AN INVESTIGATION ON THE EFFICACY OF MARBLE DUST POWDER FOR STRENGTHENING THE MARINE CLAY IN FLEXIBLE PAVEMENTS SUBGRADE
 Harsha Kiran Magapu1
Manikanta
Harsha Kiran Magapu1
Manikanta
1Harsha Kiran Magapu, Post Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, U.C.E.K, JNTUK, Kakinada, India
2Dowleswarapu Manikanta, Post Graduate Student,Department of Civil Engineering, U.C.E.K, JNTUK, Kakinada, India. ***
Abstract - The great compressibility and low shear strength of Marine Clays present a number of challenges to construction andeconomicactivities.Therefore,investigations to enhance the Geotechnical qualities of Marine Clays that make up extensive sections of coastal line have become of prime importance in recent decades. Although, there have been some systematic studies on compressibilityfeatures,very few attempts have been made to research the shear strength components of Marine Clay and the creation of methods to enhance it. The present work details the study carried out on Kakinada Marine Clay to investigate the efficiency of Marble Dust Powder(MDP) in varying proportions to increase the geotechnical characteristics and obtain optimum percentage of admixture with marine clay. In this study laboratory tests such as Atterberg’s limits, Modified Proctor Compaction test, CBR test and Cyclic Plate Load test were carried out for treated and untreated marine clay. The study showed the enhancement of the strength of Marine Clay with Marble Dust Powder.
Key Words: Marine Clay, Sub Grade, Marble Dust Powder (MDP), Stabilization, Optimum Moisture Content (OMC), California Bearing Ratio (CBR)
1. INTRODUCTION
Soilstabilizationhaveemergedaspredominantimportance in recent years. Withtheonsetof urbanization andtheensuing searchfor the increasing amounts ofhabitableland,itbecameimperativethatvasttractsof MarineClays,previouslythoughttobein-habitable,haveto bereclaimedand developed. The Marine Clays have high shrinkage and swelling behaviour when exposed to water during the monsoon that changes their density. In the summer,the soilshrinksowingtoevaporationofwater,and hardens due to increasing density, and loses its natural propertiesasdepthincreases.Theseasonalvariationsinthe groundwaterprofilethatcausechangesinmoisturecontent arewhatcausethevolumetricdeformation.
The evolution of traffic patterns and subgrade conditions, the measures and stabilization techniques to necessitate sustainable construction techniques of pavements is essential. There have been numerous issues with
embankments and deep cuttings for both railways and highways, as well as settlement of structures built on foundations made of these soils. These concerns make stabilization of Marine Clay inevitable. Stabilization is carriedoutusingvariousstabilizingmaterialssuchasLime, Cementetc.Thealternateuseof stabilizingmaterialssuch asdetritusobtainedduringminingorconstructionactivities have been increasing. Effective use of construction waste hasbeenamajorlogisticalandenvironmentalissueinlarge scaleactivities.WorthwhileUtilizationofConstructionand industrialwastematerialsisthebestwayofdisposal.Marble Dustisobtainedduringtrimming,smoothingandgrindingof marblestone. Waste marble dustwhichiswasteobtained from marble industry is used as stabilizer. Marble dust constitutes of 40% of total marble handled. The research conductedherestudiedathowaddingMarbleDustPowder toMarineClayaffecteditsproperties.
The purpose of this work is to investigate ways to increasethestrengthattributesofMarineclay.Marbledust is blended with untreated soil in a various proportions to achieve the ideal admixture level needed for soil stability. thepresentexperimentalstudyhasbeentakenupbyadding MarbleDustPowdertoMarineClay.Forbothuntreatedand treatedMarineClay,laboratorytestsliketheAtterberglimit, compactiontestandCBRtestareconductedaspartofthis comparativestudy Therefore,theinvestigationlearnedand the data produced could be applied to the pavement sub gradeandfoundationsofoffshorestructuresaswell.
2. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
Donotnumbertextheads-thetemplatewilldothatfor you.Theobjectivesofthepresentexperimentalstudyare
TodeterminethepropertiesoftheMarineClay.
ToexaminetheeffectivenessofMarbleDustin enhancing the strength parameters of Marine clay
To investigate the performance ofthe treated MarineClayasasubgradematerialforflexible pavementsundercyclicpressures.
3. MATERIALS USED

3.1 MARINE CLAY
TheMarineClaywasobtainedfromKakinadaSeaPorts LimitedinKakinadaatadepthofbetween0.3and1.0metres. OntheeasterncoastofIndiastandstheportcityofKakinada. According to geotechnical engineers, any of the already employedmethodsforimprovingthegroundmustbeapplied toalterhowthesedepositsbehave.
3.2 MARBLE DUST POWDER (MDP)

Marbleisanon-foliatedmetamorphicrockcomposedofrecrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite ortodolomite. Geologists use the "marble" to refer the metamorphosed limestone; however stone masons use term more broadly to encompass un-metamorphosed limestone.TheMarbleDustPowderwascollectedfromAstra ChemicalsPrivateLimited,Chennai,India.
Table-2
Source:AastraChemicals
4. VARIABLES TAKEN FOR THE STUDY
The studyiscarriedoutonMarineclay;marineclaytreated with Marble dust (MD) and Marine Clay with optimum of MarbleDust Powdertreatedinthefollowing percentages. Marble Dust Powder (MDP) was varied in percentages of 10%, 15%,20% and 25% by weight of marine clay throughouttheexperiment.InordertoincreasetheCBRof MarineClaytreatedwithMarbleDustPowder.
5. LITERATRE REVIEW
Dr.D.Koteswara Rao , Ch Srikanth (2019) studied “An experimentalstudyontheperformanceoftheMarineClay stabilizedwithseashellpowderandsodiumsilicateasasubgrade for the flexible pavements”. It was observed from laboratorytestresultsthattheCBRvalueoftheMarineClay hasbeenimprovedby233.4%onadditionof18%seashell powderandCBRvalueofthistreatedtheMarineClayhas beenimprovedfurther499.03%byadditionof1%sodium silicatewhencomparedwithuntreatedtheMarineClay.
SourceAastraChemicals
Harish Parimi et al. (2018) studied “A Modern and ExperimentalStudyonstabilizationofMarineClaybyusing

coirfibreforFoundation”.Itwasobservedfromlaboratory test results that the overall deformations at ultimate load carrying capacity of the treated model foundation bed at OMC have lowered by 45.0% when compared to the untreatedMarineClay.
Theresultsofalaboratoryplateloadtestrevealedthatthe treated marine clay at OMC has a higher ultimate load bearingcapacitythantheuntreatedmarineclay,increasing by142.49%.
Julia Rachel (2020) studied “A Study on the Effect of Polypropylene Fibre on Jarofix-Stabilised Cochin Marine Clay”. Itwasobservedfromlaboratorytestresultsthatthe liquid limit was discovered to decrease regardless of the amountofjarofixadded.Theuncontaminatedmarineclay's CBRvaluewas0.88%fordryconditionsand0.74%forwet conditions before being enhanced by 290% and 300%, respectively.ItwasdiscoveredthattheCBRvalueincreases continuouslyasthepercentageofjarofixrisesto30%and then falls with further addition. In tests using jarofix and synthetic fibres with the addition of and 480% for damp conditions,30%waschosenastheidealpercentage.
Najwa Wasif Jassim, Hanan Adnan Hassan (2022),studied Utilization of waste marble powder as sustainable stabilization materials for subgrade layer. The plasticity indexdecreasedbyabout22%withtheincreaseintheMD contentfrom0%to12%.Theresultsalsoindicatethatusing 9% MD reveal further increase in the plasticity index.The maximum dry density MDD of the treated soil mixture increased,whereastheoptimummoisturecontentOMCof themixturedecreasedbyabout14%,26%respectivelyas addingMDtothesoilmixturefrom0%to15%.
Ramoo Ram, Ravi Kant Pareek,observed the effect of Marble Dust on Soil Properties 2018,It reduces the liquid limit,shrinkagelimitandincreaseintheplasticityindexof the soil and reduce the swelling percentage because of changeingradationofclayeysoilbymixingmarbledust..As comparedtountreatedsoil,thepercentageincreaseinOMC at15%additionofMarbledustis22.39%duetochangein plasticityindexandliquidlimit.Theoptimumresultswere foundwhensoilwasstabilizedwith15%marbledust.The CBRvalueisincreasedfrom2.36%to14.86%.Aboveresults ofCBRtestandMDDofsoilwith20%marbleshowsthatthe CBR resultsof thissoilisgoodenough toconstructionfor mediumtrafficvolumeroads.Sowecanutilizemoremarble wasteinstabilizationprocess.

6. TESTS CONDUCTED
6.1 Differential Free Swell Index
Free swell index, is the volume increase of soil caused by being submerged in water in absence of any externalforcesforaperiodof24hours. itisconductedas
perIS2720(PartXL)-1977.Thefreeswellindexofthesoil helpsinidentifyingtheswellingpotentialofthesoil.
Freeswellindex(%)=
Vd = Soil specimen volume after immersing 24 hours in distilledwater.
Vk = Soil specimen volume after immersing 24 hours in Kerosene.
6.2 Atterberg’s Limits
Consistency limits sometimes referred to as Atterberg's limit,arethewatercontentsatwhichsoilstransformfrom oneconditiontoanother.TheLiquidLimit,PlasticLimitand thereby the Plasticity Index were determined using Casagrande’sapparatusaspertheprocedureslaiddownin IS:2720part5(1985).
6.3 Modified Proctor Compaction Test
Modifiedproctorcompactiontestusedforthedetermination ofOptimumMoistureContentandMaximumDryDensity. It wasconductedasperIS:2720part-10(1983).
6.4 California Bearing Ratio Test
TestspecimenispreparedbymixingofMarbleDustPowder indifferentpercentagesbythedryweightofsoilandMDP wasmixedthoroughlywithequivalentdryunitweightand optimummoisturecontentwhichisobtainedfromproctor test.MixedsoilsampleisplacedinfivelayersinCBRmould havingdimensionsof150mmdiameterand175mmheight andeachlayeriscompactedby55blows.Thepreparedsoil sample is soaked for four days.The loads necessary for 2.5mmand5.0mmpenetrationwerenotedandhighervalue isconsidered.
CBR(%)
6.5 Laboratory Plate Load Using Model Tank
Cyclic Plate Load Test is a field or laboratory test for determining the ultimate load carrying under an applied load. These tests were carried out on flexible pavements systemsinacircularsteeltankofadiameterof60cm .The loading was done through a circular metal plate of 10cm diameter laid on the subbase course in a model flexible pavementsystem.Thesteeltankwasplacedonthepedestal ofthecompressiontestingmachine.Twodialgaugesofleast count 0.01 mm were arranged on opposite sides for obtainingthedeformations.A5Toncapacityhydraulicjack was placed on the loading frame . Cyclic load tests were carriedoutatOMCstatecorrespondingtotirepressuresof 500,560,630,700 and 1000 kPa. Each pressure increment
was applied until there was no significant change in deformationbetweentheconsecutivecycles.Thetestingwas furthercontinuedtilltheoccurrenceoffailureofthemodel pavement to record the ultimate load These tests were carriedoutatOMCforallthemodelflexiblepavements.
7. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
7.1 Values Obtained from various tests of Untreated Marine Clay
Table 3 Properties of Untreated Marine Clay
7.2 Differential free Swell Index of Marine Clay Treated with various proportions of Marble Dust Powder
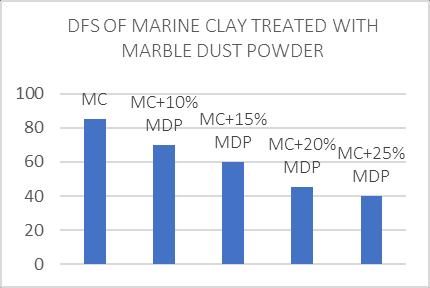

From the above table and figure it is observed that the differential free swell index of the marine clay decreases withincreasingthepercentageofmarbleDustPowder.The DFS value decreases from 82 to 66 when Marble Dust Powdercontentisincreasedfrom0to20%.
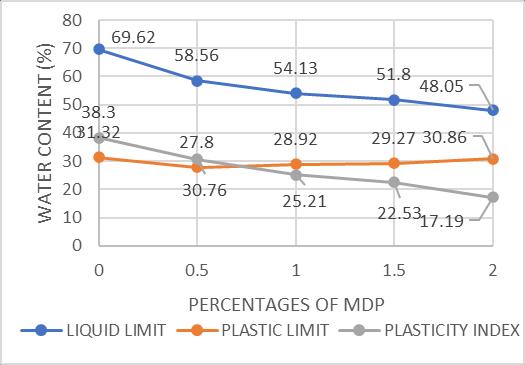
The results of Atterberg’s limit values on the marine clay withdifferentpercentagesofMarbleDustPowderareshown intheabovetableandfigure.Fromthefigurethefollowing conclusionsweremade.
Theliquidlimitofthemarineclaydecreaseswithincreasing the percentage of marble Dust Powder. The Liquid limit valuedecreasesfrom6891%to48.05%whenMarbleDust Powdercontentisincreasedfrom0to25%.
ThePlasticlimitofthemarineclaydecreasedinitiallyat10% ofMarbledustpowdercontentafterthatit increaseswith increasingthepercentageofmarbleDustPowder.
The Plasticity Index of the marine clay decreases with increasing the percentage of marble Dust Powder. The Plasticity Index value decreases from 37.89 % to 17.19 % whenMarbleDustPowdercontentisincreasedfrom0to25 %.

7.4
Dry
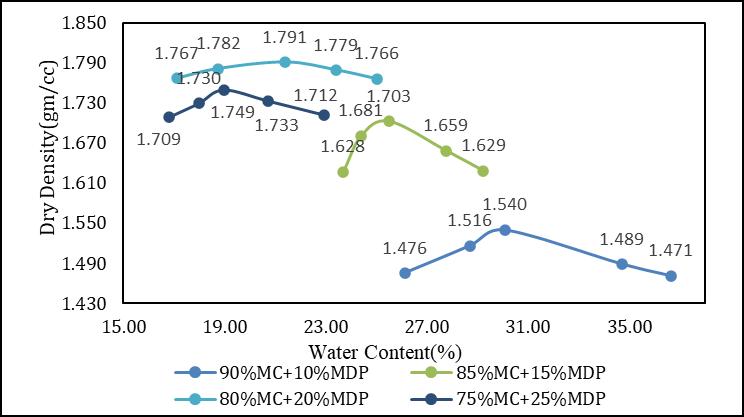
Fromtheabovetableandgraphsitsclearlyobservedthat the Maximum Dry Density of the Marine Clay is increases with Increasing the amount of Marble Dust Powder. The MDDvalueincreasesfrom1.41%to1.791%whenMarble Dust Powder content is increased from 0 to 20 %. The OptimumMoistureContentoftheMarineClayisdecreases with increasing the amount of Marble Dust Powder. The OMCdecreasesfrom33.12%to21.66%whenMarbleDust Powder content is increased from 0 to 20 % and then decreaseisobservedfrom20%to25%.
7.6
Chart-7
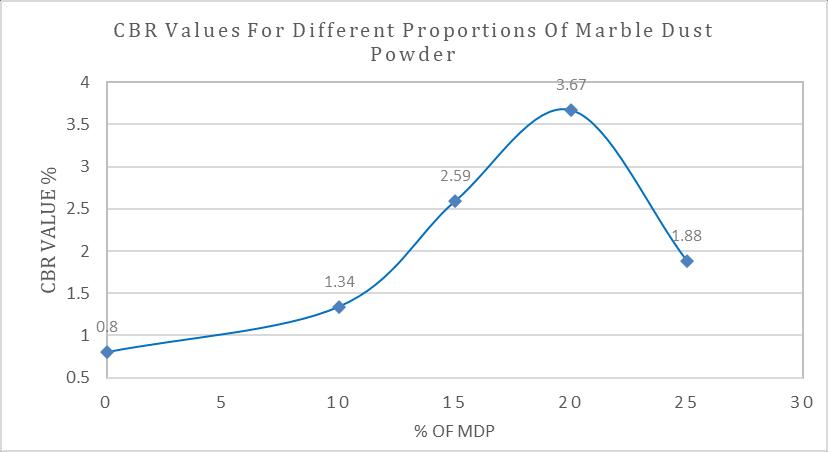
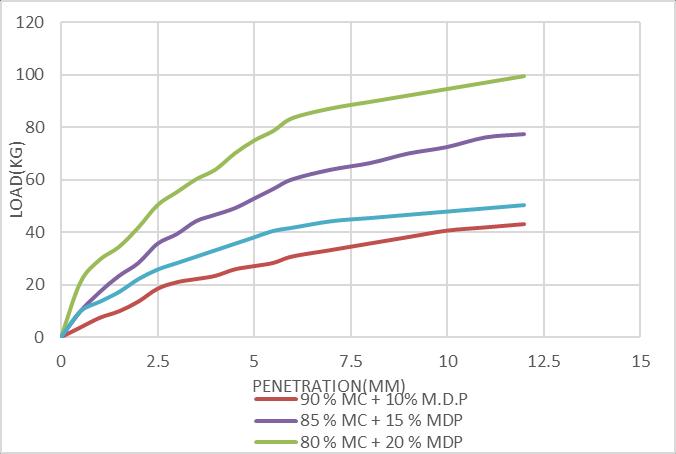
Chart-8 CBR Values of Marine Clay treated with various proportions of Marble Dust Powder
Fromtheabovetableandgraphsit’sclearlyobservedthat theCBRValueoftheMarineClayincreaseswithincreasing theamountofMarbleDustPowder.TheCBRvalueincreases from0.86%to3.67%whenMarbleDustPowdercontentis increasedfrom0to20%.
7.7 Laboratory Plate load Test of Untreated Marine Clay and Marine Clay treated with 20% of Marble Dust Powder
Chart-9 Laboratory Cyclic Plate Load Test Results Of The Untreated Marine Clay For Sub Grade Model Flexible Pavement
Chart – 10 Laboratory Cyclic Plate Load Test Results Of The Marine Clay Treated With 20% MDP For Sub Grade Model Flexible Pavement
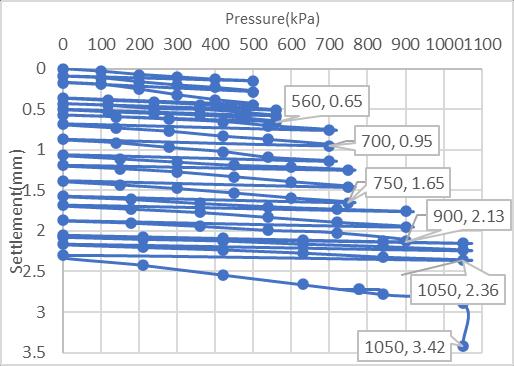

CyclicPlateLoadTestResultsofUntreatedMarineclay
ItwasobservedfromtheChart-9theUntreatedmarineclay atOMCforsubgradedsoilhasexhibitedtheultimatecyclic loadof630kN/m2withthedeformationof2.64mm.
Cyclic Plate Load Test Results of Treated Marine Clay Treatedwith20%MDPassubgrade
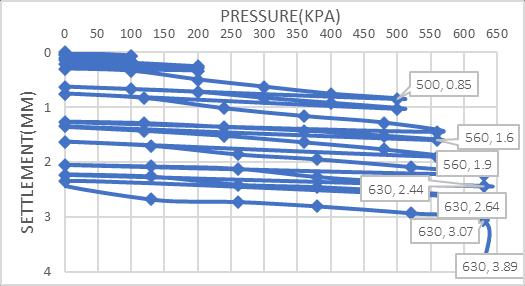
ItwasobservedfromtheFigure4.16theMarineclaytreated with20%MDPatOMCforsubgradedsoilhasexhibitedthe ultimatecyclicloadof1050kN/m2withdeformationof2.36 mm.
8. Conclusions
Itisnoticedfromthelaboratorytestresultsthatthe Differential Free Swell of Marine Clay has been reducedby41.17%ontheadditionof20%MDP
Itisobservedfromthelaboratorytestresults that theLiquidlimitofMarineClayhasbeendecreasedby 25.59%ontheadditionof20%MDP
Itisobservedfromthelaboratorytestresults that thePlasticlimitofMarineClayhasbeenincreased by4.9%ontheadditionof20%MDP
Itisobservedfromthelaboratorytestresultsthat the Plasticity Index of Marine Clay has been decreasedby41.32%ontheadditionof20%MDP
Itisnoticedfromthelaboratorytestresultsthatthe OMCofMarineClayhasbeendecreasedby35.14% ontheadditionof20%MDP
Itisnoticedfromthelaboratorytestresultsthatthe MDDofMarineClayhasbeenincreasedby28.77% ontheadditionof20%MDP
Itisobservedfromthelaboratorytestresults that the CBR of Marine Clay has been increased by 358.75%ontheadditionof20%MDP.
Itisnoticedfromthelaboratoryinvestigationsof the plateloadtest resultsthat,the ultimate cyclic pressureoftreatedMarineClaywith20%Marble Dust Powder for sub-grade flexible pavement has been improved from 630 kPa to 1050 kPa when comparedwithuntreatedMarineClay.
Itisnoticedfromthelaboratoryinvestigationsof theplateloadtestresultsthat,thetotaldeformation of treated Marine Clay with 20% Marble Dust Powder for subgrade flexible pavement has been improved by 10.60 % when compared with untreatedMarineClay.
9 . References
[1] Hitesh Bansal et al. (2013) studied“Influenceof Waste Marble Powder on characterstics of Clayey Soils”.IJSR(2013)2319-7064

[2] Dhruv Saxena et al. (2017) studied “Effects of marble Powder and fine sand on Properties of ExpansiveSoil”.(IJETT)ISSN:2231-5381,Volume52Issue(1).

[3] KoteswaraRao.D et al.. (2012), studied “A Laboratorystudyonthestabilizationofmarineclay usingsawdustandlime”. IJESAT,ISSN:2250-3676 Vol.2,Issue-4,Jul-Aug2012,pp.851-862.
[4] F Yilmaz et al.. (2016), studied “Evaluation of MarbleDustforSoilStabilization”. ICCESSEN2016, Vol.132,132.710
[5] DSV Prasad et al. (2018) studied “A Study on geotechnical properties of Marine Clay stabilized withlimeandrecron-3sfibre”.IJET,7(2.1)(2018) 32-36.
[6] C Neeladharan et al.. (2018),studied“Stabilization ofSoilbyusingMarbleDustwithSodiumSilicateas binder”. IJARTET,ISSN:2394-3777Vol.5,Issue-5.
BIOGRAPHIES
HARSHA SATYA SAI KIRAN
MAGAPU
PostGraduateStudent-2020
GeoTechnicalEngineering
UniversityCollegeofEngineering, JNTUKKAKINADA,A.P,INDIA
DOWLESWARAPUMANIKANTA
PostGraduateStudent-2020
GeoTechnicalEngineering
UniversityCollegeofEngineering, JNTUKKAKINADA,A.P,INDIA

