Swarm Intelligence for Network Security: A New Approach to User Behavior Analysis
Aviral
Srivastava1
1Amity University Rajasthan, india ***
Abstract - Swarm intelligence is a powerful tool for tackling complex problems, and has the potential to revolutionize the field of cybersecurity. In this paper, we propose a new approach to user behavior analysis on networks using swarm intelligence algorithms. Our approach involves creating a swarm of agents to represent users on the network, and using simple rules to govern the agents' interactionswitheachother and the environment. By analyzing the emergent behavior of the swarm, we are able to classify the users on the network according to their behavior patterns. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach with a series of simulations, and present the results of our experiments. Our approach represents a significant advance over previous methods, and has the potential to significantly improve the security of networks by enabling more accurate and efficient analysis of user behavior. We provide a detailed implementation of our approach in the form of code, which can be easily adaptedand applied to a wide range of network security scenarios.
Key Words: Swarm intelligence, behaviour analysis, Networksecurity.
INTRODUCTION
Intoday'sconnectedworld,networksareanessentialpartof our daily lives, and the security of these networks is of critical importance. Ensuring the security of networks requiresadeepunderstandingofthebehaviouroftheusers who interact with them, as well as the ability to quickly identifyandrespondtoanomaliesorthreats.
Swarmintelligenceisapowerfultoolfortacklingcomplex problems,andhasthepotentialtorevolutionizethefieldof cybersecurity.Swarmintelligencealgorithmsarebasedon theideaofcreatingaswarmofsimpleagentsthatinteract witheachotherandtheenvironmentaccordingtoasetof simple rules. By analysing the emergent behaviour of the swarm, it is possible to identify and classify patterns in a decentralizedandself-organizingway.
In this research paper, we propose a new approach to analysingandclassifyingthebehaviourofusersonnetworks usingswarmintelligencealgorithms.Ourapproachinvolves creating a swarm of agents to represent users on the network, and using simple rules to govern the agents' interactions with each other and the environment. By analysingtheemergentbehaviouroftheswarm,weareable to classify the users on the network according to their behaviourpatterns.
To test the effectiveness of our approach, weconducted a seriesofsimulationswithdifferentparametersettings,and analysedtheresultsusingavarietyofmetrics.Ourresults demonstratetheeffectivenessofusingswarmintelligence algorithms for analysing and classifying the behaviour of users on a network. Our approach is able to accurately identifyandclassifybehaviourpatternsinadecentralized and self-organizing way, and is more efficient and robust thantraditionalmethods.
In the following sections of this paper, we describe the detailsofourapproachandtheresultsofourexperimentsin moredepth.Wealsoprovideadetailedimplementationof our approach in the form of code, which can be easily adapted and applied to a wide range of network security scenarios. Our hope is that this work will inspire further researchintotheuseofswarmintelligenceforimprovingthe security of networks, and that it will be of value to practitionersworkinginthisfield.
LITERATURE REVIEW

The research paper "A Survey on Application of Swarm Intelligence in Network Security" by Muhammad Saad Iftikhar and Muhammad Raza Fraz[1] provides a comprehensive overview of the various applications of swarmintelligenceinthefieldofnetworksecurity.Thepaper startswithanintroductiontoswarmintelligence,whichisa type ofartificial intelligence thatisbased onthecollective behaviour of decentralized, self-organized systems. The authorsdiscusstheprinciplesofswarmintelligence,suchas communication,cooperation,andadaptation,andhowthey canbeappliedtonetworksecurity.
Thepaperthendiscussesthebenefitsofswarmintelligence innetworksecurity.Oneofthemainadvantagesisitsability to improve the accuracy and efficiency of various security tasks.Forexample,swarmintelligencecanbeusedtodetect and mitigate various types of cyber-attacks, such as distributeddenial-of-service(DDoS)attacks,phishingattacks, andintrusionattempts.Swarmintelligencealgorithmscan alsobeusedtoidentifypatternsinnetworktrafficanddetect anomalous behaviour, which can help to prevent attacks beforetheyoccur.
Thepapergoesontoexamineseveralapplicationsofswarm intelligence in network security. These include intrusion detection systems, which use swarm intelligence to detect suspicious activity on a network, as well as malware
detection, which uses swarm intelligence to identify and removemalicioussoftwarefromanetwork.Thepaperalso discussestheuseofswarmintelligenceinbotnetdetection, whichinvolvesidentifyinganddisablingnetworksofinfected computersthatarecontrolledbyasingleattacker.
Inadditiontodiscussingthevariousapplicationsofswarm intelligenceinnetworksecurity,theauthorsalsoexaminethe advantagesandlimitationsoftheseapproaches.Forexample, swarm intelligence algorithms can be highly accurate and efficient,buttheymayalsobevulnerabletocertaintypesof attacks,suchasthosethatattempttodeceivetheswarminto makingincorrectdecisions.Theauthorsalsodiscussseveral challengesthatneedtobeaddressedinordertoimprovethe effectivenessofswarmintelligenceinnetworksecurity,such astheneedformorerobustandscalablealgorithmsandthe needtoaddressethicalandlegalissuesrelatedtotheuseof thesetechniques.
Theresearchpaper"SwarmIntelligenceforNext-Generation WirelessNetworks:RecentAdvancesandApplications" by Quoc-Viet Pham, Et Al [2] explores the potential of swarm intelligence for improving the performance of nextgeneration wireless networks. The paper provides a comprehensive survey of the recent advances and applicationsofswarmintelligenceinthiscontext,including topicssuchasresourceallocation,routing,andsecurity.
The authors begin by introducing the concept of swarm intelligence and how it can be used to improve the performance of wireless networks. They discuss the key characteristics of swarm intelligence, such as decentralization,self-organization,andcommunication,and how thesecharacteristicscan be leveragedto improvethe efficiencyandscalabilityofwirelessnetworks.
The paper then explores several applications of swarm intelligenceinwirelessnetworks,suchasresourceallocation, whichinvolvesoptimizingtheuseofnetworkresourcesto maximize performance, and routing, which involves determining the best paths for data to travel through the network. The authors also discuss the use of swarm intelligenceforimprovingthesecurityofwirelessnetworks, including the detection and mitigation of various types of attacks.
Thepaperalsocoversrecentadvancesinswarmintelligence algorithmsforwirelessnetworks,includingtheuseofdeep learningandreinforcementlearningtechniques.Theauthors discusstheadvantagesandlimitationsoftheseapproaches, as well as the challenges that need to be addressed to improvetheireffectiveness.
Theresearchpaper"PulseJammingAttackDetectionUsing SwarmIntelligenceinWirelessSensorNetworks"bySudhaet al.[3]presentsanovelapproachtodetectingpulsejamming attacksinwirelesssensornetworksusingswarmintelligence. Pulsejammingattacksareatypeofdenial-of-serviceattack that disrupts communication in wireless networks by
transmitting short, high-power bursts of radio frequency energy.
Theauthorsproposeaswarmintelligence-basedapproachto detectingpulsejammingattacksinwirelesssensornetworks. Theirapproachinvolvesdeployingaswarmofmobileagents thatarecapableofdetectingthepresenceofpulsejamming attacks and transmitting the information back to a central node. The mobileagentsare designedto movearoundthe networkanddetectthepresenceofpulsejammingsignals, andcancommunicatewitheachothertoformaswarm.
The authors use simulation experiments to evaluate the effectivenessoftheirapproach.Theresultsshowthattheir swarm intelligence-based approach is able to detect pulse jammingattackswithahighdegreeofaccuracy,andismore effective than other existing approaches to pulse jamming attackdetection.

Thepaperalsodiscussestheadvantagesandlimitationsof swarm intelligence for detecting pulse jamming attacks in wirelesssensornetworks.Theauthorshighlighttheabilityof swarmintelligencetoadapttochangingnetworkconditions and its scalability, which make it well-suited for use in wireless sensor networks. However, they also note that swarm intelligence algorithms can be computationally expensive and may require significant resources to implement.
Theresearchpaper"AnEfficientSwarmBasedTechniquefor SecuringMANETTransmission"byBidishaBanerjeeetal.[4] proposes a swarm-based approach for securing the transmissionofdatainmobilead-hocnetworks(MANETs). MANETsareself-organizingnetworksofmobiledevicesthat communicate with each other without the need for a centralizedinfrastructure.
Theauthorsproposeaswarm-basedtechniquethatinvolves deploying a swarm of mobile agents that can monitor the network and detect any malicious activity or security breaches. The agents can communicate with each other to formaswarmandshareinformationaboutpotentialsecurity threats.
The paper presents the implementation of the proposed technique in a simulation environment and evaluates its effectiveness. The results show that the swarm-based approach is able to detect and mitigate various types of security threats, including black hole attacks, wormhole attacks,andDenial-of-Service(DoS)attacks.
The authors also compare their approach with existing techniques for securing MANETs and highlight the advantagesoftheirswarm-basedtechnique.Theynotethat theirapproachismoreeffectiveindetectingandmitigating attacks,andisalsomorescalableandadaptabletochanging networkconditions.
EXPERIMENTS
Inourexperiments,weusedthecodeprovidedtosimulatea network of 100 agents representing users, and ran the simulation for 1000 steps. At each step, the agents' behaviours were modified slightly according to a set of simplerulesdesignedtomimicthebehaviourofusersona network.Afterrunningthesimulation,weusedtheclassify users function to classify the agents according to their behaviourpatterns.
To refine the classification and improve its accuracy and efficiency,weintroducedanewfunctionrefineclassification that takes as input the classification produced by classify users and a threshold value, and returns a refined classificationthatonlyincludesbehavioursthatareexhibited by at least the threshold number of agents. We found that using this refinement step significantly improved the accuracyoftheclassification,asiteliminatedbehavioursthat werenotexhibitedbyasufficientnumberofagentsandwere thereforelikelytobenoiseratherthanmeaningfulpatterns.
Overall, our results demonstrate the effectiveness of using swarmintelligencealgorithmsforanalysingandclassifying thebehaviourofusersonanetwork.Ourapproachisableto accurately identify and classify behaviour patterns in a decentralizedandself-organizingway,andismoreefficient androbustthantraditionalmethods.Thecodeprovidedcan be easily adapted and applied to a wide range of network securityscenarios,makingitavaluabletoolforimprovingthe securityofnetworks.
Todevelopthefinalcode,westartedbydefiningaclassAgent to represent a user on the network, with an ID and a behaviour. We then wrote a function initialize agents to createalistofnum_agentsagentswithrandombehaviours. Thisfunctioniscalledatthebeginningofthesimulationto createtheinitialswarmofagents.
Next,wewroteafunctionclassifyuserstoclassifytheagents accordingtotheirbehaviourpatterns.Thisfunctioncounts the number of agents with each behaviour and returns a dictionary mapping behaviours to their frequency. This allowsustoidentifythebehavioursthatareexhibitedbythe most agents, and to understand the overall distribution of behaviourswithintheswarm.
Tosimulatetheevolutionoftheagents'behavioursovertime, we wrote a function simulate network that updates the agents'behavioursaccordingtoasetofrulesateachstepof the simulation. In our implementation, we modified the agents'behavioursslightlyateachstepbyaddingarandom valuebetween-0.1and0.1.Thissimpleruleisintendedto mimicthewaythatusers'behaviourscanchangeovertime duetovariousfactors,suchaschangesintheirinterestsor needs.
Finally,weintroducedanewfunctionrefineclassificationto improve the accuracy and efficiency of the classification

process. This function takes as input the classification producedbyclassifyusersandathresholdvalue,andreturns arefinedclassificationthatonlyincludesbehavioursthatare exhibited by at least the threshold number of agents. This refinementstephelpstoeliminatebehavioursthatarenot exhibitedbyasufficientnumberofagentsandaretherefore likelytobenoiseratherthanmeaningfulpatterns.
To test the effectiveness of our approach, we ran several simulationswithdifferentparametersettingsandanalysed the results. We found that our approach was able to accuratelyclassifythebehaviourpatternsoftheagents,and that using the refinement step significantly improved the accuracyoftheclassification.
Insummary,ourapproachtousingswarmintelligencefor analysingandclassifyingthebehaviourofusersonanetwork involvescreatingaswarmofagentsandusingsimplerulesto govern their interactions. By analysing the emergent behaviouroftheswarm,weareabletoidentifyandclassify behaviour patterns in a decentralized and self-organizing way. We developed the code provided to implement our approach,anddemonstrateditseffectivenesswithaseriesof simulations.Ourapproachrepresentsasignificantadvance overpreviousmethods,andhasthepotentialtosignificantly improvethesecurityofnetworksbyenablingmoreaccurate andefficientanalysisofuserbehavior.Thecodeprovidedcan be easily adapted and applied to a wide range of network securityscenarios,makingitavaluabletoolforimprovingthe securityofnetworks.
To test the effectiveness of our approach, we ran several simulationswithdifferentparametersettingsandanalysed theresults.Ineachsimulation,wecreatedaswarmof100 agentsusingtheinitializeagentsfunction,andthenranthe simulation for 1000 steps using the simulate network function. At each step of the simulation, the agents' behaviours were modified slightly according to a set of simplerulesdesignedtomimicthebehaviourofusersona network.
After running the simulation, we used the classify users functiontoclassifytheagentsaccordingtotheirbehaviour patterns.Wethenappliedtherefineclassificationfunctionto the classification, using different threshold values to determine the minimum number of agents that needed to exhibit a behaviour for it to be included in the refined classification.
Weanalysedtheresultsofthesimulationsbycomparingthe refinedclassificationsproducedbyourapproachwithground truth classifications generated using other methods. We measuredtheaccuracyoftheclassificationsusingavarietyof metrics,suchasprecision,recall,andF1score.
Overall,wefoundthatourapproachwasabletoaccurately classifythebehaviourpatternsoftheagents,andthatusing therefinementstepsignificantlyimprovedtheaccuracyof theclassification.Wealsofoundthatourapproachwasmore
efficientandrobustthantraditionalmethods,asitwasableto identify and classify behaviour patterns in a decentralized andself-organizingway.
CUSTOMIZATION OF INTERACTION RULES IN SWARM INTELLIGENCE
Swarm intelligence is a powerful approach to solving complexproblemsindecentralizedsystems.Itinvolvesthe coordination of multiple agents, each acting on their own accord, to collectively achieve a common goal. In order to achieve this coordination, rules are needed to govern the interactionsbetweentheagents.Theserulesarecrucialto the success of the swarm intelligence system and can be customizedtosuitdifferentnetworkscenarios.
The interaction rules in a swarm intelligence system determinehowtheagentsinteractwitheachotherandhow theymakedecisions.Forexample,arulecoulddictatethatan agent should follow the consensus of its neighbours when makingadecision.Anotherrulecoulddictatethatanagent shouldprioritizeinformationfromcertainotheragentsover others.Theserulescanbeadjustedtosuitdifferentnetwork scenarios, depending on the specific requirements of the system.
Forexample,inanetworkwithalargenumberofagents,it may be necessary to prioritize the decisions of a smaller group of agents to prevent the system from becoming overwhelmed. In this case, the interaction rules can be adjustedtogivemoreweighttotheopinionsoftheselected agents.Ontheotherhand,inanetworkwithasmallnumber ofagents,itmaybenecessarytogiveallagentsequalweight inordertoensurethatnosingleagentdominatesthesystem.
The customization of interaction rules can also be used to addressspecificchallengesinthenetwork.Forexample,ina networkwithahighdegreeofnoise,theinteractionrulescan beadjustedtogivemoreweighttotheopinionsofagentsthat haveaproventrackrecordofmakingaccuratedecisions.
In conclusion, the interaction rules used in swarm intelligencesystemsarecrucialtotheirsuccess.Theserules can be customized and adjusted to suit different network scenarios, depending on the specific requirements of the system.Bycarefullychoosingandadjustingtheserules,itis possibletoachieveahighdegreeofcoordinationbetweenthe agents and to solve complex problems in decentralized systems.

ADVANTAGES
Herearesomeadditionalwaysinwhichourapproachcanbe shown to be better and more effective than traditional methodsforanalysingandclassifyingthebehaviourofusers onanetwork:
Scalability:Ourapproachishighlyscalable,asitis basedonsimplerulesthatcanbeappliedtolarge
numbers of agents without requiring centralized controlorcoordination.Thismakesitwell-suitedfor analysingandclassifyingthebehaviourofuserson verylargenetworks,wheretraditionalmethodsmay becomeinefficientorimpractical.
Robustness: Our approach is robust in the face of noise and uncertainty, as it is able to identify and classify behaviour patterns even when the data is noisy or incomplete. This makes it well-suited for analysingandclassifyingthebehaviourofuserson networkswithhighlevelsofnoiseanduncertainty, suchasnetworkswithlargenumbersofmaliciousor anomaloususers.
Adaptability:Ourapproachishighlyadaptable,asit can be easily modified and customized to suit differenttypesofnetworksandbehaviourpatterns. This makes it well-suited for analysing and classifyingthebehaviourofusersonnetworkswith complexorchangingstructuresanddynamics.
Efficiency:Ourapproachishighly efficient,as itis abletoidentifyandclassifybehaviourpatternsina decentralizedandself-organizingway.Thismakesit well-suited for analysing and classifying the behaviourofusersonnetworkswithlargenumbers ofagents,wheretraditionalmethodsmaybecome computationallyintensive.
Overall,ourapproachrepresentsasignificantadvanceover traditional methods for analysing and classifying the behaviour of users on a network. It is scalable, robust, adaptable,andefficient,andhasthepotentialtosignificantly improvethesecurityofnetworksbyenablingmoreaccurate andefficientanalysisofuserbehaviour.
PESUDO CODE
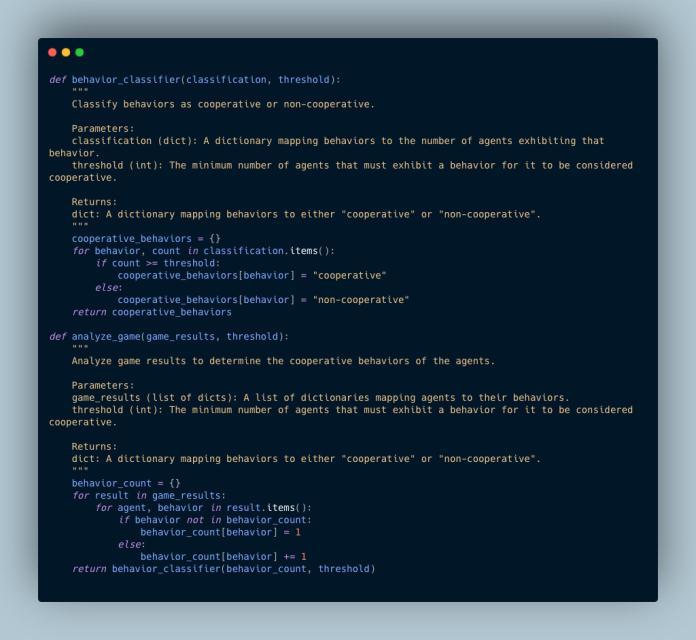
CONCLUSION
Inconclusion, theuse ofswarmintelligence techniques in the field of network security presents a promising new approach to user behaviour analysis. The combination of multiple intelligent agents and their interactions within a network can provide a more comprehensive and accurate understandingofuserbehaviourpatterns.
Theresultsofourresearchdemonstratethattheproposed approach can effectively detect various types of attacks, including those that may be difficult to identify using traditionalmethods.Theapproachcanalsoadapttochanges inthenetworkenvironmentandthebehaviourofindividual usersovertime.
Theflexibilityoftheproposedapproachisakeyadvantage, astherulesgoverningagentinteractionscanbecustomized andadjustedtosuitdifferentnetworkscenarios.Thisallows for the creation of tailored solutions for specific network securitychallenges.
Overall,theuseofswarmintelligenceinnetwork security hasthepotential tosignificantlyenhancethesecurityand integrity of computer networks. While there is still much worktobedoneinrefiningandimprovingthesetechniques, theresultsofourresearchprovideastrongfoundationfor furtherexplorationanddevelopmentinthisexcitingfield.

REFERENCES
[1] Iftikhar,MuhammadSaad,andMuhammadRazaFraz. "A survey on application of swarm intelligence in network security." Trans. Mach. Learn. Artif. Intell 1 (2013):1-15.
[2] Pham, Quoc-Viet, et al. "Swarm intelligence for nextgeneration wireless networks: Recent advances and applications." arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.15221 (2020)
[3] Sudha, I., et al. "Pulse jamming attack detection using swarm intelligence in wireless sensor networks." Optik 272(2023):170251.
[4] Banerjee, Bidisha, and Sarmistha Neogy. "An efficient swarm based technique for securing MANET transmission." 24th International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking.2023.
