Artificial Intelligence and the Field of Robotics: A Systematic Approach to Cybersecurity and Healthcare Systems
Usman Ibrahim Musa1 , Aminu Ibrahim Musa2 , Sakshi Dua31School of Computer Applications, Lovely Professional University, Punjab, India.
2Depertment of Information Technology, Ecole De Superieure De Gestion Et De Technologie, Benin.

3School of Computer Applications, Lovely Professional University, Punjab, India. ***
Abstract - A systematic review of cybersecurity and healthcare systems from the Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics perspective for the past 6 years is presented in this research. Cybercriminals nowadays are always researching new waystobreakintocorporatenetworksandstealsensitive data. People frequently adhere to the same fundamental security precautions on a daily basis, and as they use more devicesatwork,forsecurityexperts,maintainingthedataand keepingthemcurrentisbecomingmoreandmorechallenging. AI in cybersecurity is gaining importance as it contributes to overcoming the aforementioned difficulties. Additionally, the advances brought about by AI and the field of robotics have provedadvantageousforthehealthcaresector.Withtheuseof AI techniques like deep learning and machine learning, a number of healthcare systems have been developed that autonomouslydiagnosevariousdiseasesfrommedicalimages and further generate reports based on the findings. This research focuses on the role of AI and the field of robotics in enhancing the cybersecurity and healthcare sector. The research's literature demonstrates that AI in healthcare and cybersecurity is still a new and innovative field that needs to be studied further in the future. Researchers may utilize this study to get helpful tips and knowledge for their next work.
Key Words: AI,Robotics,Cybersecurity,Healthcare.
1. INTRODUCTION
Robotics and artificial intelligence are two major fields of science and engineering research. These terms are often used interchangeably to describe the development of technologiesthathelpmakemachinesintelligent.However, thereisasignificantdifferencebetweenthetwo.AIiswhat enablesrobotstofunctionlikehumans,whileroboticsisthe study of how to make them do so. Together, these technologiesholdgreatpromiseforthefuture.
A topic that in recent years has become familiar to just abouteveryone.Hardlyadaygoesbywithoutnewsmedia reportingonthelatestcyber-attack,whetherit'sconducted by criminal or government organizations. The study of strategieswemayemploytolessenthepossibilityofsuch assaults, wherever they come and for whatever reason, is knownascybersecurity.Apapersurveysthefieldofrobot learningfromdemonstration,whichisakeyaspectofAIin robotics.Theauthorsprovideanoverviewofthedifferent
techniques used for robot learning from demonstration, including inverse reinforcement learning, apprenticeship learning, and behavioural cloning. They also discuss the challengesandfuturedirectionsofthisfield[1].
AsurveysthefieldofAI-basedintrusiondetectionsystems, which are a key aspect of using AI for cybersecurity. The authorsprovideanoverviewofthedifferenttechniquesused for AI-based intrusion detection, including rule-based systems, signature-based systems, and anomaly-based systems. They also discuss the challenges and future directionsofthisfield[2].Thisresearch’sgoalistoprovide an overview of AI from the perspective of cybersecurity, includingwhatitis,howwemaydefineit,andhowwecan use it to try to enhance the security features of both businessesandourownpersonallife.Wemayconceiveofit as attempting to counteract any threat resulting from our reliance on and usage of information and communication technology. A paper surveys the field of robotic security systems, which is the intersection of robotics and cybersecurity. The authors provide an overview of the differenttypesofroboticsecuritysystems,includingthose usedforsurveillance,reconnaissance,andsearchandrescue. Theyalsodiscussthechallengesandfuturedirectionsofthis field [3]. If you think about it for a moment, this not only includes using the smartphones tablets, and desktop computers that we use for work, personal, business, or leisure, butalltheaspectsofeverydaylifethatdepend on theuseofinformationtechnology.Aresearchdiscussesthe challenges and future directions of cybersecurity for industrial control systems, which are a key aspect of the intersectionofAI,robotics,andcybersecurity.Theauthors highlighttheuniquechallengesofsecuringindustrialcontrol systems and the importance of developing new security technologiesandstandardstoaddressthesechallenges[4] Becauseinformationtechnologyissoprevalent,problems withcybersecurityaffectallofoursystemsandgadgetsthat are connected to the Internet. Almost every part of our workinglife,includingthefunctioningoffactories,transit, andofficesgloballyareincludedinthis,aswellascarsfor private and public transportation, the infrastructure bringing power and water to our houses, and many other areas.Sincepracticallyeverypartofourlifenowdependson informationandcommunicationstechnology,cybersecurity has evolved into a basic requirement for everyone. At the same time, we are aware of the numerous ways in which
moderninformationprocessingsystemsaresusceptibleto assault. One more research discusses the techniques and challengesofAI-basedmalwaredetection,whichisanother key aspect of using AI for cybersecurity [5]. It is easy to arguethatourincreasinglylinkedworldistheissueandthat weshouldchangehowweinteractwithit.However,inmost cases,goingbackisimpossible,andintruth,wealmostlikely don't want to. Modern information and communication technologieshaveasignificantpositiveimpactonourability toworkfromhome,increaseproductivity,andengageina variety of previously unimagined kinds of communication and social contact. If we accept that information and communications is here to stay, what are we going to do aboutthemajorsecuritythreatsweallface?Inthisstudy,we will introduce some of the techniques that can be used to reduce these threats, especially from the AI and Robotics perspective.Itisimportanttorealizethatprovidingsecurity isnotjustaboutmoreandbettertechnology.
A contemporary healthcare system is made up of several components, each of which gathers and analyses data. Massive volumes of data are produced by healthcare providers,intermediaries,andgovernmentprogrammeslike MedicareandMedicaid.Patientscanprovideinformationon the care they get, their health state, the results of their treatment,andrelatedexpenditures.Nearlyallofthesedata are now digitised, and some of them may be used for artificial intelligence research. Artificial intelligence has a wide range of applications in the medical field, including improving diagnostic accuracy, performing robotic procedures, discovering potential drug candidates, and choosingthemosteffectivetherapiesforparticularpatients However, much like any technology or breakthrough, artificial intelligence creates ethical questions that its creators, users, and significant stakeholders like patients may want to take into consideration [26]. We will call attentiontotheethicalramificationsofsomecomponentsof the healthcare system that, in our opinion, users and developers of AI systems should consider. Here, we'll concentrate on a specific subset of artificial intelligence applications that are most closely associated with the provision of healthcare services. What are the moral dilemmas, though? They are many. AI model systematic mistake is particularly detrimental to the healthcare industry.Consideringthattheresultsofthesemodelsmay haveanimpactoncrucial andevenlife-and-deathchoices [27]. Sometimes these deliberate mistakes can result in discriminatory judgments, especially if they target entire groupsofsociallydisadvantagedindividuals,suchaswomen, children,personsofcolour,orthosewithpoorincomes.With that being said, we will be discussing some points to take care of when it comes to robots in healthcare. The lack of transparencyinAImodelsisonesortofethicalissuethatis particularly pertinent to this technology. It's sometimes challengingor impossibleto determinehowAIderivesits judgments[28].ParticularlyiftheAImakesuseofmachine learning techniques, which implies that the models are
always evolving depending on the data they are using. BecausephysiciansandhealthcareinstitutionsdependonAI developers to produce tools and technologies that are reliable and efficient to employ on their patients, this is a particularlyseriousissueinthecontextofhealthcare[29]. However, there are currently few guidelines or rules for assessingtheefficacyandsafetyofmanyAI-basedmedical solutions.However,doctorsandotherhealthcareworkers areresponsibleethicallyandlegallyforthechoicesthatAIis increasingly guiding. Physicians and health care facilities whouseAIinwaysthatmayhaveanimpactonhealthcare choicesmustbeawareofthelimitationsofthetechniques, data, and models when they are applied to their specific patient populations. In this research, we'll concentrate on the ethical problem of competing or conflicting interests. This issue arises particularly in the area of healthcare. Robots are being employed for a variety of minimally invasive surgeries. Many modern hospitals feature robots thatfunctionoccasionallyinlieuofsurgeonsandothersthat helpdoctors.Thisiswhereartificialintelligence,specifically the field of robotics came in and had a big influence on healthcare.Someofthealgorithmsthatwerelinkedtothose robots aided them in doing activities depending on the instructionsgivenandtrainedtothemwithverygoodand highprecision.
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
1. WhatarethegeneralproblemsinCybersecurity?
2. WhatarethegeneralproblemsinHealthcare?
3. What is the significance of AI and the field of robotics?
4. WhatarethevariouscharacteristicsofAI.
5. What are the challenges of AI in Healthcare and Cybersecurityandhowtoovercomeit?
6. What is the research gap existing in AI in CybersecurityandHealthcare?
7. WhatisthefutureofAIfroma Cybersecurityand Healthcareperspective?
We have compiled the research questions listed above, andtheinformationfrom studies onArtificial Intelligence and robotics, Cybersecurity, and Healthcare is used to furtheranswerthequestions.

WHAT ARE THE GENERAL PROBLEMS IN CYBERSECURITY?
Cybersecurity is a field that deals with protecting information,communication,andnetworksfrommalicious attacks.Attackersusecyberspacetocarryouttheircrimes; thus, it's crucial to secure them. Governments and corporationsneedtolookaftertheirsystemsanddatasince
anyone can access the internet without permission. However, not all security measures are good when protectingtheinternet.
Theworldwidewebhasbecomeahavenforcybercrimein recentyears.Hackershavefoundmanynewwaystoexploit systemsanddata.Manyattackstargetgovernmentsystems. This is because our system of government is involved in much of our politics. Other targets are corporations that handleourcountry'sfinancialwealth.Manycybercrimesare committed by state agencies or other high-profile organizations. They're capable of carrying out dangerous plans in secrecy. Fortunately, there's a lot of work being done to secure cyberspace. A few of the most important generalproblemsinclude:
1.IncreaseinCyberattacks:Thenumberofcybercrimes continuestogrowannuallyascriminalorganizationstryto capitalizeontheirefforts,suchasransomwareandcryptojacking.However,in2021,oneofthebiggestconcernswas theriseofthistypeofcrime.Thenumberofcyberattacksin 2021 increased by 50% over the previous year. However, certain regions were hit harder by the attacks, such as education,healthcare,andresearch.Thismightindicatethat cyberthreatactorsareconcentratingtheireffortsinregions wheretheyaremostexposed.Anattackratethathasrisen so quickly bodes ill for 2022. Cyber threat actors' use of automation,deeplearning,andautomationtoimprovetheir techniques will only lead to a rise in the number and intensityofattacks.
2.Ransomwareattacksareontherise:Attacksinvolving ransomware are increasing. In 2017, the WannaCry epidemic brought ransomware to public attention. Ever since, a sizable number of ransomware businesses have emerged,posingacostlyandvisiblethreattoallbusinesses. In2021,ransomwareorganisationsshowntheirabilityand willingness to impact businesses in addition to their immediatetargets..Themostfamousexampleistheimperial pipeline hack. One of the primary pipelines used by the ransomwaregangDarkSidewasshutdown.
3.Mobiledevicesbringnewrisks:Theimplementationof BringYourOwnDevice(BYOD)rulesisanotherresultofthe transition to remote working. Organizations can increase employee productivity and retention by allowing them to work from their own devices, but this practise also offers importantinformationaboutsecurityandsusceptibilityto diseases that might endanger company systems and solutions. You become incapable of responding. Cybercriminals have modified their ways in 2021 to capitaliseontheuseofmohilesthatrises.Triada,FlyTrap, and MasterFred malware, among other mobile malware trojans, have all recently surfaced. These mobile trojans approachthetargetdeviceandrequesttherequiredrights throughlaxappstoresecuritymeasures,socialmedia,and othersimilarstrategies.
WHAT ARE THE GENERAL PROBLEMS IN HEALTHCARE?
1. Concerns about health equity: The health sector has long acknowledged that different demographic groups experiencevariedlevelsofhealthcare.Thesediscrepancies gobeyondonlysalariesandmedicalexpenses.Ontheother hand,environmentalinfluenceshaveasignificanteffecton healthandwellbeing.Thezipcodeisoneoftheseelements, alsoreferredtoasthesocialdeterminantsofhealth.racial andculturaldiversity,thequalityoftheairandwater,and accesstojobs,housing,education,transit,andwholesome food.Incertainareas,enduringracialandsocialinequality hasalsoputgenerations'worthofhealthatrisk.Allofthese factors have an effect on a person's overall health and capacitytogethealthcare.Healthcrisesfortheunderserved sometimesincludehospitalisationoremergencyroomvisits andincurconsiderablemedicalexpenses.
2.Opportunities(andpitfalls)oftechnology:Thecurrent health issue has numerous opportunities but also has the potentialtocausealotofissuesifnotproperlyaddressed. Dataarebeingusedmoreandmoreinhealth.Thedifficulty isinmanagingthisoceanofdata.AccordingtoaFrontiersin ICTresearch,healthcare professionalsandhealthsystems werealreadyproducingabout80MBofdataperpatientyear before the epidemic. In addition to information from electronic health records (EHRs), this data also contains informationanddetailssuchaddresses,demographics,claim andinsuranceinformation,paymenthistory,andschedules.

3. Expensive medical bills: The exorbitant expense of healthcare is arguably the most serious issue facing our present healthcare system. More than 45% of American peoplesayitisdifficulttoaffordmedicalcare,andmorethan 40%saytheypayfortreatment,accordingtoapollbythe Kaiser Family Foundation. Healthcare costs are changing people'sbehaviour,withmanyavoidingadoctorwhenillor skipping check-ups altogether. A quarter of Americans cannot afford the prescriptions they need and may skip doses or skip prescribed medications. Each of these behaviours can lead to serious health problems and, therefore,increasedmedicalcosts.
WHAT IS THE SIGNIFICANCE OF AI AND THE FIELD OF ROBOTICS?
Robots are becoming increasingly advanced both technologically and structurally. The primary focus of roboticstodayisonrepairingandsavinglives.Forexample, doctorsuserobotarmsinhospitalstoperformcomplicated surgerieswithoutputtingtheirpatientsatrisk.AIisquickly becomingessentialinmanyareasoflifeincludinghealthcare andcybersecurity.Thisisduetothefactthatitsaveslives, reducescostsandmakeslifeeasier.However,therearestill many unknown with AI, which is why it is significant to consider the positives and negatives before implementing thistechnologyinbothhealthcareandcybersecurity.AIhas alotofpotentialinhealthcare;itcanperformcomplextasks
and can help doctors treat patients more effectively. For example,itcanassetphysiciansindiagnosingandtreating diseases and also assist them in performing triage and radiology procedures. Reinforcement learning programs help medical professionals save lives by performing lifesaving surgeries on human beings. In addition, predictive modelshelpmedicalprofessionalsmanagepatients’records andidentifyissueswithpatientcaresystems.Additionally, AIhelpswithpatientcounsellingbyassistingwithdiagnosis and providing psychological support to patients and essentiallyhasthepotentialtorevolutionizeourhealthcare system

WHAT ARE THE CHALLENGES OF AI IN CYBERSECURITY AND HEALTHCARE AND HOW TO OVERCOME IT?
AI is the term given to describe the advancement of computers to perform tasks that were once reserved for humans.Ithasthepotentialtorevolutionizemanyaspectsof our lives- from health and education to military and commercial sectors. However, it is also a source of considerableconcernasitraisesquestionsregardingethics, safety,andaccountability.
AIisstillinitsinfancysotherearestillmanychallengesto overcome. For instance, AI is not very good at handling controversial or negative data, as it can have a conflictive effect on the system. It is also susceptible to adversarial behavioursincehackerscanuseAIfortheirownpurposes by programming it against the systems they target. Many CybersecurityexpertsbelievethatAIwillbemostbeneficial in situations involving classified data, where security measuresarenecessarybutimpossible.Thecybersecurity industry is getting bigger every year. As more and more peoplerelyontechnologyintheirdailylives,it'simportant to make sure these devices and computers are safe from hackers.Therearesomecybersecurityissuesthatareeasyto fix. For example, many people use the same password for their social media accounts and email girlfriend accounts. Thismakesiteasierforhackerstostealpasswordsanduse themtobreakintothoseaccounts.Theycanthenstealyour personal information and use it to commit identity theft. Anotherproblemwithcybersecurityisthatordinarypeople arenotfullyawareofhowtoprotectthemselves.Theyare also unaware of the dangers of opening emails or attachments that appear to come from people they know. Theseemailsmaycontainvirusesthatcanharmyourdevice. It could also be a phishing scam that steals your personal information.
Thefundamentalhealthcareissuehasafewotherremedies as well. Collaboration between local, state, and federal governments, as well as healthcare professionals, is necessary to find answers to the problem of excessive healthcare expenditures. To address environmental variablesandenhanceaccesstohealthcareinmarginalized neighbourhoods, it is possible to employ housing,
transportation,andcollaborationswithchurchesandnonprofit health groups. To satisfy the demands of patients, healthcare managers might put up a several kinds of programs.Example,telemedicinecanhelppatientswhodo not have access to transportation, as is the case in many ruralplaces,yetinternetconnectivityisstillanissue.Elderly homecareisoneoftheotherinitiatives.ahealthcareteam thatprioritisescommunityinvolvementandpatientcare.
WHAT IS THE RESEARCH GAP EXISTING IN AI IN CYBERSECURITY AND HEALTHCARE?
ArtificialIntelligenceandCybersecurityaretwoofthemost importanttechnologiestoday.CybersecurityandHealthcare arealsotwoareasthatarerapidlydeveloping,expanding, andgainingmorerelevanceinourdailylives.However,AI technologies have many flaws that need to be addressedwhichiswhymoreresearchisneededtomakethemmore useful.Bothareasareinastageofdevelopment;therefore, they have many challenges to overcome before they can revolutionizeourlives.
AI has a lot of potential in Cybersecurity and Healthcare since it can help detect and prevent cybercrime when we takethefieldofCybersecurity.Andinhealthcare,itcanhelp diagnoseadiseasefromitsveryearlystageandalsoreduce theworkloadonthedoctorsaswell.
Currently,Cybercrimeismostlydetectedthroughhuman involvement,whichisslowanderror-prone.AIcanalsohelp with the investigation process by analysing data collected fromvarioussourcesandidentifyingpotentialthreads.Itcan alsohelpwithcountermeasuresbydevelopingmechanisms thatstopattacksbeforetheyhappen.Withthatbeingsaid,AI has the potential to become an invaluable tool for CybersecurityandHealthcarewhenappliedpractically.
WHAT IS THE FUTURE OF AI FROM A CYBERSECURITY AND HEALTHCARE PERSPECTIVE?
Robotics and artificial intelligence have many exciting applications that will become clear once they're ready for usebythepublic.Fornow,thesetechnologiesareprimarily used in scientific research or in niche applications by professionalsonly.However,there'snoshortageofinterest from amateurs who want to create their own robot companions.It'sclearthatthesetechnologieshaveahuge future.
AI has many applications- from natural language processingtopatternrecognitionandwillchangeourlives inmanyyearswhenwetakealookathowitchangesandis changing our daily lives from the perspective of cybersecurityandhealthcare.ItisveryobviousthattheAI hasaverylargeandgoodfuture.
2. METHODOLOGY
Severalresearchpapersusedinthisresearchwereexplained inthispart.Consequently,weprovideandclarifythecurrent surveys in all the areas of this research including AI and Robotics,Cybersecurity,andHealthcare.

A. APPLICATIONS OF AI IN CYBERSECURITY DEFENCE
TheAImodelprovideshighlypowerfuldefensivecapabilities for cybersecurity protection that will help defend various systems against cyberattacks and support digital forensic investigations.Havingsaidthat,wehighlightafewoftheuses ofAIincybersecuritydefense.Additionally,weencouragethe reader of this research to look at these publications for additional information on AI's role in cybersecurity protection.
i. AI for malware detection and classification: This termsimplystandsfor“MaliciousSoftware”whichisactually dangerousinshort.Itisadocumentthatcontainsprograms orcodeswhichismostlydeliveredoveranetwork[1][2].It isproducedorplannedtoemployvariousmethods,suchas ransomware, spyware, viruses, trojans, and adware, to damagetargetcomputersystems,mobiledevices,andonline applications.[3][4].
Several algorithms and techniques have been used to detectmalware[5].DetectionofmalwareusingAItechniques canbedonewhenamodelistrainedusingadatasetthatcan helpinclassifyingthetypeofmalware[6].
ii. AI for network intrusion detection: Many programmers created and suggested network intrusion detection solutions. Ding et al. [7] presented a real-time anomalydetectiontechniqueandwassuccessfulinachieving high accuracy. Additionally, after conducting K-means clustering,AlomandTaha[8]attainedarespectableaccuracy of91.86%.Chenetal[9]providedanexampleofhowdeep convolutionalneuralnetworks(DCNNs)areusedtoidentify DDoSassaults.Someotherresearcherswhoworkedonthe sametopicincludeMirskyetal.[10],Biswas[11],Clements, etal.[12],andXiaetal.[13].
iii. AI for traffic identification and classification: At a time,severalapplicationsareflowinginanynetwork,andthe one and single most important phase in identifying and recognizing multiple classes is the use of network traffic classification. A researcher [14] utilized a deep learning modeltodistinguishtheflowingoftrafficinanetworkafter diving it into 25 protocols, he was successfully able to get 100% and 91.74%, depending on the type of protocol. Anotherresearch[15]usedaConvolutionalNeuralNetwork (CNN)modeltodistinguishtheclassesoftrafficandalsotry torecognizetheapplicationcategory.
iv. AIforspamdetection:Spamemails,toputitsimply, areanyunwelcomeorvirus-containingemails.Inadditionto
acting as a detector of all those viruses, spam detection systemsalsoworkasapreventerofemailsbystoppingthem from introducing viruses into one's inbox. One of the techniques that developers have suggested is an autoencoderthatfunctionsandfurtherdistinguishesspammail by Mi et al. [16], with a 95% accuracy rate. A different researcher created a machine-learning approach and algorithmicphishingemaildetectionsystem[17].Thereader ofthispapercanrefertothefollowingworksrelatedtothis byAksuetal.[18],Yietal.[19],andBenavidesetal.[20].
v. AI for insider threat detection: A document that demonstratesandclearlyexplainshowtoexamineandassess auser'ssystemlogsusingaDNNorRNNmodel,aswellas howtofindabnormalitiesthatmightleadtoaninsiderthreat incident.Tuoretal.[21]describedhowtodothis.
vi. AIfordigitalforensics:AItechnologybecomemost significantininvestigationsnowadaysandalsoimprovesthe methodsandwaysofdetectingcybercrime.Thespecialistsof forensicsfoundthisveryusefulasithelpsthemineffectively andquicklyfindtheactualsourceandcauseoftheproblem, ontheotherhand,theuseofAIindigitalforensicsavesalot of money and time. Some machine-learning techniques or algorithmshavebeenutilizedtoclassifyfilefragments.For example,papersarewrittenbyBeebeetal.[22],Axelssonet al.[23],andCalhoun&Coles[24].Anotherresearcher[25] proposedatechniquethatworksbasedondeeplearningfor filefragmentclassification.
B. APPLICATIONS OF AI IN HEALTHCARE
i. Disease Detection systems: One of the most significant tasks in healthcare is the detection of various diseases. it lessens the stress on doctors, because those systems may be replaced to run automatically instead of manually for various other duties. . Researchers have suggestedamethodin2019thatmightassistphysiciansin identifying and categorizing skin conditions, such as melanomaandeczema[26].Amachinelearningalgorithmis usedindetectingskincancerwhereitdifferentiateshealthy skinfromdiseasedoneandhighaccuracywasachieved[27]. Manysystemsforbraincancerclassificationhavealsobeen inventedbydeveloperswhichincludeanapproachbyShaet al [28],they developeda system using deepConvolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs) to detect brain tumors after Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) generated the highqualityimagesoftheinsideofthebrain.Thereaderofthis research can also go through these articles for disease detection systems: Ahmad et al. [29], Ahmad et al. [30], Shabbiretal[31],andHussainetal[32].
ii. Test Analysisand Diagnosis:Because all those AIbasedappswillhaveahugeinfluenceoninterpretingmedical scans, including X-rays, MRI pictures, CT scans, and many more, it is getting simpler for physicians to simply comprehendtheproblemoftheirpatientswhenthereisanAI application.Astheeffortassociatedwithscanninganalysisis
lessened,medicalphysiciansfeelmoreatease[33].TheAIbasedapproachwillassistinrealizingandcomprehending whether any gene might cause cancer while evaluating biologicaldatasuchasDNAandRNA[34].TheAIcanhelp identify any disease risk or existence. The characteristics depend on outside factors [35]. It further helps in alerting peopleaboutanydisease-infectedarea[36].
iii. Chatbots:Thesedays,hospitalsandotherclinicshold a number of websites, mobile applications, and web applications.Thesewebsites,mobileapplications,andweb applicationsfeaturechatbotsthatacttoaidpatientsdirectly fromwheretheyareandtrytolearnmoreabouttheirhealth issues[37].Everytimeapatiententersahospital,thefirst thing the medical staff does is screen the patient to learn about their beginning circumstances. In this situation, AI chatbots can take the role of these time-consuming procedures [38]. Additionally, chatbots may be used as interactingagentsbetweenlanguageprocessingandspeech recognition technology [39]. As a whole, majority of the modernhealthcareinstitutionshavethesekindsofchatbots whichhelppatientsindifferentways[40].
iv. Health Monitoring: When it comes to patient preventionthroughconditionmonitoring,thisiscrucial.The monitoringsystemmayoccasionallybeabletokeepapatient in their present state when an illness is caught early by informing the doctors. Algorithms and AI approaches are usedtoassistit.Asmarthealthmonitoringsystemhasbeen proposedbysomeresearchers[41],thesystemiscapableof keepingtrackofpatients’healthanditalsocontainsafeature thatenablespatients'familiestoaccessandcheckontheir patient’s health status. Anandh [42] created a system that uses AI algorithms to provide body temperature. Papers writtenbySoppimathetal[43]andSrinivasanetal.[44]can becheckedtogetmorehealthmonitoringsystemsthatwere trainedbasedonAIalgorithmsandtechniques.

v. Digital Consultation: The world is getting increasinglydigital;thus,thisisafairlybroadarea.Adigital consultation is just a video call between a doctor or other healthcareprofessionalandapatientmadepossiblethrough asmartphoneoronlineapplication.Throughthesetools,the patient and the doctor will communicate. Examples of the evolutionofdigitalhealthcareincludepatients'engagement in the development and higher expectations for patient accesstohealthcare[45,46,47].Mostprimarycaredoctors can now operate from home, and in this scenario, digital consultationwillundoubtedlyoccur[48,49].Thisreadercan check [50] and [51] to get more ideas about digital consultationsandtheircost-effectiveness.
C. DATA SOURCE
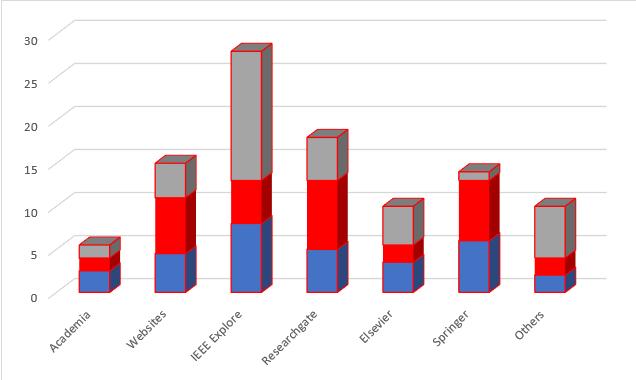
Theliteratureinthispaperismadeupofseveral research publicationsandarticlesfromdifferentsources.Fig.1shows thepictorialorgraphicalrepresentationofthedatasources used in this research and their respective percentages.
beseeninfig.2.
D. EXPLORATION CRITERIA
As mentioned in the abstract that this research will focus more on the area of AI and robotics in cybersecurity and healthcareforthepast6yearswhichisfrom2017to2022.In light of the foregoing, we gathered all the references and brought out the percentage of the papers used in this research for each and every respective year. The pictorial representationofthesameisshowninfig.3whereallthe percentagesareclearlystated.
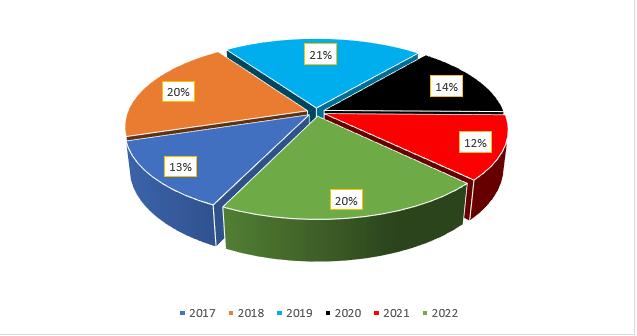
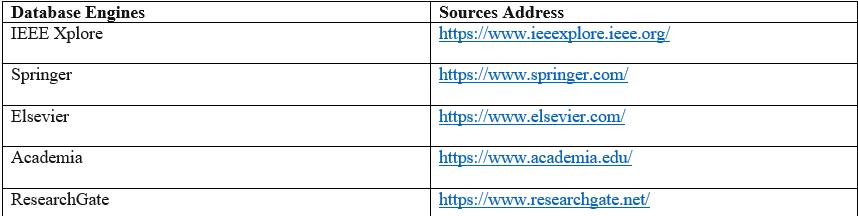
Additionally,wehavemadeatableofthedatabasesandtheir respectiveURLsthatwereallusedinthisresearchwhichcanFig.1. ResearchPapersfromDataSources. Fig.2. DatabaseEnginesandtheirURLs Fig.3. PercentageofResearchPapersfrom2017to 2022.
Cybersecurity is an ever-evolving field, and the systems developedinthepastfiveyearshavebeeninstrumentalin helping protect individuals and organizations from cyber threats.Inthisarticle,wewilltakealookatsomeofthemost importantcybersecuritysystemsdevelopedinthepastfive years in Table.1.Let's first examinehow machinelearning (ML)andartificialintelligence(AI)haveevolvedinthefield of cybersecurity. Systems that can identify and respondto cyberthreatsinreal-timehavebeendevelopedusingAIand ML.Thesetechnologiesarecapableofanalyzingvastvolumes ofdatatospottrendsandabnormalitiesthatcanpointtoan impending attack. Systems thatcan recognizeand reactto harmfulcodehavealsobeencreatedusingAIandML,aswell assystemsthatcandetectandrespondtophishingattacks. These are just a few of the many cybersecurity systems developedinthepastsixyears.Asthefieldofcybersecurity continues to evolve, new and improved systems will be
developed to protect individuals and organizations from cyberthreats.

[8] 2017 Cybersecuritynetworkintrusion detectionwithunsuperviseddeep learning
[53] 2017 Convolutionalneuralnetworks' abilitytoidentifynewassaultsis evaluated.
[54] 2017 developedarecurrentneural network-basedintrusiondetection system(RNNs)
[55] 2017 Aninnovativefuzziness-based semi-supervisedlearningstrategy thatusesunlabelleddatawith supervisedlearningalgorithm assistanceimprovestheclassifier's performanceforIDS.
Attainedarespectableaccuracy of91.86%
TheCNNmodelobtainedan 81.57%ofaccuracyrate.
TheRNNmodelhasan83.28% detectionrateinthebinary classification,accordingtothe results.
Obtainedveryhighaccuracyon theproposedalgorithm.
Usabilityissues
Highdimensionaldata
PersonalIntegrity
TheaccuracyoftheJ48, NaïveBayes,NBtree, Randomforests,Random tree,multi-layer perceptron,andSupport VectorMachine(SVM)is lowerthantheproposed algorithm
[57] 2018 Asafemalwaredetectionsystem usingencryption Achieved98.93% Efficiency
[58] 2018 AnAndroidmalwarefamily categorizationhasbeenproposed, alongwitharepresentativesample selection.
[59] 2018 forunsupervisedfeaturelearning,a non-symmetricdeepautoencoder (NDAE)hasbeensuggested.
[60] 2019 amethodtoidentifymalwarebased ontheincidenceofopcodes
FalDroid–94.2% Usability
atrainingtimereductionofup to98:81%andan improvementinaccuracyof 5%.
Thesuggestedmethodcan identifytheviruswithabout 100%accuracy.
Hugeamountofcomplex
Lessnumberofdatasets.
[61] 2019 UsingdataandAPIs,toidentify malware
[56] 2019 examinationofextracted characteristicsfrombig-data sourcesinrealtime.

[63] 2019 Itwasshowedhowtofindmalware payloadsinanumberoffiletypes, includingPortalDocumentFile.pdf andMicrosoftDocumentFile.doc.
[64] 2019 Deeplearning-basedproposed methodforvirusdetectionusing behaviourgraphs
[66] 2020 proposedadynamictechniquefor detectingandpredictingWindows malware
[67] 2020 suggestedusingamethodcalled SourceFindertolocatemalware sourcecoderepositories.
[68] 2021 Theyprovideanovelapproachfor automatichyperparameter optimizationbasedonBayesian optimizationtoproducethebest possibleDNNdesign.
AUC99.3% Privacy
TruePositiveRatio,Precision, RecallandF1>99%,FPR< 0.1%
Theaccuracyoffinding ransomwarewas91.7%and 94.1%,respectively.
Effectiveness
Limitedincrementalrate
Accuracyof98.60% Unstructured
Prediction–0.997 FPRof0.000 FNRof0.007
Accordingtotheresearch,the suggestedmethodlocates malwarerepositorieswith89% precisionand86%recall.
BO-GPobtainedthehighest accuracyscores,with82.95% fortheKDDTest+datasetand 54.99%fortheKDDTest-21 dataset.accuracy.
Trust
Poorunderstandingof safety
Appropriateness
[54] DeepLearningApproachfor IntrusionDetectionUsingRecurrent NeuralNetworks
Randomforests,NBtree,J48, Naive
randomtree,multilayerperceptrons,andSVM
Binaryclassification(Normal, Anomaly)andfivecategory classificationsusingtheRNN-IDS model(Normal,DoS,R2L,U2R, andProbe).
unlabelledsamplesassisted withasupervisedlearning algorithm.
[87] BinaryandMulti-ClassMalware ThreadsClassification
[60] DetectionofAdvancedMalwareby MachineLearningTechniques
[68] Bayesianhyperparameter optimizationfordeepneural network-basednetworkintrusion detection
[57] Asecureencryption-basedmalware detectionsystem
[67] Sourcefinder:Findingmalware sourcecodefrompubliclyavailable repositories
[62] DisarmingVisualization-based ApproachesinMalwareDetection Systems
[8] Networkintrusiondetectionfor cybersecurityusingunsupervised deeplearningapproaches
[61] ASSCA:APIsequenceandstatistics featurescombinedarchitecturefor malwaredetection
[63] Anovelmalwaredetectionsystem basedonmachinelearningand binaryvisualization
[53] IntrusionDetectionUsing ConvolutionalNeuralNetworksfor RepresentationLearning
[66] AdynamicWindowsmalware detectionandpredictionmethod basedcontextualunderstandingof APIcallsequence
[64] Malwaredetectionbasedondeep learningofbehaviourgraphs
[58] Androidmalwarefamilial classificationandrepresentative sampleselectionviafrequent subgraphanalysis
[56] Aninvestigativestudyonmotifs extractedfeaturesonrealtimebigdatasignals
[59] Adeeplearningapproachto networkintrusiondetection.
NaïveBayes(NB)andGaussian DiscriminantAnalysis(GDA)
MachineLearningTechniques
DeepNeuralNetworkAlgorithms
Privacy-PreservingNaïveBayes Classifier(PP–NBC)
MachineLearningTechniquesin detectingtheMalware
Visualization-basedtechniques
K-meansClustering
Dynamicbehaviour
Neuralnetworkanddeep learningareusedinthedetection ofthe malware.
Intestingtheset,17extraattack kindswereadded,andanew attackwasalsofound.
UsingMarkovchainsequenceto depictthelinkbetweenAPI functionstorepresentmalware andgoodware
StackedAutoEncodersandthe Behaviour-basedDeepLearning Framework(BDLF)
MaleVisDataset
KaggleMicrosoftmalware classificationchallengedataset
NSL-KDDdataset
4-GramAPIFragmentSequence
NotIdentified
MallmgDataset
NSL-KDDdataset
Malicioussamplesfromvirus ShareandVirusTotal,aswellas samplesfromWindows7and WindowsXPsystemexefiles
Notmentioned
NSL-KDDdataset
IntelligentandSecurity InformaticsDatasetsBrazilianmalware-dataset

MalwaresamplesfromVX heaven
FallDroid GenomeProjectDataset,Drebin Dataset,FallDroid–I,FallDroid -II
Visualizationanddeeplearning techniqueswereused
BystackingtheNDAEs,alayerwiseunsupervised representationlearningmethod wasproduced.
TheVirusSharecommunityhas 9virusfamilies,eachwith1000 variants
KDDCup’99andNSL-KDD datasets
Inthepastsixyears,healthcaresystemshaveundergonea dramatic transformation. Advances in technology, data analytics, and artificial intelligence have enabled the developmentofnewandimprovedhealthcaresystemsthat are revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered. These systemsaredesignedtoimprovepatientoutcomes,reduce costs,andprovidebetteraccesstocare.

Table.3 below presents some of the most significant healthcare systems developed in the past six years. These systems are designed to address a variety of healthcare needs,frompatientmonitoringanddiagnosistopopulation
health management. Each system is designed to provide a uniquesetoffeaturesandbenefitstohealthcareproviders andpatientsalike.Thesehealthcaresystemsarejustafewof themanythathavebeendevelopedinthepastfiveyears.As technologycontinuestoadvance,healthcareproviderswill continuetodevelopnewandimprovedsystemstoimprove patientoutcomesandreducecosts.
oftenutilised(Classifiedas unknownimages)
[83] 2022 DetectionandClassificationof BrainTumourthatare generatedbyMRI
Overallaccuracyof98.87%in classificationanddetection Hugeamountofcomplex
[84] 2022 ChatbotSystemforWomen’s Healthcare 96%forpredictionofPCOS Restrictions(Onlyfor Women)
[85] 2022 DetectionofSkinCancerusing differentalgorithms Accuracyoftheproposed ensembleis93.5% Trust
[52] 2022 ClassificationofSkinLesion Overall,of98%Accuracyin ClassifyingSkinLesion Privacy
Table 4. SummaryofDatasets,Samples,andMethodologyusedinthePastAI-BasedHealthcareSystems
Reference Title of Paper Methodology
[84] IntelligentMedicalChatbotSystemfor Women’sHealthcare
[83] ARobustApproachforBrainTumour DetectioninMagneticResonanceImages usingFinetunedEfficientNet
[76] Artificialintelligenceinhealthcarein developingnations:Thebeginningofa transformativejourney
[85] SkinCancerDetectionUsingCombined DecisionofDeepLearners
LogisticRegression Algorithm,Machine LearningAlgorithm,and KNN.
DeepConvolutionalNeural Network Brats2015BrainTumour Dataset
SWOTAnalysis Review*
SVM,NaïveBays,andKNearestNeighbour
ISICPublicDataset
[71] Artificialintelligenceinhealthcare:Past, presentandfuture SupportVector/Neural Networks Review*
[78] Region-of-InterestBasedTransferLearning AssistedFrameworkforSkinCancer Detection
[70]
Dermatologist-levelclassificationofskin cancerwithdeepneuralnetworks
[80] BrainTumourDetectionusing ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork
[69] Amachinelearningalgorithmfor identifyingatopicder-mastitisinadults fromelectronichealthrecords
[52] SkinLesionClassificationSystemusingaKNearestNeighbourAlgorithm
[81] Unboxtheblack-boxforthemedical explainableAIviamulti-modalandmulti
ConvolutionalNeural Networks(CNNs)
DermIS
DeepLearningAlgorithms NotSpecified
SVMs,K-NN,multi-layer perceptron,NaiveBayes, andrandomforest algorithms
MachineLearning Algorithms
K-NearestNeighbour Approach(KNN)and ConvolutionalNeural Network
HAM10000
ISICDataset

ISICPublicDataset
Rule-basedDecision SupportSystem Review*
centredatafusion:Aminireview,two showcasesandbeyond
[72] Deepneuralnetworksshowanequivalent andoftensuperiorperformanceto dermatologistsinonychomycosisdiagnosis: automaticconstructionofonychomycosis datasetsbyregion-basedconvolutional deepneuralnetwork
[77] BrainTumourDetectionusingDeep LearningModels
[82] Skinlesionsclassificationinto eightclassesforISIC2019usingdeep convolutionalneuralnetworkand transferlearning
[79] Analysisofbasicneuralnetworktypesfor automatedskincancer classificationusingFireflyoptimization method
[75] Integrateddesignofdeepfeaturesfusion forlocalizationandclassification ofskincancer
[65] Anon-deviceinferenceappforskincancer detection
[73] Automatedskin diseaseidentificationusingdeeplearning algorithm
[74] Diagnosisof skindiseasesusingconvolutionalneural networks
The past six years have seen a dramatic shift in the way healthcaresystemsaredevelopedandimplemented.With theadventofnewtechnologiesandtheincreasingemphasis onpatient-centeredcare,healthcaresystemshavebecome moreefficientandeffective.Table4highlightedsomeofthe varioushealthcaresystemsdevelopedinthepastsixyears, theirmethodologies,andthedatasets&samplesused.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND ROBOTICS
The goal of the computer science field of artificial intelligence(AI)istodevelopintelligentmachinesthatcan think and behave like humans. AI is used to develop computer systems that can solve complex problems, recognizepatterns,andlearnfromexperience.AIsystems can be used to automate tasks, such as scheduling, data analysis, and decision-making. AI is also used to develop robotsthatcaninteractwithhumansandtheenvironment. AIhasapplicationsinmanyindustries,includinghealthcare, finance, and transportation.AI can be used to improve
ConvolutionalNeural Networks(CNNs) Not
ConvolutionalNeural NetworkandVGGNet
DeepConvolutionalNeural NetworkinAdditionto GoogleNet
HM1000
ISICDataset
NeuralandFuzzyApproach ISICDataset
OtsuAlgorithm,Alexand VGG-16Model
ConvolutionalNeural NetworkusingTensorflow
InceoptionV2,InceptionV3, MobileNet
ConvolutionalNeural Networks
HAM10000
ISICDataset
ISICDataset

Dataset
customer service,automate manufacturingprocesses,and develop autonomous vehicles. AI is also used to develop virtual assistants, such as Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant, which can understand natural language and respondtovoicecommands.AIisanever-evolvingfieldof research,anditspotentialapplicationsarelimitless.
AIissignificantlyinfluencingcybersecurityandhealthcare. AIisbeingutilizedincybersecuritytodetectthreatstothe networkmorerapidlyandaccuratelythaneverbefore.AIbased systems are able to recognize harmful behavior, identifymaliciousactors,andrespondtothreatsinreal-time. This is helping to reduce the amount of time recognized takes to detect and respond to cyber threats, as well as reducingthecostofrespondingtothem.
Inhealthcare,AIisbeingusedtodiagnoseandtreatdiseases moreaccuratelyandquicklythaneverbefore.Doctorsmay makemoreaccuratediagnosesandadministerbettercare when using AI-based systems, which can analyse vast
volumesofdatatofindpatternsandtrendsinpatienthealth. Inordertocutcostsandincreaseefficiency,AIisnowbeing utilizedtoautomateadministrativechoreslikeappointment schedulingandinsuranceclaimprocessing.

AIappearstohaveabrightfutureinbothcybersecurityand healthcare.Morerapidlyandpreciselythanever,AImaybe usedtodetectandaddresscyberthreats.AImayalsoassist healthcare businesses better secure patient data by identifyingpossiblesecurityflaws.Healthcarepractitioners mightconcentrateonmorecrucialactivitiesbyusingAIto automatemenialchores.AImayalsobeusedtoexaminevast volumes of data and find patterns and trends that can be utilizedtoenhancepatientoutcomesandtreatment.Finally, AIcanautomateillnessdiagnosisandtreatment,freeingup medicalexpertstoworkonmorechallengingsituations.
CharacteristicsofArtificialIntelligence
1. Automation:Artificialintelligence(AI)isabletodo thingslikerecognizepatterns,makejudgements,andsolve problemsthatwouldtypicallyneedhumanintelligence.Data analysis, natural language processing, and picture identification are a few examples of complicated jobs and processesthatAIcanautomate.
2. MachineLearning:AIiscapableoflearningfromits environment and experiences. Through machine learning algorithms,AIcanlearnfromdataanduseittoimproveits performance.Ontheotherhand,Machinelearningisatype ofartificialintelligence(AI)thatenablescomputerstolearn withoutexplicitprogramming.Thegoalofmachinelearning istobuildcomputerprogramsthatcanaccessdataanduseit tolearnforthemselves.Thelearningprocedureoccurswith observationsordata,suchasexamples,directexperience,or teaching, in order to uncover patterns within the information and enhance future judgements based on the examples we provide. The basic objective is to enable computerstolearnindependentlyofhumansandadapttheir behaviorasaresult.
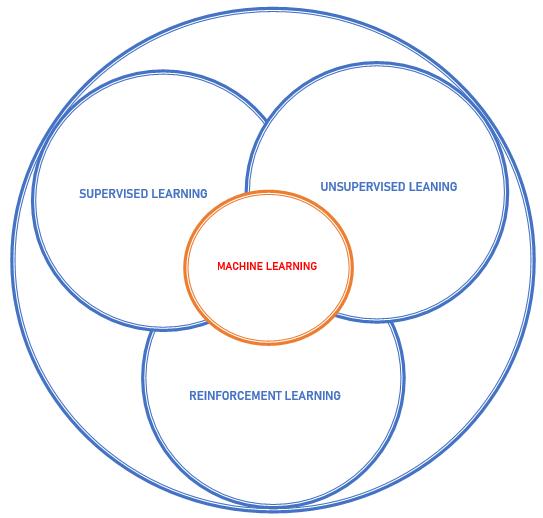
i. SupervisedLearning:Thiskindofmachinelearning algorithmmakespredictionsusinglabeleddata.Alabelled datasetwithinputdataandtheassociatedpredictedoutput isusedtotrainthealgorithm.Afterthat,thesystemmakes predictionsonfresh,unlabeleddatausingthelabelleddata.
ii. Unsupervised Learning: This is a kind of machine learningmethodthatgeneratespredictionsfromunlabeled data. An unlabeled dataset, which consists of input data withoutanycorrespondingpredictedoutput,isusedtotrain thealgorithm.Afterward,theprogrammakespredictionson fresh,unlabeleddatausingtheunlabeleddata.
iii. ReinforcementLearning:Thisisanalgorithmthat uses rewards and punishments to learn. The algorithm is trainedonanenvironment,whichcontainsinputdataand thecorrespondingrewardsorpunishments.Thealgorithm
thenusesrewardsandpunishmentstomakedecisionsand takeactionsintheenvironment.
Fig. 4. TypesofMachineLearning
3. Natural Language Processing: AI can understand and process natural language, such as spoken words and written text. This allows AI to interact with humans in a more natural way. Similarly, the goal of the artificial intelligence (AI) branch of natural language processing (NLP) is to give computers the ability to comprehend, analyze,andmodifyhumanlanguage.Toanalyzetext,NLP algorithmsareemployed,allowingcomputerstounderstand thestructureandmeaningofthelanguageinordertoextract insightsfromtextdata.NLPcanbeusedtoautomatetasks such as sentiment analysis, text classification, and entity extraction.
4. Adaptability:AIiscapableofadaptingtochanging environmentsandconditions.AIcanlearnfromitsmistakes andusethedatatoimproveitsperformance.Ontheother hand,AdaptabilityinAIreferstotheabilityofanAIsystem to adjust its behavior in response to changes in the environment or the user’s preferences. This allows the AI systemtoremaineffectiveandefficientovertime,evenas the environment or user preferences change. This is important for AI systems that are used in dynamic environments, such as self-driving cars, where the environmentisconstantlychanging.Adaptabilityalsoallows AIsystemstolearnfromtheirmistakesandimprovetheir performanceovertime.
5. Automated Reasoning: AI can reason and draw conclusionsfromdata.ThisallowsAItomakedecisionsand solveproblems withouthumanintervention.Ontheother hand, automated reasoning is a subfield of artificial intelligence(AI)thatfocusesonusingcomputerstoreason logically about a given problem. Automated reasoning systemsusealgorithmstoanalyzeasetoffactsandrulesto drawlogicalconclusions.Automatedreasoningsystemscan beusedtosolveproblemsinmanydifferentareas,suchas
mathematics, law, medicine, engineering, and philosophy. Automated reasoning can also be used to create new knowledgebycombiningexistingfactsandrules.Automated reasoningsystemsarebecomingincreasinglyimportantin thedevelopmentofAIsystems,astheycanhelptoreduce theamountofmanuallaborrequiredinproblem-solving.
6. AutonomousAgents:AIcanactindependentlyand autonomously.ThisallowsAItotakeactionwithouthuman inputordirection.Ontheotherway,Autonomousagentsin AIarecomputerprogramsthatcanactindependentlyina given environment. They are able to perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve theirgoals.AutonomousagentsareusedinmanyareasofAI, consisting computer vision, NLP, and machine learning. Autonomousagentscanbeusedtoautomatetasks,suchas scheduling,planning,anddecision-making.Theycanalsobe usedtointeractwithhumans,suchasinvirtualassistants, catbots,andautonomousvehicles.Autonomousagentscan beusedtoimprovetheefficiencyofexistingsystems,aswell astocreateentirelynewsystems.
TheRoboticsField
Roboticsisafieldofengineeringthatfocusesonthedesign, construction, and operation of robots. It involves the application of mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering principles to the design, manufacture, and operation of robots. Robotics is used in a variety of applications,includingmanufacturing,medical,military,and spaceexploration.Roboticsengineeringinvolvesthedesign, construction, and operation of robots. This includes the developmentofroboticsystems,sensors,andactuators,as well as the integration of these components into a functioning robotic system. Robotics engineers must also considerthesafetyandreliabilityoftherobot,aswellasits abilitytointeractwithitsenvironment.Roboticsengineers mustalsoconsidertheapplicationoftherobot.Thisincludes thedevelopmentofalgorithmsforrobotcontrol,navigation, andmanipulation.Roboticsengineersmustalsoconsiderthe ethicalimplicationsoftheirwork,asrobotsareincreasingly being used in a variety of applications, including those involving human interaction. Robotics engineering is a rapidly growing field, and the demand for qualified engineers is increasing. Robotics engineers are in high demandinavarietyofindustries,includingmanufacturing, medical,military,andspaceexploration.Asthetechnology continuestoadvance,thedemandforroboticsengineersis expectedtocontinuetogrow.
Roboticsisbecomingincreasinglyimportantinmanyareas of our lives. Robotics can be used to automate processes, reducelaborcosts,andincreaseefficiency.Roboticscanalso beusedtoimprovesafety,reducehumanerror,andincrease accuracy. Robotics can also be used to explore new environments, such as space, and to perform dangerous tasks that would otherwise be too risky for humans.
Additionally, robotics can be used to improve healthcare, such as through surgical robots and robotic prosthetics. Finally,roboticscanbeusedtoimprovethequalityoflifefor people with disabilities, by providing them with more independenceandmobility.
Thefutureofroboticsisanexcitingone.Roboticstechnology isadvancingrapidly,anditisexpectedtocontinuetodoso inthecomingyears.Roboticswillcontinuetobeusedina varietyofindustries,frommanufacturingtohealthcare,and eveninthehome.Asrobotsbecomemorecapableandmore intelligent,theywillbeabletotakeonmorecomplextasks andinteractwithhumansinmoremeaningfulways.Inthe future, robots may be able to perform tasks that are currentlytoodifficultordangerousforhumanstodo.They may also be able to provide companionship, help with householdchores,andprovideassistancetotheelderlyand disabled. As robotics technology continues to evolve, it is likelythatrobotswillbecomeanintegralpartofourlives.
Different Types of Robotics
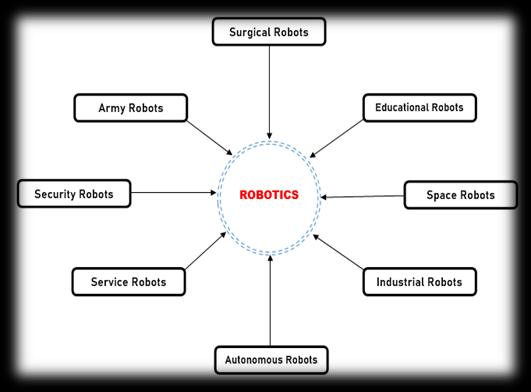
Fig.5 FewTypesofRobotics
1. Surgical Robotics: These are robotic systems that areusedtoassistinsurgicalprocedures.Theyaredesigned toimprovetheaccuracyandprecisionofthesurgeon,andto reducetheriskofcomplicationsanderrors.Surgicalrobots typically consist of a robotic arm attached to a console, which is operated by the surgeon. The robotic arm is equipped with various tools and instruments, such as a camera,scalpel,andforceps,whichareusedtoperformthe surgery.
2. ArmyRobotics:Thisistheuseofrobotsandrobotic technologyinmilitaryapplications.Thisincludestheuseof unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), unmanned ground vehicles(UGVs),unmannedunderwatervehicles(UUVs),and other robotic systems for reconnaissance, surveillance, targetacquisition,andothermilitarymissions.

3. Security robotics is the use of robots to provide security services such as surveillance, access control, and perimeterprotection.These robotsaretypicallyequipped withsensors,cameras,andothertechnologiestodetectand respond to potential threats. They can be used to patrol areas,monitoraccesspoints,anddetectintrusions.Theycan also be used to provide real-time information to security personnel,allowingthemtoquicklyrespondtoanysecurity incidents.
4. Service Robotics: Service robots are designed to interactwithhumansandprovideassistanceinavarietyof tasks.Examplesofservicerobotsincludevacuumcleaners, medicalrobots,andpersonalassistantrobots.
5. AutonomousRobots:Autonomousrobotsarerobots that are capable of making decisions and acting independently without any human input. Examples of autonomous robots include self-driving cars, unmanned aerialvehicles(UAVs),andsearchandrescuerobots.
6. Industrial Robotics: Industrial robots are used in manufacturingandproductionprocessestoautomatetasks suchaswelding,painting,assembly,andpackaging.These robotsaredesignedtobehighlyaccurateandefficient,and areoftenusedinhazardousenvironments.
7. Space Robotics: Space robots are designed to operate in space and are often used for exploration and research.ExamplesofspacerobotsincludetheMarsrovers, spaceshuttles,andsatellites.
8. Educational Robotics: Educational robots are designedtoteachstudentsaboutroboticsandprogramming. Theserobotsareoftenusedinclassroomsandcanbeusedto teach students about robotics concepts such as sensors, motors,andprogramminglanguages.
When we talk about how Robotics will impact the cybersecurity and healthcare sector, we will consider the following;
Robotics is increasingly being used in the field of cybersecuritytohelpprotectnetworks,systems,anddata from malicious attacks. Robotics can be used to automate andstreamlinemanyofthetedious,manualtasksassociated withcybersecurity,suchasvulnerabilityscanning,malware detection,andpatchmanagement.Roboticscanalsobeused todetectand respond tothreatsin real-time,allowingfor fasterandmoreeffectiveresponsestocyberattacks.
Robotics can also be used to help identify and mitigate potential threats before they become a problem. By using machine learning and artificial intelligence, robotics can analyze data and detect patterns that may indicate a potential threat. This can help organizations identify and address potential threats before they become a major problem.
Robotics can also be used to help organizations better understand their security posture. By using robotics to analyze data and identify potential vulnerabilities, Organizationsmayenhancetheirsecurityposturebyhaving abetterunderstandingofit.Inthiscase,itcanbeofhelpto organizations better protect their networks, systems, and datafrommaliciousattacks.
Finally,roboticscanbeusedtohelporganizationscomply with security regulations and best practices. Robotics can help organizations automate the process of ensuring that their networks, systems, and data are compliant with security regulations and best practices. This can help organizationsreducetheriskofnon-complianceandensure thattheirnetworks,systems,anddataaresecure.
Similarly,theimpactoftheroboticsinthehealthcaresector mayincludethefollowing;

Roboticsinhealthcareisarapidlygrowingfieldthathasthe potential to revolutionize the way healthcare is delivered. Robotics can be used to automate mundane tasks, reduce errors,andimprovepatientoutcomes.Roboticscanhelpin the accuracy improvement and speed of diagnosis and treatment. For example, Robotic systems can evaluate medicalphotosandfindanomaliesfasterandmoreprecisely than humans. This can help to reduce the time it takes to diagnoseandtreatpatients.
Roboticscanalsohelptoreducetheriskofmedicalerrors. Roboticsystemscanbeprogrammedtofollowprotocolsand proceduresmoreaccuratelythanhumans,reducingtherisk ofmistakes.Roboticscanalsohelptoimprovethesafetyof medicalprocedures.Roboticsystemscanbeusedtoperform minimally invasive surgeries, reducing the risk of complicationsandimprovingpatientoutcomes.
Roboticscanalsohelptoimprovetheefficiencyofhealthcare delivery.Roboticsystemscanbeusedtoautomatemundane taskssuchasdispensingmedications,reducingtheamount of time it takes to complete these tasks and freeing up healthcareprofessionalstofocusonmoreimportanttasks.
Finally,roboticscanhelp to improve accesstohealthcare. Robotic systems can be used to provide remote consultations and treatments, allowing patients to access healthcare from anywhere in the world. This can help to reducethecostofhealthcareandmakeitmoreaccessibleto people who may not have access to traditional healthcare services.
3. CONCLUSION
Inconclusion,AIandroboticsarerevolutionizingthewaywe approach cybersecurity and healthcare systems. AI and robotics are providing us with more efficient and secure solutionsforbothindustries,allowingustobetterprotect ourdataandimprovehealthcareoutcomes.AIandrobotics
arealsoprovidinguswithnewopportunitiesforautomation, which can help reduce costs and increase efficiency. The potentialforAIandroboticstorevolutionizecybersecurity andhealthcaresystemsisimmense,anditisimportant to continuetoexploreanddevelopthesetechnologiesinorder to maximize their potential. The integration of AI and robotics in cybersecurity and healthcare systems is a promisingdevelopmentthatcouldrevolutionizethewaywe protectourdataandprovidemedicalcare.AIandrobotics have already been used to detect and respond to cyber threats,automatemedicaldiagnosis,andassistwithsurgical procedures. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely thatAIandroboticswillbecomeevenmoreprevalentinthe healthcareandcybersecurityindustries.Thiscouldleadto improvedsecurity,increasedefficiency,andbetterpatient outcomes. Ultimately, the use of AI and robotics in healthcareandcybersecuritysystemscouldhaveapositive impactonsocietyasawhole.
4. FUTURE DIRECTION
AIincybersecurityandhealthcareisexpectedtocontinueto growinthefuture.AI-basedsystemscanbeusedtodetect and respond to cyber threats, as well as to detect and prevent healthcare fraud. AI may be employed to automatically analyse massive volumes of data to find patternsandanomaliesthatmayindicateasecuritybreach or healthcare fraud. AI can also be used to create more secure and efficient healthcare systems, such as by automating the process of scheduling appointments and managing patient records.Inaddition,AIcanincreasethe precisionandefficiencyofmedicaldiagnosisandtherapy,as wellastoprovidepersonalizedhealthcareservices.Finally, AIcanbeusedtocreatemoresecureandefficienthealthcare systems, such as by automating the process of scheduling appointmentsandmanagingpatientrecords.
5. REFERENCES
[1] M.Ahmad,“Malwareincomputersystems:Problems and solutions,” IJID (International Journal on InformaticsforDevelopment),vol.9,p.1,042020.

[2] N. Milosevic, “History of malware,” Digital forensics magazine,vol.1,no.16,pp.58–66,Aug.2013.
[3] S. Gupta, “Types of malware and its analysis,” International Journal of Scientific Engineering Research, vol. 4, 2013. [Online]. Available: https://www.ijser.org/researchpaper/Types-ofMalware-andits-Analysis.pdf
[4] Statista.Anumberofworldwideinternethostsinthe domain name system (dns) from 1993 to 2019. [Online]. Available: https://www.statista.com/statistics/264473/numberofinternet-hosts-in-the-domain-name-system/
[5] F. Kamoun, F. Iqbal, M. A. Esseghir, T. Baker, “AI and machinelearning:Amixedblessingforcybersecurity”.
[6] H.S.Anderson,A. Kharkar,B. Filar,B.Roth,“Evading machinelearningmalwaredetection,”BlackHatUSA 2017, July 22-27, 2017. https://www.blackhat.com/docs/us-17/thursday/us17-Anderson-Bot-VsBot-Evading-Machine-LearningMalware-Detection-wp.pdf, accessed November 6, 2018.
[7] N. Ding, H. Ma, H. Gao, Y. Ma, and G.Tan, “Real-time anomalydetectionbasedonlongshort-termmemory andGaussianMixtureModel,”Computers&Electrical Engineering,vol.79,pp.1-11,2019.
[8] M.Z.Alom,andT.M.Taha,“Networkintrusiondetection for cybersecurity using unsupervised deep learning approaches,” In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON),Dayton,OH,USA,pp.63–69,2017.
[9] J.Chen,Y.Yang,K.Hu,H.Zheng,andZ.Wang,“DADMCNN:DDoSattackdetectionviamulti-channelCNN,” InProceedingsofthe11thInternationalConference onMachineLearningandComputing:ICMLC'19,pp. 484-488,2019.
[10] Y. Mirsky, T. Doitshman, Y. Elovici, A. Shabtai, and A. Kitsune, “An ensemble of autoencoders for online network intrusion detection,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.09089,pp.1-15,2018.
[11] S.K.Biswas,S.K,“Intrusiondetectionusingmachine learning:Acomparisonstudy,”InternationalJournalof Pure and Applied Mathematics, vol. 118, no. 19, pp. 101-114,2018.
[12] J.Clements,Y.Yangy,A.A.Sharma,H.Huy,andY.Lao, “Rallyingadversarialtechniquesagainstdeeplearning for network security, arXiv preprint arXiv:1903.11688v1,pp.1-8,2019
[13] S. Xia, M. Qiu, M. Liu, M. Zhong, and H. Zhao, “AIenhanced automatic response system for resisting network threats,” In M. Qiu (Ed.): SmartCom 2019, LNCS11910,pp.221–230,2019.
[14] Z. Wang, “The Applications of Deep Learning on Traffic Identification”, BlackHat, 2015, https://www.blackhat.com/docs/us15/materials/us15-Wang-The-Applications-Of-Deep-LearningOnTraffic-Identification-wp.pdf ,accessed March23, 2019.
[15] M. Lotfollahi, R. Shirali, M.J. Siavoshani, and M. Saberian, “Deep packet: A novel approach for
encrypted traffic classification using deep learning,” arXivpreprintarXiv:1709.02656,pp.1-13,2017.
[16] G.Mi,Y.Gao,andY.Tan,“Applystackedauto-encoderto spamdetection,”InProceedingsoftheInternational ConferenceinSwarmIntelligence,Beijing,China,pp. 3
15,2015.
[17] M.Alauthman,M.Almomani,M.Alweshah,W.Omoush, and K. Alieyan, “Machine learning for phishing detection and mitigation,” In: Machine Learning for Computer and Cyber Security, B. Gupta, and Q.Z. Sheng,(eds),pp.1-27,Taylor&Francis,2019.
[18] D. Aksu, Z. Turgut, S. Üstebay, and M.A. Aydin, “Phishing analysis of websites using classification techniques,”pp.251–258.Springer,Singapore,2019.
[19] P.Yi,Y.Guan,F.Zou,Y.Yao,W.Wang,andT.Zhu,“Web phishingdetectionusingadeeplearningframework,” Wirel.Commun.Mob.Comput,pp.1–9,2018.
[20] E.Benavides,W.Fuertes,S.Sanchez,andM.Sanchez, M.” Classification of phishing attack solutions by employing deep learning techniques: A systematic literaturereview,”inÁ.RochaandR.P.Pereira(eds.), DevelopmentsandAdvancesinDefenseandSecurity, SmartInnovation,SystemsandTechnologiesvol.152, pp.51-64,2020.
[21] A.Tuor,S.Kaplan,B.Hutchinson,N.Nicholsand,andS. Robinson, “Deep learning for unsupervised insider threat detection in structured cybersecurity data streams,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.00811, pp. 1-9, 2017.
[22] N.L.Beebe,L.A.Maddox,L.Liu,andM.Sun,“Sceadan: Usingconcatenatedn-gramvectorsforimprovedfile and data type classification,” IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 1519–1530,2013.
[23] S.Axelsson,“Thenormalisedcompressiondistanceas afilefragmentclassifier,”DigitalInvestigation,vol.7, no.8,pp.S24–S31,2010.
[24] W.C.Calhoun,andD.Coles,“Predictingthetypesoffile fragments,”DigitalInvestigation,vol.5,pp.S14–S20, 2008.
[25] Q.Chen,Q.Liao,Z.Jiang,J.Fang,S.Yiu,G.Xi,etal,“File fragment classification using grayscale image conversionanddeeplearning,”InProceedingsofthe IEEESymposiumonSecurityandPrivacyWorkshops, pp.140-147,2018.

[26] N. Soliman A. ALEnezi. “A Method of Skin Disease Detection Using Image Processing and Machine Learning”ProcediaComputerScience163(2019)85–92.
[27] KritikaSujayR,PoojaSureshY,OmkarNarayanP,Dr. Swapna B.”Skin disease detection using machine learning”IJERTVol.9.Issue3.2021.
[28] H.A.Shah,F.Saeed,S.Yun,J.-H.Park,A.PaulandJ.-M. Kang,"ARobustApproachforBrainTumorDetection in Magnetic Resonance Images Using Finetuned EfficientNet," in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 6542665438,2022,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3184113.
[29] A. H. Abdel-Gawad, L. A. Said and A. G. Radwan, "OptimizedEdgeDetectionTechniqueforBrainTumor Detection in MR Images," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 136243-136259, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3009898.
[30] A.S.Musallam,A.S.SherifandM.K.Hussein,"ANew Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Automatic Detection of Brain Tumors in Magnetic ResonanceImagingImages," inIEEEAccess,vol.10, pp. 2775-2782, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3140289.
[31] M.Rizwan,A.Shabbir,A.R.Javed,M.Shabbir,T.Baker andD.Al-JumeilyObe,"BrainTumorandGliomaGrade Classification Using Gaussian Convolutional Neural Network," inIEEEAccess,vol.10,pp.29731-29740, 2022,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3153108.
[32] MahbubHussain,JordanJ.Bird,andDiegoR.Faria“A Study on CNN Transfer Learning for Image Classification”ContributionsPresentedatthe18thUK WorkshoponComputationalIntelligence,September 5-7, 2018, Nottingham, UK. January 2019 DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-97982-3_1
[33] A.KumarandS.Joshi“ApplicationsofAIinHealthcare SectorforEnhancementofMedicalDecisionMaking and Quality of Services,” in 022 International ConferenceonDecisionAidSciencesandApplications (DASA)|978-1-6654-9501-1/22/$31.00©2022IEEE |DOI:10.1109/DASA54658.2022.9765041.
[34] “UnderstandingCancerusingMachineLearning| by Pier Paolo Ippolito | Towards Data Science.” https://towardsdatascience.com/understandingcancerusing-machine-learning-84087258ee18 (accessedAug.14,2021).
[35] A.MaharanaandE.O.Nsoesie,“UseofDeepLearning toExaminetheAssociationoftheBuiltEnvironment WithPrevalenceofNeighborhoodAdultObesity,”JAMA
Netw.Open,vol.1,no.4,pp.e181535–e181535,Aug. 2018,doi:10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2018.1535.

[36] P. Kostkova, “A roadmap to integrated digital public healthsurveillance,”Proc.22ndInt.Conf.WorldWide Web-WWW’13Companion,pp.687–694,2013,doi: 10.1145/2487788.2488024.
[37] M. Bryant, “Hospitals turn to chatbots, AI for care | Healthcare Dive,” Healtcare Dive, 2018. https://www.healthcaredive.com/news/chatbotsaihealthcare/516047/(accessedAug.14,2021).
[38] A.KumarandS.Joshi“ApplicationsofAIinHealthcare SectorforEnhancementofMedicalDecisionMaking and Quality of Services,” in 022 International ConferenceonDecisionAidSciencesandApplications (DASA)|978-1-6654-9501-1/22/$31.00©2022IEEE |DOI:10.1109/DASA54658.2022.9765041.
[39] A.JoumanHajjar,“6ChatbotApplications/UseCases in Healthcare in 2021,” AI Multiple, 2021. https://research.aimultiple.com/chatbot-healthcare/ (accessedAug.14,2021).
[40] K.Kalinin,“HealthcareChatbots:RoleofAI,Benefits, Future, Use Cases, Development.” https://topflightapps.com/ideas/chatbots-inhealthcare/(accessedFeb.16,2022).
[41] A.Mihat,N.MohdSaad,E.Shair,A.AslamandR.Abdul Rahim, "SMART HEALTH MONITORING SYSTEM UTILIZING INTERNET OF THINGS (IoT) AND ARDUINO",AsianJournalOfMedicalTechnology,vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 35-48, 2022. Available: 10.32896/ajmedtech.v2n1.35-48
[42] R. Anandh and G. Indirani, "Real Time Health Monitoring System Using Arduino with Cloud Technology",AsianJournalofComputerScienceand Technology, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 29-32, 2018. Available: 10.51983/ajcst-2018.7.s1.1810.
[43] V. Soppimath, A. Jogul, S. Kolachal and P. Baligar, "Human Health Monitoring System Using IoT and CloudTechnology-Review",InternationalJournalof AdvancedScienceandEngineering,vol.5,no.2,p.924, 2018.Available:10.29294/ijase.5.2.2018.924-930.
[44] C.Srinivasan,G.CharanandP.SaiBabu,"AnIoTbased SMARTpatienthealthmonitoringsystem",Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 18, no. 3, p. 1657, 2020. Available: 10.11591/ijeecs.v18.i3.pp1657-1664.
[45] Regeringskansliet. Vision e-hälsa 2025 –gemensamma utgånspunkter för digitalisering i
socialtjänst och hälso – och sjukvård. Socialdepartementet och SKL; 2016. https://www.regeringen.se/499354/contentassets/7 9df147f5 b194554bf401dd88e89b791/vision-ehalsa-2025-overenskommelse.pdf Accessed 12 June 2020.
[46] Baird B, Charles A, Honeyman M, Maguire D, Das P. Understandingpressuresingeneralpractice.London: King’sFund;2016
[47] Greenhalgh T, Shaw S, Wherton J, Vijayaraghavan S, Morris J, Bhattacharya S, et al. Real-world implementation of video outpatient consultations at macro,meso,andmicrolevels:mixed-methodstudy.J MedInternetRes.2018;20:e150.
[48] ChenJ,LanYC,ChangYW,ChangPY.Exploringdoctors’ willingnesstoprovideonlinecounselingservices:the rolesofmotivationsandcosts.IntJEnvironResPublic Health.2019;17:110.
[49] Allen TD, Golden TD, Shockley KM. How effective is telecommuting?Assessingthestatusofourscientific findings.PsycholSciPublicInterest.2015;16:40–68
[50] SKR.Statistikomhälso–ochsjukvårdsamtregional utveckling 2018; 2018. https://skr.se/ekonomijuridikstatistik/statistik/ ekonomiochverksamhetsstatistik.1342.htmlAccessed 12June2020.
[51] EkmanB.Costanalysisofadigitalhealthcaremodelin Sweden.PharmacoeconOpen.2018;2:347–54.
[52] M.Q.Hatem“SkinLesionClassificationSystemUsinga K-Nearest Neighbour Algorithm”, Hatem Visual ComputingforIndustry,Biomedicine,andArt(2022) https://doi.org/10.1186/s42492-022-00103-6
[53] Z. Li, et al. Intrusion Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Representation Learning. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing(pp.858-866).Springer,Cham,November 2017.
[54] C. Yin et al. Deep Learning Approach for Intrusion Detection Using Recurrent Neural Networks. IEEE Access,5,21954-21961.
[55] R. Ashfaq, et al. Fuzziness based semi-supervised learning approach for intrusion detection system. Fuzzinessbasedsemi-supervisedlearningapproach forintrusiondetectionsystem.InformationSciences, 378,484-497,2017.
[56] S.T.AhmedandK.KPatil,“AnInvestigativestudyon motifs extracted features opn real-time big-data signals”, in Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Emerging Technological Trends (ICETT), Kollam, India, IEEE, 2016, pp. 1-4. Doi: 10.1109/ICETT.2016.7873721

[57] Z.Lin,X.Fei,S.Yi,M.Yan,X.Cong-CongandH.Jun,“A secureencryption-basedmalwaredetectionsystem.” KSIITransactiononInternetandInformationSystems (TIIS),Vol.12,no.4,April2018,pp.1799-1818.Doi: 10.3837/tiis.2018.04.022.
[58] M.Fan,J.Liu,X.Luo,K.Chen,Z.Tian,Q.Zheng,andT. Liu, “Android malware familial classification and representativesampleselectionviafrequentanalysis” IEEE Transaction on Information Forensics and Security,Vol.13,No.8August2018,pp.1890-1905, doi:10.1109/TIFS.2018.2806891.
[59] N.Shoneetal.Adeeplearningapproachtonetwork intrusiondetection.IEEETransactionsonEmerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2(1), 41-50, 2018.
[60] S. Sharma, R. Challa, and S. Sahay, Detection of AdvancedMalwarebyMachineLearningTechniques: ProceedingsofSoCTA2017,012019,pp.333–342.
[61] L.Xiaofeng, J. Fangshuo, Z. Xiao, Y. Shengwei, S. Jing and P. Lio “ASSCA: API sequence and statistics features combined architecture for malware detection”,ComputerNetworks,Vol.157,July2019, pp.99-111,doi:10.1016/j.comnet.2019.04.007.
[62] L.S.Fasci,M.Fisichelle,G.Lax,andC.Qian“Disarming Visualization-basedApproachesinMalwareDetection Systems” in Computers&Security·December2022 DOI:10.1016/j.cose.2022.103062
[63] I. Baptista, S. Shiaeles, and N. Kolokotronis, “A novel malwaredetectionsystembasedonmachinelearning andbinaryvisualization,”052019,pp.1–6.
[64] F.Xiao,Z.Lin,Y.SunandY.Ma,“Malwaredetection based on deep learning of behaviour graphs”, Mathematical Problems in Engineering, Vol.2019, February 2019, pp. 1-10, doi: 10.1155/2019/8195395.
[65] DaiXF,SpasićI,MeyerB,ChapmanS,AndresF(2019) Machinelearningonmobile:Anon-deviceinference appforskincancerdetection.In:Abstractsofthe4th international conference on fog and mobile edge computing, IEEE, Rome, 10-13 June 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/FMEC.2019.8795362
[66] E.AmerandI.Zelinka,“Adynamicwindowsmalware detectionandpredictionmethodbasedoncontextual understandingofAPIcallsequence”,Computersand Security, Vol. 92, February 2020, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2020.101760.
[67] M.O.F.Rokon,R.Islam,A.Darki,E.Papalexakis,andM. Faloutsos,“Sourcefinder:Findingmalwaresource-code frompubliclyavailablerepositories,”inRAID,2020.
[68] M.Mohammad,S.Hossain,H.Hisham,H.F.MdJobair, V. Maria, K. Md Abdullah, A. R. Mohammad, A. Muhaiminul I., C. Alfredo, and W. Fan, “Bayesian hyperparameter optimization for deep neural network-based network intrusion detection,” IEEE InternationalConferenceonBigData,2021.
[69] Gustafson E, Pacheco J, Wehbe F, Silverberg J, ThompsonW. A machine learning algorithm for identifyingatopicder-matitisinadultsfromelectronic healthrecords.2017IEEEInternationalConferenceon HealthcareInformatics(ICHI).2017;2017:83 90.
[70] EstevaA,KuprelB,NovoaRA,KoJ,SwetterSM,Blau HM,et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer withdeep neural networks. Nature. 2017;5427639:115 8
[71] F.Jiang,Y.Jiang,H.Zhi,Y.Dong,H.Li,S.Ma,Y.Wang,Q. Dong,H.Shen,andY.Wang,‘‘Artificialintelligencein healthcare:Past,presentandfuture,’’StrokeVascular Neurol., vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 230–243, 2017, doi: 10.1136/svn-2017-000101.
[72] HanSS,ParkGH,Lim W,KimMS,Na JI,ParkI, etal. Deep neuralnetworks show an equivalent and often superior performanceto dermatologists in onychomycosis diagnosis: automaticconstruction of onychomycosis datasets by region-based convolutional deep neural network. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0191493
[73] Patnaik SK, Sidhu MS, Gehlot Y, Sharma B, Muthu P (2018) Automated skin disease identification using deep learning algorithm. Biomed Pharmacol J11(3):1429–1436. https://doi.org/10.13005/bpj/1507
[74] Rathod J, Waghmode V, Sodha A, Bhavathankar P (2018)DiagnosisofSkindiseasesusingconvolutional neuralnetworks.In:Abstractsofthe2ndInternational lconference on electronics, communication and aerospace technology. Coimbatore: IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECA.2018.8474593
[75] AminJ,SharifA,GulN,AnjumMA,NisarMW,AzamF etal(2020)Integrateddesignofdeepfeaturesfusion
for localization and classification of skin cancer. Pattern Recogn Lett 131:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2019.11.042
[76] A.Mahajan,T.Vaidya,A.Gupta,S.Rane,andS.Gupta, ‘‘Artificial intelligence in healthcare in developing nations:Thebeginningofatransformativejourney,’’ Cancer Res., Statist., Treatment, vol. 2, no. 2, p. 182, 2019,doi:10.4103/crst.crst_50_19
[77] S. Grampurohit, V. Shalavadi, V. R. Dhotargavi, M. Kudari, and S. Jolad, ``Brain tumor detection using deeplearningmodels,''in Proc.IEEEIndia CouncilInt. SubsectionsConf.(INDISCON),Oct.2020,pp.129_134.

[78] R. Ashraf, S. Afzal, A. Rehman, S. Gul, J. Baber, M. Bakhtyar, I. Mehmood, O. Song, and M. Maqsood, “Region-of-InterestBasedTransferLearningAssisted FrameworkforSkinCancerDetection”,IEEEACCESS, Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3014701
[79] BalajiMSP,SaravananS,ChandrasekarM,Rajkumar G,KamalrajS(2021)Analysisofbasicneuralnetwork typesforautomatedskincancerclassificationusing Fireflyoptimizationmethod.JAmbientIntellHuman Comput 12(7):7181–7194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-02394-0
[80] G. Kumar, P. Kumar, and D. Kumar, ``Brain tumor detection using convolutional neural network,'' in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Mobile Netw. Wireless Commun. (ICMNWC),Dec.2021,pp.1_6.
[81] G.Yang,Q.Ye,andJ.Xia,‘‘Unboxtheblack-boxforthe medical explainable AI via multi-modal and multicentredatafusion:Aminireview,twoshowcasesand beyond,’’2021,arXiv:2102.01998.
[82] Kassem MA, Hosny KM, Fouad MM (2020) Skin lesionsclassificationintoeightclassesforISIC2019 usingdeepconvolutionalneuralnetworkandtransfer learning. IEEE Access 8:114822–114832.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3003890
[83] H.A.Shah,F.Saeed,S.Yun,J.Park,A.Paul,andJ.Kang, “A Robust Approach for Brain Tumor Detection in Magnetic Resonance Images Using Finetuned EfficientNet”, IEEE ACCESS Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3184113
[84] S. Polekar, S. Wakde, M. Pandare, P. Shingane, “Intelligent Medical Chatbot System For Women’s Healthcare” ITM Web of Conference 44, 03020 920 (2022)
https://doi.org/10.1051/itmconf/20224403020.
[85] A.Imran,A.Nasir,M.Bilal,G.Sun,A.Alzahrani,andA. Almuhameed,“SkinCancerDetectionUsingCombined Decision of Deep Learners”, IEEE ACCESS, Digital Object Identifier 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3220329.
[86] H. Rafiq, N. Aslam, M. Aleem, B. Issac, and R. H. Randhawa“AndroMalPack:enhancingtheML-based malware classification by detection and removal of repackedappsforAndroidsystems”,ScientificReports |(2022)12:19534|https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598022-23766-w
[87] Ahmed,I.T. Jamil,N.;Din, M.M.Hammad,B.T. Binary andMulti-ClassMalwareThreadsClassification.Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12528. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122412528
