Design and Development of a 3-axis Pick and Place Robot for Industrial Use

Abstract - The primary goal of this research and development project is to Design and develop a pick and place robot for industrial use. The system is so designed that it eliminates human error and human intervention to get more precise work. This robotic arm can pick and place objects. The robot was designed, assembled, implemented in various fields such as; in bottle filling industry, and packing industry, and then programmed using a pneumatic circuit. The end effector is designed to grab the object, lift it and place it in the desired location.
1. INTRODUCTION
Theuseofpickandplacerobotsiscommoninproduction lines with repetitive tasks. A human doing the same task over and over again will be inefficient and mentally disturbedbecauseitbecomesarepetitive,tedioustaskwith ease,andspeed:allowingforfastercycletimesandaccuracy incomparisontohumancounterparts.Theconsistentoutput along with its quality and repeatability are unmatched. Industrialrobotsaremachinesthatareusedintheindustry, and they are usually automatically controlled and reprogrammable.Theycanbeusedinthreeormoreaxes, whichmakesthemversatileandabletodoavarietyoftasks. The design of the robot was determined by the cylinder specificationsandweightrequirementsoftherobot.Inthe industrialmanufacturingsector,pickandplacerobotshave been used in a variety of material-handling applications rangingfrompalletizinganddepalletizing,casepicking,bin picking, kitting, machine loading and unloading, parts feeding,andpartsdelivery.Suchrobotswithimprovements havealsobeenusedinstorage/retrievalsystemsandcase packingandsorting.
1.1 Methodology
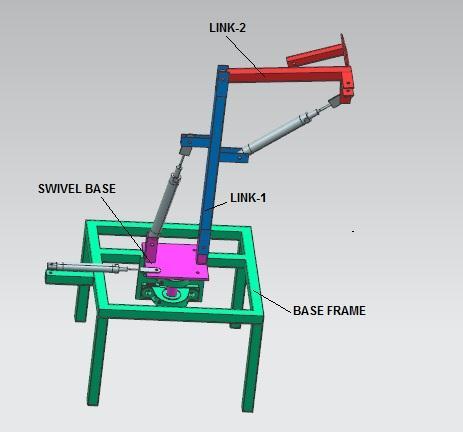
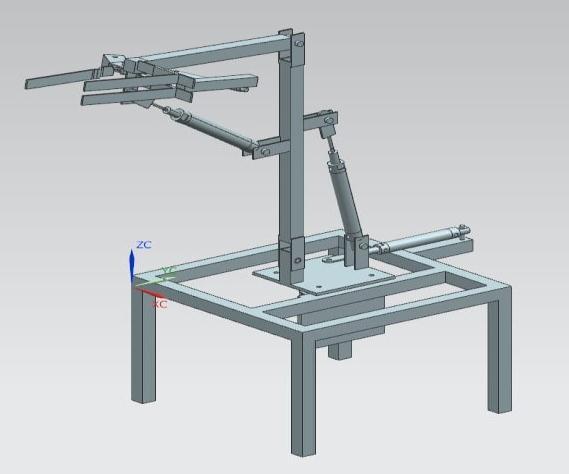
Theprojectentailsthedesign,construction,andpneumatic circuitry of a 3-DOF robot. This design served as the inspiration for the robot's fundamental mechanics. Following pneumatic cylinder selection, the required link lengthsweredeterminedandmadeusingcarbonsteelbars. Thefinaldesignoftherobotisasfollows.Thedesignofthe robot underwent significant changes throughout the assembly.
1.2 System Description
Theprojectconsistsofthedesign,andbuildingofa3-DOF robot,thepneumaticcircuits
2. Selection of Material

2.1. Material Selection for Frame
Function-Tosupporttheload
Objective-ToreducetheWeight
Constraint-Forces,andLength
Variable-Sizeandmaterialselection
2.3. Working
As Pneumatic air is the main source for working of the project.Themainairsourcewillbesuppliedtothepower pack of the project which includes 4 no. of 5/2 handoperatedvalves.
Thefirst5/2Valvegivenforrotationofallthelinksmeans alllinksassemblywillberotatedtowardsthestrokelength ofthefirstcylinder.
Thesecond5/2Valveisgivenfortakingmomentagainstthe centralpivotpointanditisplacedatsomedistancefromthe centralarmwhichisvertical.
Third 5/2 Valve given for taking moment against inclined notperfecthorizontalbutgivenlengthwisemomenttoup anddown.
Fourth5/2Valvegivenfortakingforkmoment.
3. Force Analysis
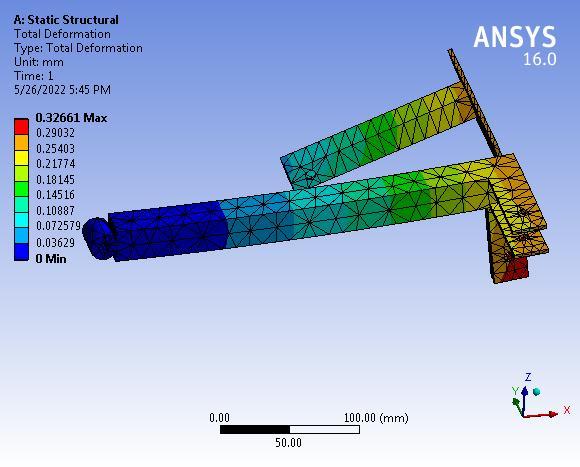
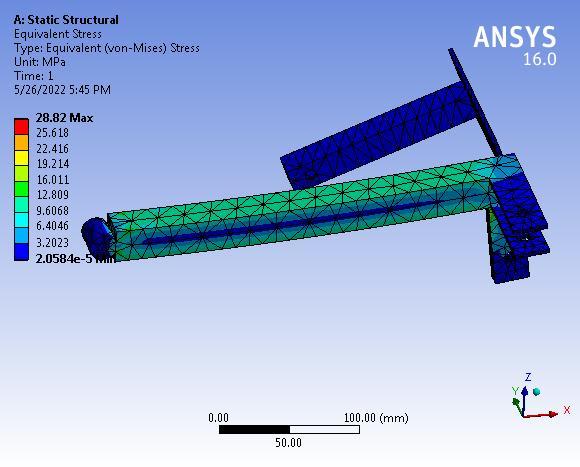
Theanalyticalstressis28.82MPatherebysuggestingthat thedesignoflink-2issafeunderagivensystemofforces.

The maximum deformation is 0.32661 mm which is very negligiblehencethelink-2issafeundera givensystemof forces.
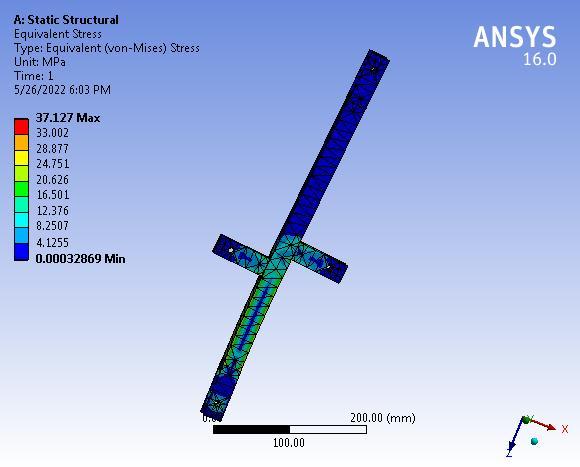
Theanalyticalstressis37.127MPatherebysuggestingthat thedesignoflink-1issafeunderagivensystemofforces.
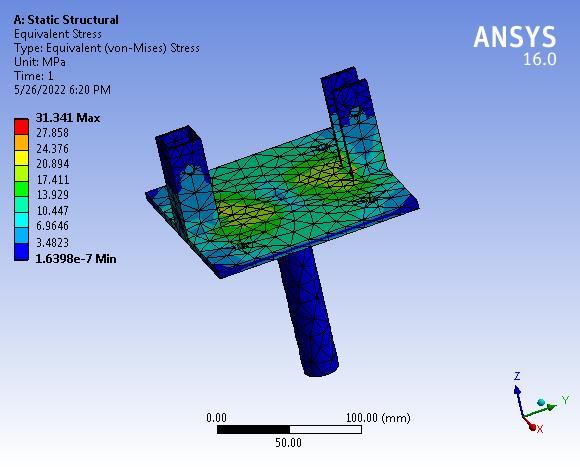
Theanalyticalstressis31.341MPatherebysuggestingthat thedesignoftheSwivelbaseissafeunderagivensystemof forces.

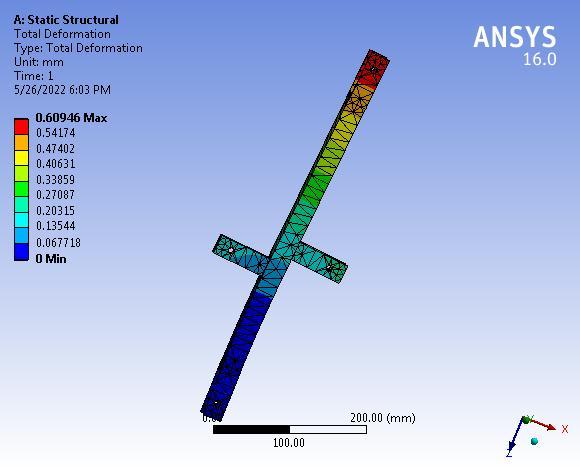
The maximum deformation is 0.609 mm which is very negligiblehencethelink-1issafeundera givensystemof forces.
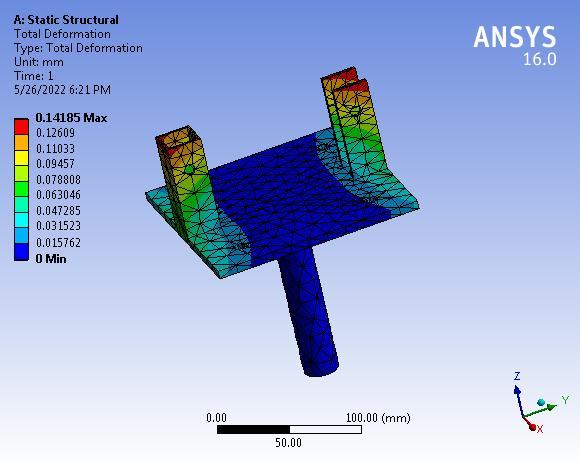
The maximum deformation is 0.14185 mm which is very negligiblehencetheSwivelbaseissafeunderagivensystem offorces.
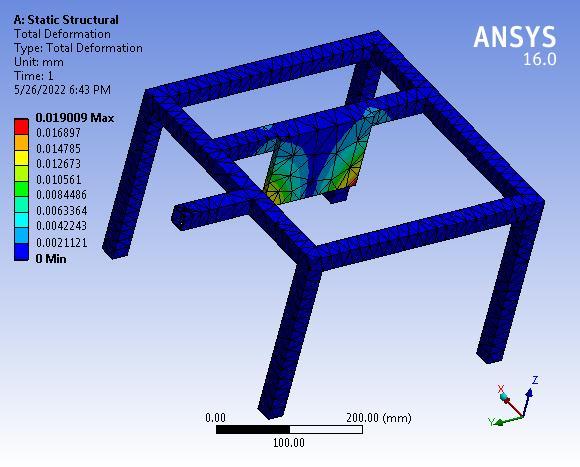
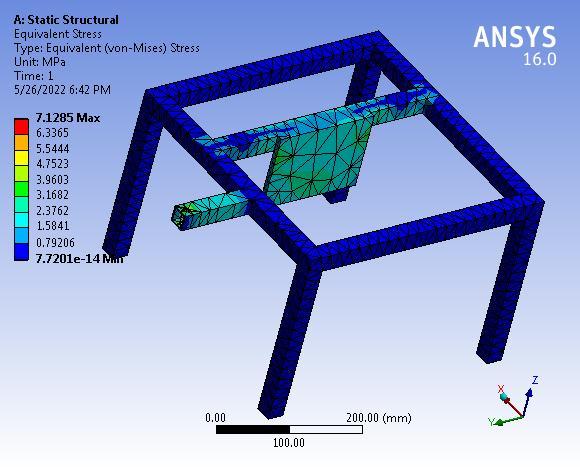
3.4 Base Frame
Von-mises Stresses:
Theanalyticalstressis7.1785MPatherebysuggestingthat thedesignoftheBaseFrameissafeunderagivensystemof forces.
3. CONCLUSION
The system works well till 12 kg but fails at 13 kg. The analyticalstressis37.127MPatherebysuggestingthatthe designoflink-1issafeunderagivensystemofforces.The maximumdeformationis0.609mmwhichisverynegligible hencethelink-1issafeunderagivensystemofforces.The analytical stress is 28.82 MPa thereby suggesting that the designoflink-2issafeunderagivensystemofforces.The maximum deformation is 0.32661 mm which is very negligiblehencethelink-2issafeundera givensystemof forces. The analytical stress is 31.341 MPa thereby suggestingthatthedesignoftheSwivelbaseissafeundera given system of forces. The maximum deformation is 0.14185mmwhichisverynegligiblehencetheSwivelbase issafeunderthegivensystemofforces
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to take this opportunity to thank Prof. J.V.ChopadeandPimpriChinchwadcollegeof Engineering and Research, Ravet for the invaluable support, guidance, andfacilitiesprovided.
REFERENCES
[1] NishigandhaPatel1,VaibhavAhuja1,ShaunakHedaoo1, Tushar Rotti1, A Review Paper on the Pick and Place RoboticArm,IRJETVolume08|02,February2021.
[2] AutomationofMobilePickandPlaceRoboticSystemfor Small Food Industry, IEEE 2012. Mir Sajjad Hussain TalpurandMurtazaHussainShaikh.

[3] DesignandImplementationofMulti-HandlingPickand PlaceRoboticArmbyS.Premkumar,K.SuryaVarman, andR.Balamurugan,IJETTMarch2016.
[4] Pick and Place Robotic ARM Using PLC, Abhiraj Bhalerao,PrasadDoifode,KunalChopade,andJitendra Gaikwad,IJERTAugust2019.
[5] S.Mohanavelan,M.MadhanKumar,K.Mohanprabhu,M. Narendhiran4,B.OmAdhavan,DesignandAnalysisof PickandPlaceRobot,IJESC2019.
[6] Dr.T. Sunil Kumar, K. Sarath, Sd.Famil, A.V.S.Bhagyesh andSk.Althaf,Design,andfabricationofpickandplace roboticarm,ResearchGateAugust2020
The maximum deformation is 0.019 mm which is very negligiblehencethebaseframeissafeunderagivensystem offorces.
