International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1Associate Professor, Department of Information Technology, KKR & KSR Institute of Technology and Sciences(A), Guntur, India.
2,3,4,5Undergraduate Students, Department of Information Technology, KKR & KSR Institute of Technology and Sciences(A), Guntur, India. ***
Abstract - With today's technology, each person's online presence opens the door to a massive informational vast collection that can be used for a broad variety of applications, ranging from analyzing market trends to understanding the general emotional state of the population. Text and sentiment analysis is now lot simpler than it was a few years ago because to advances in technology and NLP approaches. Each Tweet's label reflects a variety of disasterrelated data that could be used in many ways during an emergency response. When someone tweets a warning about a crisis or impending tragedy and our BERT models immediately identify this, we are able to respond as quickly as possible, which helps to save lives. BERT is a free machine learning framework for handling natural language (NLP). Our project's primary goal is to determine whether or not a tweet refers to a genuine disaster.
Words: Tweets, Bidirectional Encoder RepresentationsfromTransformers(BERT),NLP,Disaster
The traditional method of classifying texts usually uses Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machine, Naive Bayes, Gradient Boosting, and other basic machine learning models. In order to feed text sequences into classifiers, which may experience the issue of typing error and producenoisywordsforthecorpus,thesemethodsrequire pre - processing and feature engineering processes to encodetextsequencesinvectorform.
The method for compressing text into vector forms affects how well the model performs. In this case, comprehending word context is crucial for analyzing a tweet's intention. A tweetlikethiscanbeanexample:"Sheclaimsthatnooneis to blame for her disease. It was merely a natural accident. Despitetheterm"accident"beingincluded,itdoesnotrefer to any danger or emergency but rather describes a typical discourse. Let's say that a similar tweet would read, "He had a workplace accident, I was hurt." In this context, "accident" refers to a catastrophe, and the tweet is describing an emergency. The two examples demonstrate howasinglewordcanhaveseveralmeaningsdependingon itscontext.
Therefore,it'scriticaltocomprehendwordcontextinorder toevaluatetheattitudeandaimofatweet.
Various researchers suggested various approaches of decipheringaword'smeaning.
Using neural network-based techniques, such as Skip-gram andFastText,itispossibletolearnwordembeddingsfrom enormous word corpora, which is useful for completing many NLP tasks. These techniques are also employed for Twitter data sentiment analysis. The static embedding offered by such embedding learning techniques, however, only applies to a single word in a document. As a result, in the two examples given above for these techniques, the definitionoftheword"accident"wouldremainthesame.
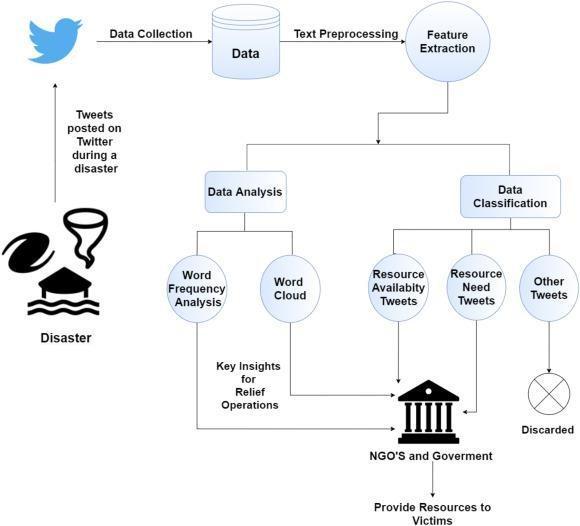
Duringanyemergencysituation,TwitterorFacebookserve asaplatformforinformationdissemination.Location,user, incident type, personal harm, and infrastructure damage areall included in thisdata. The informationindicatesthat the crisis is under control and For rescue operations, damage and location estimation is done. However, it is tough to rescue because of the speed and volume of information that come at one, making it harder to distinguish vital information from irrelevant. Our model aims to automatically extract important information and classifications.
Theamountoftimeavailabletoprotectpeopleduringan incident is limited. Therefore, the rescue/protection effort should be launched as soon as feasible. Twitter is now a significant communication tool platform. By disseminating the information or word of the damage, it greatly aided. It becamemoredifficultforcommunitiesaffectedbydisasters and rescue teams to act promptly since it was harder to distinguishsignificantonesfromirrelevantones.OurBERT technology, which aids in deciphering the meaning of ambiguous language in text, can rapidly identify tweets
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
regardingemergenciesorloomingdisasters.Thiswouldbe abletorespondmorequicklythanusual,savinglives.
Recognizing pertinent posts on the social network, in this case Twitter, is the main goal. Recent advancements in the field of NLP have had an impact with common techniques forthisparticulartypeofchallenge.
Recent research has revealed that deep learning is among thefinesttechniquesformanagingnaturallanguage.
Fordeep learning, the supervised training procedure using alotofdataproducesstrongresults.Adeeplearningmodel called BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)wascreatedbyGoogle.SinceGooglemadeit available,themajorityofushaveaccepteditanduseditfor a variety of text classification jobs. One of the most recent NLP development milestones, the release of BERT marked thestartofanewphaseinthefield.
Social networking sites like Facebook and Twitter have beenextremelypopularinrecentyearsasameansofonline communication that generates massive amounts of data. Additionally, during disasters, people post enormous amounts of timely and relevant information on these platforms, which is beneficial to the charitable organisations for disaster relief efforts. However, it is not simpletochanceuponandidentifytweetsandpostingsthat areconnectedtoacurrentevent.Forthepurposeoffinding tweetslinkedto the disaster,manydifferentmethodshave been devised. Some of these methods have relied on conventional machine literacy techniques, but more recently,DeepLearningtechniqueshavebeenadvocatedas efficient means to categorise tweets in emergency situations. Here is a quick rundown of the popular models. Do not use abbreviations in the title or heads unless they areunavoidable.
Regarding conventional methods, Avvenuti et al. have created a social media-based system for earthquake discovery that is based on tweets and Twitter replies. To cut down on irrelevant material, characteristics like URLs, citations, words, characters, punctuation, and shoptalk and derogatory language are also utilised in bracket stages. They eventually developed a temporal analysis burst finding method that counts the amount of communications within a time window. While the authors in used Support VectorMachine(SVM)asaclassifiertofirstfilterirrelevant tweetsbeforeminingTwitterdataforreal-timeearthquake detection.Then,aprobabilisticmodelthatincorporatesthe
toxic process is created for temporal analysis in order to determinethetimeatwhichtheearthquakeoccurred.
Recently,somemethodshavesuccessfullyclassifiedtweets duringacatastropheeventusingdeeplearningtechniques. As an example, Caragea et al. have suggested an ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks-basedmethodologyisused to find instructive messages in social media aqueducts during crisis occurrences. On numerous datasets of dispatches from flooding events, this strategy has been demonstrated to significantly outperform models that employ the "bag of words" and n-grams as features. Text mining utilising Natural language processing has produced a number of noteworthy and laudable research achievements.
[1] The authors Hamid Bagheri and Md Johirul Islam had developed much predictive model for sentiment analysis of twitter (Bagheri H , Islam Md J, 2017) . They usedTextblobpythonlibraryfortextprocessingandNLTK for Natural language Processing. They classified tweets based on movies, politics, fashion, fake news, justice and humanityinto3categoriesoftweets–positive,neutraland negative.
[2] The authors Ali Hasan, Sana Moin, Ahmad Karim, and Shahaboddin Shamshirband had collected tweets pertainingtocertainpoliticaltopicsandhastagsoriginating in Pakistan and did sentiment analysis of the tweets using NaiveBayesandSVMclassifier(HasanA,MoinS,KarimA, Shamshirband S , 2018) . They used Textblob , SentiWordNet and WWSD for text analysis and did a comparison after classifying the tweets into positive , neutralandnegativecategories.
[3] TheauthorsAurangzebKhan,BaharumBaharudin, LamHong Lee, KhairullahKhanhadworkedinthe field on text mining ofNLPusingfeatureextraction (tokenization, stop-words removal , stemming) ,feature selection (document vector representation) and did a comparative study of text classification using SVM , Naive Bayes and KNN(KhanA,BaharudinB,LeeLH, KhanK,2010) .
[4] Jermaine Marshall , Dong Wang Authors showed that Mood-Sensitive Truth Discovery For Reliable Recommendation Systems in Social Sensing. This work is motivated by the need to provide reliable information recommendation to users in social sensing. Social sensing has become an emerging application paradigm that uses humans as sensors to observe and report events in the physicalworld.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page168
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Afunctional requirement specifieshowa system or oneof its components should function. A function is defined as a collectionofinputs,behaviors,andoutputs.Italsorelieson thekindofsystemthatusestheprogramme,theanticipated users,andthekindofsoftware.
• Windows7
• Numpy
• Keras
• Seaborn
• TensorfFlow
• GoogleCollab
Google Collab: Google Collab was created to give anyone who requires accesstoGPUsandTPUsforbuildingamachinelearningor deeplearning model freeaccesstothem.Amoreadvanced version of Jupyter Notebook is Google Collab. The interesting capabilities that each contemporary IDE offers are abundant in Google Collab, in addition to many others. Belowisalistofsomeofthemorefascinatingaspects.
Features of Google Collab:
• Interactive tutorials for learning neural networks andmachinelearning.
• Create and run Python 3 programs without a local setup.
• UsetheNotebooktorunterminalcommands.
• ImportdatafromoutsideresourceslikeKaggle.
• YournotebooksshouldbesavedtoGoogleDrive.
• No-costcloudcomputing,GPUs,andTPUs.
• IntegratewithTensorFlow,PyTorch,andOpenCV.
• Directlyimportorpublishto/fromGitHub.
• Processor-i3
• Memory-2GBRAM
A non-functional requirement is one that specifies criteria ratherthanspecificbehavioursthatcanbeusedtoevaluate howwellasystemoperates.
The following are qualities of a system, sometimes known asnon-functionalrequirements:
• Legal or Regulatory: Which industry's regulations mustaproductabideby?
• Performance: Examine how well the product respondstouseractivity.
• Usability:Theproductissimpletouse.
• Theapplicationoughttorunonanyplatform.
• It'simportanttopreserveconsistency.
• It needs to consistently anticipate the same outcomeforsimilardata.
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT),amodelthatwehavesuggested,givesembeddings of a word based on its context terms. When performing various NLP tasks including entity recognition, text classification, and text summarization. Traditional embedding learning techniques were outperformed by the BERT model. However, it is intriguing to learn how contextual embeddings could aid in comprehension of literature relating to disasters. Due to this, we intend to examine the catastrophe prediction job utilizing Twitter data in this study using both context-free and contextual embeddings. For the prediction job, where the word embeddings are usually used as input to the models, we apply several conventional machine learning techniques and neural network models. Contextual embeddings performbetter,aswedemonstrate.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
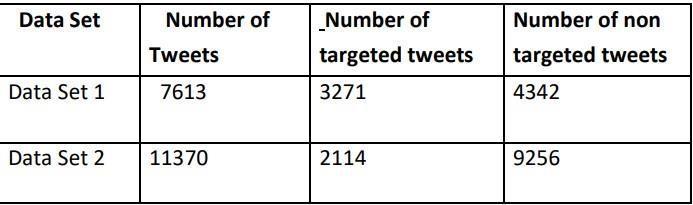
We used the Kaggle dataset for this study. "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/laxmimerit/twitterdi saster-predictiondataset/master/train.csv" allowed users to download the dataset. We evaluate if a particular tweet specifically mentions a disaster based on its 10873 comments.57.03%ofthe10,873datapointsweremadeup of tweets about disasters, leaving the remaining data. The datasetweutilizedincludestheinformationlistedbelow.
• Id(tweetidentification),
• text(thecontentofthetweet),
• location:locationthetweetwassentfrom
• keyword:Arelevantkeywordinthetweet
• target:Outputthattellsifatweetisarealdisaster (1)ornot(0)
Fig:disastertweetsclassification

Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT)
Google AI Language researchers published a document titled BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) in their journal. It is an advanced Transformer.
Coding stack. The Book Corpus dataset and Wikipedia are used to train it. By presenting cutting-edge research in a variety of NLP techniques, such as Question Answering Natural Language Inference (MNLI), it sparked interest in the machine learning community. It makes use of Transformer, an attention mechanism that understands how words in a sentence relate to one another in context. Transformer's original design supports the following mechanisms: a decoder that produces a mission predictor and an encoder that receives text input. Only the encoder technique is needed because BERT's goal is to construct a languagemodel.
• DataCollection
• DataPreprocessing
• DataVisualization
BERT:
BERT, which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, is based on Transformers,adeeplearningmodelinwhicheveryoutput element is connected to every input element, and the weightingsbetweenthemaredynamicallycalculatedbased upon their connection. (In NLP, this process is called attention.) Historically, language models could only read textinputsequentially eitherleft-to-rightorright-to-left- but couldn't do both at the same time. BERT is different because it is designed to read in both directions at once. This capability, enabled by the introduction of Transformers, is known as bidirectionality. Using this bidirectional capability, BERT is pre-trained on two different, but related, NLP tasks: Masked Language ModelingandNextSentencePrediction.
Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a supervised machine learning algorithm used for both classification and regression. Though we say regression problems as well its best suited for classification. The objective of SVM algorithmistofindahyperplaneinanN-dimensionalspace thatdistinctlyclassifiesthedatapoints.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
TF-IDF TF-IDF stands for “Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequency”. This is a technique to quantify wordsinasetofdocuments.Wegenerallycomputeascore foreachwordtosignifyitsimportanceinthedocumentand corpus. This method is a widely used technique in InformationRetrievalandTextMining.
We use two separate data sets with varied counts for this project, train our models on both sets of data, and then evaluate the outcomes. In the data set, there are 7613 tweets, of which 43% are about disasters and the rest are not. In data set 2, there are 11370 tweets, or a fairly big amount, of which 18.5% are about disasters. On both data sets,ourBERTmodelperformsmoreaccurately.
available in many languages, avoiding the time-consuming and resource-intensive model training directly on tweets from scratch, allowing to focus only on their finetuning; availableplaintextcorporaarelargerthantweet-onlyones, allowing for better precision in the prediction of language usage. In order to further determine its applicability and generalizability, the suggested approachwill also betested and evaluated in relation to additional datasets, languages, andsocialmediasources,suchasFacebookpostings.
[1] Becken,S.;Stantic,B.;Chen,J.;Alaei,A.R.;Connolly,R.M. Monitoring the environment and human sentiment on the Great Barrier Reef: assessing the potential of collectivesensing.J.Environ.Manag.2017,203,87–97. [CrossRef][PubMed].
[2] Takeshi Sakaki, Makoto Okazaki, and Yutaka Matsuo. Earthquake shakes twitter users: real-time event detection by social sensors. In Proceedings of the 19th international conference on World wide web, pages 851–860.ACM,2010.
[3] Devlin J, Chang M. W, Lee K, and Toutanova K BERT: Pretraining of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding 2019 Conference of the North AmericanChapteroftheAssociationforComputational Linguistics: Human Language TechnologiesProceedingsoftheConference.
[4] Hasan A , Moin S, Karim A , Shamshirband S (2018). Machine learningbased sentiment analysis for twitter accounts. Mathematical and Computational Applications,23(11),1-15.
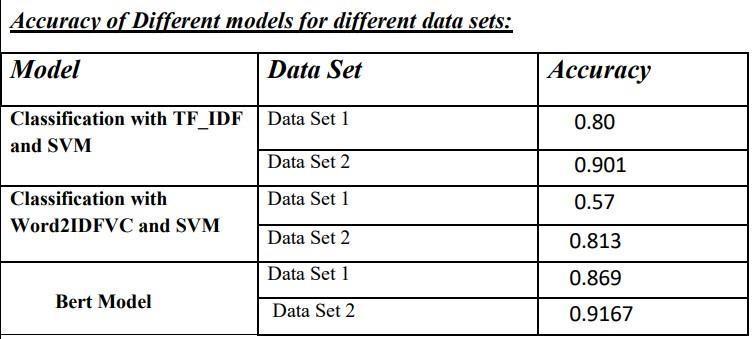
WecaninferfromthistablethattheBERTmodelhasmore accuracythanthe other two models for both data sets. For dataset 1, the accuracy of TF IDF and SVM is.80, and when we train and test the model using further data sets, the accuracyrisesasaresultoftheadditionaldatasets.Dueto the second model's use of less data than the first, we see thatdataset2'saccuracyishigherthandataset1's.Lastbut notleast,ourBERTmodelhasamaximumaccuracyof.9167 andgreataccuracyinbothdatasets.
Thisproject'sgoal wasto developa BERTlanguage modelbasedmethodfordeterminingifatweetisadisasterornot. Itwassetupasatwo-steppipeline,withthefirststepentail pre-processing steps to convert Twitter lingo, including emojis and emoticons, into plain text, and the second step utilizing a version of BERT that was pre-trained on plain text to fine-tune and classify the tweets with respect to their polarity. Pretrained language models are widely
[5] Bagheri H , Islam Md J (2017). Sentiment analysis of twitter data. Computer Science Department Iowa State University,UnitedStatesofAmerica.
[6] https://towardsdatascience.com/bert-explainedstateof-the-art-language-model-fornlp%02f8b21a9b627
[7] https://towardsdatascience.com/workflow-ofamachine-learning-project-ec1dba419b94
[8] https://www.kaggle.com/c/twitter-sentimentanalysis2
[9] https://towardsdatascience.com/tf-idf-fordocumentranking-from-scratch-in-python-on-realworlddataset-796d339a4089
[10] https://www.tutorialspoint.com/google_colab/what_i s_google_colab.htm
[11] https://www.applause.com/blog/functionaltestingtypes-examples