Heart Failure Prediction using Different MachineLearning Techniques
1Prof. Information Technology, AISSMS Institution of Information Technology, Pune, Maharashtra, India
2Student, Information Technology, AISSMS Institution of Information Technology, Pune, Maharashtra, India
3Student, Information Technology, AISSMS Institution of Information Technology, Pune, Maharashtra, India
4Student, Information Technology, AISSMS Institution of Information Technology, Pune, Maharashtra, India

5Student, Information Technology, AISSMS Institution of Information Technology, Pune, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - A heart disease is a type of condition that affects the heart and blood vessels. It can also be referred to as cardiovascular disease. Getting the right diagnosis and treatment of heart disease is very important in order to improve the quality of healthcare. Clinical data analysis faces a significant problem when predicting cardiovascular disease. The current situation of applying conventional approaches in practically the whole medical field is being revolutionized and changed by Machine Learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence, and Big Data. With the use of machine learning (ML), it has been possible to make predictions and judgments from the vast amount of data generated by the healthcare sector. In this paper, we present several Machine Learning models and attain the best model to improve the precision of cardiovascular disease prediction. Different feature selection techniques and many well-known strategies are used to improve the accuracy.
Key Words: Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, Cardiovascular Disease, Feature Selection, Heart Disease Prediction
1.INTRODUCTION
Anumberofcontributingriskfactors,namelydiabetes,high bloodpressure,excessivecholesterol,anirregularpulserate, andmanyotherfactors makeitchallengingtodiagnoseheart disease(HD).Theseverityofcardiacdiseaseinhumanshas been determined using various data mining and neural network techniques. Several Classifiers namely Random Forest, K-Nearest Neighbour(KNN), Logistic Regression and Naïve Bayes Since cardiac illness has a complex character,itrequirescautiousmanagement.Failuretodoso could harm the heart or result in premature death. To identify different types of metabolic syndromes, data mining and the perspective of medical research are employed.Heartdiseasepredictionanddataanalysisboth greatly benefit from data mining with classification. HD is often diagnosed by a doctor after reviewing the patient's medicalhistory,theresultsoftheirphysicalexam,andany concerningsymptoms.However,theresultsofthismethod of diagnosis do not reliablyidentify heart diseasepatients.
Additionally, analysis is costly and computationally challenging. To tackle these problems, a non-invasive diagnosissystembasedonclassifiersofmachinelearning (ML) must be created. To identify the best-suited machine learning model we compare the accuracies of different classification models and find out the best fit model with the best accuracy. Due to the dimensionality constraint, it is required to reduce the dimensionality of dataforavarietyoflearningtasks.Thechoiceoffeatures has a significant impact on a variety of applications, including making buildings simpler, improving learning outcomes,andproducingclearandcomprehensibledata. Due to the large amount of dimensions in big data, selecting features from it is a difficult task that leads to significant issues. Additionally, there are difficulties choosing features for structured, heterogeneous, and streaming data, as well as problems with scalability and stability. The feature selection issues must be overcome forlargedataanalytics.
On the other hand, effective machine learning requires an appropriate model. Naturally, a strong machine learning modelisonethatexcelsbothondatathatisn'tseenduring training (otherwise, the model would only learn the trainingdata)andondatathathasn'tbeenseenbefore.To test every classifier using data, and discover that they correctlyclassify50%ofthecasesonaverage.Additionally, whena modelistrainedandtestedonadataset,adequate cross-validation methodologies and performance evaluationcriteriaareessential.
Inthepaper,thesectionsarestructuredasfollows.
The literature related to the problem has been discussed in Section 2. In Section 3 the System Architecture is discussed. In Section 4 the Research Methodologies which consistofDataSet,DataCollection,andPreprocessingalong with classification Techniques are discussed. The Theoretical and mathematical knowledge of feature selection and classification algorithms are discussed in detail.Further,theConclusionandtheFutureScopeofthe study have been discussed in detail in Sections 5 and 6 respectively. The last section consists of acknowledgment and references which made this study possible.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
ResearchershaveproposedanumberofmachinelearningbaseddiagnosistechniquestodetectVariousDiseasesinthe literature review. In order to demonstrate the significance of the suggested work, this research study offers multiple machine learning-based diagnosis approaches that are currently being used. "Intelligent Machine Learning Approach for Effective Recognition of Diabetes in EHealthcareUsingClinicalData",isapaperpublishedbyA.U. Haq,J. P.Li, J.Khan, M.H.Memon,S.Nazir, S.Ahmad,G. A. Khan,andA.Ali.Inthispaper,theyhaveproposedadiabetes diagnosissystemutilizingmachinelearningtechniques.On the diabetic data set, a clinical dataset created from a patient's clinical history, the proposed method has been tested.Fortheselection of highlysignificantfeatures, they have also presented a filtering technique based on the DecisionTree(IterativeDichotomiseralgorithm).AdaBoost and Random Forest, two ensemble learning algorithms, have also been employed for feature selection, and also comparison of the performance of the classifier with wrapper-basedfeatureselectionapproachesisdone.
In "Optimal Multi-Stage Arrhythmia Classification Approach", apaperpublishedbyJ.Zhengetal.,The12-leadsurfaceECGbased multi-stage arrhythmia classification algorithm has been refined to reach the accuracy performance level of qualified cardiologists. A revolutionary feature extraction technique, a three-step noise reduction stage, and an ideal classification model with precisely calibrated hyperparameters make up thenew methodology. On patients with no other cardiac conditions, the best method which included a a unique feature extraction approach using the Low Band Pass filter, Robust LOESS, Non-Local Means smoothing, and average scores of the observed variable of ratios of interval lengths and magnitudes of peaks and valleyshasattainedaveryhighaccuracy.
In "A novel integrated diagnosis method for breast cancer detection"apaperbyA.U.Haq,J.Li,M.H.Memon,J.Khan, and S. U. Din, Support vector machine, a type of machine learning model, has been used to categorize breast cancer patients into malignant and benign groups. They have employed Chi-square and Minimal Redundancy Maximum Relevancealgorithmstochoosemorepertinentfeaturesfrom thebreastcancerdatasetinanefforttoimprovethemethod's classificationperformance.Themodelistrainedandtested usingthetraining/testingsplittingtechnique.Additionally, performance assessment metrics have been used to examine the model's performance. The experimental findings showed that on the subset of features chosen by the Minimal Redundancy Maximal Relevance feature selection approach, the classifier support vector machine had the best classificationperformance.WhencomparedtotheMinimal Redundancy Maximal Relevance algorithm, the support vectormachineperformedpoorlyonfeatureschosenbythe Chi-squarefeatureselectionapproach. They concludedfrom
the study of the experimental data that the performance of the integrated system based on Minimal Redundancy Maximal Relevance and Support Vector Machines is high because more appropriate features were chosen, leading toveryhighaccuracy.
In"Anewmethodofassessingcardiacautonomicfunction anditscomparisonwithspectralanalysisandcoefficientof variationofR-Rinterval"apaperbyMToichi1,TSugiura, T Murai, A Sengoku Ten healthy participants participated inapharmacologicalexperimenttotestanovelnon-linear techniquefor measuring cardiac autonomic function. Each of the novelapproaches used theLorenz plot,spectral analysis, andcoefficientofvariationtoexaminetheR-Rintervaldata collected under a control condition, in the autonomic blockade by atropine, and in the blockade by propranolol. With the help of their methodology, they were able to derive two measurements, the cardiac sympathetic and vagal indices, which represent the vagal and sympathetic systemsseparately.Comparedtotheindicesderivedbythe other two approaches, these two were determined to be more trustworthy. They projected that this method will eventually be more accurate and practical for the noninvasive measurement of short-term cardiac autonomic function.

In"ANewAutomaticIdentificationMethodofHeartFailure UsingImprovedSupportVectorMachineBasedonDuality OptimizationTechnique"apaperpublishedbyGamalG.N. Geweid(Member, IEEE), and Mahmoud A. Abdallah, For detection of Heart Disease using ECG signals, a new automatic technique utilizing an upgraded support vector machine model was put forth. This is especially pertinent toECGsignalsforthediagnosisofHFDastheinitialstepin treating and caring for patients generally and specifically those with early heart disease to increase their chance of survival as a whole. In order to detect HFD in ECG data, a hybrid strategycombining dual SVMand a nonparametric algorithmispresentedinthisstudy.Thishybridapproach improvestheprecisionandreliabilityofearlyheartfailure classes' identification and diagnosis. To create two SVM models, the nonparametric approach is used to train the SVM and its dual. The dual problem offers a second perspective that is sometimes better and more straightforward than the initial Problem. This feature compares the outputs of the SVM model and those of the dualSVMmodelinordertoidentifyheartfailurediseasein ECGsignals.Whencomparedtootheralgorithmstowhich thestudyrefers,experimentsdemonstratethatthehybrid technique generates good results, is more effective, and boosts the accuracy of Heart failure disease identification withreasonableaccuracyof94.97%.
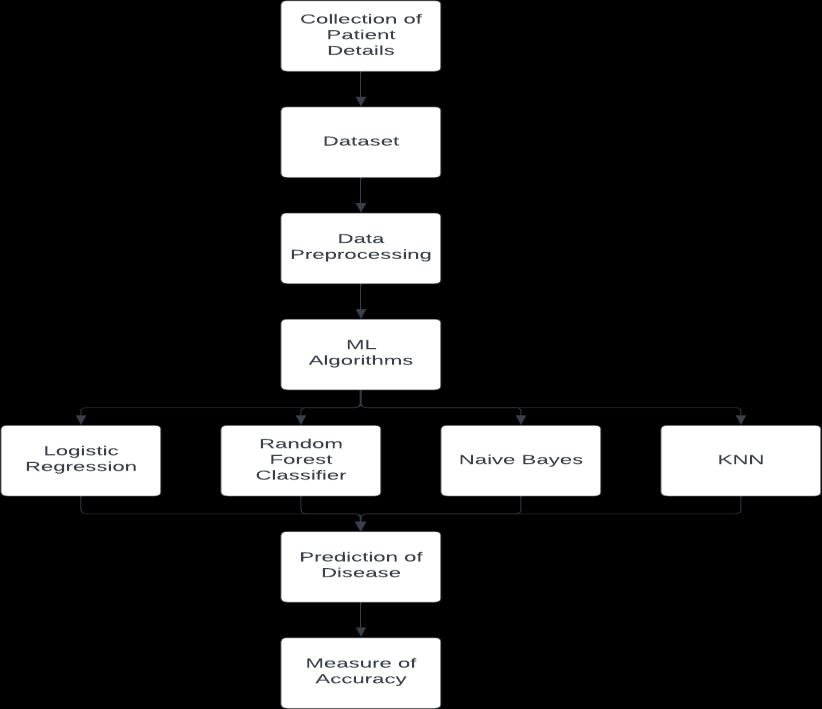
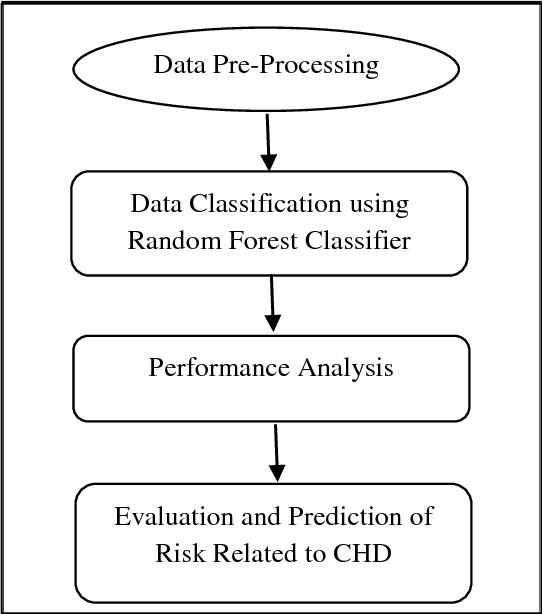
3. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Dataset collection is the act of gathering information containing patient specifics. The method of selecting characteristics chooses the relevant qualities for heart
disease prediction. To accurately forecast cardiac disease, several classification approaches will be applied to preprocessed data. The accuracy of several classifiers is compared using the accuracy measure. Dataset collection is the act of gathering information containing patient specifics.The method of selecting characteristics chooses the relevant qualities for heart disease prediction. The accessibledata resources arelocated,thenfurther chosen, cleansed, and transformed into the required form. To accurately forecast cardiac disease, several classification approacheswillbeappliedtopreprocesseddata.
3. Serumcholesterolinmg/dl
4. Fastingbloodsugar>120mg/dl
5. Restingelectrocardiographicresults(values
0,1,2)
6. Maximumheartrateachieved
7. Exerciseinducedangina
8. Oldpeak=stdepressioninducedby exerciserelativetorest
9. Theslopeofthepeakexercisestsegment
10. Numberofmajorvessels(0-3) coloredbyflourosopy,
11. 0 = normal; 1 = fixed defect; 2 = reversable defect the names and social security numbers ofthepatientswererecentlyremovedfromthe database,replacedwithdummyvalues.

B. Data Collection and Preprocessing
A collection of methods known as data preparation are usedondatatoenhanceitsquality.Thesemethodsinclude addressing missing values, changing the type of feature, and many more. Data analysis that has not been thoroughly checked for these issues may yield false findings. Therefore, before doing any analysis, the representation and quality of the data must come first. Especially in computational biology, data preparation is frequently the most crucial stage of a machine learning project. For the foundation of our heart disease prediction system, we first gather a dataset. We divide the dataset into training and testing data once it is collected. The learningofthepredictionmodeltakesplaceonthetraining dataset, and the evaluation of the predictionmodel occurs onthetestingdataset.
Fig-1: SystemArchitecture
4. RESEARCH METHODS
By investigating the four classification methods listed above and doing a performance analysis, the suggested studyforecastscardiacdisease.Effectivelypredictingifthe patienthascardiacdiseaseisthestudy'smaingoal.
Themedicalexpertinputs thenumbersfromthepatient's healthreport.Theinformationisusedtofeedamodelthat forecaststhelikelihoodofheartdisease.Fig.depictsthefull procedure.
A. Dataset
The Heart Failure Prediction Data Set is utilized in the study. It has been downloaded online from Kaggle. The dataset contains various input features, which are broken downintothefollowingcategories:
C. Classification
To identify the model's outcome from several labels or categorical input data, classification is a supervised machinelearning model that uses a label's output. The classifier model is created based on several well-known labelledor classifiedfeatures oftheinputdata. The model was then evaluated using the test set to see how many of the model's known targets there were, and it was attempted to rectify any unknown targets. It is possible to doclassificationonbothstructuredandunstructureddata. Classificationistheactofcategorizingagivencollectionof dataintoclasses.
Predicting the class of the provided data points is the firststep in the procedure. The terms target, label, and classesare frequently used to describe the classes. The task of estimating the mapping function from discrete input variables to output variables is known as classification predictive modelling. Finding the class or category that the new data will belong to is the key objective.
Logistic Regression
Random Forest Classifier
resultbyconsideringoneormoreindependent variables. Sincethevariablebeingusedtoquantify,itis a dichotomousvariable, the output will only have two possiblepossibilities.
Thegoaloflogisticregressionisto identify the relationship that best fits the dependent
It is a machine learning classification algorithm that selectsa variableandasetofindependentfactors.Incomparison tootherbinaryclassificationtechniquesliketheclosest neighbour, it performs better because it unbiasedly describesthecontributingfactorsclassification.
Both classification and regression techniques employ Random Forest algorithms. In order to generate predictions,it builds a tree for the data. Using Random Forest on huge datasets generate the same outcome from the missing values. Samples produced by the Classifier can store adecision tree so you may utilize it later. Additionalinformationcanbeobtainedbymakinga forecastaftercreatingarandomforestbyusingaclassifier developedinthefirstrandomforeststage.
Graph-1: LogisticRegressionGraph
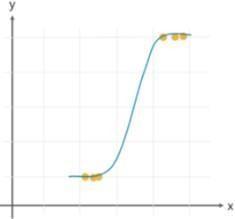
Thismethodinvolvesanalyzingacollectionofdatathat includes a dependent variable and one or more independentvariablesinordertoforecasttheresultofa binary variable, which has only two possible possibilities. The dependent variable's nature is categorical. The independent variables are known as predictors, whilethe dependentvariable is alsoknown as the target variable. In a specific version of linear regression called logistic regression, we can only predicttheresultofacategoricalvariable.Bymeansof thelogfunction,itforecaststhelikelihoodoftheevent. In orderto forecast the category value, we employ the Sigmoid function or curve. The result (win or lose) is determinedbythethresholdvalue. Sigmoid
Logistic
A strong statistical analysis method is regression analysis. Ina data collection, a dependent variable that interests us is utilized to forecast the values of other independentvariables.Regressionissomethingthatwe frequentlyencounterinanintuitiveway.
Fig-2: RandomForestClassifier
Usingrandomforestalgorithm,wecanobtainaccuracy HighAccuracyforpredictionofheartdisease

Naïve Bayes
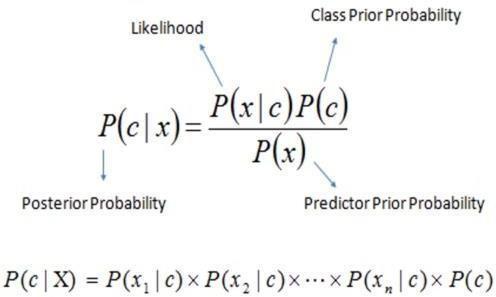
The family of straightforward "probabilistic classifiers" known as "Naive Bayes Classifiers" in statisticsisbasedontheapplicationofBayes'theorem with strong (naive) independent assumptions between the features. Althoughthey are some of the simplest Bayesian network models, theymay achieve high levels of accuracy when combined with kernel density estimation. Naive Bayes classifiers are very scalable since the number of parameters needed is linearinthenumberofvariables(features/predictors) inalearningjob.Whencomparedtomanyothertypes of classifiers, maximum-likelihood training can be performed in linear timeby evaluating a closed-form expression as opposed to being costly approximated iteratively. In the statistics literature, naïve Bayes classificationmodelsgobythetitlessimpleBayesand independentBayes.
Neighbors
Formula
KNN isa lazilysupervised machinelearningtechnique that uses distance measurements to predict and categorizeunknowndatafromknowndata.The distance metric is used to determine the distance between each point in the training data and each point in the testing data. Fundamentally, the k-nearest neighbour classifier depends on a distance metric. The more accurately that metriccaptureslabel similarity, the more accurate the classification. The Minkowski distance is the most popularoptionwhichis:
dist(x,z)=(d∑r=1|xr−zr|p)1/p
Withk-NN,allcomputationispostponeduntilafterthe function has been evaluated and the function is only locallyapproximated. Since this technique depends on distance for classification, normalizing the training data can significantly increase accuracy ifthe features reflect several physical units or have distinct sizes. Assigning weights to neighbor contributions may be a helpful strategy for both classificationand regression, making the closer neighbourscontribute more to the average thanthefarther neighbours.As an illustration, a typical weighting method assigns each neighbour a weight of 1/d, where d isthe distance between the neighbours.
5. CONCLUSION
The long-term saving of human lives and the early detectionof irregularities in heart problems will be made possible by identifying the processing of raw healthcaredataofheartinformation.Toprocesstheraw data and deliver a fresh and original insight into heart disease, machine learning techniques were applied in this study. Prediction of heart disease is difficult and crucialinthemedicalindustry.However,ifthedisease
is discovered in its early stages and preventative measures are implemented as soon as feasible, the fatality rate can be significantly reduced. In this Study, Various Machine Learning Algorithms have been studiedand analyzed. This Study will help us obtain the best Machine Learning Model for Efficient Heart Disease Prediction with the most accuracy. Our study's use of feature selection algorithms to identify the right features that improve classification accuracy and reduce the diagnosis system's processing time is another novel component. We'll put additional feature selection algorithms as well as optimization algorithms in the future to increase a prediction system's abilitytodiagnoseHeartDisease.
6. FUTURE WORK
In the future work, More machine learning classification algorithms and data pretreatment approaches may be usedinsubsequentworkstoprovideoutcomes.
In light of the fact that more data equals more accurate results,itfollowsthatalargeamountofdatawillresultin better prediction. Since the patient may not always havetimetovisitthedoctor,thisissuecanberesolvedby creating a website or smartphone application with a graphical user interface. This website streamlines the prediction process and allows patients to access the results at home by simply entering their risk factors.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
First and Foremost, We are thankful to our college AISSMS Institute of Information Technology and the EngineeringDepartmentandourGuideMr.PriteshPatil, Associate Professor, AISSMS Institute of Information Technology.AspecialwordofgratitudetoDr.Meenakshi Thalor, Head of Department, Information Technology and Engineering Department, AISSMS IOIT college of Engineering,forhercontinuousguidanceandsupportfor ourprojectwork.
REFERENCES
[1] C. for Disease Control and Prevention, “FastStats, ” Deaths and mortality, Cdc.gov, May 2017, Accessed: Mar. 23, 2021. [Online]. Available: https: //www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/deaths.htm
[2] A. U. Haq, J. P. Li, J. Khan, M. H. Memon, S. Nazir, S. Ahmad,G. A. Khan, and A. Ali, ‘‘Intelligent machine learning approach for effective recognition of diabetes in E- healthcare using clinical data,’’ Sensors, vol. 20, no.9,p.2649,May2020.

[3] C for Disease Control and Prevention, “Atrialfibrillation| cdc.gov, ” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, May 2020, Accessed: Mar, 23, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/atrial_ fibrillation.htm
[4] Z D. G. Ary, L. Goldberger, and A. Shvilkin, “QRS Complex- an overview | ScienceDirect Topics„ ” Sciencedirect.com, Goldberger’s clinical electro cardiography,2017,Accessed:Mar.23,2021.[Online]. Available: https: //www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-anddentistry/qrs-compleM.Young,TheTechnicalWriter’s Handbook.Mill Valley, CA: University Science, 1989.
[5] A. U. Haq, J. Li, M. H. Memon, J. Khan, and S. U. Din, ‘‘A novel integrated diagnosis method for breast cancer detection,’’J.Intell.FuzzySyst.,vol.38,no.2,pp.2383–2398,2020.
[6] P. Virtanen et al., “SciPy 1.0: Fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in python,” Nature Methods, vol. 17, pp.261–272,2020.
[7] J. Zheng et al., “Optimal multi-stage arrhythmia classification approach,” Sci. Rep., vol. 10, no.1,pp.1– 17,2020
[8] “Tian Chi-ECG-abnormal-event-prediction, ”GitHub, 2019. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/NingAnMe/TianChi- ECG-abnormalevent prediction. Tianchi Hefei High-Tech Cup Ecg Human-MachineIntelligenceCompetition,2019.
[9] Alivecor, Inc., Alivecor.com, 2020, Accessed: Mar. 23,2021.[Online].Available:https://www.alivecor.com/#
BIOGRAPHIES
Prof. Pritesh Patil InformationTechnology Professor

AISSMS Institute of InformationTechnology
Dhanashri Gundal BE IT Student
AISSMS Institute of Information Technology
Shravani Ghadge BE IT Student
AISSMS Institute of Information Technology
Ankita Kawade BEITStudent



AISSMSInstituteofInformation Technology
Rohit Bharmal BEITStudent

AISSMSInstituteofInformation Technology

