International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1Lecturer, Dept. of EEE, Ahsanullah University of Science & Engineering, Dhaka, Bangladesh 2Software Engineer, Zantrik, Dhaka, Bangladesh 3Professor, Dept. of EEE, RUET, Rajshahi-6204, Bangladesh ***
Abstract - Electroencephalogram (EEG) data can be used to extract information using machine learninganddeep learning methods. The research is primarily concerned with how they might be used to identify mental illnesses like schizophrenia and epilepsy. We present two methods for diagnosingepilepsy, the first approach is to utilize the Welch power spectral density for feature extraction and multiple classifiers (Kernel SVM, Naive Bayes, Random Forest) for the classification approach using the datasets offered by the Zenodo organization. We also present a different method called ChronoNet (second approach), in which each 1D convolution layer makes use of numerous filters with progressively longer durations. The next phase involves stacking layers of feedforward-connected deep gated recurrent units (GRUs) on top of one another. When applied to the data from the Temple University Hospital EEG Corpus using the Keras framework, the suggested ChronoNet design (with five 1D convolution layers of varying filter size) produced an accuracy of roughly 97.20%. Using the data from the Repository for Open Data for EEG in Schizophrenia, we present two methods for diagnosing schizophrenia here. While the second method uses Keras to generate a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), the first method extracts features using extractors including mean, standard deviation, kurtosis, skewness, and root mean square as well as Logistic Linear Regression Classifier. For epochs = 10, we were able to attain a maximum accuracy of 85.11% in the instance of schizophrenia for the second approach.
method of assessing someone's brainwave activity is the electroencephalogram(EEG).
Duetotheimmenselaborinvolvedinidentifyingseizures byhumanexpertsandthelargenumberofepilepsypatients, numerousattemptshavebeenmadetodevelopautomatic seizuredetectionsystems.Fourmethodsareusedtoidentify seizures,withthebestclassificationresultsbeingproduced by random forest (RF), decision tree (DT) algorithm C4.5, SVM+RF,andSVM+C4.5[1].Estimatedentropyandsample entropyobtainedbyWPDareusedasfeatures,whileSVM andextremelearningmachineareemployedasclassifiers,in [2]forthegoalofdetectingepileptic episodes.Inorderto minimize the number of variables, WPD and kernel PCA (KPCA) are also utilized in [3]. Due to exceptional achievements[4-5],deeplearningtechniques,particularly CNNs, have recently garnered substantial attention in the fieldofEEGsignalprocessing.
Aperson'slifemaybeseriouslyindangerasaresultofan epileptic seizure. The neurological disorder known as epilepsyisbroughton bytheimproperdischargeof brain neurons. The most important tool for the diagnosis of epilepsy is the Electroencephalogram (EEG), which demonstrates how epileptic seizures manifest as distinct, typically rhythmic signals that frequently precede or coincide with the initial observed changes in behavior. Schizophrenia is a mental illness that causes a variety of challengeswithdailyactivities.Peoplewithschizophrenia have hallucinations, delusions, and a disconnection from reality.Aperson'smentalcapabilitiesandoverallbehavior suffer from schizophrenia. A non-invasive, cost-effective
Schizophreniahasavarietyofsymptoms,includingformal mental illnesses and disruptions in thought flow or sequence. In terms of risk factors, complications, clinical manifestations, course, response to treatment, and functionalresult,schizophreniaisasevereandcomplicated mental condition. It currently ranks as one of the major causesofdisabilityworldwide,affectingalotofpeople.In the analysis of EEG signals in schizophrenia patients, classificationisanimportantgoal.Theeffectivenessoffirstgeneration entropy measures, including approximate (ApEn),sample(SampEn),andfuzzyentropy(FuzzyEn),in terms of the classification of EEG signals is calculated [6]. The accuracy of the classification of the healthy and schizophrenic patient was assessed using Support Vector Machines (SVMs), Decision Trees, k-Nearest Neighbor Classifiers, Random Forest Classifier Artificial Neural Networks(ANN),andConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(CNN) inthefeatureclassificationstate[7].
Thisstudyprovidestwocomparativeanalyses:firstoneis to discriminate between healthy and epileptic patients (using two methodologies) and the second one is to differentiate between healthy and schizophrenic patients (utilizingtwomethods).
Thefirstcomparisonanalysispresentedinthispaperisto distinguish between healthy and epileptic individuals
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
utilizing two approaches. The first method involves categorizing epileptic seizures using features extracted in the frequency domain from the Welch power spectral density.Themean,standarddeviation,minimumvalue,and maximum value of the epoch signal fluctuations were measured using the datasets available from zenodo organization. These measurements were used to train a classifier(kernelSVM,RandomForest,NaiveBayes,Decision tree) to calculate its accuracy, loss, confusion matrix, sensitivity, and specificity. In terms of the Nigerian data, kernelSVMprovidesthehighestlevelsofaccuracyamong theclassifierswhichissignificantlyhigherthantheaccuracy oftherelevantwork[8].Thesecondapproachusesanovel recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture named ChronoNet.Weimplementedfiveconvolutionallayersinthe ChronoNet,whichimprovesaccuracy(97.20%)inKerasby roughly6.2%morefromarelatedwork[9]drawingideas from1Dconvolutionlayers[10]gatedrecurrentunits[11], inceptionmodules[12],anddenselylinkednetworks[13].In this study, we compared the accuracy rates of these two techniquesinvolvedinApproachI(Differentiatingbetween EpilepticandHealthyPeople).
The study also presents a comparative assessment to distinguish between healthy and schizophrenic patients using two approaches: one is used to extract frequency domain features (using feature extractors like mean, standard deviation, kurtosis, skewness, and rms) and a variety of classifiers (Logistic Linear Regression, Gradient Boosting Classifiers), and the other makes use of deep convolutional neural networks (CNN) in the Keras framework.Whensubjectbasetestingwasconductedusing ourmodelwitha15-layereddeepCNNmodel,wewereable toreachamaximumaccuracyof85.11%,whichisabout4% betterthantheworkthatwasdonepreviously[7].
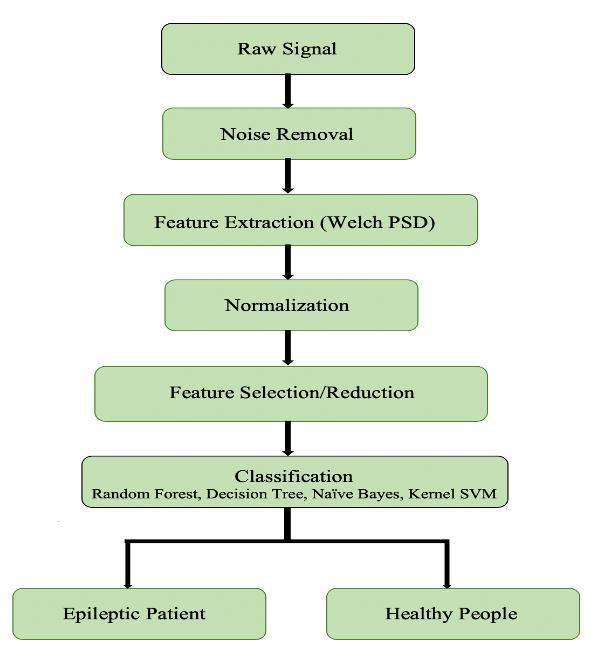
Intotal,212Nigerianstookpartinthesurvey.Inthedataset, therewere112(Males67,Females45)epilepticseizure prone patient while 92(Males67, Females25) people werehealthy.Thefourteen-channelEEGhasaresolutionof 16 bits and a sample rate of 128 hertz. The subjects were dividedintotwogroups:Control(subjectswhowereingood health)andEpilepsy(subjectswhowerepronetoepileptic seizures). Fig. 1 shows the EEG signal and power spectral density of one participant having an epileptic seizure. The electrodepositioncorrespondstotheglobal10-20system. Theepochs'lifespanwassettotenandtraining-testingratio is80:20.
Features that correspond to various epochs within an individual were used in the analysis as input for the
categorization model. The Welch Power Spectrum method contributestotheclassificationmodel'sfeatureextraction. Four classifiers' output parameters were evaluated in comparison (Kernel SVM, Random Forest, Decision Tree, Naive bayes). The three variables considered in the performanceevaluationofthesuggestedworkareasfollows: [14,15]:
Accuracy=(TN+TP)/(TP+TN+FN+FP)
Sensitivity=TP/(TP+FN)
Specificity=TN/(TN+FP)
F1Score:TheF1-score,isameasureofamodel'saccuracyon adataset.
F1Score=(2∗(������������∗������������������))/((������������+������������������))
Where,TP=truepositive FN=falsenegative, FP=falsepositive TN=truenegative
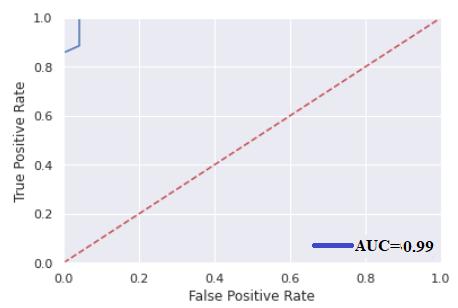
The proportion of accurately identified seizure time periodstonon-seizuretimeperiodsisconsideredaccuracy. Sensitivityassesseshowwell seizuresarerecognizedover time. The percentage of correctly identified non-seizure segmentsiswhatismeantby"specificity."Aclassifierwitha highlevelofspecificitycanquicklyidentifysegmentsthatare seizure-free.TheflowchartinFig.2displaysthismethod.The values of the aforementioned parameters for the different classifiersusedontheNigeriandatasetareshowninTable1. The ROC curve (receiver operating characteristic curve) representsthemodel'soverallperformance.
AROCcurveisshownalongwiththevalueofAUC(Area UnderCurve)forthebestperformingclassifierinFig.3.
Five-foldcrossvalidationisusedhereforthevalidation purpose. Five-fold accuracies [0.99198026,0.99198026, 0.991363360.99136336,0.99136336].Theaverageaccuracy is0.9916101172115978forNigerianDataincaseofKernel SVM.
V.T. Van Hees et.al.[8] extracted each wavelet levels of Theta(4–8Hz),delta(1-2Hz),delta(2-4) Hz,alpha (8–16 Hz), beta (16–32 Hz), and gamma (32–64 Hz) using the RandomForestClassificationapproach.Theywereonlyable tocategorizeNigeriandatawithanaccuracyof0.78%(0.02 standarderrors),butourmethodproducedaccuracyresults of99.16%,98.49%,and98.28%usingKernelSVM,Random Forest,andDecisiontree,respectively.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Classifier Accuracy (%) Sensitivit y (%) F-1 Score (%)
(a) (b) Fig -1:(a)TheEEGsignal,(b)PowerSpectralDensityof oneepilepticsubject Fig -2:FlowchartoftheApproachI(Powerspectral densitymethod)
Random Forest 9848 9915 9924 9932 Decision Tree 9837 9904 9918 9932
NaiveBayes 7223 99.76 8375 7217 KernelSVM 99 16 9916 99 58 1 00
Table -1: PerformanceParametersforNigeriandata Fig -3:ROCcurvewithAUCvalueforKernelSVM
Precision (%)
TheTUHEEGCorpuscontains23257EEGrecordingsfrom 13551patients[16].Intheoveralldataset,73%oftheEEG data points could be assigned to abnormal sessions. A demographically balanced subset of the TUH EEG Corpus was hand-selected to establish the TUH EEG Abnormal Corpus. This subgroup consisted of 1529 normal EEG sessionsand1488aberrantEEGsessions,thebulkofwhich wererecordedatasamplingrateof250Hz.Thetrainingset contained 1190 abnormal and 1223 normal data, and the testsetcontained298abnormaland306normaldataasa result of further splitting. Filtering the raw data and removingallnon-eegsignalallowedforextremelyaccurate results.
Inceptionlayerswithexponentiallyrisingkernellengths areusedwithdenselycoupledrecurrentlayerstoproduce 1D convolution layers. In this study, GRUs are utilized in place of LSTMs since they require fewer parameters and enablefastergeneralizationwiththesameamountofdata. Theinceptionmodulemakesuseoffiltersofvarioussizesas
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
opposedtostandardconvolutionalneuralnetworks,which useasingle,uniformlysizedfilterinaconvolutionlayerto capturefeatures[17].Thefollowingconventionsareused throughout the paper to define Conv1D and GRU layers: (layername,filterlength,numberoffilters,stridesize)and (layer_name,numberoffilters).
Theinput/firstlayerofthemethodis(20000,22),where 20000 is the length of the signal and 22 is the number of channels.FiveconvolutionlayersreceivetheInputLayeras input.Eachlayerhasadifferentkernelsize(2,4,8,32,64),and eachlayerhasthesamenumberoffiltersandstrides(32,2). Each convolution layer's output is merged so that, when combined,eachlayergeneratesanoutputchannelof32and receives160channels.Fiveconcatenationlayersarecreated afterthefirstconcatenationbyrepeatingthestructure.We havefourGRUlayersafterthisblock.ThefifthConcatenation Layer provides input to the first GRU layer, which then outputstothesecondGRUlayer.Theoutputsofthefirstand second GRU levels are then combined. The output of the third GRU layer is (625,32). When the activation function wasultimatelybuilt,theoutputofthethirdGRUlayerwas concatenatedwiththeoutputsofthefirstandsecondGRU layers.
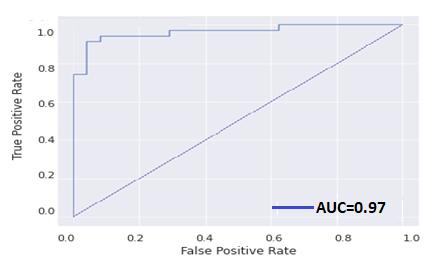
Table 2 displays the suggested ChronoNet Model's description.Abandpassfilterwithabandwidthof1–30Hz anda samplingfrequencyof 128Hzwasusedtofilterthe EEGdata.Forthefive-convolutionlayer,the"relu"activation functionwasused.BecausetheGRUlayerisbinary,weused the "sigmoid" activation function. The model was then trained using the parameters optimizer = "adam," loss = "binarycrossentropy,"andmetrics="accuracy"usingthe keras Framework. The Splitting of training and testing is 80:20forthisapproach.Theaccuracyafterfittingthemodel is97.20%,whereasRoyS.et.etal.[17]usedlinearlyvarying filter lengths of 3, 5, and 7 in a 1D convolution layer to produceanapproximate89.15%accuracyduringtraining. Five-foldCrossValidationisutilizedtovalidatetheproposed ChronoNet Model. Table 3 shows the values of the performanceparametersfortheChronoNetconfiguration. Fig.4showstheROCcurvewithAUCvaluefortheproposed ChronoNet Model. Table 4 shows the Comparison of the AccuracyforDifferentConfigurationofChronoNetMethod.
Table -2: Parameterdetailsofeachlayeroftheproposed ChronoNetmodel
Name of Layers Output Shape Kernel Size Stride
InputLayer
Convolutionlayer (conv1d_1-conv1d_5)
ConcatenationLayer1 (Concatenatingfiveconv1d (1-5)layer)
20000×22 - -
10000×32 2,4,8,32 ,64 2
10000×16 0 - 2
ConvolutionLayer (conv1d_6-conv1d_10)
ConcatenationLayer2 (Concatenatingfiveconv1d (6-10)layer)
ConvolutionLayer (conv1d_11-conv1d_15)
ConcatenationLayer3 (Concatenatingfiveconv1d (11-15)layer)
ConvolutionLayer (conv1d_16-conv1d_20)
ConcatenationLayer4 (Concatenatingfiveconv1d (16-20)layer)
5000×32 2,4,8,32 ,64 2
5000×160 - 2
2500×32 2,4,8,32 ,64 2
2500×160 - 2
1250×32 2,4,8,32 ,64
1250×160 - 2
ConvolutionLayer (conv1d_21-conv1d_25) 625×32 2,4,8,32 ,64 2
ConcatenationLayer5 (Concatenatingfiveconv1d (21-25)layer)
625×160 - 2 GRU_1 625×32 -GRU_2 625×32 -ConcatenationLayer6 (ConcatenatingGRU_1and GRU_2layer)
625×64 -GRU_3 625×32 -ConcatenationLayer7 (ConcatenatingGRU_1, GRU_2andGRU_3layer)
625×96 -GRU_4 32 -Dense 1 - -
Table-3:PerformanceparametersfortheChronoNetMethod Method name Accuracy (%) Sensitivity (%) PPV (%) F1 Score (%) ChronoNet Model 97.2 97.78 95.65 96.70
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Fig -4:ROCcurvewithAUCvaluefortheproposed ChronoNetModel
ComparisonoftheAccuracyforDifferent ConfigurationofChronoNetMethod
No. of Convolution al Layer (conv 1d)
No. of Blocks No. of Epochs Batch Size Accuracy (%)
5 5 120 12 97.2(±0.02 standarderrors)
8 8 120 12 33.33(±0.03 standarderrors)
6 6 100 10 95.56(±0.04 standarderrors)
6 6 50 8 93.33(±0.03 standarderrors)
6 6 80 5 94.44(±0.01 standarderrors)
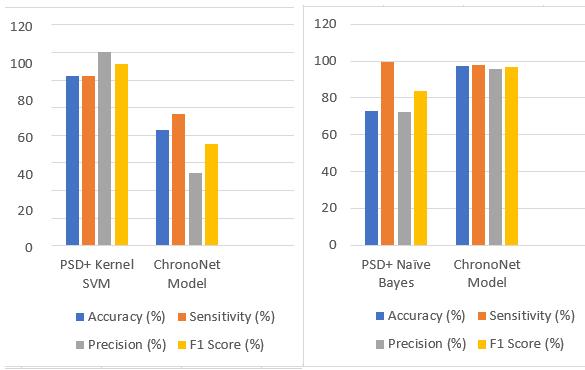
In this study, two techniques were used to determine if a patientwasseizure-proneornot.ThesuggestedChronoNet model was more stable for any type of data than the first methodsinceithighlighted themostimportantaspects of the data. While different classifiers were suitable for different types of data, a proposed ChronoNet design that addressestheissueoftrainingaccuracylossbroughtonby disappearing or expanding gradients incorporates several filters with exponentially variable lengths in the 1D convolutionlayersanddenseconnectionsintheGRUlayers. Thesignificantdifferencesbetweentheperformancemetrics of the two approaches are shown in Fig.5 (comparison between ChronoNet and PSD+Kernel SVM/Naïve bayes is shown to exhibit the novelty of the proposed ChronoNet model).
Fig -5:Significantdifferencesbetweentheperformance metricsofthetwoapproachesfordetectingEpilepsy
3 APPROACH II: CLASSIFYING SCHIZOPHRENIA USING LOGISTIC LINEAR REGRESSION AND DEEP CNN
3.1 Method I: Logistic Linear Regression
14paranoidschizophreniapatientsand14healthycontrols participatedinthestudy.19EEGchannels(Fp1,Fp2,F7,F3, Fz, F4, F8, T3, C3, Cz, T4, T5, P3, Pz, T4, T6, O1, O2) were usedinthetypical10-20EEGmontagetogatherthedataat asamplingrateof250Hz.Thedurationoftheepochswas setto25.Thefeatureextractors(mean,standarddeviation, kurtosis,rootmeansquare,skewness,etc.)wereutilizedto extractthevaluabledatafromthedataset. Thefeatureshave then all been concatenated to create a list of feature sizes (1142, 228). 12 (228/19) features from the list were received. The Training and testing ratio is 70:30 for this approach.
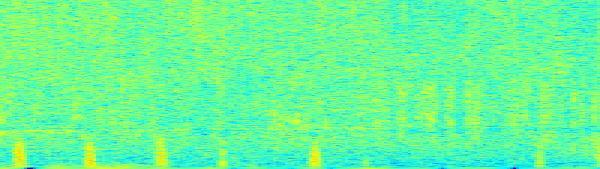
Alogisticregressionmodelisappliedtothedataafterit has been scaled for classification. Grid-SearchCV (CV=10) and 10-fold cross validation are combined to improve the performanceofthemodel.Afterfittingthemodel,itgivesan accuracyof69.8%whichisapproximately15%betterthan therelatedwork[18]forthe10-foldcrossvalidation.The eventrelatedspectralperturbation(ERSP)isshowninFig.6 for the clear understanding of the healthy people and schizophrenia patient. The Flow chart of the suggested methodisshowninFig.7.
The pre-processing part for the method II is same as the methodIfordeterminingschizophreniaaswehaveusedthe same dataset. The parameters for the proposed 15-layer Deep CNN model is shown in Table 5. Next, we used optimizer = "adam," loss = "binary cross entropy, “and metrics="accuracy"totrainthemodel.Wehaveusedthe "sigmoid" activation function. Splitting of training and
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
testingisselectedas80:20forthisapproach. Aftertraining the model, we set the batch size =10 and Epochs =10. To validate the proposed Deep CNN model, Five-fold cross validationisusedhere.Weachievedamaximumaccuracyof 85.11%, which is better than the work that was done previously[7,18].
(a) (b)
Fig -6:Theeventrelatedspectralperturbation(ERSP)of the(a)schizophreniapatientand(b)healthypeople
Fig -7:FlowchartoftheApproachI(LogisticLinear Regressionmethod)
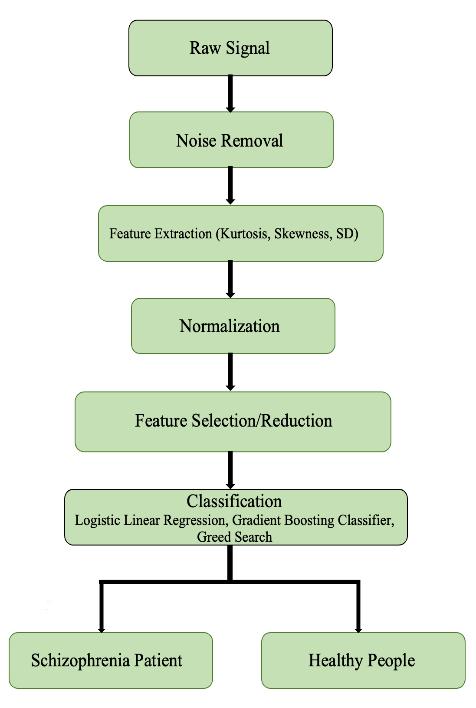
Table-5: Parameterdetailsofeachlayeroftheproposed CNNmodel Layers Name of Layers Output Shape Kernel/Pool Size Stride
Convolution 6248×5 3 1
MaxPooling 3124×5 2 2
Convolution 3122×5 3 1
MaxPooling 1561×5 2 2
Convolution 1559×5 3 1
MaxPooling 779×5 2 2
Convolution 777×5 3 1
Average Pooling 388×5 2 2
Convolution 386×5 3 1
Average Pooling 193×5 2 2
Convolution 191×5 3 1
Average Pooling 95×5 2 2
Convolution 93×5 3 1
Global Average Pooling
5 - -
Dense 1 - -
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
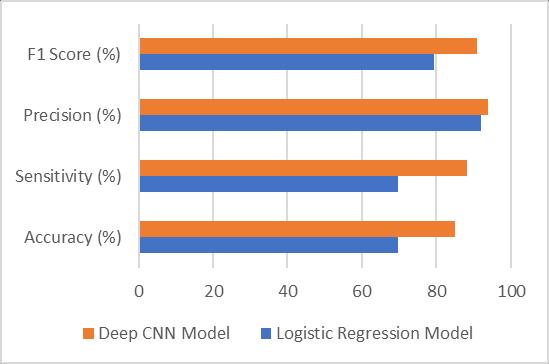
Twomethodswereillustratedfordeterminingschizophrenia. Amongthetwomethods,DeepCNNperformedbetterthan themethodusinglogisticlinearregression.Ifweincreasethe number of convolutional layers, the proposed Deep CNN Method provides better accuracy along with a trade-off betweenfiltersizeandkernelsize.Thesignificantdifferences betweentheperformancemetricsofthetwoapproachesfor thedetectionofschizophreniaisshowninFig.8
Fig -8:Thesignificantdifferencesbetweenthe performancemetricsofthetwoapproachesforthe detectionofschizophreniapatient
Two Comparison tables (Table 6 and 7) are shown in this sectiontoexhibitthenoveltyoftheworkwiththeexisting works.Tomakeitclear,afaircomparisonismadewiththe existing works for detecting Epilepsy (Approach I) using Proposed ChronoNet Method in Table 6, while Table 7 is drawntoshowthecomparisonoftheproposedDeepCNN network for detection of Schizophrenia patient with the relevantworks.
Table -6: Comparisonchartoftherelatedworkswiththe proposedmodel(ChronoNetModelforDetectingEpileptic Patient)
Network Layer Classifier Dataset and validation Accurac y (%)
DeepGated RNNnetwork [17]
14
1D-CNN[19] 23
1D-CNN[20] 15
SoftMax TUHEEG 5-foldcross validation (CV)
89.15
SoftMax TUHEEG 10-foldCV 79.34
SoftMax CHB-MIT 84
Train,Test validation
1DCNNLSTM[21] 7 Sigmoid TUHEEG 30-foldCV 89.73
DeepCNN and bidirectional LSTM[22]
CNNinspired byFBCSP [23]
Proposed Work ChronoNet
- SoftMax SEEDand DEAPdataset 10-foldCV
15 SoftMax CHB-MIT dataset 5-fold stratifiedCV
18 Sigmoid TUHEEG datasetand 5-foldCV
SEED:81 .54 DEAP:72 .38
90.9
97.20
Table -7: Comparisonchartoftherelatedworkswiththe proposedmodel(ProposedCNNModelforDetecting SchizophrenicPatient)
Networks Classifier Dataset and validation Accuracy (%)
AnalysisofEEG signalin Schizophrenia Detection[7]
Deepneural networklayerwiserelevance Propagation [25]
Multimodal Multivariate Pattern Recognition Analysis[26]
DeepLearning UsingfMRI[27]
Convolutional neuralnetwork [28]
SoftMax RepODforEEG inSchizophrenia 5-foldcross validation(CV)
SoftMax Multi-sitefcMRI rawdataset 1-foldCV
81.5 Discriminant DeepLearning withFunctional Connectivity MRI[24]
SoftMax Resting-state fMRIdataset 10-foldCV
- MindResearch NetworkCOBRE 20-foldCV
SoftMax MindResearch NetworkCOBRE 10-foldCV
Sigmoid National Instituteof Standardsand Technology (NIST) 5-foldstratified CV
81(leavesite-out transfer classificatio n)
82
Maximum accuracy= 75
84.3
Maximum accuracy= 70
Proposed Work:
DeepCNN Network(For Detecting Schizophrenia)
Sigmoid RepODforEEG inSchizophrenia 5-foldCV
85.11
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

AnEEG'sabilitytodetectabnormalbrainactivityisoftenthe firststepindiagnosinganeurologicaldisorder.Sincemanual EEGinterpretationisacostlyandtime-consumingactivity, anyclassifierthatautomatesthisfirstdistinctionwillhave theabilitytoshortentreatmentperiodsThisstudyemployed two methods for identifying epileptic patients and schizophreniafromhealthyones.Althoughthefirstmethod (welch spectral density) gives a very high accuracy than ChronoNetforEpilepsyclassification,Thelatteroneprovides stable result for all type of data. The Deep CNN Model outperformsthemethodinvolvinglogisticLinearRegression fordetectingschizophreniapatient.
[1] G.Wang,Z.Deng,andK.S.Choi,"DetectionofEpileptic SeizuresinEEGSignalswithRule-BasedInterpretation by Random Forest Approach": Springer International Publishing,2015.
[2] Y.Zhang,B.Liu,X.Ji,andD.Huang,"ClassificationofEEG Signals Based on Autoregressive Model and Wavelet PacketDecomposition,"NeuralProcessingLetters,vol. 45,pp.1-14,2017.
[3] C. Yang, Z. Deng, K. S. Choi, and S. Wang, "Takagi–Sugeno–KangTransferLearningFuzzyLogicSystemfor the Adaptive Recognition of Epileptic Electroencephalogram Signals," IEEE Transactions on FuzzySystems,vol.24,pp.1079-1094,2016.
[4] A.Craik,Y.He,andJ.L.Contreras-Vidal,“Deeplearning forEEGclassificationtasks:areview,”JournalofNeural Engineering,vol.16,no.3,p.031001,Feb.2019.
[5] A. Shoeibi et al., “Epileptic Seizures Detection Using Deep Learning Techniques: A Review,” International Journal ofEnvironmental Researchand PublicHealth, vol.18,no.11,p.5780,May2021.
[6] Cuesta–Frau,David&Miro,Pau&Jordan,Jorge&Oltra Crespo, Sandra & Picó, Antonio. (2017), "Noisy EEG signals classification based on entropy metrics. Performance assessment using first and second generation statistics". Computers in Biology and Medicine,vol.87,2017,pp.141-151.
[7] Mahato, S., Pathak, L. K., and Kumari, K. “Detection of Schizophrenia Using EEG signals”, Data Analytics in Bioinformatics: A Machine Learning Perspective. Beverly,MA:ScrivenerPublishingLLC,2021,pp.359–390.
[8] V.T. Van Hees, E. Van Diessen, M.R. Sinke, J.W. Buitenhuis, F. Van Der Maas, L. Ridder, “Reliable and automatic epilepsy classification with affordable,
consumer-gradeelectroencephalographyinruralsubSaharanAfrica”,BioRxiv,324954(2018).
[9] Roy S., Kiral-Kornek I., Harrer S.,”Chrononet: A deep recurrent neural network for abnormal eeg identification.”, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 11526,Springer,Cham(2018),pp.47-56.
[10] J. Heaton, “Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville:Deeplearning:TheMITPress,2016,800pp, ISBN: 0262035618,” Genetic Programming and EvolvableMachines,vol.19,Oct.2017.
[11] Kyunghyun Cho, Bart van Merriënboer, Dzmitry Bahdanau,andYoshuaBengio.2014.“OntheProperties of Neural Machine Translation: Encoder-Decoder Approaches”. In Proceedings of SSST-8, Eighth Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in StatisticalTranslation,pages103–111,Doha,Qatar.
[12] Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov,D.,Erhan,D.,Vanhoucke,V.,&Rabinovich,A, “Going deeper with convolutions”, In 2015 IEEE ConferenceonComputerVisionandPatternRecognition (CVPR),pages1–9,2015.IEEE.
[13] Huang,G.,Liu,Z.,VanDerMaaten,L.andWeinberger, K.Q.,“DenselyConnectedConvolutionalNetworks”, In ProceedingsoftheIEEEConferenceonComputerVision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, 21-26 July 2017, 4700-4708
[14] W. Zhou, Y. Liu, Q. Yuan, and X. Li, "Epileptic Seizure Detection Using Lacunarity and Bayesian Linear Discriminant Analysis in Intracranial EEG," IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 60, pp. 3375-3381,2013.
[15] A. H. Shoeb, "Application of machine learning to epileptic seizure onset detection and treatment," in International Conference on Machine Learning, 2009, pp.975-982.
[16] L.deDiegoandS.Isabel,“AutomatedInterpretationof Abnormal Adult Electroencephalograms,” MS Thesis, TempleUniversity,Jan.2017.
[17] Roy S., Kiral-Kornek I., Harrer S.,”Chrononet: A deep recurrent neural network for abnormal eeg identification.”, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 11526,Springer,Cham(2018),pp.47-56
[18] Oh, Shu Lih, Jahmunah Vicnesh, Edward J Ciaccio, RajamanickamYuvaraj,andURajendraAcharya.2019. "Deep Convolutional Neural Network Model for Automated Diagnosis of Schizophrenia Using EEG Signals"AppliedSciences9,no.14:2870.
Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page249
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[19] Yıldırım, U. B. Baloglu, and U. R. Acharya, “A deep convolutional neural network model for automated identification of abnormal eeg signals,” Neural ComputingandApplications,pp.1–12,2018.
[20] Z. Wei, J. Zou, J. Zhang, and J. Xu, “Automatic epileptic EEGdetectionusingconvolutionalneuralnetworkwith improvements in time-domain,” Biomedical Signal ProcessingandControl,vol.53,p.101551,Aug.2019.
[21] H. RaviPrakash et al., “Deep Learning Provides Exceptional Accuracy to ECoG-Based Functional LanguageMappingForEpilepsySurgery,”Frontiersin Neuroscience,vol.14,May2020.
[22] A. Samavat, E. Khalili, B. Ayati and M. Ayati, "Deep LearningModelWithAdaptiveRegularizationforEEGBased Emotion Recognition Using Temporal and FrequencyFeatures,"inIEEEAccess,vol.10,pp.2452024527,2022.
[23] I.Jemal,N.Mezghani,L.Abou-AbbasandA.Mitiche,"An Interpretable Deep Learning Classifier for Epileptic SeizurePredictionUsingEEGData,"inIEEEAccess,vol. 10,pp.60141-60150,2022.
[24] L.-L.Zengetal.,“Multi-SiteDiagnosticClassificationof SchizophreniaUsingDiscriminantDeepLearningwith FunctionalConnectivityMRI,”EBioMedicine,vol.30,pp. 74–85,Apr.2018.
[25] W.Yanetal.,“Discriminatingschizophreniafromnormal controls using resting state functional network connectivity: A deep neural network and layer-wise relevance propagation method,” in 2017 IEEE InternationalWorkshoponMachineLearningforSignal Processing,MLSP2017-Proceedings,2017,pp.1–6.
[26] C. Cabral et al., “Classifying Schizophrenia Using MultimodalMultivariatePatternRecognitionAnalysis: EvaluatingtheImpactofIndividualClinicalProfileson theNeurodiagnosticPerformance,”SchizophrenicBull, vol.42,no.suppl_1,pp.S110–S117,Jul.2016.
[27] Zheng, JinChi & Wei, XiaoLan & Wang, JinYi & Lin, HuaSong&Pan,HongRun&Shi,YuQing.,‘’Diagnosisof Schizophrenia Based on Deep Learning Using fMRI,’’Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine,pp.1-7,2021.
[28] Raymond Salvador, María Ángeles García-León, Isabel Feria-Raposo, Carlota Botillo-Martín, Carlos MartínLorenzo, Carmen Corte-Souto, Tania Aguilar-Valero, “Fingerprints as Predictors of Schizophrenia: A Deep LearningStudy,”SchizophreniaBulletin,2022.
SENJUTI RAHMAN received the B.Sc. degree from Rajshahi University of EngineeringandTechnology,Bangladesh, in 2016 in electronics and telecommunicationengineering.Currently, she is pursuing the M.Sc. degree in electricalandelectronicengineeringfrom thesameuniversity.From2018to2022, shewasworkingasalecturerinthedepartmentofEEEin EasternUniversity(EU),Dhaka,Bangladesh.From25thJuly, 2022shejoinedAhsanullahUniversityofEngineeringand TechnologyasaLecturerintheEEEdepartment.Shehasa totalof7conferencepapersinICECTE2016,ICEEE2017, ICRPSET 2022, ICECE 2022, ICCIT 2022, 4IREF 2022 and twojournalshabeenacceptedattheEuropeanJournalof ElectricalEngineeringandComputerScience(EJECE).Four of her research work are under process. Her research interests include Biomedical Engineering, Machine Learning,andDeepLearning

Author’s formal p hoto
Author’s formal p hoto
MD MEHEDI HASAN received the B.Sc. degree from Rajshahi University of Engineering and Technology, Bangladesh, in 2016 in electronics and telecommunicationengineering.From2017 to 2019, he was working as a Junior SoftwareEngineeratSmartAspectsLtd.In Dhaka, Bangladesh. Recently, from December,2019hejoinedasaSoftwareEngineeratZantrik, Dhaka, Bangladesh. His research interests include Biomedical Engineering, Machine Learning, and Deep LearningBiomedicalEngineering,MachineLearning,Deep Learning,ComputerVision,DataScience.Hisworkingarea covers Android Mobile Application Development, Web Development, Database Management, Machine Learning, DeepLearning.Hehasagoodgraspof someprogramming languages, such as Java, C#, Python, C++, SQL. He has completedtwoonlinecourses,AIforMedicalDiagnosis-an onlinenon-creditcourseauthorizedbyDeepLearning.AIand offeredthroughCourseraandMachineLearningProjectsfor Healthcare on Udemy. He has 5 international conference papersinICEEE2017,4IREF2022,ICECE2022,ICCIT2022 and two journals have been accepted at the European Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EJECE). Four of his recent research works are under process.

DR.AJAYKRISHNOSARKAR hasreceived Ph. D in Electronic and Computer Engineering from Griffith University, Australia,M.ScinEEEfromJapanandB.Sc. in EEE from RUET, Bangladesh. He is currently working as a professor in the department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering(EEE)atRajshahiUniversityof
Author’s formal p hoto

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2023, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page251
Engineering and Technology (RUET), Rajshahi-6204, Bangladesh.HeiscurrentlythememberofIEEE;Instituteof Engineers Bangladesh (IEB) and he had the position in different organizing and technical committees in different internationalconferencesatBangladeshandabroad.Heisa reviewer of several journals such IEEE Access, IEEE PhotonicsJournal,ComputersandElectronicsinAgriculture etc.andtechnicalpaperssubmittedindifferentinternational conferences in Bangladesh and abroad. His research interests include Sports and Biomedical Engineering, PhotonicCrystal Fiberand Biosensors,Microwaveand RF circuits&Devices,Microwaveabsorptions,ThinFilms.