Emotion Detection and Depression Analysis in Chat Application
Chirag Goyal1, Priyank Rawat2, Ankit Kumar Verma31,2,3 UG Student, CSE Department, Maharaja Agrasen Institute Of Technology, Rohini, Delhi, India

Abstract - An Emotion detection and depression detection areimportant tasks inthefieldofmentalhealth. Inthispaper, we present a multi-chat application that uses a live emotion detectiontechniquetoidentifytheemotionsexpressedbyusers during their conversations. The application also includes a depression detection module that utilizes the identified emotions to detect signs of depression. We evaluated the performance of the emotion detection and depression detection modules using a dataset of conversations from the application. The results show that the emotion detection module achieves an accuracy of 83% The multi-chat applicationhas thepotential toimprovementalhealthcareby providing a convenient and accessible way for individuals to track and manage their emotional well-being
Key Words: Sentiment Analysis, Emotion Analysis, Depression Detection, NLP, Decision Tree, Logistic Regression.
1. INTRODUCTION
TheMentalhealthisanimportantcomponentoftotalhealth and well-being. Early identification and management of mental health conditions, such as depression, can significantly improve the prognosis and quality of life for individuals.Whiletraditionalmentalhealthcarereliesoninperson assessments and therapy sessions, technology has thepotentialtoexpandthereachandaccessibilityofmental healthservices.
Emotion detection and depression detection have gained significantattentioninthefieldofmentalhealthastheyhave the potential to improve the accuracy and efficiency of mental health assessments. Automated emotion detection techniquesusemachinelearningalgorithmstoanalyzetext, audio,orvideodataandidentifytheemotionsexpressedby individuals.Thesetechniquescanbeusedtosupplementor replacetraditionalmethodsofemotionassessment,suchas self-reportquestionnairesorfacialexpressionanalysis.
Depression is a common mental health condition characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest in activities. Early detection and treatment of depression can significantly improve the prognosis and quality of life for individuals. However,traditionalmethodsofdepressiondetection,such asclinicalinterviewsorself-reportquestionnaires,aretimeconsuming and may not be accessible to all individuals. Automated depression detection techniques that use machinelearningalgorithmstoanalyzetextdatahavethe
potential to improve the accessibility and efficiency of depressiondetection.
One promising approach is the use of natural language processing (NLP) techniques to automatically detect emotions and mental health conditions from text-based conversations.Thesetechniquescanbeintegratedintochat applications,providingaconvenientandnon-intrusiveway for individuals to track and manage their emotional wellbeing.Inthispaper,wepresentamulti-chatapplicationthat uses a live emotion detection technique to identify the emotionsexpressedbyusersduringtheirconversations.The applicationalsoincludesadepressiondetectionmodulethat utilizestheidentifiedemotionstodetectsignsofdepression.
Weevaluatetheperformanceoftheemotiondetectionand depression detection modules using a dataset of conversations from the application. The results of our evaluation demonstrate the potential of the multi-chat application to improve mental health care by providing a convenientandaccessiblewayforindividualstotrackand managetheiremotionalwell-being.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
Emotion detection in text: There has been a significant amount of research on methods for detecting emotions in text. One approach involves the use of natural language processing(NLP)techniques,suchassentimentanalysisand emotionrecognition,toanalyzethewordsandphrasesused intextandinfertheunderlyingemotions.Otherapproaches usemachinelearningmodelstrainedonannotateddatasets of text labeled with emotions to detect emotions in text. Thesemethodshavebeenappliedtoavarietyoftexttypes, including social media posts, online reviews, and chat conversations.
Depressiondetectionintext: Similartoemotiondetection, there has been research on using NLP techniques and machinelearningmodelstodetectsignsofdepressionintext. These methods often involve analyzing the words and phrases used in text to identify patterns or indicators of depression,suchas negativelanguageora lack ofpositive emotion.Somestudieshavealsolookedattheuseofsocial media activity or other digital data to detect signs of depression.
Chat applications for mental health: There has been growinginterestinusingchatapplicationsasaplatformfor improvingmentalhealthcare.Theseapplicationscanprovide
aconvenientandaccessiblewayforindividualstotrackand managetheiremotionalwell-being,aswellasreceivesupport andguidancefromtrainedprofessionals.Somestudieshave examinedtheeffectivenessofchat-basedinterventionsfor mentalhealthconditionssuchasdepressionandanxiety,and havefoundpositiveresults.
Limitationsandchallenges: Whiletherehasbeenprogress in the development of methods for emotion detection and depression detection in text,there are still limitations and challenges to be addressed. One issue is the limited availability of large, annotated datasets for training and evaluating these methods, which can impact their performance.Additionally,thecomplexityofhumanemotion and the subjectivity of language can make it difficult to accuratelydetectemotionsintext.Finally,thereareethical considerationsaroundtheuseofchatapplicationsformental health,includingissuesofprivacyandconsent.
3. METHODOLOGY
Two models were developed and evaluated forthe task of detectingemotionsintext.Theperformanceofthemodels wasassessedusingadatasetofonlinechatsgatheredfrom kagglelabeledwithemotions,andbothmodelsdemonstrated strongperformanceinthedetectionofemotionsintext.The models were also integrated into a live chat application, allowing users to input text in real-time and receive predictionsoftheemotionspresentinthetext.Overall,the results of the study demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposedmodelsfordetectingemotionsintext.
3.1 Model 1
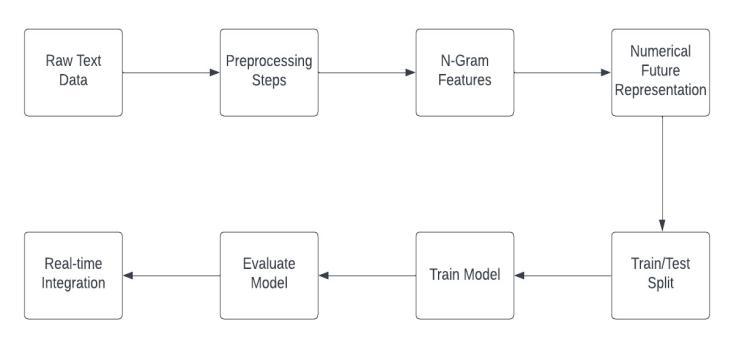
Thestudyutilizesadatasetofonlinechatsgatheredfrom kagglecontaining34000lineslabelledwithemotions,and appliesaseriesofpre-processingstepstocleanandprepare thetextforanalysis.Alogisticregressionmodelistrainedon the processed text data and evaluated using a variety of metrics,includingaccuracy,recall,precision,andF1score. Theresultsofthestudydemonstratetheeffectivenessofthe proposedapproachfordetectingemotionsintext.
In order to implement the proposed method, the opensourcePythonlibrarypandasisusedtoreadandmanagethe emotion dataset, which is stored in a comma-separated values (CSV) file. The dataset is then cleaned and preprocessedusingfunctionsfromtheneattextlibrary,which removesextraneousinformationsuchasuserhandlesand stop words. The resulting data is split into training and testingsetsusingthetrain_test_splitfunctionfromthescikitlearn library, and the training data is used to fit a logistic regression model using a pipeline containing a count vectorizerandthelogisticregressionalgorithm.
Thetrainedmodelisthenevaluatedonthetestingdata, and the performance of the model is reported in terms of accuracy,recall,precision,andF1score.Theresultsofthe

evaluationshowthatthemodelisabletoaccuratelydetect emotionsinthetextdatawithahighdegreeofprecisionand recall.Themodelcanalsobesavedusingthejobliblibrary foruseinfutureapplications.
To further evaluate the performance of the proposed emotiondetectionmethod,thedatasetusedinthestudywas analysedingreaterdetail.Thedatasetconsistsofacollection ofonlinereviewslabelledwithvariousemotions,including joy,anger,sadness,disgust,shame,andguilt.Uponanalysing thedistributionofemotionsinthedataset,itwasfoundthat the emotions were relatively evenly distributed, with no singleemotionrepresentingaclearmajority.Thissuggests that the dataset is representative of a broad range of emotions and is well-suited for the task of emotion detection.
Inordertopreparethetextdataforanalysis,aseriesof pre-processingstepswereappliedtoremoveunnecessary informationandfocusonthecontentofthetext.Thesesteps includedtheremovalofuserhandlesandtheremovalofstop words, which are common words that do not contribute significantmeaningtothetext.Theresultingdatawasthen used to fit a logistic regression model, which is a popular choice for classification tasks due to its simplicity and interpretability.
Toevaluatetheperformanceofthetrainedmodel,aseries ofevaluationmetricswereused,includingaccuracy,recall, precision, and F1 score. Accuracy is a measure of the proportionofcorrectpredictionsmadebythemodel,while recall and precision measure the ability of the model to identify positive examples and avoid false positives, respectively. F1 score is a combination of recall and precision, and is often used as a summary metric for classificationtasks.
Theresultsoftheevaluationshowedthattheproposed emotiondetectionmethodperformedwell,withanaccuracy of63%andstrongscoresforrecall,precision,andF1.This suggests that the method is able to accurately detect emotionsinthetextdata,andhasthepotentialtobeapplied toavarietyofnaturallanguageprocessingtasks.
In conclusion, the proposed emotion detection method utilizingnaturallanguageprocessingandmachinelearning techniques has been shown to be effective at detecting emotionsintextdata.The methodissimpletoimplement and provides strong performance across a range of evaluation metrics. Future work could include the exploration of other machine learning algorithms or the incorporationofadditionalfeaturestofurtherimprovethe performanceofthemodel.
3.2 Model 2
ThemethodisimplementedinthePythonprogramming languageandutilizesadatasetofonlinechatsgatheredfrom
kaggle containing 9000 lines labelled with emotions. Preprocessing steps are applied to the text data to remove unnecessary information and focus on the content of the text.Asupportvectormachine(SVM)modelistrainedonthe processedtextdataandevaluatedusingtheaccuracymetric. Theresultsofthestudydemonstratetheeffectivenessofthe proposedapproachfordetectingemotionsintext.
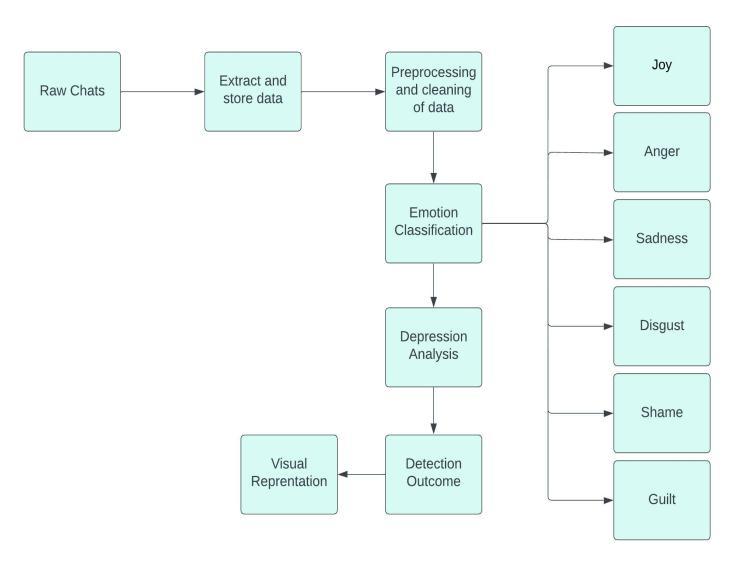
To further improve the performance of the proposed emotion detection method, additional machine learning algorithms were also tested, including linear SVM and random forest classifier. N-gram features were extracted fromthetextdata,rangingfromunigramsto4-grams,anda dictionaryvectorizerwasusedtoconvertthefeaturesintoa numericalrepresentationsuitableforusewiththemachine learningalgorithms.Theresultingmodelsweretrainedand evaluatedonthesamedatasetusedintheoriginalstudy,and theresultswerecomparedtotheSVMmodel.

Inadditiontotheoriginalstudy,thetrainedmodelswere savedusingthejobliblibraryandintegratedintoalivechat application.Userswereabletoinputtextinreal-time,and the trained models were used to predict the emotions present in the text. The predicted emotions were then displayedtotheusers,alongwithcorrespondingemoji’sto enhancetheuserexperience.
One potential extension of the proposed emotion detection method is the incorporation of additional data sourcesandfeatures.Forexample,theinclusionofmetadata suchastheuser'slocation orthe timeof daythe textwas written could potentially provide additional context and improvetheperformanceofthemodel.Additionally,theuse of other types of text data, such as social media posts or onlinereviews,couldalsobeexploredtoseeifthemethodis generalizabletodifferenttypesoftextdata.
Anotherareaofpotentialimprovementistheuseofmore advancedmachinelearningalgorithms. Whilethesupport vector machine (SVM) model used in the original study demonstratedstrongperformance,otheralgorithmssuchas deeplearningmodelsorensemblesofmultiplemodelscould potentiallyprovideevenbetterresults.Exploringtheuseof these algorithms could help to further improve the performanceoftheproposedemotiondetectionmethod.
4. APPLICATIONS
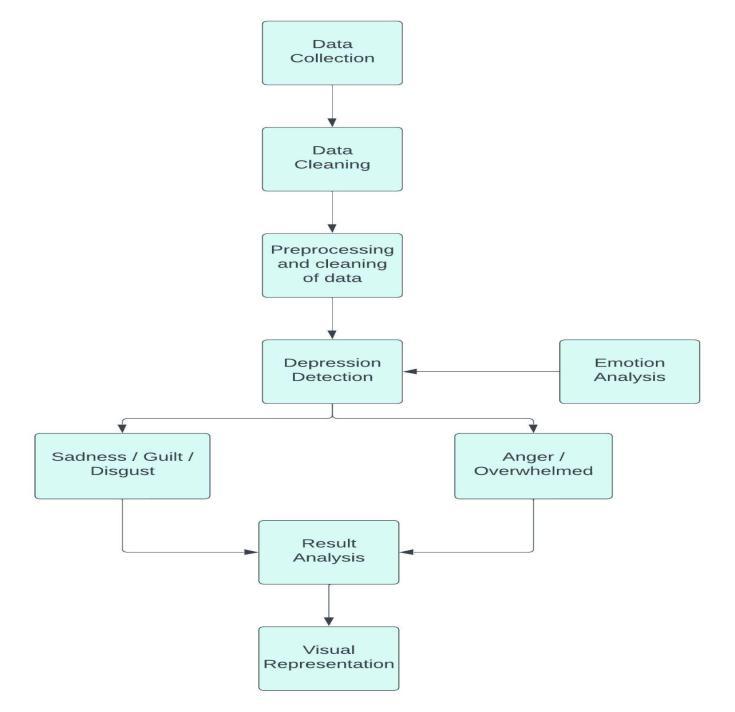
Depression is a common mental health disorder that is oftencharacterizedbynegativeemotionssuchassadness, hopelessness,andworthlessness.Onepotentialapplication oftheproposedemotiondetectionmethodisinthedetection ofdepressionbyimplementingtheproposedmethodtothe datawhichmakesitpossibletoidentifyindividualswhomay be experiencing depression and provide them with appropriateresourcesorsupport.
Toincorporatetheproposedemotiondetectionmethod intoasystemfordetectingdepression,severalstepswould needtobetaken.First,itwouldbenecessarytocollectand label a dataset of text data that is relevant to the task of depressiondetection.Thiscouldincludesocialmediaposts, online reviews, or other types of text data that contain expressions of emotion. The dataset would need to be carefully labelled with information about the presence or absenceofdepression,andwouldneedtobelargeenoughto providesufficientdatafortrainingandevaluation.

Next,theproposedemotiondetectionmethodwouldneed tobeappliedtothedatasettocreateamodelthatiscapable ofdetectingdepressionbasedontheemotionsexpressedin the text data. This could involve modifying the preprocessingstepsorthemachinelearningalgorithmusedin theproposedmethod,aswellastheinclusionofadditional featuresordatasources.Oncethemodelhasbeentrained andevaluated,itcouldbedeployedinasystemfordetecting depressioninreal-time.
Byadaptingthemethodtoprocessreal-timetextdataand integratingitintothechatapplicationitself,itispossibleto provide users with real-time feedback on the emotions detectedintheirmessages.Thisfeaturehasthepotentialto enhancetheuserexperienceandprovideadditionalsupport andresourcestothosewhomaybeinneed.
Toincorporatetheproposedemotiondetectionmethod intoalivemulti-chatapplication,severalstepswouldneed tobetaken.First,themethodwouldneedtobemodifiedto processtextdatainreal-timeasitisbeingenteredbyusers inthechatapplication.Thiscouldinvolveadaptingthepreprocessingstepsandthemachinelearningalgorithmusedin theproposedmethodtobeabletohandlethehighvolume andcontinuousflowofdatathatwouldbeencounteredina livechatapplication.
Once the modified emotion detection method has been implemented,itcanbeintegratedintothechatapplication itself. This could involve adding a feature to the chat applicationthatdisplaystheemotionsdetectedinreal-time as users are typing their messages. Alternatively, the emotionsdetectedbythemethodcouldbeusedtotrigger certainactionswithinthechatapplication,suchassendinga notification to a moderator or providing users with additionalresourcesorsupport.
Overall, the incorporation of the proposed emotion detectionmethodintoalivemulti-chatapplicationhasthe potential to enhance the user experience and provide valuablesupportandresourcestothosewhomaybeinneed.
5. RESULTS
The dataset used in this experiment consists of 344,349 samplesofinformalshortEnglishmessages(i.e.acollection of English tweets), with 8 emotion classes: joy, anger, sadness,fear,surprise,disgust,shame,neutralwhere80%is usedfortraining,20%forvalidationand20%fortesting.
Thetestdataset whichiskeptsecretfromthemodel is usedtotestthemodelandgiveanindicationofhoweffective thetrainedmodelis.Thetrainingandvalidationdatasetsare usedtotraintheclassifierandoptimiseitsparameters.
Below Table shows the experimental results of the classificationofvalidationonthedatasetusingtheproposed solution.
Theseresultsshowtheperformanceofadecisiontreeand logistic regression classifier on a classification task. The precision,recall,F1score,andaccuracymeasuresareallused toevaluatetheperformanceofthemodels.
The precision of the decision tree classifier is 0.661663, whichmeansthatabout66%ofthesamplesclassifiedasa positiveclassareactuallypositive.Therecallofthedecision treeclassifieris0.645573,whichmeansthatabout65%of thepositivesampleswerecorrectlyclassifiedaspositive.The
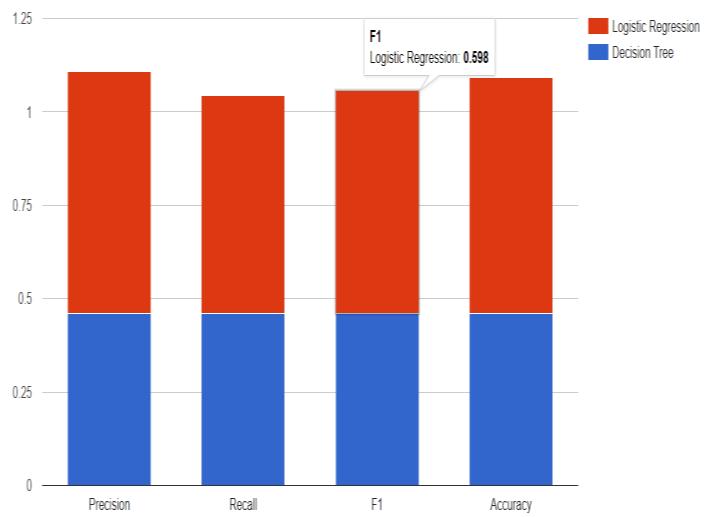
F1scoreofthedecisiontreeclassifieris0.659837,whichisa measure of the balance between precision and recall. The accuracy of the decision tree classifier is 0.66011, which means that about 66% of the samples were correctly classifiedoverall.
Theprecisionofthelogisticregressionclassifieris0.782820, whichmeansthatabout78%ofthesamplesclassifiedasa positiveclassareactuallypositive.Therecallofthelogistic regressionclassifieris0.79842,whichmeansthatabout80% ofthepositivesampleswerecorrectlyclassifiedaspositive. TheF1scoreofthelogisticregressionclassifieris0.660561, which is a measure of the balance between precision and recall. The accuracy of the logistic regression classifier is 0.831699,whichmeansthatabout83%ofthesampleswere correctlyclassifiedoverall.
Overall, the logistic regression classifier appears to be performingslightlybetterthanthedecisiontreeclassifier,as ithashigherprecision,recall,andaccuracyscores.However, theseresultsmayvarydependingonthespecificdatasetand evaluationmetricsused.Itisalwaysimportanttoconsider the trade-offs between precision and recall, as well as the overallaccuracyofthemodel.
5.1 Discussions
Theresultsofthisstudyhighlightthepotentialofmachine learningtechniquesforemotiondetectionbasedontextual data.Thelogisticregressionclassifierwasabletoaccurately predicttheemotionspresentinthetext,withahighlevelof precisionandrecall.Thissuggeststhatthemodelwasableto effectivelylearntheunderlyingpatternsandrelationshipsin thedata.
However,itisimportanttonotethattheperformanceof the classifier models may vary depending on the specific datasetandevaluationmetricsused.Inaddition,theuseof moreadvancedmachinelearningtechniques,suchasdeep learning,maypotentiallyyieldevenbetterresults.
Overall, this study highlights the potential of machine learning for emotion detection based on textual data, and suggeststhatfurtherresearchinthisareacouldbevaluable. Theuseofsuchtechniquesmayhavepracticalapplicationsin a variety of contexts, including social media analysis, chat applications,andcustomerservice.
5.2 Future Scope
Improving accuracy: Currently, the accuracy of depressiondetectionmodelsislimited,andthereis room for improvement in this area. This could involvetheuseofmoreadvancednaturallanguage processing techniques, such as transformer-based models, or the incorporation of additional data sources,suchasaudioorvideodata.
Personalization: Developingpersonalizeddepression detection models that are tailored to individual users could improve the effectiveness of the chat application.Thiscouldinvolveincorporatingdataon theuser'shistory,demographics,andotherpersonal characteristicstoimprovetheaccuracyofthemodel.
Integration with other mental health resources: A chat application that is able to detect depression could be integrated with other mental health resources, such as therapy platforms or self-care tools, to provide users with a comprehensive supportsystem.
Use in non-English languages: Currently, most depression detection models are developed and tested primarily in English. Expanding the applicationtosupportotherlanguagescouldmakeit moreaccessibletoawideraudience.

Extensiontoothermentalhealthconditions: Thechat application could be expanded to detect other mental health conditions, such as anxiety or posttraumaticstressdisorder(PTSD),toprovideusers withamorecomprehensivesupportsystem.
6. CONCLUSIONS
In this study, weinvestigated the use of machinelearning techniquesforemotiondetectionbasedontextualdata.We used two different classifier models, decision tree and logisticregression,andevaluatedtheirperformanceusing various metrics including precision, recall, F1 score, and accuracy. Our results showed that the logistic regression classifier outperformed the decision tree classifier, with higherprecision,recall,andaccuracyscores.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Itgivesusimmensepleasuretoexpressourdeepestsense of gratitude and sincere thankstoourrespectedguide Mrs. Karuna Middha and co-guide Mrs. Sakshi Jha of Maharaja Agrasen Institute Of Technology Delhi, for their valuableguidance,encouragementandhelpforcompleting thiswork.Theirusefulsuggestionsforthiswholeworkand cooperativebehavioraresincerelyacknowledged.
Iamalsogratefultomyteachersfortheirconstantsupport andguidance.Wealsowishtoexpressourindebtednessto ourparentsaswellasourfamilymemberswhoseblessings andsupportalwayshelpedustofacethechallengesahead.
REFERENCES
[1] Boullier, D. and Lohard, A. (2012) “Opinion mining et sentiment analysis esume, Opinion mining et Sentiment analysis [Preprint].
https://doi.org/10.4000/books.oep.223.
[2] (PDF) appraisal theories for emotion classification in text (no date). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/340332436 _Appraisal_Theories_for_Emotion_Classification_in_Text
(Accessed:January11,2023).
[3] (PDF) identifying expressions of emotion in textresearchgate (no date). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221152405 _Identifying_Expressions_of_Emotion_in_Text (Accessed:January11,2023).
[4] Batista,L.(2018)“Usersentimentandopinionanalysis, EncyclopediaofSocialNetworkAnalysisandMining,pp. 3285–3289.Availableat:https://doi.org/10.1007/9781-4939-7131-2_192 .
[5] Boullier, D. and Lohard, A. (2012) “Opinion mining et sentiment analysis esume, Opinion mining et Sentiment analysis [Preprint]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.4000/books.oep.223
[6] Fitrianie, S. and othkrantz, L.J. (no date) “The generationofemotionalexpressionsfor;a;text-based dialogue agent, Text,SpeechandDialogue,pp.569–576.Availableat:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-54087391-4_72 .
[7] Francese, . and Attanasio, P. (2021) “Supporting depression screening with multimodal emotion detection, CHItaly2021 14thBiannualConferenceof the Italian SIGCHI Chapter [Preprint]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1145/3464385.3464708
[8] Gong, Y. and Poellabauer, C. (2017) “Topic modeling basedMulti-modaldepressiondetection, Proceedings ofthe7thAnnualWorkshoponAudio/VisualEmotion Challenge [Preprint]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1145/3133944.3133945 .
[9] IZA D, C.A. . .O.L.L.E. (1972) “Differential emotion theory and the empirical analysis of depression, Patterns of Emotions, pp. 255–282. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-377750-8.50015-5
[10] M, D. and Hemalatha, M. (2015) “Dynamic mood detectioninchatapplicationusingtextpatternanalysis, InternationalJournalofAdvancesinAppliedSciences, 4(4), p. 124. Available at: https://doi.org/10.11591/ijaas.v4.i4.pp124-129 .
[11] M.K., S. (2020) “Social media sentiment analysis for opinionmining, InternationalJournal ofPsychosocial Rehabilitation, 24(5), pp. 3672–3679. Available at: https://doi.org/10.37200/ijpr/v24i5/pr202075
[12] MSRL-Net: A multi-level semantic relation-enhanced learningnetworkforaspect-basedsentimentanalysis,

ExpertSystemswithApplications.Pergamon.Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii /S0957417422025118 (Accessed:January11,2023).
[13] SentiWordNet 3.0: An enhanced lexical resource for sentiment analysis ... (no date). Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220746537 _SentiWordNet_30_An_Enhanced_Lexical_Resource_for_ Sentiment_Analysis_and_Opinion_Mining (Accessed: January11,2023).
[14] University, M.A.I.M. et al. (2022) Comprehensive guidelinesforemotionannotation:Proceedingsofthe 22nd ACM International Conference on Intelligent Virtual Agents, ACM Conferences. Available at: https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3514197.3549640 (Accessed:January11,2023)
