutions that can identify a fake variety of multimedia materials and prevent the inaccurate information from being circulated. To understand how deepfakes function, several experiments have lately been conducted, and several deep learning-based methods have been developed to recognize deepfake videos. This Survey paper provide a detailed study of the methods, algorithms used to create fake Videos also the detection methods whichareusedtodetectthisfakeVideo.
I. Introduction

Digital videos are becoming a highly prevalent type of digital asset due to the rise and popularisation of social networks. Social media platforms or social network platform refers to group interactions where individuals produce, share, or exchange knowledge. Despite great benefits, Social media is used to share fake information, fake news, and fake videos. Deepfake is the term for digital media that has been altered, such as pictures or videos, in which the resemblance of another person has been substituted in lieu of that person's image or video. Deepfakehasregularlybeenusedtooverlaythefacesof actor/actress over obscene photographs and videos. athering the aligned faces of two different people, and trainingan auto-encoder arethesteps in the creation of
Deepfake pictures. Deep learning has changed the rules of the game, necessitating the use of multimedia audio visual forensics to find new solutions quickly. It has also been utilised to create false information and rumours for politicians [1-3] There are many ways to identify fake images, but the majority of them either assess differences from what a typical camera pipeline would look like or extract particular picture modifications from the final image [4,5]. It has been shown that image noise [6] works well as a signal for splicing detection i.e., copy and paste mechanism from an image to another. Despite considerable advancements,therearestillseveralfundamentalissues remain that should be addressed for the purpose of improving deepfake detection algorithm. Image detection algorithms and techniques cannot be used for videosbecauseofthesubstantial loss oftheframesdata and compression in the video [7] This paper presents the fake video creation technique and video editing procedures as well as study tackles the issue of identifyinganddetectionofeditedvideoorfakevideos.
II. Deepfake Video Generation:
The majority of these fake videos are made using deep learningtechniques.
Theparalleltrainingoftwoautoencodersisthecoreand centralconcepthere.Theframeworkofanauto-encoder consist of the interconnection of a decoder network and an encoder network. The encoder's function is to conducta dimensionreductionbyencodingtheinput or entry layer data into a fewer variable. The decoder’s objective is to use those factors to generate an outcome thatcloselyresemblestheoriginalinput.
DeeplearningtechnologiescalledGenerativeadversarial networks (GAN) can be used to produce phoney images orphotos,movies,videosthataredifficultforhumansto identify from the actual thing. In this technique a data set is utilised to train models, whicharesubsequentlyusedtoproducephoneypictures and movies. The model has the ability to produce credibleandrealisticimagesandvideoswithanincrease in dataset. Thus for realistic result the large amount of datamustbefeedtothemodel
Architecture
1. Face Swapping:
TheFaceSwappingtechniqueisManipulationtechnique. The method known as "swapping" involves a video that substitutes one person's visage with another person's [8].
Agenerativemethodmustbeusedtoprocesseachframe ofthetargetvideoinordertoaproduceafaceswapping video. The autoencoder, which is frequently employed for data reconstruction tasks, served as the foundation for the majority of the deepfake algorithms used in face swapping.
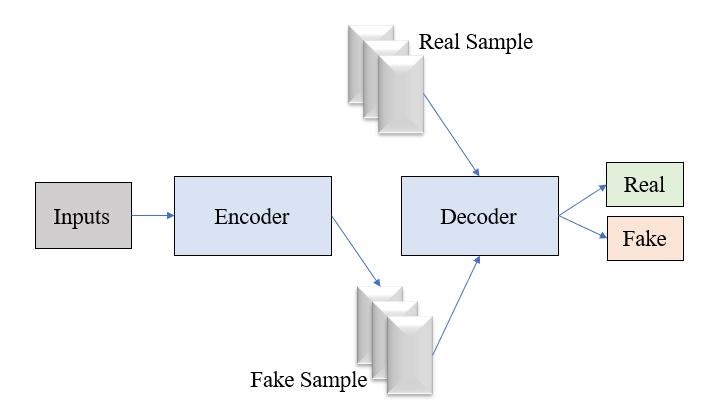
Throughout the training period, the common traits and featuresfromsourcevideofaceandtargetvideofaceare extractedbytwoencoders.Theseextractedfeaturesand traits are feed to two decoders in order to reassemble thefaces.Toexchangeandswitchfacesbetweenoriginal video frames and destination video frames, two autoencoders have been trained. The encoder first extracts latent features from the image, which are then usedbythedecodertoconstructareplicaoftheoriginal
At the end of the training phase, one of the decoders generates latent face and feed it to another decoder to reconstruct face. The Generated face will have same featurelikeoriginaloneifandonlyiftheautoencoderis trainedwell.
Previousworkshowshowswappingoffaceisperformed using different method for example, In unrestricted conditions, a typical fully convolutional network was used by Nirkin et al. [9]Similarly Natsume et al. [10] presented an area that separates GAN(RSGAN) for swappingoffaces
ConvolutionNeuralNetworkwasusedbyKorshunovaet al. [11] to develop a face swapping method. Real time faceswappingmethodwasproposedbyWangetal.[12] For privacy protection a face was procedure was proposedbyMahajanetal.[13]
2. Face Reenactment:
This technique involves changing of facial expression of an individual's face in a video [14]. In this technique the process to perform face reenactment A monocular face reconstruction method is used to derive the low-dimensional parameter for exampleheadpositionandexpressionofthesourceand target videos. Scene illumination and identification parametersarekeptwhenperformingfacereenactment, butheadattitude,expression,and eyegazingfactorsare altered. On this modified parameter the fake images of the target are regenerated. The conditional input of our new renderer video conversion network is then provided with these images. A new rendering video conversion network takes this fakeimageasconditional input,afterthat,thenetworkistrainedtotransformthis artificial input into a realistic output. The conditioning space time volumes are delivered to the network in a slidingwindowmethod.Inordertoobtaincompleteand bettertimeconsistencyina video. Kimetal.[15],Zhang etal.[16],Nirkinetal.[17], Doukas etal.[18],Caoetal. [19] developed a number of algorithms, including RNN, encoderdecoder,GANs,asinglelandmarkconverterthat includesageometryawaregenerator,taskagnosticGAN basedschemes.SimilarlyRGBvideofeedswithreal-time facialreenactmentswheredevelopedbyThiesetal.[20].
III. Deepfake Video Detection:
In recent approaches deep learning was utilised to abruptly extricate important and discriminating properties in order to identify fakeness in video Falsevideodetectionisviewedasaconundrumofbinary a binary distinction, where the distinction between genuine and manipulated videos is made using classifiers.
Visual artifacts inside frames and Temporal CharacteristicsacrossFramesarethetwocategoriesinto which fake video detection is divided.
1. Visual Artifacts Inside Video Frames: Inthisdetectionmethodthevideosarebrokendown into frame and then visual artifacts are examined within each frame in order to obtain discriminant feature.
To identify authenticity of videos, a deep or shallow classifierisfedwiththesefeatures.

Deep Classifier:
Deepfake videos are frequently produced at low and limited resolutions, which calls for the use of an affine face warping technique that is resize, rotate, and shear thefacestomatchtheoriginalsappearance.Convolution Neural Network (CNN) models such as ResNet50, ResNet152 [21], VGG16 [22], and ResNet101 can
recognise the distortions left by this technique owing to the resolution discrepancy between the distorted face regionandthebackgroundinformation
In [23] based on the relics spotted during the face warping stage of deepfake generating algorithms, there was a suggestion for a deep learning technique to recognisedeepfakes
In [24] The capsule network is proposed for detection fake images and videos. The initial purpose of the capsule network was to overcome the shortcomings of CNNs when employed for inverted graphics job which seek to identify the actual 8mechanisms that produce representationsoftheenvironment[25].
Shallow classifiers:
Most deepfake detection algorithms concentrate on artifacts or discrepancies between actual and false videos.
In2019Yangetal.[26]offeredanidentificationmethod basedontrackingvariationsin3Dheadpositions,which are calculated utilising 68 facial areas in the essential face recognition system. Due to a flaw in the method used to create fake images, false image can be detected by 3-dimensional head positions examination. Retrieved features are feed to a SVM classification model in order to achieve high accuracy.
The presence of global inconsistency and lack of an imprecise or wrong assessment of occurrence of illumination, or an improper reverence of the actual configuration are what lead to the graphical abnormalities.Deepfakesareidentifiedusing featuresof texture derived from the face area based on facial point ofinterest,missingfactsandinsightsintheteethandeye area,texturefeatures.
2. Temporal Patterns Across Video Frames:
In this method Deep recurrent network (RNN) models are mostly run down to identify phoney videos. In[27]Sabiretal.usedthespatiotemporalpropertiesof video streams to detect since the deepfake synthesis process does not successfully ensure temporal coherence.
It is hypothesised such a modest degree distortions caused by facial alterations will surplus oneself as temporal artifacts with discrepancies among frames because video editing is done frame by frame. To take advantage of temporal differences between frames,aRecurrentConvolutionalNetworkaccordingto the incorporation of the convolutional network Dense Net [28] and gated recurrent unit cells [29] was developed.
The long short term memory (LSTM) and CNN are used inthetemporal-awarepipelinemethodtofinddeepfake videos, this technique was proposed by Guera et al [30] since there was temporal inconsistencies between frames and intra-frame inconsistencies present in fake videos. Using CNN, frame-level features are extracted, andtheLSTMisthenusedtobuilda temporal sequence descriptor.
In [31] Li et al. proposed the use of eye blinking as a physiological indication to identify deep fakes. A person blinks much less frequently in deepfakes than in unaltered videos. For the purpose of predicting dynamic state, Li et al. [31] crop eye regions from the videos and spread them across long term recurrent convolutional networks (LRCN). TheLRCNismadeupofafeature and attributeextractorbasedonConvolution Neural Network,a component of sequence learning based on long short term memory (LSTM), and a state prediction component based on a fully connected layer to forecast the likelihood of an eye open or closure.
IV. Conclusion
DeepfakesorArtificialintelligencegeneratedordigitally altered videos, pose a serious threat to the reliability of face recognition technology and the veracity of online information. The study shows that even if cutting-edge facial image manipulation techniques provide aesthetically appealing outcomes, trained forgery detectors can still spot them. The artificial intelligence researchcommunity will be benefited fromsuchkindof detection methods in order to create efficient strategies for combating deepfakes. To further strengthen present false detection systems, more work is required as, there are many artifacts that cannot be detected in the compressed video. Presence of extra blurriness in video creates difficulty for algorithm to detect the fake videos. Thus it is necessity for future more technique should be presented in order to deal with advancement in deep learning. Robustness is frequently used to assess how well detection algorithms work under various degradations.Inthefuture,increasingtheresilienceand robustness of current detection techniques will be crucial.
References:
[1]Natarajetal.(2019),“DetectingGANGeneratedFake Images Using Co-Occurrence Matrices”. Electronic Imaging,2019,532-1-532-7
[2] Wang et al. (2020), “CNN-Generated Images Are Surprisingly Easy to Spot... for Now”. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern

Recognition, Seattle, 13-19 June 2020, 8695-8704. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00872
[3] Hsu et al. (2018), “Learning to Detect Fake Face ImagesintheWild”.2018IEEEInternationalSymposium onComputer,ConsumerandControl(IS3C),Taichung,68December2018,388-391.
[4] H. Farid et al (2009), “A Survey Of Image Forgery Detection”. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 26(2):26
25,2009.
[5] J. A. Redi et al.(2011), “Digital image forensics: a booklet for beginners”. Multimedia Tools and Applications,51(1):133–162,2011.
[6] T. Julliand et al. (2015), “Image noise and digital image forensics”. In Y.-Q. Shi, J. H. Kim, F. Perez-Gonz ´ alez, ´ and I. Echizen, editors, Digital-Forensics and Watermarking: 14th International Workshop (IWDW 2015), volume 9569, pages 3–17, Tokyo, Japan, October 2015.
[7]Afcharetal.(2018),“MesoNet:acompactfacialvideo forgery detection network”. In 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security (WIFS),pages1–7.IEEE,2018.
[8] Tolosana et al. (2020), “Deepfakes and beyond: A survey of face manipulation and fake detection” . Inf. Fusion2020,64,131–148.
[9] Nirkin et al. (2018), “On Face Segmentation, Face Swapping, and Face Perception”. In Proceedings of the 13thIEEEInternationalConferenceonAutomaticFace& Gesture Recognition, Xi’an, China, 15–19 May 2018; pp. 98
105.
[10] Natsume et al. (2018), “RSGAN: Face Swapping and Editing Using Face and Hair Representation in Latent Spaces”.arXiv2018,arXiv:1804.03447.
[11] Korshunova et al. (2017), “Fast Face-Swap Using Convolutional Neural Networks”. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–27 October 2017; pp. 3697–3705.
[12] Wang et al. (2018), “ Robust and Real-Time Face SwappingBasedonFaceSegmentationandCANDIDE-3” In Proceedings of the PRICAI 2018: Trends in Artificial Intelligence, Nanjing, China, 28–31 August 2018; pp. 335–342.
[13] Mahajan et al. (2017), “SwapItUp: A Face Swap ApplicationforPrivacyProtection”.InProceedingsofthe IEEE 31st International Conference on Advanced

InformationNetworkingandApplications(AINA),Taipei, Taiwan,27–29March2017;pp.46–50.
[14] Juefei-Xu et al. (2022), “Countering Malicious DeepFakes: Survey, Battleground, and Horizon”. Int. J. Comput.Vis.2022,130,1678–1734.
[15]Kimetal.(2018),“Deepvideoportraits”.ACMTrans. Graph.(TOG)2018,37,1–4.
[16] Zhang et al. (2020), “Freenet: Multi-identity face reenactment”. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF ConferenceonComputerVisionandPatternRecognition, Seattle,WA,USA,13–19June2020;pp.5326–5335.
[17] Nirkin et al. (2019), “FSGAN: Subject agnostic face swapping and reenactment”. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVFInternational ConferenceonComputerVision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7184–7193
[18] Doukas et al. (2021), “Head2Head++: Deep Facial Attributes Re-Targeting”. IEEE Trans. Biom. Behav. IdentitySci.2021,3,31
43.
[19] Cao et al. (2020), “Task-agnostic Temporally Consistent Facial Video Editing”. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.01466
[20] Thies et al.(2016), “Face2face: Real-time face captureandreenactmentofRGBvideos”.InProceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2387–2395
[21] Kaiming et al. (2016), “Deep residual learning for image recognition”. In Proceedings of the IEEE ConferenceonComputerVisionandPatternRecognition, pages770–778,2016.
[22] Karen Simonyan and Andrew Zisserman(2014). “Verydeepconvolutionalnetworksforlarge-scaleimage recognition”.arXivpreprintarXiv:1409.1556,2014.
[23] Yuezun Li et al (2018), “Exposing deepfake videos by detecting face warping artifacts”. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.00656,2018
[24] Nguyen et al. (2019), “Capsule forensics: Using capsulenetworkstodetectforgedimagesandvideos”.In IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pages 2307–2311. IEEE, 2019.
[25]Hintonetal.(2011),“Transformingauto-encoders” In International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks,pages44–51.Springer,2011.
[26] Yang, X., Li, Y. and Lyu, S. (2019) Exposing Deep Fakes Using Inconsistent Head Poses. 2019 IEEE InternationalConferenceonAcoustics,SpeechandSignal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, 12-17 May 2019, 82618265.
[27] Sabir et al. (2019), “Recurrent convolutional strategies for face manipulation detection in videos” Proceedingsof theIEEEConference onComputer Vision andPatternRecognitionWorkshops,3(1):80–87,2019.
[28] Huang et al. (2017), “Densely connected convolutional networks”. In Proceedings of the IEEE ConferenceonComputerVisionandPatternRecognition, pages4700–4708,2017.
[29]Cho etal.(2014), “Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation”.arXivpreprintarXiv:1406.1078,2014

[30]Gueraetal.(2018),“Deepfakevideodetectionusing recurrent neural networks”. In 15th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal based Surveillance(AVSS),pages1–6.IEEE,2018.
[31] Li et al. (2018), “In ictu oculi: Exposing ai created fake videos by detecting eye blinking”. In 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security(WIFS),pages1–7.IEEE,2018.
[32] Donahue et al. (2015), “Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description”. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2625–2634,2015
[33] Nguyen et al.(2019), “Deep Learning for Deepfakes Creation and Detection: A Survey”. In Computer Vision andImageUnderstanding,2019.
