Drug Supply Chain Supervision System

Abstract- The problem of fake drugs has spread toevery country and is now so severe that everyone is paying close attention to it. According to a report, the phoney medication industry is worth $10B annually. According to WHO, over a million people every year pass away from using bogus medications. A major problem is the distribution of counterfeit medications. A major contributor to drug counterfeiting is a broken supply chain. Our medicine supply chain has numerous flaws. In the current supply chain environment, either no essential information is transmitted between theparties during the hand-off process or only a little amount of useless information is given, which has resulted in counterfeiting. Not only does the use of a fake medication harm patients' health, but it also coststhe real manufacturer money. In this scientific paper, we've described how we used blockchain to addressthis issue and summarised the entire procedure using several diagrams. Traceability, visibility, and security are all been added to the medication supply chain using blockchain technology. The medications will be tracked by this planned system from their point of creation to their final destination that is the customer.
Keywords: Blockchain, Pharmaceutical, Supply chain, Counterfeiting, Drug
1. INTRODUCTION
Counterfeit drugs industry is worth billions of dollars and continuously expanding. As per the estimations given by WHO, more than a million people die every year due to illicit and fake drugs making it one of the main contributors to global deaths. Pharmaceutical industries are struggling to tackle this issue due to major loopholes presentinthesupplychain.TheNarcoticsControlBureau, the central law enforcement agency of India responsible for combating drug trafficking, has recently asked young engineers of India to come up with a prototype system which could be integrated into existing pharmaceutical supply chains to overcome the loopholes. In the present supply chain, tracking of information only exists from the manufacturer, after they have received the raw materials. But the most effective way to tackle counterfeiting is to establish records from the source of raw products itself. This proposed system will track the drugs from origin of raw materials to the end consumer, incorporating traceability, visibility and security into the drug supply chain.
Drugs are chemical substances formulated for different purposes. They are used as medicines to cure/control any illness or for recreational use to induce such a state in whichapersonwhohastakenitfeelsasenseofenjoyment or leisure. One can only get medicinal drugs if you have a proper prescription given by a doctor. Pharmacists verify the authenticity of the prescription before handing out the medicines to the patient. There are already existing systems to keep track records of prescription drugs from store to patient. To track supply from the manufacturer to the final consumer, there is, however, no reliable mechanism.
1.1 Objective
The project's fundamental aim is to maintain the safety, securityandreliabilityofpharmaceuticalsupply.
Itwillhelpreducetheriskofdrugshortages.
Itwillreduceillegaltraffickingofmedicinaldrugs.
Itwillensurethedrugissoldtothepersonwith prescriptiononly.
Toreducesupplyofillicitandrecreationaldrugs.
Totrackthesupplychainofdrugsfrommanufacturerto enduser.
Todevelopadecentralizedtrackandtracesystemfor dataprivacy,transparencyandauthenticity.
1.2 Need for System
Shipment visibility: Lack of tracking and visibility of shipments can cause problems and jeopardise demanding delivery operations likesame-dayand onehour delivery. Supply chain and logistics operations may suffer from poor freight visibility. Reduced revenue, ineffective delivery processes, subpar customer service, and higher transportation risks are possibleoutcomes.
Mutable and Invalid source: Duetothemanufacturing and supply company's centralised administration of all supply chain facts, there is asignificant risk that data will be altered in the company's interest and used to misleadcustomers.
Loss of reputation due to fake products in market: As mentioned above, the centralised design of the system makes it vulnerable to forged authentication andaccess.Hackersormiddlemenmayalsoalterdata, harmingthecompany'sreputation.
Slow Process and Error prone paperwork: When managingaworldwidesupplychaininthetwenty-first century, the traditional methods of separating manufacturing from marketing and shipping from accounting don't function well. Organizations that are networked can collaborate on supply chain managementmoresuccessfullythansiloedbusinesses. The time-consuming paperwork is another aspect of theoldmethod.
1.3 Problem Statement
Indian law states that a pharmacist may only dispense prescription medications with a doctor's prescription. In addition to the name of the drug(s), its potency, dose, and periodofuse,aprescriptionmustalsoincludethedoctor's name, address, and registration number. Prescription medications and the "precursors" the ingredients are increasingly being diverted for use in illegal drug recreation. As a result, the NDPS statute covers these medications. However, we lack a means to monitor the movement of these pharmaceuticals and the legitimacy of the delivery to the final consumer. The suggested approachwouldmakeitpossibletotracethemovementof these prescription medications from their maker to their final consumer. The proposed solution would ensure that the drugs are delivered only to the person with the doctor’sprescription.
1.4 Present Theory
In the current system, there is a way for consumers to quickly determine whose firm made the goods by just scanning the QR code. Drug supply chain performance managementisessentialformeetingthegrowing
consumer demand for products that are reliable, high- quality, sustainablyproduced,andhaveaprovenance.Drugsupply chainperformancemanagementattemptstoguaranteethe product's safety, quality, and authenticityfor customers and businesses. The availability of fake medications is likewise growing in tandem with the rise in drugdemand. Therefore,itmustbereducedimmediately.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
1. Prasad Nayak B, Preetham VK, Rutika Shinde (2022) In this initiative, they introduced a fresh use of blockchain technology in the healthcare industry. They talked about the issues with the current pharmaceutical sector supply chain management system and how blockchain technologymaybeutilisedtofightdrugsupply fraud by enhancing transparency and visibility. It is
explained how the identity mechanism of the blockchain operates and how exchanging medical data is made feasible by protecting data about the products' sources. Inorder to build a blockchain-based pharmaceutical supplychain, theyunderline the various techniques, blockchainvariations,andthird-partysolutions thatcanbeused.Theyconcludedbyoutliningtheoperation of the suggested system and giving an example of how different participants will find itstraightforwardtouse.In order to enhance the current supply chain, management model, and supply chain commodities, a blockchain strategy is described in this article. Additionally,supply chain items help connect people from various geographical locations. As a result, a distributed ledger must be created by the supply chain. The distributed ledgercontains all of the transactions and transportation data from the aforementioned drug supply chain. Nobody will make an assault attempt, that much is certain. In addition, we recommended using a manufacturer-provided QR code system to communicate with users. The benefit of this is that anyone may learn about the product's integrity, from the maker to the consumer,andhowtouseitproperly.
This realism review describes partial or complete PTTSimplementations. They examined 21 papers on thedeployment of such systems in Turkey, which served as ourbenchmark country, as well as in Denmark, Ethiopia, Germany, Hong Kong, India, Iran, Pakistan, Poland, Taiwan,the UK, and the USA. They specifically draw attention to the political, social, and economic backdrop variables that have been identified as facilitating orimpedingthe(planned)implementation in these mostly high- and middle-income contexts. Government backing is theprimarypoliticalcontextual component, followed by legislation and regulation. Supply chain actors' support is the first social contextual component, followed by awareness, knowledge, and skill. Investments are the primary economic contextual component, followed by technical and digital requirements. Overall, they draw the conclusion that PTTS adoption is significantly impacted by the interaction ofcontextualfactors.
The record-keeping feature of blockchain has transformedseveral economic sectors, bringing immense value andupheaval in the global economy. Blockchain technology hasmadeitpossibletodoawaywithexpensive intermediariesinthe healthcare industry, which has led to the elimination of antiquated and ineffective crossorganizational processes. Additionally, the invention has given patients backcontroloftheirdatabyallowingthem secure access to their prescription and medical records.

One of the lessons learned from developing and implementing the SecureRx framework forprescriptions is the potential of record-keeping technology to foster effective and efficient sharing of information about prescriptions while ensuring security. The SecureRx framework has highlighted the role of the decentralised and shared permission blockchain in enabling healthcareproviderstoaccessdatabankswithoutneeding approvalfromtheframework.
3. DESIGN
3.1 Software Components used in Prototype
Solidity - Solidity is the principal programminglanguage for assembling smart contracts utilized in the Ethereum blockchain. It is a contract-based language, which implies that smart contracts are liable for putting away the entirety of the programming reasoning on which the Ethereum blockchain runsWheelassembly.
Inthisarticle,theylookedintotheissueofdrugtraceability within pharmaceutical supply chains and highlighted its importance,particularlytoguardagainst fakemedications. They successfully created and tested a blockchain-based pharmaceutical supply chain solution that enables decentralised drug tracking and tracing. Their suggested approach, in particular, makes use of smart contracts within the Ethereum blockchain to ensure automated recording of events that are accessible to all involved stakeholders. These smart contracts enable tamperproof recordings of occurrences along the supply chain. In terms of the quantity of gas used to carry out the various operations that are triggered within the smart contract, theyhaveshownthatoursuggestedmethodiseconomical. Additionally, the security analysis performed has demonstrated that our suggested solution achieves protection against malicious attempts targeting the availability, integrity, and non-repudiation of transaction data, which is crucial in complex multi-party settings like the pharmaceutical supply chain. As part of our ongoing work to improve the effectiveness of pharmaceutical supplychains,theyintendtoconcentrate onexpanding the system that has been presented in order to achieve completetransparencyandverifiabilityofdruguse.
There is a pressing need to improve medical health care services in light of recent advancements in network and Internet technology. Various topics pertaining to the management of the medication supply chain have been explored in this study. This article also addresses how blockchain technology can solve these problems in a transparent and safe way. To combat the problems with drug counterfeiting, blockchain can be utilised to add traceabilityandvisibilitytothedrugsupplychain.Ashared ledger model with a decentralised blockchain architecture has also been presented, which not only stops drug fraud butalsostrengthens,makes transparent,andincreases the reliabilityofthedrugsupply.Loopholesinthepresentdrug supply chain can be closed using the suggested paradigm. Additionally, the blockchain framework model that has beendevelopedcanbeeffectiveforreal-timetracking,such as scheduling product deliveries, in addition to preventing thesaleofcounterfeitpharmaceuticals.

8.226 |
Metamask - Users of the cryptocurrency wallet Metamask can control their digital assets using a browserextensionoramobileapp.
Goerli test network - Goerli is an Ethereum test network that allows for blockchain development testing before deployment on Mainnet, the main Ethereumnetwork.
Truffle - Truffle is the ecosystem's development, assetpipeline,andtestingframework
Infura - Infura is a Web3 backend and Infrastructureas-a-Service (IaaS) provider that offers a range of services and tools for blockchain developers. This includes the Infura API (Application Programming Interface)suite.
Web3Js - Web3.js is Comprehensive. Everything you need to start interacting with the Ethereum blockchain Community-driven. Opensourceand continuously updatedsince2015Modular.
Angular - The Angular Team at Google and anetwork ofpeople and businesses are the driving forces behind the TypeScript-based free and opensource web applicationframeworkknownasAngular.
3.2 Hardware Components
• IntelCorei5/i7
• 4/6GBRam
• 500GBHarddisks
3.3 Implementation
Asshowninthegivenfigure,theadmindeploysthesmart contracts to the Ethereum Blockchain and authenticates and registers the entities of the chain. Supplier registers a new raw material and the raw material contract is deployed for the newly created raw material. CorrespondingTransactionContractisalsodeployedforthe newly created raw material. The raw material is then registeredsuccessfully.
Supplier transfers the raw material to the Transporter. Supplier updates the product status and creates a Transaction in the Transaction Contract. Transporter transfers the raw material to the manufacturer. Manufacturer verifies the source of the rawmaterial and also updates the product status and creates a transaction in the transaction contract. The manufacturer registersa newmedicine.MedicineContractisdeployedfor the newly created medicine. Corresponding Transaction Contract is also deployed for the newly created medicineand the medicine is registered successfully. Manufacturer transfers the raw material to the Transporter and updates the product status and creates a transaction in the transaction Contract. Transporter transfers the raw material to the Wholesaler and the wholesaler verifies the source of theraw material. Wholesaler updates the product status andcreatesatransactionintheTransaction Contract.Thenthewholesaler transfers the raw material to the Transporter and updates the product status and creates a transaction in the Transaction Contract. Transporter transfers the rawmaterialtotheDistributor. Andthedistributorverifiesthesource of the raw material. Distributor then updates theproductstatusandcreatesa transaction in the Transaction Contract. The distributor transfers the raw material to the Transporter. and updates the product status and creates atransaction in the Transaction Contract. Distributor transfers the raw materialtothePharma.
Therearecomplexinteractionsandflowofdataamongthe pharmaandthecustomerofthesupplychain. The process isdividedinto4partsi.e.,managingcustomerinformation, managingdruginformation,managingsalesandgenerating stocks. Pharma is responsible to provide right medicine to customers as per doctor prescribed and update medicine status.Duetolackoftransparencyinthecurrentsystem,it is extremely difficult for customers or buyers to know the value of the products. It is also very difficult to investigate the tampering within the supply chain when thereissuspicionofillegal or unethical practices. But now using our system the customers can view the whole transaction of drugs and beassuredaboutthereportsof the medicine they are purchasing resulting in increase in customersatisfactionandtransparencyinthesystem.
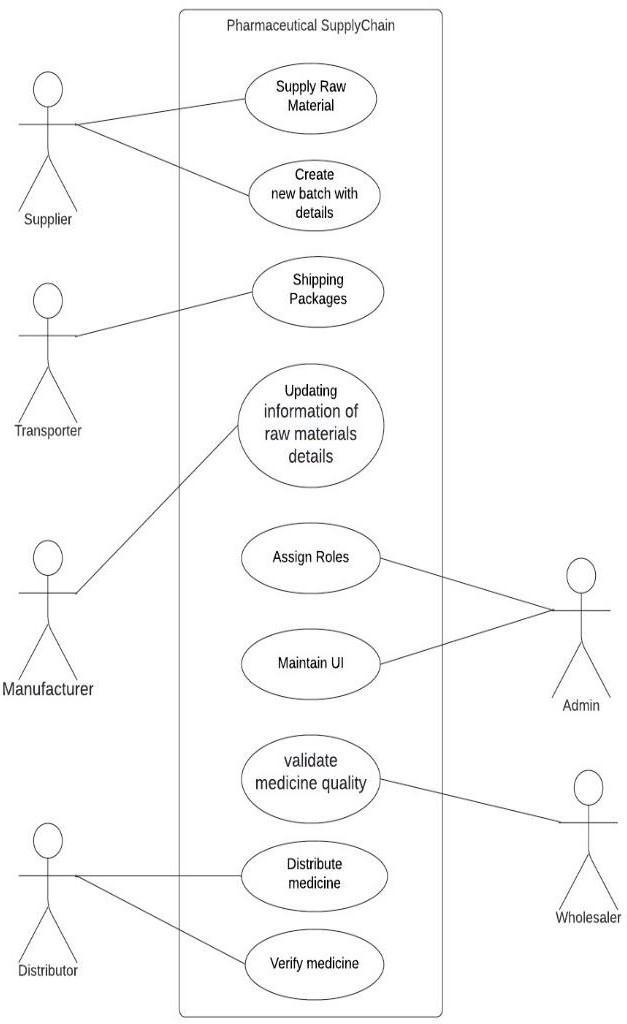
3.4 System Description
Admin: Admin register new users and assign roles accordingtotheirwork.
Supplier: Supplier supplies raw materials by creating a newbatchwithdetailsofthefarm.
Transporter: Transporters are responsible for shipping packages/consignmentfromonestagetoanother.
Manufacturer:Themanufacturerisinchargeofproducing fresh batches of medication for delivery to wholesalers or distributors by updating information about the raw material details (such as batch ID and consumption units thatareutilisedtoproduce newbatchesofmedicationand amount).
Wholesaler: Wholesaler is responsible to receive medicinefromManufacturerandvalidatemedicinequality, thentransfertoDistributor.
Distributor: Distributor is responsible to distribute medicine to pharmacies and do verification on medicine qualityandcondition.
Pharma: Pharma is responsible to provide the right medicinetocustomersasperdoctorprescribedandupdate medicinestatus.

4. FUTURE SCOPE
InFuture,wewilldevelopanandroidversionofthesystem. Keep on adding new smart contracts so as to remove any remote possibility of security breach. Continuous upgradation of UI to provide user friendly interface. Our methodology shows how blockchain technology has the abilityto promote efficient prescription data sharing while upholding the security of the original data sources. Our project can be expanded to solve further interoperability problems in the healthcare industry. Additionally, it can give patients quick,safeaccess totheirmedicationhistory.
Moreover, there is potential for using it to offer identity management for stakeholders in the healthcare industry. Blockchain applications for identity management hold greatpromisebutfurtherresearchisneeded.
5. CONCLUSION
Through this project, we have looked into the difficulty of
drug traceability within pharmaceutical supply chains, emphasisingitsimportanceinparticulartoguardagainstfake medications. We have created and tested a blockchainbased pharmaceutical supply chain solution that enables decentralised drug tracking and tracing. Our suggested solution specifically makes use of smart contracts within the Ethereum blockchain to achieve automated recording of events that are accessible to all participating stakeholders as well as the cryptographic principles underlying blockchain technology to achieve tamper-proof logs of events within the supplychain.Interms ofthequantityofgasusedtocarryout the various operations that are triggered within the smart contract, we have shown that our suggested method is economical.Additionally,thesecurity analysis performed has demonstrated that our suggested solution achieves protection against malicious attempts targeting the availability, integrity, and non- repudiation of transaction data,whichiscrucialincomplexmulti-party settings like the pharmaceutical supply chain.In order to achieve end-to-end transparency and verifiability of drug use, we intend to extendthesuggestedsystem as part of our ongoing efforts to improve theefficiencyofpharmaceuticalsupplychains.
REFERENCES
[1] Prasad Nayak B, Preetham V K, Sandeep Kulkarni, Sreejith, Mrs. C K Vanamala, Drug Supply Chain ManagementUsingBlockchain,IJRES,2022
[2] Joeke Kootstra, Tineke Kleinhout-Vliek, Implementing pharmaceutical track and-trace systems: a realistreview,IEEE,2021

[3] May Alnafrani, Subrata Acharya, SecureRx: A blockchain-basedframework foranelectronic prescription systemwithopioidstracking,Elsevier,2021.
[4] Prashant Gajera, Akshay Gondaliya, Jenish Kavathiya, A Blockchain-Based Approach for Drug TraceabilityinHealthcareSupplyChain,IEEE,2020.
[5] Prashant Gajera, Akshay Gondaliya, Jenish Kavathiya, A Blockchain-Based Approach for Drug TraceabilityinHealthcareSupplyChain,IEEE,2020
[6] Monalisa Sahoo, Sunil Samanta Singhar, A Blockchain Based Model to Eliminate Drug Counterfeiting,Springer,2020
[6] A. Bougdira, A. Ahaitouf, and I. Akharraz, ‘‘Conceptual framework for general traceability solution: Description and bases,’’ J. Model. Manage.,vol. 15, no. 2, pp.509–530,Oct.2019.
[7] K.AlHuraimelandR.Jenkins. (2020). SmartTrack. Accessed: May 26, 2020. [Online]. Available: https://smarttrack.ae/
[8] A. Seiter, ‘‘Health and economic consequencesof counterfeitdrugs,’’Clin.Pharmacol.Therapeutics,vol.85, no.6,Jun.2020.
