STEGANOGRAPHY: COMPLETE OVERVIEW OF RELEVANT TECHNIQUES AND METHODS
 S M Ali Zaidi1 , Piyush Kumar Gupta2
S M Ali Zaidi1 , Piyush Kumar Gupta2
Abstract - With the exponential rise of digital multimedia content, the data hiding techniques came into popular demands in order to securely transmit information around. This review paper focusses on one such technique of data hiding i.e., steganography. It is the art and science of embedding secret messages in a normal message in a way that anyone without knowledge of hidden message cannot suspect the presence of the message, except sender and receiver. Proper analysis has been done and the data collection for review were taken from several research databases namely, Springer, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar and IEEE Explorer to increase the scope of objectivity of this paper
Key Words: Steganography,Cryptography,Image,Audio and Video Steganography, Steganalysis, Data Hiding, Embedding,LSB.
1. INTRODUCTION
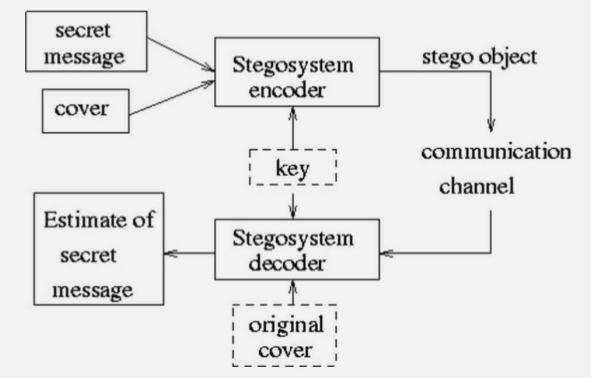
Steganography, the word itself is derived from the Greek words‘stegos’and‘grafia’whichmeanscoverandwriting respectively, thus making it covered writing or hidden writing[1].Itisthepracticeofconcealingafile,amessage, imageoraudio/videoinanotherfileinordertosafeguard and protect the information being hidden. The concealed message is present in the file in a way such that it cannot be recovered without the help of sender/receiver who knows how to extract the hidden message. images, audio, video, and texts can be represented as digital data . However, new issues also arose and have been explored(Art. 2001;Zhao et al., 1998), such as data securityindigitalcommunications,copyrightprotectionof digitized properties, invisible communication via digital media,etc.Stega-imageisthenameofthecoverdocument that contains the hidden message. Steganography and steganalysisaretermsusedtodescribethistechniqueand its vice-versa respectively. This system is depicted in Figure 1 as hiding data or messages in the cover medium at the sender or source end and retrieving the concealed data from the steganographic document at the receiver end.Steganographycanbeusedinfourdifferentways:
1.Usingtext
2.ImageSteganography

3.AudioSteganography
***
4.VideoSteganography
Fig.1SimpleSteganographicModel
While cryptography focuses on keeping the contents of a communication secret using various encryption techniques, steganography focuses on keeping the existence of a message hidden [4], as we shall describe later. Steganography and cryptography are two methods forkeepinginformationsafefromunapprovedaccess,but neitherisflawlessandmaybeintercepted[4]
Imperceptibility, Robustness and Embedding Techniques are the three very important factor for any successful steganographicsystems.
•The safety of steganography technologies that hide the secret message in the embedded video is directly connected to imperceptibility. Because of the great
imperceptibility, the embedded video has a low modificationrateandgoodvisualquality.
•The second prerequisite, robustness, assesses the steganography method's resistance to assaults in steganography. The need of resilience is due to the fact that the embedded message might be damaged by a variety of purposeful and inadvertent assaults, such as network transmission, packet loss, video cutting, and scalingprocesses.
•Thethirdprerequisiteneedisembeddingcapacity,which is defined as the total number of hidden messages that may be inserted into a digital movie. The more hidden messages that can be inserted, the better the embedding capacity.
2. HISTORICAL BACKGROUND
Throughout the history, there are many instances when different techniques were used to hide a secret message and one of the most popular of such cases is that of Histiaeus, a Greek ruler who used the steganography technique by shaving the head of one of his slaves and writing the secret message on it and had waited for the hairstoregrowsothathecansendtheconcealeddata.
3. RELATED WORKS
With extensive research works and study in the field, hereby is a list of some important researches mentioning the name of their authors, topic of study, advantages and limitations to give a brief explanation of trends that follows in the previous research works and the topics of special significancethatallowstoexploreandunderstand moreaboutthiseverpopularwayofconcealingimportant messages.
CitationsTitleofthepaper Methodology Advantages Disadvantages Evaluation
[12] AnoverviewofImage Steganography
Different steganographic techniquesand spatialandtransform domainmethods, steganalysis preventionand detection,
Proposedtechniquestokeepin checkimagesteganography methodsaccordingto Imperceptibiliyrules
SecurityofLSBsteganographic techniqueisslightlyimproved.
Robustnessagainst statisticalattacksand imagemanipulation needstobeincheck.
Moresensitivityfor steganalysistoolsand providing unsuspiciousfiles
Thepapergaveabriefoverviewof howimagesteganographycan changethewholehidden communicationscenarioand proposedseveraltechniqueswith theirrulestofollow.
VideoSteganography :Areview
Thereview methodologyofthis workcontainsdata hiding,visualquality, methodsand techniques, embeddingand capacity
Brieflydefinesthetechniques usedintheconcealmentof datainavideo. Othermethodsandtheir importanceinthefieldwere introduced
Thefirsttaskistodevelopavideo steganographysystemthat achievesafairtrade-offbetween visualquality,embeddingcapacity, andresilienceagainstavarietyof unanticipatedassaults.
Digitalaudio steganography: Systematicreview, classification,and analysisofthecurrent stateoftheart
DataSecurityby Steganography
Datagathering, techniqueanalysis, majorbehaviour construction, and similarity-based categorizationareall partofthereview approachforthis project.
Usefulnessandimportanceof differenttechniquesandtheir harmswerebrieflyexplained andhighlightedthrough variousresearchjournals.
Acomparisonofthe performanceofthe studiedapproaches, Thediscrepancyin assessment methodologiesand embedding environmentsinthe evaluatedapproaches allowsforthis comparison.

Understandingwithstatisticaldata ofpreviouspapersandpresent findingsisbeneficialand important.
Securingdataand informationthrough different steganographic methods.
LSBalgorithmsinvariations wereproposedwhich optimizedthequalityofstegoimagethroughbitinvert techniqueImplementationof steganography,and futureapplicationswere explored.
Noimportancewere giventoother steganographic methodssuchasvideo audio,ortextandonly image steganographywas explored.
Steganographyisveryusefulinthe fieldofdatasecurityand protectionifcorrectly implemented.Secretinformation maybeutilisedtovalidatevital businesstransactionsanduser authenticationviasteganography.
4. CRYPTOGRAPHY, STEGANOGRAPHY AND STEGANALYSIS
4.1 Cryptographyand Steganography
Cryptography is also the method or techniques of hiding messages, but unlike Steganography the messages are hidden using a set of complex codes that can only be decoded by the the one for whom the crypted data was made for. A special key is used for the decoding or deciphering ofthe code and it can be passed through one on one communication between sender and receiver[6][7].One camouflages a message in a file/image/video or audio whereas other uses encoding methodstoconcealit[8].
4.2 SteganographyandSteganalysis
While cryptography and steganography were very much similartoeachother,ontheotherhandsteganalysisisthe complimentofsteganography.Insimplerwordsifwelook intoitfromanopponent’spointofview,Steganalysis[9]is the practice of preventing stealthy and concealed communications, which is the main role ofsteganography to provide with messages stealthily. Its primarygoal is to checkwhetherasecretishiddeninamessageorpackage, ornotandidentifyingthesecretmessageinducedfiles
5. CATEGORIES AND CLASSIFICATION
Digital files or data, such as picture, video, text, music, network protocol, and DNA, are commonly used as communication mediums/carriers. Secretinformation is embedded in many digital mediums using their unique qualities. Text steganography, for example, employs line/word shifting encoding [8], and emoticons were recently used in textual chat to accomplish hidden Communication. For incorporating hidden information in audiosteganography, phase coding, spread spectrum, and low-bitencodingarecommonlyused.
Hidden message can also be placed in packet payloads, packet headers inside another medium, and even retransmissionsteganography,whichusesthebehaviourof acknowledgement and retransmission of packets. The featuresofrandomnessinDNAmaybeusedtoincorporate the hidden data in DNA-based steganography, i.e., A approach that uses a numerical mapping table tomap the DNA sequence for encoding secret data was recently published. Image and audio steganography are frequently combinedinvideosteganography.
Among all the other steganographic methods the, most widely and popularly used technique is image steganography since images are the one that are most broadlyusedontheinternet.
5.1 IMAGE STEGNOGRAPHY
An Image Steganographic method is generallyassessed by the following major goals: Firstly, what is the maximum embedding payload that can be achieved? Secondly, how similar is the stego-image to its cover picture in terms of visualimagequality?Thirdly,intermsofsecurity,howcan a stego-image withstand various steganalysis recognition attacks? As a result, the optimal steganographic approach mustconcurrentlyachievetheabovegoalsofstrongability, acceptable visual picture quality, and undetectability. However, high-payload steganographic techniques frequently create distortion errors in stegoimages,makingthemsensitivetosteganalysis.
To create hidden data embedding, several ways have been developed, the majority of which involve a unique methodology. They may be further classified into numerouscategoriesdependingontheirimplementationif we classify them according to model / approach based techniques. We put them into several groups despite the fact that it is hard to classify them all exactly. We usually divide them according to their embedding domain which areoftwotypes,SpatialDomainandTransformDomain.

5.1(A) SPATIAL DOMAIN
Also known as image domain, it embeds a message in the intensity of the image pixels directly, Bit-wise approaches that employ bit insertion and noise modification are referred to as "simple systems" in image domain techniques. Lossless image formats are best for image domain steganography, and the approaches are usually determined by the picture format. Following are themostoftenutilisedspatialdomaintechniques:
1) LeastSignificantBit,popularlyknownasLSB.
2) PixelValueDifference,orPVD.
3) Exploiting Modification Direction (EMD) based methods.
4) EdgebasedMethods
LEAST SIGNIFICANT BIT(LSB)
Least significant bit (LSB) Steganography is a basic and well-known method for concealing bigger amounts of secret information in a cover image with little visual alterations. It operates by substituting secret message bits for the LSBs of (randomly chosen) selected pixels in the cover picture. A stego- key can determine the order of embeddingortheselectionofpixels.
It is a general, and easier approach for embedding information in a The Least Significant Bit (LSB) is a straightforward steganography approach. It embeds the data into the cover, like all steganographic techniques, so
that it cannot be noticed by a casual viewer[10]. The approach replaces some of the information in a pixel with data from the picture. Normally, the most-right bits of a cover file's bytes are replaced by an LSB algorithm. If a portion of the cover picture C(i,j) is missing, C(i, j) is unaltered if the bit of SM or the secret message to be embedded is equal to it, else C(i, j) is set to a bit of SM which is also known as secret message. Secret Message (SM).Theletter'C,'forexample,hasanASCIIcodeof67in decimal, which corresponds to 01000011 in binary and before concealing (embedding) a hidden message, bits of thepicturepixelsare:
Pixel1:111110001100100100000011
Pixel2:111110001100100100000011
Pixel3:111110001100100100000011
The LSB (Least Significant Bit) algorithm embeds or concealsthe01000001bitsoftheletter'A'intothepicture pixelstoproduce:
Pixel1:111110001100100100000010
Pixel2:111110001100100000000010
Pixel3:111110011100100100000011
PIXEL VALUE DIFFERENCE(PVD)
The pixel-value differencing (PVD) method determines howmanysecretbitsshouldbeinsertedbycomparingthe values of two successive pixels in a block. It calculates the payload by the difference value between two consecutive pixels by selecting two successive pixels and building a quantizationrangetablewhichgivesgreatimperceptibility to the stego picture. Furthermore, it has the benefit of transportingahighnumberofpayloadswhileyetretaining visualintegrityafterdataembedding.
EXPLOITING MODIFICATION DIRECTION(EMD) BASED METHODS
EMD (exploiting modification direction) has been a very well- known embedding approach for maintaining steganographic image integrity. During the embedding process in the EMD, the secret digit is generally changed using the (2n + 1)-ary system, where n is the number of coverpixels.Thedistortionrange'smaximumpixelvalueis just(1).Toputitanotherway,theEMDusesacertainbase to identify the local fluctuation of pixel intensity in a picture,allowingpixelsinhightextureareastoencodethe more hidden information. In comparison to the LSB and PVD processes, the EMD may produce high visual quality. The highest capacity of the EMD approach, on the other hand,isupto1.16bppforanumberof(n=2)twopixels.
Asthenumberofchosenpixelsisincreased,theembedding payload reduces dramatically. As a result, many EMD-
based strategies for improving embedding capacity have beendeveloped.
EDGE BASED METHODS
The edge adaptive encoding approach is a popular embeddingstrategyinthespatialdomain.Whenpixelsina smoothareaofanimagearedirectlymodifiedinthespatial domain, the result is a visual distortion. Edge adaptive embedding schemes have thus evolved to keep visual distortiontoaminimum.
5.1(B) TRANSFORM DOMAIN TECHNIQUES
Instead of manipulating the picture itself, transformation or Image domain techniques modify the image's orthogonaltransform.

Thefrequencycontentofapicturecanbeprocessedusing Image domain methods. The frequency domain image enhancement approach works by computing a 2-D discrete unitary transform of the picture, such as the 2-D DFT, then modifying the transform coefficients using an operator M, after which the inverse transform is applied. The image's orthogonal transform contains two components:magnitudeandphase.Thefrequencycontent ofthe picture makesupthe magnitude. The phaseisused to restore the spatial domain of the picture. Because the typical transform domain allows action on the image's frequency content, high frequency features such as edges and other subtle information may be easily increased. Steganography with JPEG pictures was considered to be impossible at first because they employ lossy compression, which causes sections of the image data to be changed. The JPEG compression process is split into twostages:lossyandlossless.Thelossystageincludesthe DCT and quantization phases, whereas the lossless stage includes the Huffman encoding used to further compress thedata.Betweenthesetwoprocesses,steganographycan takeplace.
Discrete Wavelet Transform(DWT)
The DWT transform is described as a wavelet transformation that uses translations that obey established rules and a discrete collection of wavelet scales. When converting a spatial domain to a frequency domain, the wavelet transform is utilized. On a pixel-by-

pixel level, the wavelet transform distinguishes high frequencyand lowfrequencyinformation, whichmakes it useful in picture stenographic models. Because images at low frequency at various levels can give equivalent resolution, Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) is chosen overDiscreteCosineTransforms(DCT).
Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)
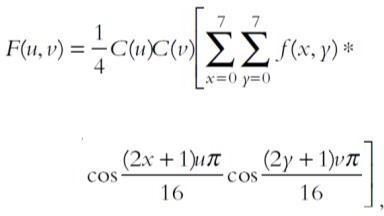
Thisapproachusesasumofcosinefunctionstorepresent a static sequence of data information that may vary in frequency.Thesearesignificantinavarietyofengineering and scientific applications, including lossy audio compression,suchasMP3files,andpictures,suchasJPEG files, where little high-frequency components are discarded. For every image pixel which is a coloured component,Thediscretecosinetransformationisused by theJPEGimageformattotransformsuccessive8×8pixel blocksoftheimageinto64DCTcoefficientseach.TheDCT coefficientsF(u,v)ofan8×8blockofimagepixelsf(x,y) aregivenby
Below is the table to highlight the difference between algorithmsofDCTandDWTtechniques.
lawenforcement,copyrightprotection,andaccesscontrol, among others . Because the human visual system is less sensitivetosubtlechangesindigital material,particularly digital video, video steganography is a technique for hidingmessagesandconcealingthefactoftransmission.It has lately gained in popularity for two key reasons: With the rapid expansion of computer applications, the information security problem is becoming increasingly important.[13]Types:
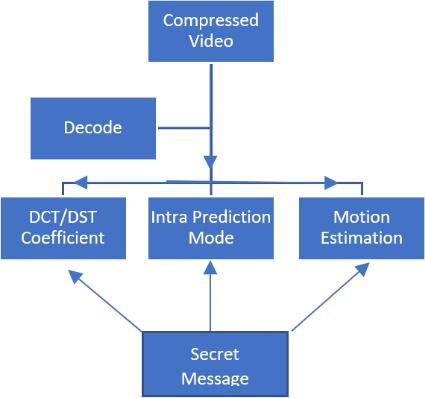
5.2(A) BASED ON INTRA EMBEDDING

Below is the table to highlight the difference between algorithmsofDCTandDWTtechniques.
Intra-embedding merges the video coding embedding process with syntactic features like intra- prediction, motion estimation, and DCT coefficients: As illustrated in the above figure, the sender embeds a hidden message intothevideoprocess.The commonvideocodingformats H.26X and MPEG-X have a high compression ratio, and following compression coding, most of the video data redundancy is eliminated, making it more difficult to insertmoredataintothecompressedvideostream.

5.2(B) BASED ON PRE EMBEDDING
The transmitter embeds the cryptic message in the noncompressed video stream before compressing it, and the receiver decodes the compressed video received and extracts the secret message from the original video. Preembeddedvideosteganographytreatsthevideosequence as a collection of frames. Spatial and transform domain approaches are used in pre-embedding video steganography.
5.2(C) BASED ON POST EMBEDDING
5.2VIDEO STEGANOGRAPHY
Datahidingisabranchofvideosteganography,whichisa method that embeds messages into cover contents and is utilizedinavarietyofdomainsincludingmedicalsystems,
The transmitter directly embeds secret messages into compressed bitstream, while the receiver extracts secret messages directly from the received embedded compressedvideobitstreaminthepost-embeddingvideo steganographyprocess.Becauseofformatcomplianceand computational complexity,itisnotpossibletoincludethe entirebitstream.
5.3 AUDIO STEGANOGRAPHY
This is a technique for concealing information in audio signals. The signal is modified when data is encoded in it. Thischangeshouldbeundetectabletothehumanear.[14] Audio steganography is more stunning than image steganography due to the properties of the Human AuditorySystem(HAS)suchasbigpower, powerfulrange ofhearing,andhighrangeofaudiblefrequency.
The chart below briefly explains the usage of different techniques, and embedding behaviors with method distributions,whereitcanbeeasilyderivedthatthemost popular technique is Selective based embedding with overall 26%usagespectrumoverothermethodsofAudio Steganography. Secondly, we have sequential or linear embedding with 21% of overall audio data hiding methods.
3. CONCLUSIONS
Thispapergivesabriefoverviewofsteganographyandits origins,fromancienttimestomoderndaysandthefuture that it awaits for. An extensive research work has been donetosystematicallyreviewthepossibilitiesintheworld of steganography and getting more familiar with the techniques and methods that are in popular use and the methodsthatcanbeappliedinactiontoovercomethe previously used techniques(steganalysis).LSB, PVD, EDM, DWT, DCT, and other useful methods were implied and derived in order to get a better understanding of the field, it can be concluded that steganography has a great potential despite the challenges with other data hiding techniques.
REFERENCES
[1] Kirti Chopra, Ishpreet Singh Virk "Image Steganography Using Edge Detection Technique." International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering6.12(2018):222-227.
[2] S.Bansal, Data Securityby Steganography, InternationalJournalofScientificResearchinNetwork Security and Communication, Vol.7, Issue.1, pp.10-12, 2019.
Similarly, other constitutes rest 53% of the overall techniques includes error minimizing based embedding(12%), frequency masking and amplitude thresholding(18%), Pattern matching based embedding(7%),PhaseEncoding(5%),etc.

6. STEGANALYSIS:DETECTING STEGANOGRAPHY
Analysis of a cover message of any kind to detect any hiddensecretcodeissteganalysis.Justlikesteganography, steganalysis also uses several different techniques to detect and check for any concealed information in the givenmessage.
Someofthetechniquesarebrieflydiscussedbelow:Image, Audio and Video Steganalysis: As we know that image steganography has been very popular, the reverse technique,i.e.,Imagesteganalysishasalsocaughtmillions ofattentionandinterests.
Audiosignalsaredatastreamswithalargecapacity.Echo and phase over audio signals, there are several steganalysis techniques for concealment. The phase steganalysis method investigates the fact that phase coding is used inappropriately in each audio segment, causingchangesinphasedifference.Statisticaltechniques canalsoaidinthedetectionofhiddenaudiosignals,where lineamentselectionandclassifierconstructionarecritical.
[3] Das, R.; Tuithung, T.,"A novel steganography method for image based on Huffman Encoding," Emerging Trends and Applications in Computer Science (NCETACS),20123rdNationalConferenceon,vol.,no., pp.14,18,30-31March2012
[4] Wang,H&Wang,S,“Cyberwarfare:Steganographyvs. Steganalysis”, Communications of the ACM,47:10, October2004.
[5] Anderson, R.J. & Petitcolas, F.A.P., “On the limits of steganography”, IEEE Journal of selected Areas in Communications,May1998.

[6] Joseph, A., and V. Sundaram. "Cryptography and steganography–Asurvey."(2011).
[7] Manoj I.VenkataSai, and B. Tech. "Cryptography and steganography. "International Journal of Computer Applications1.12(2010):63-68.
[8] Sangale, Adinath, et al. "secure messaging using cryptography,steganographyandqrcode."
[9] Li, Bin, et al. "A survey on image steganography and steganalysis." J.Inf. Hiding Multim.Signal Process.2.2 (2011):142-172.
[10] Saleh, Mohammed A. "Image steganography techniques-a review paper." International Journal of AdvancedResearchingComputerand Communication Engineering,ISSN(2018):2278-1021.
[11] More, Nitesh Kumar and Sipi Dubey. “JPEG Picture Compression Using Discrete Cosine Transform.” (2012).
[12] Morkel,Tayana&Eloff,Jan&Olivier,Martin.(2005).An overviewofimagesteganography.1-11.
[13] Yunxia Liu , Shuyang Liu , Yonghao Wang, Hongguo Zhao, Si Liu , Video Steganography: A Review, Neurocomputing(2018),
[14] Digital audio steganography: Systematic review, classification, and analysis of the current state of the art.
[15] Juned Ahmed Mazumder, K. Hemachandran, 2012, Review Of Different Techniques Used In Recent Steganography Researches, international journal of engineering research & technology (ijert) Volume 01, Issue08(October2012)

