International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Abstract: Neural Network based techniques are being continuously evolved for classification of lung nodules detection. Different algorithms based on soft computing and hard computing has been developed to apply on nodule detection. In current research, an intelligent technique inspired from neural network algorithm have been applied and evaluated successfully to classify lung nodule. Feature extraction based on grey level covariance matrix integrated gradient (GLCMIG) technique is applied. Various texture based features like entropy, energy are extracted for nodule CT scan images then classification based on these features has been done with Intelligent Neural Network Algorithm (INNA). A contrast has been madewithothertechniquestochecktheefficiencyoftheproposedmethod.Simulationresultsshowsthatproposedtechnique achieved98.99%accuracytoclassifycancerdatasetswhichismoreas comparedothertechniquesinliterature.Performance parameters like TP rate, ROC and Precision are highest for proposed method amongst other method. Hence, proposed algorithmisoptimumtoclassifylungnoduledetection.
OnceapulmonarynodulehasbeennoticedbyCT,anumberofimagingmodalitiescanbeutilizedtoassistancesupplementary notice the likelihood of malignancy. The bulk of facts involve FDG PET alongside or lacking CT. Studies have additionally assessed the utility of scintigraphic methods retaining 99m-technetium (99m Tc)-labeled compounds alongside solitary photonemissionCT(SPECT),MRIencompassingdiffusion-weighted(DW)andvibrantcontrast-enhanced(DCE)imagingand DCE-CT.PETandPET-CT.PET-CTisacross-sectionalimagingmethodthatprovidesbothanatomicalandusefulinformation.It hascometoberesolutelyinstitutedintheassociationpathwaysofcountlessmalignancies,encompassinglungcancer.
Keywords –GLCMIG, INNA, ADT, RFA, RTA
Pulmonarynodulesarewellorpoorlycircumscribed,considering roundedconstructionsthatmaterializeonimagingasfocal opacities and by instituted meaning are≤3 cm in diameter and encircled by aerated lung (table 1). They might be solitary or countlessanddonothaveassociatedabnormalitiesinthethorax,suchaslymphadenopathyorpleuraldisease.Thismeaning isnowadaysnormallyrangedtoencompassnodulesinlinkalongsidethepleura.Thenowadayscomprehensiveuseofhelical multi-detector line CT has made it commonplace to notice, incidentally, nodules <1 cm in diameter as well as SSNs that are slightlyorwhollyground-glassopacities.Thesetiniernodulesarguablypresentalargerclinicalexaminationthantheirlarger counterpartsandaresubsequentlyencompassedinthescopeofthistopic.Whereasappropriate,guidanceistailoredtothese disparate clusters even nevertheless it must be noted that in the works precise definitions are not always given and a collection of words are used. This case provides an adequate synopsis of the lung nodules that can furnish a momentous examinationfortheclinicians.Thedetectionofpulmonarynodulesiscommon.InpopulacesexperiencingCTscreeningandat an elevated chance of lung cancer, nodules are noticed in 20–50% of people, reliant on the size of the cut-off point for delineating a nodule. The bulk of these nodules are puny and benign but a slight will be malignant and, according to the NationwideLungScreeningExamination(NLST),competenttreatmentwillsconsequenceinareductioninmortality.Itisvital to have clear guidance considering the most competent method to grasp these nodules and an assessment of how data from screening studies can be utilized to escort the method on supplementary populaces and individuals. It is acknowledged that the bulk of the facts learned from this case come from states beyond the UK and that there are potentially vital contrasts in populacesasaconsequenceoftheirgeographicallocation.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Data mining [1] is the process of digging data for discovering latent patterns which can be translated into valuable information. Data mining usage witnessed unprecedented growth in the last few years. Of late the usefulness of data mining techniques has been realized in Healthcare domain. This realization is in the wake of explosion of complex medical data. Medical data mining can exploit the hidden patterns present in voluminous medical data which otherwise is left undiscovered.Dataminingtechniqueswhich areappliedtomedicaldataincludeassociation ruleminingforfindingfrequent patterns, prediction, classification and clustering. Traditionally data mining techniques were used in various domains. However, it is introduced relatively lateintotheHealthcaredomain.Nevertheless,asontodaylotofresearchisfoundinthe literature. This has led to the development of intelligent systems and decision support systems in Healthcare domain for accurate diagnosis of diseases, predicting the severity of various diseases, and remote health monitoring.[18] Especially the dataminingtechniquesaremoreusefulinpredictingheartdiseases,lungcancer,andbreastcancerandsoon.Thedatamining techniques that have been applied to medical data include Apriori and FPGrowth, [19]unsupervised neural networks, linear genetic programming, Association rule mining, Bayesian Ying Yang , decision tree algorithms like ID3, C4.5, C5, and CART , outlierpredictiontechnique,[20]Fuzzyclusteranalysis,classificationalgorithm,BayesianNetworkalgorithm,NaiveBayesian, combination of K-means, Self Organizing Map (SOM) and Naïve Bayes, [21]Time series technique,combination of SVM, ANN andID3,clusteringandclassification,SVM,,FCM,k-NN,andBayesianNetwork.
Umar et al[1] applied data mining techniques for birth outcomes. Cong et al.[2] stated that hereditary syndromes can be detectedautomaticallyusingdataminingtechniques.Haietal.[3]discussedmedicaldataminingthroughunsupervisedneural networks besides a method for data visualization. They also emphasized the need for preprocessing prior to medical data mining.Carshenetal[4]identifiedtheneedfordataminingmethodstominemedicalmultimediacontent.Shariq[5]identified problemsinmedical data mining.Theproblemsinclude missing values, data storage with respect to temporal data and multi-valued data, different medicalcodingsystemsbeingusedinHospitalInformationSystems(HIS).Sunil[6]exploredand analyzedtwoprogrammingmodelssuchasneuralnetworks,andliniergeneticprogrammingfor medicaldatamining.Thanh et al[7] proposed and implemented a symbolic rule extraction workbench for generating emerging rule-sets. Xiang et al.[8] exploredtheusageofrule-setsas resultsofdataminingforbuildingrule-basedexpertsystems. Markus etal[9]proposedan algorithmforextractingassociationrulesfrommedicalimagedata.Theassociationruleminingdiscoversfrequentlyoccurring
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
items in the given dataset. Doron et al [10] proposed a classification method based on Bayesian Ying Yang (BYY) which is a threelayeredmodel.Theyappliedthismodeltoclassifyliverdiseasethroughautomaticdiscoveryofmedicaltrends.Adepele et al.[11] proposed architecture for mining geno-medical data in heterogeneous and grid-based distributed infrastructures. Cindy et al.[12] focused on decision tree data mining algorithm for medical image analysis. Especially they studied on lung cancerdiagnosisthroughclassificationofx-rayimages.Jeongetal.[13]presentedanoutlierpredictionmethodforimproving performanceofclassificationaspartofmedical data mining. Jannetal[14]applied fuzzy clusteranalysis for medical images. They used decision tree algorithm to classify mammography into normal and abnormal cases. Safwan et al[15] applied classification algorithmto diagnose cardio vascular diseases. For classification effectiveness they focused on two feature extraction techniques namely automatic feature selection and expert judgment. Yanwai et al[16] introduced web based data miningfortheapplication oftelemedicine.Tsang etal[17]presented anapproachtointegratePSO rulemining methodsand classifier on patient dataset. They used Particle Swarm Optimization technique as well. The results revealed that, their approachiscapableofperformingsurgerycandidateselectionprocesseffectivelyinepilepsy.
Anintelligentneuralnetworkalgorithm(INNA)isatrainedfeedforwardneuralnetworkmodelthatmapssetsofinputdata ontoasetofappropriateoutputs.AnINNAconsistsofnumerouslayers of nodes in a directed graph, with each layer fully connected to the next one. Except forthe input nodes, each node is a neuron with a nonlinear activation function. INNA utilizesa learningrulecalledbackpropagation fortrainingthenetworkthroughattributeselectionfeature withenhanced learning rate. INNA is a modification of the conventional neural network and can distinguish data that are not linearly separable



International Research Journal
Engineering
Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
. The Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) and associated texture feature calculations are image analysis techniques. Given an image composed of pixels each with an intensity (a specific gray level), the GLCM is a tabulation of how often differentcombinationsofgraylevelsco-occur in an image or image section Texture feature calculations use the contents of the GLCMtogiveameasureofthevariationinintensityatthepixelofinterest.Manytexturebasedfeaturesareextracted from CT lung images with nodule presence using GLCM based gradient approach. Features extracted are autocorrelation, contrast, entropy, energy, Dissimilarity, cluster shade, cluster prominence. These features are selected based on their mathematicaluniformityandlinearityascomparedtootherfeaturesbasedonshape,location,coloretc.
Autocorr Contrast Entropy DissimilrCshade Cprom Energy
23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 0.97 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 0.97 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66 23 0 0.56 0 -0.75 1.3 0.65 23 0 0.56 0 -0.75 1.31 0.65 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66 23.1 0 0.55 0 -0.75 1.31 0.66
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
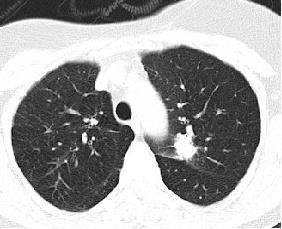
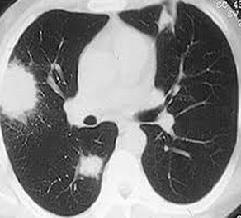
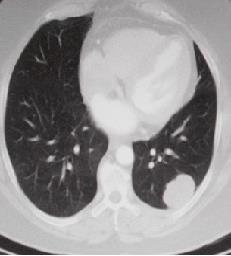
Fig.1CTscansLungNoduleImages
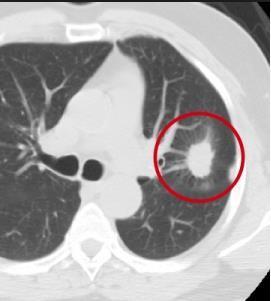
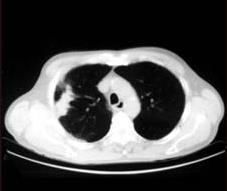
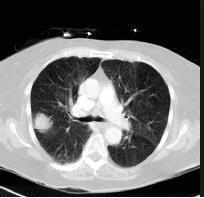
V Simulation Results
Comparativeanalysis is doneforchecking the effectiveness ofthe proposedmethod. As observedinTable1., wecansee thatproposedmethodINNAishavinglowcomputationtimeascomparedtoothertechniques.
Table 1. Computation Time for different Decision Tree Algorithms
Techniques Time taken to buildmodel(sec)
RandomTreeAlgorithm 0.1 AlternateDecision 0.05 Algorithm RandomForestAlgorithm 0.2 ProposedMethod 0.03
Table
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Table 3.AccuracybyClasswithRTA
Class Recall TP Rate FP Rate Precision F-Measure ROCArea
Non-Cancerous 0.6 0.6 0 1 0.75 0.6
Cancerous 1 1 0.4 0.714 0.833 0.6 WeightedAvg. 0.8 0.8 0.2 0.857 0.792 0.6
Table4.AccuracybyClasswith RFA
Class Recall TPRate FPRate Precision F-Measure ROCArea
Non-Cancerous 0.851 0.851 0.624 0.763 0.805 0.691 Cancerous 0.376 0.376 0.149 0.516 0.435 0.691 WeightedAvg. 0.71 0.71 0.483 0.69 0.695 0.691
Table 5.AccuracybyClasswithADA
Class Recall TPRate FPRate Precision F-Measure ROCArea
Non-Cancerous 0.6 0.6 0 1 0.75 0.6 Cancerous 0.6 1 0.4 0.714 0.853 0.6 WeightedAvg. 0.6 0.8 0.2 0.865 0.671 0.6
Intable6,wecanseethatproposedmethodachievedhighestaccuracyascomparedtootherdataMiningtechniques.
Technique Proposed Meth od RFA RTA ADA NFR FR AA ATS AND Accuracy % 98% 82% 80% 84% 95% 94% 85.3% 89.6% 88.6%
Table 7.AccuracybyClasswithINNA
Class Recall TP Rate FP Rate Precision F- Measure ROC Area
Non- Cancerous 1 1 0 1 1 1 Cancerous 1 1 0 1 1 1 Weighted Avg. 1 1 0 1 1 1
From Table 7., we can see that True positive rate ,precision of solution, F measure and ROC value is highest for proposed techniqueINNAascomparedtoother methodsasshownintable 2,3,4,5.Hence,proposed method INNAiseffectiveintesting parameters.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
TheproposedINNAbasedapproachevolvedasoptimalapproachtoclassifythecancerimages witharemarkableaccuracyof 98% and fast computation time of 0.03 seconds as comparedto other technique and other classification methods. With suchhighaccuracyin proposedmethod,itwillbeeasytoidentifythecancerandnoncancerpatientsfromdifferentattributes oflungnoduleforlargedatachunkswhereotherdecisiontreealgorithmsfailtoachievehighaccuracy.
TheauthorswouldliketothankthemanagementofGNDECforprovidingfacilitiestocarryoutthiswork.
[1] UmairAbdullah(2008). “AnalysisofEffectivenessofAprioriAlgorithminMedicalBillingDataMining”.Proceedingsof IEEE.,pp.1-5.
[2] Cong-RuiJiandZhi-HongDeng. (2009).MiningFrequent Ordered Patterns withoutCandidateGeneration. Proceedingsof IEEE., pp.1-5.
[3] Hai-TaoHeandShi-LingZhang.(2007).“ANewmethodforIncrementalUpdatingFrequentpatternsmining”, Proceedingsof IEEE, pp.1-4.
[4] CarsonKai-SangLeung,ChristopherL.CarmichaelandBoyuHao.(2007).“EfficientMiningofFrequentPatternsfrom UncertainData”,.Proceedingsof IEEE ,pp.489-494.
[5] ShariqBashir,ZahidHalim,A.RaufBaig.(2008).,”MiningFaultTolerantFrequentPatternsusingPatternGrowth Approach”.Proceedingsof IEEE ,pp.172-179.
[6] Sunil Joshi and Dr. R. C. Jain. (2010). “A Dynamic Approach for Frequent Pattern MiningUsingTranspositionof Database”,Proceedingsof IEEE,pp.498-501.
[7] Thanh-Trung Nguyen. (2010).”An Improved Algorithm for Frequent Patterns MiningProblem”,Proceedingsof IEEE, pp.503-507.
[8] Xiaoyong Lin and Qunxiong Zhu. (2010). “Share-Inherit: A novel approach for miningfrequentpatterns”, Proceedingsof IEEE,pp.2712-2717.
[9] Markus Brameier and Wolfgang Banzhaf. (2001).”A Comparison of Linear GeneticProgrammingandNeural NetworksinMedicalDataMining”,Proceedingsof IEEE ,pp.1-10.[10]DoronShalviandNicholasDeClaris.,(2008).“An UnsupervisedNeuralNetworkApproachtoMedicalDataMiningTechniques.”,Proceedingsof IEEE ,pp.1-6.
[11] Adepele Olukunle and Sylvanus Ehikioya, (2009). “A Fast Algorithm for Mining
AssociationRulesinMedical ImageData”,Proceedingsof IEEE,.pp.1-7.
[12] Cindy L. Bethel and Lawrence O. Hall and Dmitry Goldgof (2007). “Mining for
ImplicationsinMedicalData.”, Proceedingsof IEEE , pp.1-4.
[13] Jeong-YonShim,LeiXu(2009).“MedicalDataMiningModelforOrientalMedicineVIA
ByBinaryIndependentFactor analysis”,Proceedingsof IEEE ,.pp.1-4.
[14] Jenn-Lung Su, Guo-Zhen Wu, I-Pin Chao (2001). “The Approach of Data Mining Methods For Medical Database “,Proceedingsof IEEE ,pp.1-3.
[15] Safwan Mahmud Khan Md. Rafiqul Islam Morshed U. (2006). “Medical Image ClassificationUsinganEfficientData MiningTechnique”,Proceedingsof IEEE,pp.1-6.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

[16] Yanwei Xing, Jie Wang and Zhihong Zhao (2007). “Combination data mining methods withnew medical data to predictingoutcomeofCoronaryHeartDisease”. Proceedings of IEEE.pp.1-
[17]Tsang-HsiangCheng,Chih-PingWei,VincentS.Tseng(2009).“FeatureSelectionforMedicalDataMining:Comparisonsof ExpertJudgmentandAutomaticApproaches”.
[18] Mohammad Saraee, George Koundourakis, Babis Theodoulidis. (2007). “EasyMiner: Data Mining In Medical Databases”,Proceedingsof IEEE,pp.1-3.
[19] Sam Chao(2009) “An Incremental Decision Tree Learning Methodology Regarding Attributes In Medical Data Mining”.ProceedingsoftheEighthInternationalConferenceonMachineLearningandCybernetics,Baoding, pp.101-105.
[20] My Chau Tu AND Dongil Shin (2009). “A Comparative Study of Medical Data Classification Methods Based on DecisionTreeandBaggingAlgorithms.”,Proceedings of
Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072 5. Proceedingsof IEEE.pp.1-6. IEEE pp.1-5.
[21] Vili Podgorelec, Marjan Heriko Maribor, (2006).,” Improving Mining of Medical Data by Outliers Prediction.”, Proceedingsof IEEE, pp.1-6.
[22] S.Ozekes, O.OsmanandO.N.Ucan.”Noduledetectioninlungsregionthat’ssegmentedusing geneticcellularneural networksand3Dtemplatematchingwithfuzzyrulebasedthresholding”,Vol.9,No.1,pp.1-9,Feb.2008.
[23] S.G. Armato 3rd , M. B. Altman, J. Wilkie, S. Sone, F. Li, K. Doi, and A. S. Roy. ”Automated lung nodule classification followingautomatednoduledetectiononCT:Aserialapproach”,Med.Physics,Vol.30,No.6,pp.1188-1197,June2003
[24] M. Dolejsi and J. Kybic, ”Automatic two-step detection of pulmonary nodules,” in Proceedings of SPIE, ser. Medical Imaging2007:Computer-AidedDiagnosis,M.L.GigerandN.Karssemeijer,Eds.,vol.6514.SPIE,February2007,pp.1-12.
[25] J. S. Kim, J. H. Kim, G. Cho, K. T. Bae, ”Automated Detection of Pulmonary Nodules on CT Images: Effect of section thicknessandreconstructioninterval”,JournalofRadiology,Vol.236,pp.295-299,2005