International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net
1Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Kali Charan Nigam Institute of Technology, Banda,(U.P.) (India)
2Director, Kali Charan Nigam Institute of Technology, Banda,(U.P.)(India)
3Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Kali Charan Nigam Institute of Technology, Banda,(U.P.) (India) 4Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Kali Charan Nigam Institute of Technology, Banda,(U.P.) (India) 5Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Kali Charan Nigam Institute of Technology, Banda,(U.P.) (India) ***
Abstract - In civil engineering, the foundation is critical for any land base construction and must be able to withstand the incoming loads without failing. In some areas, the soil may be poor and unable to withstand the incoming stresses. Soil stabilization is required in such circumstances. Redsoilcovers 10.6% of the Indian geographical area. Thecolourofredsoilis due to a high percentage of iron in the soil. Red soil is used in this research. In this research an attempt to study various geotechnical properties and improved the red soil properties by adding different percentages of polypropylene and lime.
In this study red soil is collected and transported from the district of Jalgaon in northern Maharashtra. For this study we take polypropylene as 0.5%, 1%, 1.5% and constant 4% of Lime added to the soil.
Key Words: Soil stabilization, Red Soil, Polypropylene, Lime,CBRetc.
Soil stabilizationisa processthataltersandimprovesthe engineeringpropertiesofthesoilinordertomakeitmore suitableforbuilding.Soilstabilizationisacivilengineering technique for refining and improving soil engineering properties including mechanical strength, permeability, compressibility,hardness,andplasticity.Thebasesoilserves asthefoundationforanyconstructionproject,forahouse,a road,oranairport.Furthermore,soilisanessentialbuilding materialtostandanystructure.Asaresult,soilshouldhave propertiesthatenableittoformasolidbase.
Soilstabilizationisacommonpracticeintheconstructionof airfields,parkinglots,landfills,embankments,highwaysand foundations,waterwaymaintenance,agriculture,andmining sites.
Soil stabilization is a critical component of various civil engineeringprojects.Withoutremovingtheentiresoil,the most effective technique is to use appropriate accessible
methods and materials to enhance the soil qualities. As a result,soilstabilizationisthoughttobethebeststrategyfor improvingsoilgeotechnicalparameters.Chemicaladditives, thermal energy, compaction, and plant-based or synthetic fiber reinforcingareall commonstabilizationapproaches. Straw,coir,palm,sisal,andjuteareexamplesofplant-based fiberreinforcementmaterialsthatareinexpensive.Synthetic fiber reinforcing materials, such as polypropylene, nylon, rubber,orplastic,canalsohelpreducewaste.Researchinto the use of waste materials to stabilize soil is currently a globaltrend,assurpluswastematerialsposepublicsafety andlogisticalissuesintermsofdisposal.
Inthisstudy,thefollowingmaterialswereused:
i) RedSoil
ii) Polypropylene
iii) Lime
The soil sample for this study was taken in the district of Jalgaon in northern Maharashtra. The earth is a bright crimsoncolor.Redsoilisatypeofsoilthatformsinwarm temperatures and is common in damp climates with deciduous or mixed woods. The red soil's texture ranges fromsandytoclay,withloamaccountingforthemajorityof it.
Polypropylene's starting material is nonnumeric C3H6, a completely hydrocarbon compound. Polypropylene fibers have particularly beneficial qualities due to their form of polymerization,highmolecularweight,andthewaytheyare processed into fibers. Polypropylene fiber is a single fiber withadiameterof0.034mmandcomesinlengthsof6mm, 12mm,and20mm.
R.S Balagoudra et.al,(2017)carriedstudyonblackcotton soil with PPF (0%, 0.25%, 0.50%, 0.75%, and 1%) and constant4%lime.Thebestresultshowsat0.75%PPFwith 4%lime
S.A. Hussein, A.A Hussein (2019)conductedastudyonthe effect of polypropylene fiber on expansive soil. they use polypropyleneas0.5%,1%,2%ofthedryweightofsoiland testconductedon1Dconsolidationtest,UCS,cyclicswell, and swelling test. They discovered that mixing 2% PPF produces the best results. and with increased PPF percentage,thereanincreaseinUCSupto51%andreduced theswellingpressureandfreeswellabout69%and79.1%. Compressibilityalsodecreasedbyadding2%PPF
T.N Dave et.al (2020)Theuseofpolypropylenefires(PPF) for the stabilization of expansive soil obtained from DedicatedFreightCorridor(DFC)projectsiteBhestannear Surat. In this research.PPF has been mixed with soil in proportionsof0.75%,1.5%,2.0%,2.25%,and2.5%.
Tharini et.al (2020)thelaboratoryconductedforstudythe performance on Black cotton soil reinforced with polypropylenefibermixedat0.2%,0.3%,0.4%,and0.5%.. ThesoilwasgatherednearPSNACollegeofEngineeringand Technology,Dindigul,TamilNaidu,India
Forthisstudywetakepolypropyleneas0.5%,1%,1.5%and constant 4% of Lime added to the soil and done the experiment on red soil. In Laboratory we have done experiments on Atterberg Limit (Liquid limit and Plastic limit),CompactionTest,CaliforniaBearingRation(CBR),and UnconsolidatedUndrainedTriaxialTest(UUtriaxialtest).
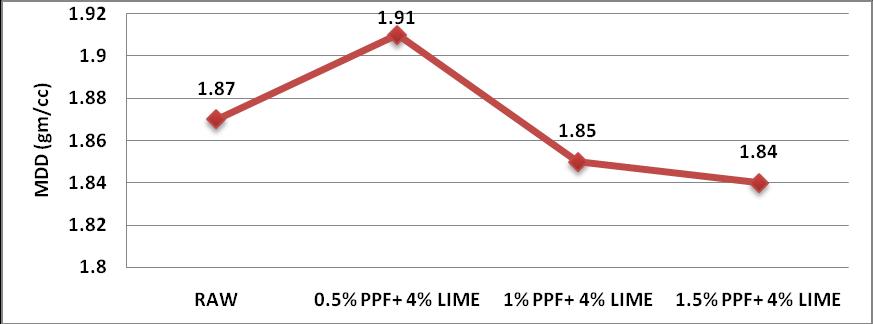
5.1 Effect of Polypropylene and Lime on Heavy Compaction on Red Soil

Limeisalsoknownascalciumoxideandhasthechemical formula CaO. It is manufactured by heating Calcium carbonate (CaCO3). When lime is being used in soil stabilization process, it primarily increases strength and minimizesswellsandshrinks.However,moreadditionsmay reducesoilplasticity,andexcesslimeapplicationpromotes brittlefailure,atypeofsoilfailurethatresultsinarapidand significantlossofstrengthwhenithappens.ThePercentage oflimeusedinthisexperimentisconstantat4%.
Someresearchershaveattemptedtosubstitutestandard stabilizerswithavarietyofwastematerialsthatareboth cost-effectiveandimprovesoilgeotechnicalqualities.
5.1.1 Effect on Maximum Dry Density
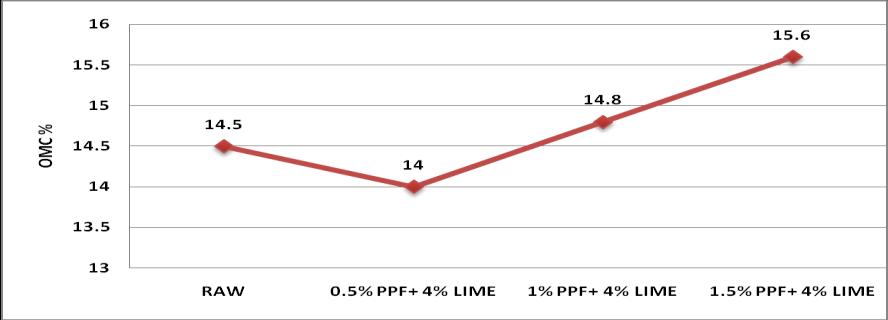
1) Whenwestabilizedtheredsoilwith0.5%PPFand 4% lime, OMC decreased to 14% and MDD increasedto1.91gm/cc.Thenafterincreasingthe Percentages of PPF and lime OMC value goes on increasingandtheMDDvaluedecreases.Fromthe Compaction Point of view, 0.5% of PPF and 4% Limegivesthebestresult
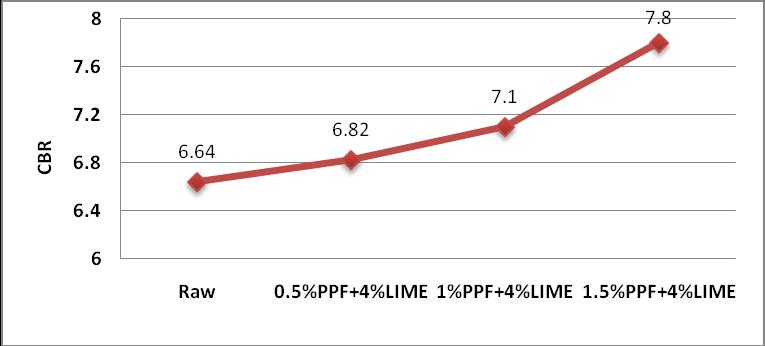
2) ThesoakingCBRvalueincreasesasthepercentages of PPF and Lime increases. The percentage increased in CBR value when red soil is blended with polypropylene fiber with constant Lime is 17.46%whencomparedtorawsoil.
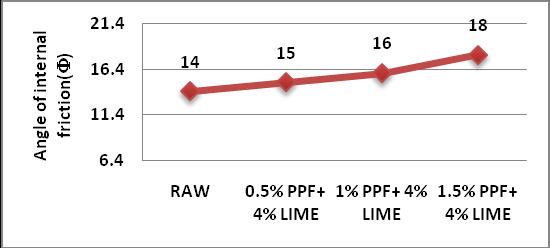
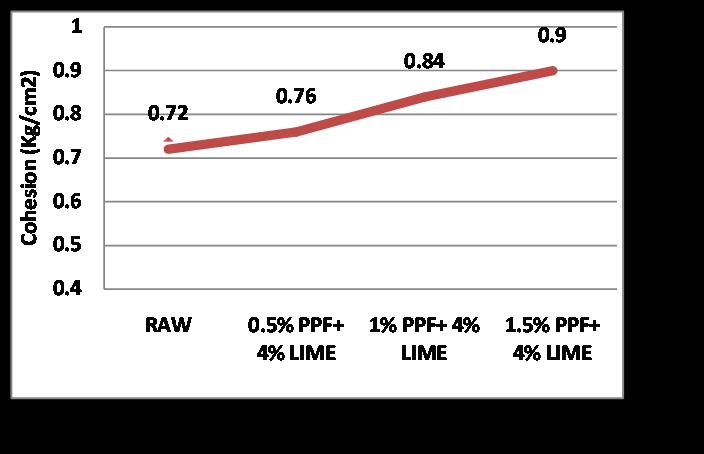
3) ThePercentageincreasedincohesionis25%asthe PPF and Lime increases and the percentage increasedinangleofinternalfrictionis28.57%.
4) AngleoffrictionincreaseswhenthepercentofPPF andLimeinRedsoilincreases
[1] Hussein,S.,Journal,H.A.-C.E.,and2019, undefined, “StabilizationofExpansiveSoilsUsingPolypropylene Fiber,”core.ac.uk.
[2] Taha,M.,Feng,C.,Technology,S.A.-A.inP.,and2020, undefined, “Influence of Polypropylene Fibre (PF) Reinforcement on Mechanical Properties of Clay Soil,”hindawi.com.

[3] Ali,N.,Proceedings,V.R.-M.T.,and2020, undefined, “EffectofPolypropyleneFibreonSwellingBehaviour ofBlackCottonSoil,”Elsevier.
[4] Dave,T.N.,Patel,D.,Saiyad,G.,andPatolia,N.,2020, “Use of Polypropylene Fibres for Cohesive Soil Stabilization,” Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, Springer,pp.409–417.
[5] ofIndianStandards,B., IS 2720-5 (1985): Methods of Test for Soils, Part 5: Determination of Liquid and Plastic Limit.
[6] ofIndianStandards,B., IS 2720-7 (1980): Methods of Test for Soils, Part 7: DeterminationofWaterContentDry Density Relation Using Light Compaction
[7] ofIndianStandards,B., IS 2720-8 (1983): Methods of Test for Soils, Part 8: DeterminationofWaterContentDry Density Relation Using Heavy Compaction
[8] ofIndianStandards,B., IS 2720-16(1987):Methodsof
Test for Soils, Part 16: Laboratory Determination of CBR.
[9] ofIndianStandards,B., IS 2720-12(1981):Methodsof
Test for Soils, Part 12: Determination of Shear Strength Parameters of Soil from Consolidated Undrained Triaxial Compression Test with Measurement of Pore Water Pressure
[10] “IS2720(PART11)-1993 IndianStandardMethodsof
Test for Soils Determination of the Shear Strength Parameters of a Specimen Tested in Unconsolidated Undrained Triaxial Compression without the Measurement Of Pore Water Pressure(First Revision).
[11] balagoudra,R.,krishna,V.,yaligar,H.,andProfessor, A., 2017, Soil Stabilization Using Lime and Polypropylene Fiber Material
