Automated Intracranial Neoplasm Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Mr. P. Veeresh Kumar1 N. Geetha Gayathri G. Harika T. Lakshmi6 Ch. Sai Poojitha , G. Vyshnavi51 Associate Professor Department of Information Technology, KKR & KSR Institute Of Technology And Sciences(A), Guntur, India

2,3,4,5,6 Undergraduate Students ,Department of Information Technology , KKR & KSR Institute Of Technology And Sciences(A), Guntur, India ***
Abstract - A brain tumor is nothing but an abnormal collection of cells in the intracranial. The skull that surrounds the brain is very hard, so when a tumor grows insidethebrain, it puts pressure on the skull and can cause serious damage. It is regarded as one of the most dangerous diseases in both children and adults. About 11,700 people are diagnosed with brain tumors each year. It accounts for 85–90% of all central nervous system tumors. The 5-year survivalratefor malignant brain tumors is approximately 34% for men and 36% for women. Accurate diagnosis, detection of brain tumors , and early initiation of appropriate treatment are essential to prolonging a patient's life expectancy. Brain tumor segmentation is one of the most important andlaborious tasks in the field of medical imaging. Manual classification with human assistance can lead to inaccurate predictions and diagnoses. Additionally, this is a daunting task when there is a large amount of data that needs tobesupported. Braintumors are highly variable in appearance, and there are similarities between tumor tissue and normal tissue, thus making the extraction of tumor regions from images difficult. There are different types of imaging tests, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, used to detect brain tumors. In this study, computed tomography (CT) scan images are used to identify brain tumors. Deep learning (DL) is the latest technology that provides more efficient results in detection and classification. In this paper, a model is developed by detectingtumors usinga convolutional neural network. In our study, CNN achieved 97.87% accuracy.
Key Words: Brain Tumor, Magnetic Resonance Image (MRI), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Deep Learning, Tensor Flow, Keras.
1. INTRODUCTION
Weusemedicalimagingtechnologytogetaglimpseinside thehumanbody.Themostdifficulttaskistodiagnoseand classify tumors or cancers. According to statistics, brain tumors are one of the most important types of cancer in termsofmortality.TheInternationalAgencyforResearchon Cancer (IARC) reports that worldwide, more than one millionpeoplearediagnosedwith4,444braintumorseach year, and the mortality rate is steadily increasing year by
year. Those under the age of 34 To date, doctors have implementedover4,444advancedmethodstoidentifymore painfultumorsinpatients.UsingCT(computedtomography) andMRI(magneticresonanceimaging)scans,doctorscan now dissect abnormalities in different parts of the body. Brain tumors have recently gained momentum due to the increased demand for labour savings and the clinical evaluation of large amounts of medical data. This type of imageprocessingandanalysisinvolvescomplexcalculations ofdataaswellasvisualizingandunderstandingthatdata. Brain tumors can originate from abnormal, precancerous, cancerous, harmful, harmless, or non-cancerous cells that form in the brain. He divides malignant tumors into two types: those that originate in the brain and subsequent cancerousgrowthsthatcanspreadtodifferentareasofthe human body. Under these conditions, cancer metastasizes within the patient's body and is said to have a very low survivalrateandahighmortalityrate
1.1 Brain Tumor
Thebrainisasofttissuemassthatresemblesaspongethat iscoveredinbone.Thebrainislinedwithadelicatelayerof tissue,includingcerebrospinalfluid.Betweenthebrainand the ventricles, there is cerebrospinal fluid. The cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem are the three components that makeupthebrain.Thebrainreactstoexternalstimuli.The cerebellummaintainsthebody'sequilibrium.Thebrainand spinal cord are linked by the brainstem. A brain tumor is recognized as an overgrowth of the numerous cells that make up the brain. Primary and secondary cells are both present.Whilesecondarycellsaresparedbymetastasisfrom otherpartsofthebodytothebrain,primarycellscomefrom the brain itself. Some metastases spread rapidly. Some metastasesspreadfairlyquicklyandexhibitsymptomslike seizures, speech difficulties, nausea, and blurred vision. It canbefatalifnottreatedinatimelymanner.Thisisdueto EDA,whichisbroughtonbydecreasedbloodflowandthe subsequentdeteriorationofhealthytissueasaresultofthe skull's constrained interior and growing intracranial pressure.Electronichealthcaresystemsandmagneticfield information technology aid clinical professionals in giving patientsbettercare.Abraintumorcanaffectothernearby
structures and is distinguished by its position, image intensity, shape, and size. If the tumor is accompanied by emphysema, the intensity of other nearby areas is also changed. Benigntumor andmalignanttumorarethetwo tumors . Due to their fixed size and slow growth, benign tumors are not regarded as harmful. The tissues around benign tumors are unaffected by them. A birthmark is an illustrationofabenigntumor.Cancercanbetreatedwhenit isinthepremalignantstage,whereasignorancecancause cancer. Cancer is the name for a cancerous tumor. They begin to grow around nearby tissue after some time has passedsincetheirgeneration.Malignanttumorscanbefatal andgrowquickly.Forpatients,earlydetectionofmalignant tumors is very beneficial. To achieve the highest level of accuracy,varioustechniqueshavebeeninvestigatedforthe automated detection and classification of malignancies. Furthermore, hospitals are able to achieve extremely low false-negativerates,whichraisesthedemandforcomputer support.Mostobserverscanidentifythepresenceofspecific characteristicsthat identify malignancy.MRIis frequently used to recognize and highlight specific internal body structures.representsmagnetism.imagingusingresonance. Astrongmagneticfieldandbodyradiowavesareusedinan MRItoproducepreciseimages.Duetoitsabilitytoachieve highspatialresolutionandbettersoft-tissuecontrast,itisa crucialandusefultoolfortheaccuratediagnosisofdisease aswellasforthetreatmentandmonitoringofdiseaseusing imagingmodalities.
Segmentation of magnetic resonance (MR) images of the brain is key to diagnosing malignancies and other neurological abnormalities. Image segmentation is a preprocessingstepthathelpsdivideanimageintosmaller segments.Imagesaredividedbyclassesorsubsets.Thisis useful because the segmentation allows us to focus on regionsofinterest.SegmentationofMRIimagescanalsobe performed manually, but it is time-consuming and less accurate.
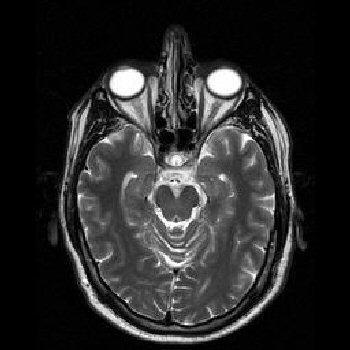
NoTumor
2. LITERATURE REVIEW

[1] K. B. Vaishnavee and K. Amshakala proposed an Automated MRI brain image segmentation and tumor detectionusingSOM-clusteringandProximalSupportVector Machine classifier. Photograph segmentation is a critical approachnoticeablyusedtoextractsuspiciouspartsfrom clinical photographs, which include MRI, CT scan, mammography, and so forth. With this motivation, SOM clusteringisproposedinthispaperforimagesegmentation ofbrainMRIscans.Thisproposedworkproposeseffective segmentationandclassificationusingHFS-SOMandPSVM. Aftersegmentation,theresultingimageisgivenasinputto his PSVM classifier, followed by feature extraction and selectionusingGLCM-PCA.Experimentalresultsshowthat the proposed system has a high accuracy rate and a low error rate. In the future, the system could be improved to supportothertypesofcancerimageswithafewchangesat boththesegmentationandclassificationstages.Weneedto supportalargenumberofinputs,andweneedtoimprove the accuracy rate. To achieve this, swarm-based feature selectioncanaddmorefeaturestoimprovetumordetection andclassificationresults.
[2]G.BirareandV.A.ChakkarwardevelopedanAutomated Detection of Brain Tumor Cells Using Support Vector Machine. Thousands of people receive a brain tumor diagnosiseachyear.Whileitisofsignificantimportanceto separate,find,andextractcontaminatedtumorregionsfrom magneticresonanceimagingfordiagnosticevaluation,itis time-consumingandpronetohumanerror.Togetaround these restrictions, segmentation and classification techniquesthatareautomatedandsemi-automaticarenow being deployed. As a result, we created automatic segmentation using the K-means technique and a brain tumor identification module that uses a support vector machineclassifiertoidentifytumorswhilealsoextracting Otsu-thresholdcharacteristicsfromtheoutputsegmented imageusingagrayscaleoccurrencematrix.Theaccuracyof theexperimentalresultswas98.51%.Overall,thisapproach produces excellent outcomes. Future work on medical
diagnostics may involve the development of additional algorithms,likemulticlassSVM.
[3]A. Kumar, A. Ashok and M. A. Ansari introduced Brain TumorClassificationUsingHybridModelOfPSOAndSVM Classifier.Medicalimaging isaveryimportantprocessfor the diagnosis of any disease today. MRI is usually used to detect the presence and type of tumor. The process of classifying brain tumors is very complicated. There are various procedures in medical image processing, such as image segmentation, image extraction, and image classification.Differenttypesoffeaturesareextractedfrom segmenteddata.MRIimages,includingintensity,shape,and texture-basedfeatures.Inthispaper,machinelearningwas used to create an online database of MRI images of brain tumors.Theparticleswarmalgorithmwasusedtocreatethe model optimization (PSO) algorithm for feature selection, and then a support vector machine (SVM) classifier was used. used to classify tumor types on current brain MRI images .Using the PSO-SVM classification model gives 95.23% accuracy when all 14 features are included, comparedto86.82%forthenaiveSVMclassifier.Similarly, thespecificityis94.8%andthesensitivityis100%.Inthe future, we hope to apply this concept to bio-inspired algorithms and compare them all to different medical images.
[4]R.Ahmmed,A.S.Swakshar,M.F.HossainandM.A.Rafiq developedClassificationoftumorsanditstagesinbrainMRI usingsupportvectormachineandartificialneuralnetwork. Cells are the smallest unit of tissue, and their abnormal growth causes tumors in the brain. In this study, support vectormachine(SVM)andartificialneuralnetwork(ANN)basedclassificationoftumorsandstageinbrainMRIimages ispresented.Anintegrationoftemperature-basedK-Means andmodifiedfuzzyC-Means(TKFCM)clusteringalgorithms is used to segment MRI images based on the grayscale intensitiesofsmallportionsofbrainimages.TheKvalueof the temperature-based K-Means algorithm is higher than thatofconventionalK-Means,andtheautomaticallyupdated membership of FCM eliminates the contour problem of tumor area detection. There is a second method used to classifytumorsintobenignandfourmalignantstagesusing ANN. The accuracy of classification of normal and tumor brainsbythisproposedmethodisupto97.37%withabit error rate (BER) of 0.0294, which is superior to other methods.

[5]C. Saha and M. F. Hossain designed MRI brain tumor images classification using K-means clustering, NSCT and SVM. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has justified its potentialasanovelimagingtoolfortheanatomicalstudyof brain tissue. Manual classification of a large number of patientMRIbrainimagesisaverytime-consumingprocess andpronetoerror;therefore,thereisaneedtodevelopa fastandaccurateautomaticschemeforclassifyingMRIbrain images.Inthisarticle,weuseK-meansclustering,thenon-
subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT), and support vectormachines(SVM)toautomaticallyclassifyMRIbrain imagesasnormalifnotumorispresentandabnormalifa tumorispresent.WepresentaschemeforcategorizingThe preprocessingstageofthisproposedschemeusesamedian filter to remove noise and improve the resolution of MRI brainimages.Then,usingK-meansclustering,segmentthe MRI image of the brain. Due to the salient properties of NSCT, such as multi-scale, multi-orientation, and shift invariance, NSCT is applied to segmented images. Seven features are then extracted from the NSCT sub-band coefficients, and these features are applied to a support vector machine for the classification of MRI brain images. The effectiveness of this method is evaluated in terms of sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy, and this method achieves98.86%classificationaccuracyonGRBkernelSVM. This scheme has been compared with other classification schemes for MRI brain images and provides satisfactory results,demonstratingtheefficacyofourscheme.However, furthervalidationoftheproposedhybridschemeisneeded withfurthertestingandtrainingonMRIbrainimagesfrom differentdatabasesandconsiderationofotherperformance evaluationparameterstobeaddressedinfuturework.
3. SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS SPECIFICATION
3.1 Software Requirements
OperatingSystem:anyWindowsOS
Libraries:Keras,TensorFlow,Numpy,Scikit-Learn Matplotlib,OpenCV
Editor:CollabNotebook
Technologies:Python
3.2 Hardware Requirements
Processor:i3
RAM:4GB
Harddisk:512GB
3.2.1 Hardware Configuration
Processor:Intelcorei5orabove.64-bit,quad-core,2.5GHz minimumpercore.
Ram:4GBormore.
Harddisk:10GBofavailablespaceormore.
Display: Dual XGA (1024 x 768) or higher resolution monitors.
Operatingsystem:Windows
3.2 Functional Requirements
Python3.6.2orlater,PIP,andNumPy1.13.1forWindows.
Pip
NumPy
Pandas
Anaconda
JupyterNotebook
TensorFlow
Keras
4. METHODOLOGY
Theproposedprocedureisdividedintovariousstagesand eachstageisexplainedindetail.
Imageinput
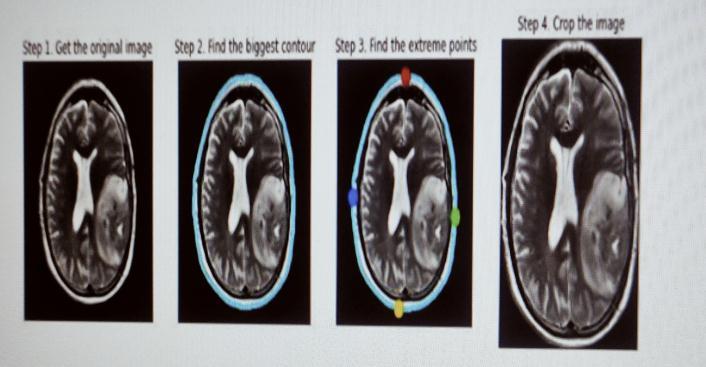
ImagePreprocessing
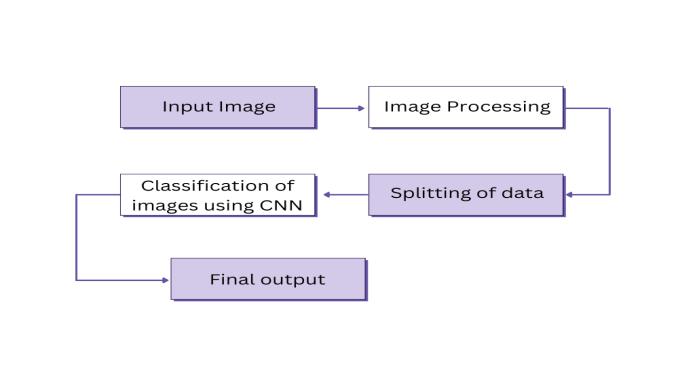

SplittingDataforTrainingandTesting
ClassifyingBrainTumorImagesUsingCNNs
ObtainingOutputsandValidatingModels
Image Input
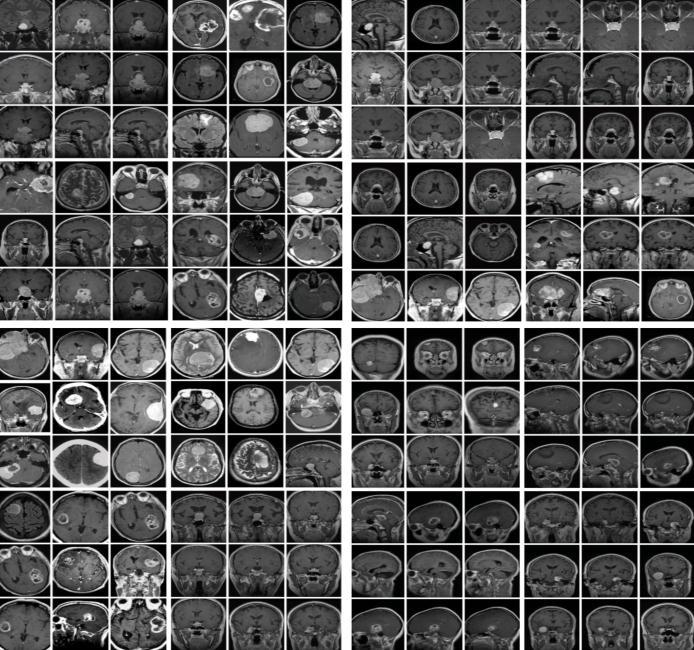
The input is MRI image. The images used here are in .jpg format. The MRI image dataset is obtained from publicly availablesources.Theseimagesaredividedintotwoyesand nofolders,eachcontainingimageswithandwithoutbrain tumors.
Thetrainingandtesting bothdatasetscontainsimageswith and withouttumors.Laterwetrain our system using
Trainingdatasetandwetestourmodelontestdatasetwe mustnottestonthesametraindatasetifwedosotheremay bechancesofgettinginaccurateresultssowetestontesting dataset
Image Preprocessing
MRIimagesacquiredfromapublicsourcecannotbedirectly suppliedforprocessing.Theseimagescontainnoise,suchas external noise and noise generated by the patient’s movement during the MRI scan. For efficient brain tumor detection,theymustberemovedandimagesenhanced.
•Grayscaleconversion:importedimagesinjpgformatare firstconvertedfromRGBmodelstograyscaleimages.
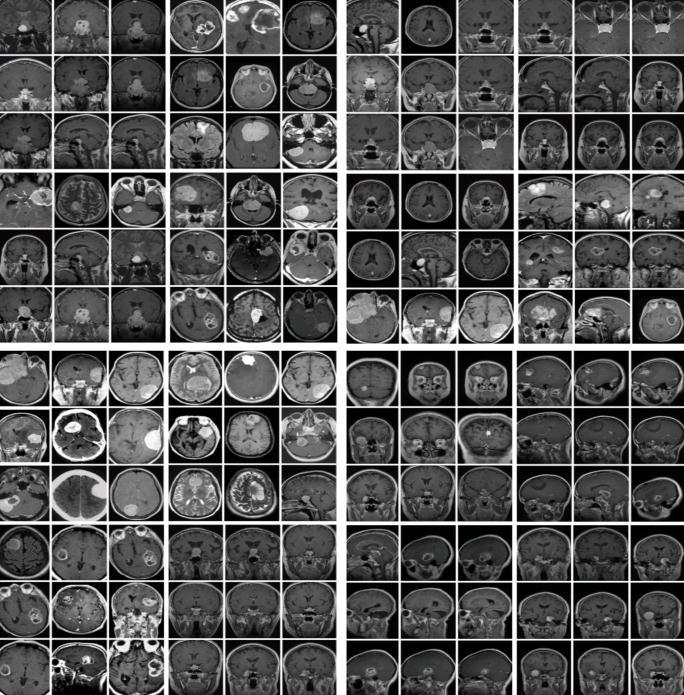
• Image resizing: Grayscale images are resized from their currentsizetoaconvenient200x200sizeforconsistency.
•MedianFiltering:Theresizedgrayscaleimageismedian filteredtoremoveexistingnoiseandreduceedgeblurring effects.

•High-passfiltering:Themedianfilteredimageishigh-pass filtered and enhanced by adding a resized image to the resultingimage.
Splitting Data for Training and Testing
Testing the model on the same data it was trained on willresult in overfittingand poor performance inrealworldscenarios.Toavoidthis,splitthedataintotwoparts:a trainingsetandatestset.Normalpracticeisan80/20split.
In this, we split the dataset into training and testing sets using the train_test_split() function from the scikit-learn package.Thesamplesize chosenis0.2(i.e.,20%fortesting and80%fortraining).Classification,likeanykindofmedical image,isthebestwaytoidentifyanimage.Allclassification algorithmsarebasedonpredictionsofimagesinwhichone or more features are present, and each of these features belongstooneofseveralclasses.Anautomaticandreliable convolutionalneuralnetwork(CNN)classificationmethodis used. This makes the structure robust and helps identify details.ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(ConvNetorCNN)isa deep learning algorithm that takes in an input image and assigns importance to different aspects or objects in the imagetodistinguishthemfromeachother.ConvNetrequires less preprocessing when compared to other classification algorithms. While the primitive method requires manual developmentoffilters,ConvNethastheabilitytolearnthese filtersandpropertieswithsufficienttraining.ConvNetcan successfullycapturethespatialandtemporaldependencies of images by applying relevant filters. This architecture improvesmatchingwithimagedatasetsbecausethenumber of relevant parameters is reduced and the weights are reusable. In other words, the network can be trained to better understand image sophistication. The role of the ConvNet is to reduce the image to a manageable form without losing important features necessary to get good predictions.Inthisstep,weneedtoimportKerasandother packagesthatwewillusewhenbuildingCNN.
Sequential
Toinitializetheneuralnetwork,wecreateanobject oftheSequentialclass.
classifier=Sequential() Convolution
Toaddaconvolutionallayer,calltheAddfunction ontheclassifierobjectandpasstheparametersto
Convolution2D. The first argument for a feature detector is the number of feature detectors to create. The second and third parameters are the dimensionsofthefeaturedetectormatrix.Weused 256 feature detectors for the CNN. The next parameteristheinputshape,whichistheshapeof the input image. Images are converted to this formatduringpreprocessing.
Iftheimageisblackandwhite,itisconvertedtoa 2Darray;iftheimageiscolored,itisconvertedtoa 3D array. In this case, we assume that you are workingwithcolor.Theinputshapeisatuplethat containsthenumberofchannels(threeforcolour images)aswellasthedimensionsofeachchannel's 2Darray.
IfyouarenotusingaGPU,itisrecommendedtouse lowerdimensionalitytoreducecomputationtime. The last parameter is the activation function. The classificationoftheproblemofimagesisnonlinear. Therefore,weuseacommutationfunctiontoensure that we do not have negative pixel values during computation. This is how the nonlinearity is achieved.
Pooling
PoolingLayer:Thisisanotherlayerwherethematrixstarts. Thislayerisaddedtoreducethenumberofparametersin thematrix. This prevents overfittingthe model.Thereare twotypesofpooling.
MAX_POOLING:Getthemaximumvalueofthepatchhere. AVG_POOLING:Herewegettheaveragevalueofthepatches.
Flattening
Allpooledfeaturemapsarecollectedandcombined inthisstepandplacedina singlevectorforinputto thenextlayer.
Theflattenfunctionflattensallfeaturemapsinto onelongcolumn.
classifier.add(Flatten())
Dropout Layer
Thisisanoptionallayerthatcanbeaddedtothemodel.This layerpreventsoverfittingbyomittingsomeunits.
Fully Connection
Thenextstepistousethevectorsobtainedabove as inputs to the neural network using the Keras Densefunction.Thefirstparameterisprinted.This isthenumberofnodesinthehiddenlayer.Through experimentation, we can determine what is the
mostappropriatenumber.Thehigherthenumber of dimensions, the more computational resources arerequiredtofitthemodel.Acommonmethodis tochoosethenumberofnodesinpowersoftwo.
classifier.add(Dense(output=64))
Thenextlayerweneedtoaddistheoutputlayer.In thiscase,weexpectabinaryresult,soweusethe sigmoidactivationfunction.Ifyouexpectmorethan oneresult,usetheSoftMaxfunction.

Theoutputhereis1.Thisisbecauseweonlyexpect thepredictedprobabilitiesoftheclasses.
classifier.add(highdensity(output=1,activation= 'sigmoid'))
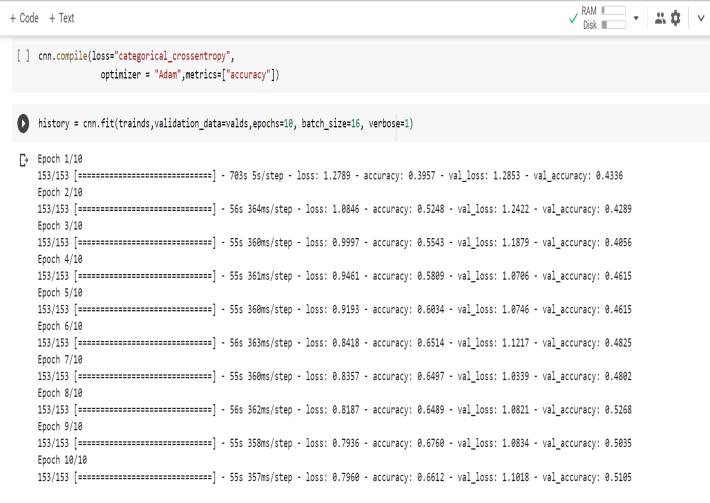
Obtaining outputs and validating models
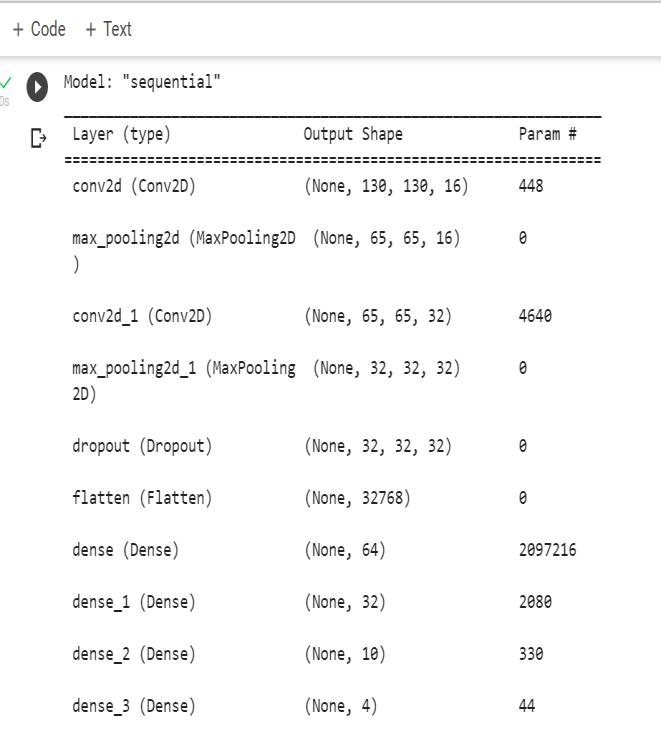
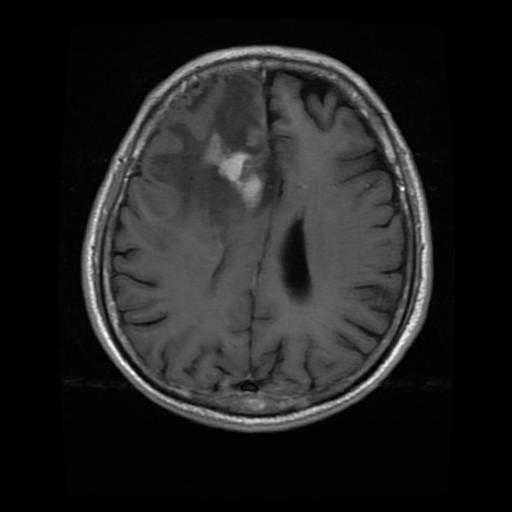
This will give you the output when the image is given as input,alongwithapercentageofconfidenceandinformation aboutwhetheratumorispresentornot.
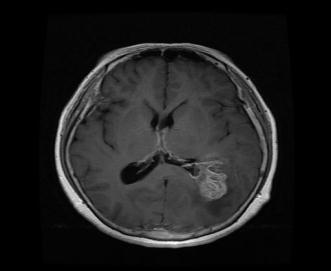
5. RESULTS
Inmethodology,wearehavingvariousstagesinthissection, andtheoutputofeachstagewillbedescribed
Infirststagewesuccessfullyconvertedtheinputimage(an OpenCV image) to grayscale using edge detection after applying pre-processing. Edge-based segmentation on an imageclassifiespixelsasedgeornon-edgedependingonthe filteroutput.Inregion-basedsegmentation,theimagewas subjected to regional maxima in order to group adjacent pixelswithsimilarvalues.TheCNNmodelwastrainedand testedbeforetheK-meanstechniquewasusedtoidentifythe regionofinterest(ROI),whichwasthenexaminedforthe presenceofatumor.
6. CONCLUSIONS
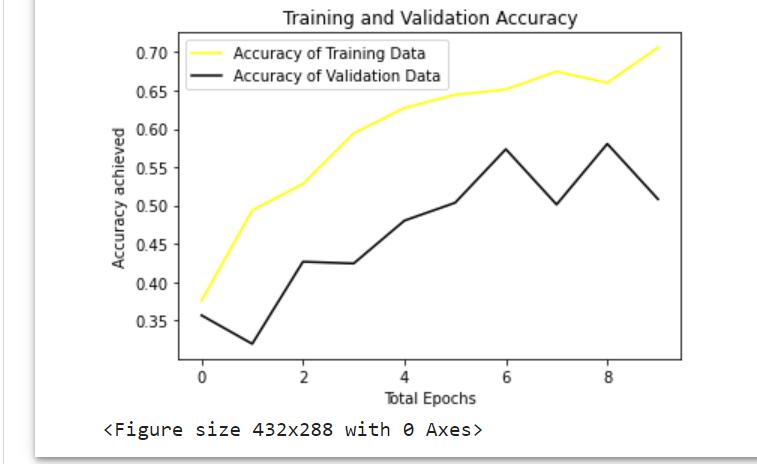
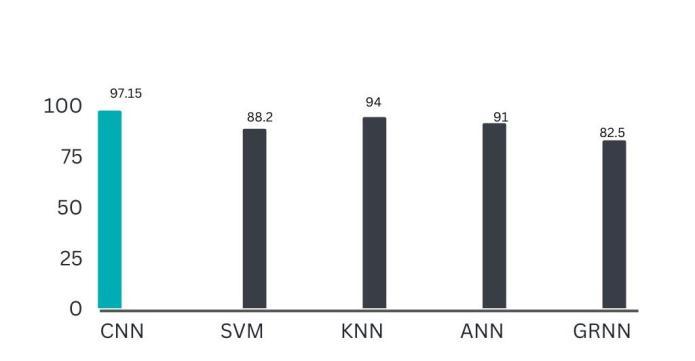
Inthispaper,weusedCNNStodetectbraintumors,andwe successfullyimplementedallfeaturesandtesteditacrossall possibletestcaseswithsatisfactoryresults.Themaingoalof this project is to improve the accuracy with minimal computation time and less complexity, to achieve high validation accuracy and very low validation loss, and to reducethetimerequiredtodetectbraintumors.Compared topreviouslyproposedalgorithms ithasmoreaccuracyand detects tumor in less time. It is about 97.15% accurate, whereasSVMisonly88%accurate.Finally,thegoalofthis projectisachievedbyusingCNN.
7. REFERENCES
[1] K.B.VaishnaveeandK.Amshakala,"AnautomatedMRI brainimagesegmentationandt tumordetectionusing SOM-clustering and Proximal Support Vector Machine classifier," 2015 IEEE International Conference on EngineeringandTechnology(ICETECH),Coimbatore,India, 2015,pp.1-6,doi:10.1109/ICETECH.2015.7275030.
[2] G.BirareandV.A.Chakkarwar,"AutomatedDetectionof BrainTumorCellsUsingSupportVectorMachine,"20189th InternationalConferenceonComputing,Communicationand NetworkingTechnologies(ICCCNT),Bengaluru,India,2018, pp.1-4,doi:10.1109/ICCCNT.2018.8494133.
[3] A. Kumar, A. Ashok and M. A. Ansari, "Brain Tumor Classification Using Hybrid Model Of PSO And SVM Classifier," 2018 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication Control and Networking (ICACCCN),GreaterNoida,India,2018,pp.1022-1026,doi: 10.1109/ICACCCN.2018.8748787.
[4] R. Ahmmed, A. S. Swakshar, M. F. Hossain and M. A. Rafiq, "Classification of tumors and it stages in brain MRI usingsupportvectormachineandartificialneuralnetwork," 2017InternationalConferenceonElectrical,Computerand Communication Engineering (ECCE), Cox's Bazar, Bangladesh, 2017, pp. 229-234, doi: 10.1109/ECACE.2017.7912909.

[5] C. Saha and M. F. Hossain, "MRI brain tumor images classification using K-means clustering, NSCT and SVM," 2017 4th IEEE Uttar Pradesh Section International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Electronics (UPCON), Mathura, India, 2017, pp. 329-333, doi: 10.1109/UPCON.2017.8251069.

