International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1,2School of Computer Applications, Lovely Professional University, Punjab, India. 2Computer Science Department, Federal Polytechnic Damaturu, Yobe, Nigeria ***
Abstract - Intracranial tumors simply known as brain tumors have proven to be one of the pressing causes of human mortality globally. One of the most challenging responsibilities in medical image processing nowadays is the detection of brain malignancies. Thesetumor types areformed by a mass of aberrant cells, and the percentage of individuals diagnosed with brain cancer is growing in relation to the aging population, which is a global health concern. Early identification and diagnosis of brain disorders can have a significant impact on efforts to treat them. Given the aforementioned, deep learning approaches can assist notably in overcoming the above-stated challenges. In detecting and classifying brain/intracranialtumors fromMedicalResonance (MR) images, which is one of the advancedmethods inthefield of medicine, we developed a deep learning modelanddeployed it to a web application that works using Convolutional Neural Networks (ConvNet) based on Transfer Learning (TL). This system is capable of identifying and distinguishing tumors among three major classes of brain tumors which are;Glioma, Meningioma, Pituitary, and normal images as well with very high accuracy.
Key Words: Intracranial tumor, Brain tumor, ConvNet, TransferLearning,MRI,DeepLearning,Detection.
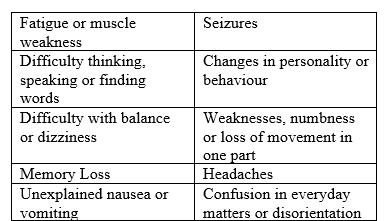
One of the most prevalent cancers in the world is brain tumours.Thesetumoursoccurinthebrainandspinalcord and are usually caused by uncontrolled cell manipulation. Thesymptomsofbraintumoursvarybasedonthepartof the brain affected. These include headaches, weakness, vomiting, seizures, blurred vision, fever and more. Most patients experience progressive weakness and altered mental function as the tumour grows. Many dies from secondary complications caused by the tumour-related illness.Eventhoughtreatmentsareavailable,doctorsneed todetectbraintumoursearlytosavepatients’lives.
Doctorsuseanumberoftechniquestodetectbraintumours. CTscanisoneofthemthatusesX-raystocreate3Dimageof the patients’ inner organs and structures. Magnetic ResonanceImaging(MRI)isanadvancedversionofCTscan thatusesstrongermagneticfieldsandtransversesgreater lengthandbreadth.MRIsarealsoeffectiveatdetectingsoft tissueanomaliesliketumoursandcysts.Inaddition,doctors useadvancedbiochemistrytechniquestodetermineifthere
areanydiseaseslikecancerinthepatients’body.Bloodtests canalsorevealiftherearecancerousgrowthsordiseasesin thebloodstreamthataffectthebrain’sbloodvessels.
Anaberrantmassofcellsgrowingwithinoroutsideofyour brain is called a brain tumour. Brain tumours can be malignant, which is cancerous, or non-cancerous which is knownasbenign.
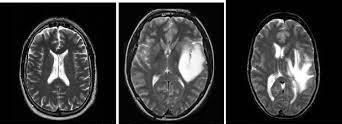
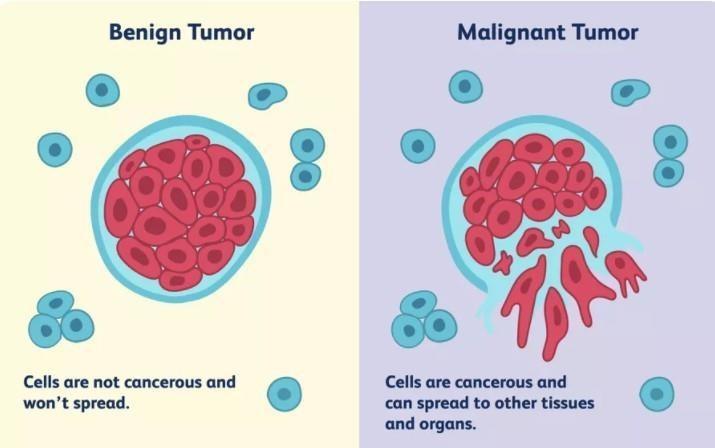
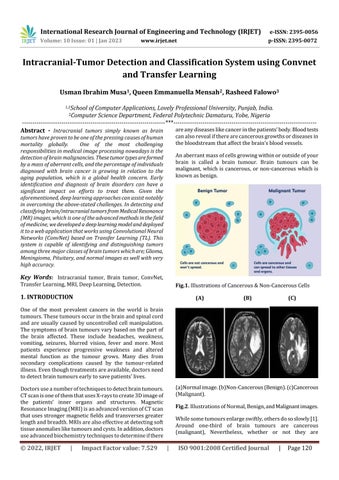
Fig.1. IllustrationsofCancerous&Non-CancerousCells (A) (B) (C)
(a)Normalimage.(b)Non-Cancerous(Benign).(c)Cancerous (Malignant).
Fig.2.IllustrationsofNormal,Benign,andMalignantimages.
Whilesometumoursenlargeswiftly,othersdososlowly[1]. Around one-third of brain tumours are cancerous (malignant), Nevertheless, whether or not they are
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
malignant,braintumourscanaffectyourhealthandtheway yourbrainfunctionsiftheyenlargetothepointwherethey strainonnearbytissue,bloodvessels,andnerves.Primary tumours are tumours that form in the brain. Secondary tumoursarecancersthatdevelopinanotherareaofthebody beforespreadingtothebrain.Thereareatleast120 differentkindsofbraintumoursandCentralNervousSystem (CNS)disorders.In2021,brainandCNScancerswillbethe causeof18,600adultdeathsand3,460deaths inchildren under the age of 15 according to the American Cancer Society[2].TheNationalBrainTumourSociety(NBTS)has identifiedsomeofthefrequentsymptomsofbraintumours, thesearehighlightedbelow;
models that can cut administrative costs while enhancing patientneeds.[6].Overtime,deep-learningmedicalimaging technology has been utilized in numerous sectors. These include chatbots that are driven by AI and can recognise trendsinpatients'symptoms.Deeplearningalgorithmshave been vital in the identification of certain malignancies, pathology,diagnosisofunusualdisorders,andidentification ofvarioustumours.Deeplearningisessentialtoeachofthese fieldsbecauseitgivesthemedicalexpertinsightsthatenable earlyproblemdetectionandhighlycustomisedandpertinent patienttreatment.Themethodthatspecifiesthetaskandthe data is hidden behind the intricacy of the artificial intelligence, neural network,andcomputerthat runsdeep learning.Thesedeeplearningalgorithmshavebeenutilised to improve the outcomes in a variety of medical imaging fields,suchasthestudyofbraintumours,breastcancer,and abnormalitiesoftheheadandneck.
When it comes to identifying and studying brain tumours, magneticresonanceimagingisthebestoption.TheMRIwill produce a large amount of data and specifics about the tumourwhenitexaminesabraintumour.Aradiologistwill alwayshaveahugeamountofsourcestodrawfromwhen establishingadiagnosis,butfewtestingtools.
[14]. Magnetic Resonance (MR) images are analysed for abnormalities and choices are made by a physician or radiologistaspartoftheconventionalprocedureforfinding brain cancers. However, it heavily depends on a doctor's medicalknowledge;differencesinlevelsofexperienceand the characteristics of pictures make a diagnosis with the naked eye more difficult [3]. Considering that they have a numberofirregularitiesornoisydata,theimagesaredifficult foradoctortoassessinashortamountoftime.Interpretinga largequantityofdata becomesincreasinglydifficultasthe volume of information rises. A brain tumour’s manual identification becomes increasingly time and moneyconsuming. Deep learning, specifically neural networks, accelerates considerable significance when it achieves positiveoutcomes.ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(CNNs) excelingainingabilitiesandofferinginfiniteaccuracy.Many applicationsfordeeplearninghavebeenproposed,suchas voicerecognition,objectdetection,patternclassification,as wellasotherdecision-makingtasks[4],[5].
ImpactofDeepLearningandArtificialIntelligenceinMedical
Imaging:ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(CNN)inmedical imagingisprimarilyresponsibleforignitinginterestindeep learning. Convolutional Neural Networks CNN is a potent methodforlearningmeaningfulrepresentationsofpictures and some other structured data. Deep learning has the potentialtoadvancehealthcare,andthereisroomtodeploy
Numerousattemptstoevaluatemultiparameterquantitative MRI data to assess the information content of the organ's afflictedregionhavebeenmade,buttheirimpacthasbeen significantlylessthanthatofstandardMRIresearch[22].
They typically comprise two phases: localization and characterization. Their variability and accuracy may be controlled in two ways: by automating ROI collection and standardisingquantitativefeatureextraction,respectively.
The bulk of methods depend on one of the alternative viewpoints:segmentationapproachesareconventionalthat focusedonafewbasicMRImaps,whileapreliminarymanual ROI delineation is devoted to more sophisticated feature extraction methods. Through the use of image processing tools,thesizeofthebraintumouriscalculated.Thetechnique can only be used on cancers that resemble one another; it cannotbeusedonnewlydiscoveredtumourkinds.Wehave thusconcludedthatweneedtotrainthedevicewitharange of tumour types in order to increase tumour detection accuracy.
A variety of deep learning neural networks have been employed by other frameworks, such as Artificial Neural Networks(ANN),tocreateaccurateresults,butsuchplans andsystemsrequiredalotofhardwarecomputing,whichled tosloweryields.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
In this study, we proposed an automated brain tumour detection, segmentation, and classification system. When MagneticResonanceImaging(MRI)producesimagesofthe insideofthebrain,thesystemwilldetectifanypartofthe imagehastumour,iftheregionofthetumourisfound,the algorithm used in the system will help in categorizing the kind of tumour that is present in the image. And a report statingtheconditionofthedetectedimagewillbeproduced bythesystem.
Deeplearningandimageprocessingtechniqueshavebeen proposed by researchers in identifying and categorising brain tumours. Some of the most recent approaches are presentedinthisliterature.
BrainTumourIdentificationandClassificationofMRimages using deep learning techniques by (Zheshu Jia and Deyun Chen),inthispaper,basedondeeplearningmethods,aFully Automatic Heterogeneous Segmentation Utilising Support Vector Machine (FAHS-SVM) has been developed for the segmentationofbraintumours.Thecurrentstudysuggests theinclusionofanovel,totallyautomatedapproachbased onanatomical,morphological,andrelaxometryfeaturesto separatetheentirecerebralvenoussystemintoMRIimaging [7]. A Robust Approach for Brain Tumour Detection in MagneticResonanceImagesUsingFinetunedEfficientNetby (Hasnain Ali Shah, Faisal Saeed, et al.), using a deep ConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(CNN),theirsuggestedlayers are optimised to effectively categorise and detect brain tumour pictures using the EfficientNet-B0 based model. Applyingmultiplefiltersisoneoftheimageenhancement strategies used to improve the quality of the photos [8]. Optimized Edge Detection Technique for Brain Tumour DetectioninMRImagesby(AhmedH.Abdel-Gawadetal.),in this paper, a method for identifying the edges of a brain tumourusinganMRscanofthepatient'sbrainissuggested. First of all, the picture properties are enhanced using the Balance Contrast Enhancement Technique (BCET), which givesmedical imagessuperiorcharacteristics.Then,using the relevant training dataset, the suggested Genetic Algorithms(GA)edgedetectionmethodisusedtoidentify the fine edges [9]. A New Convolutional Neural Network ArchitectureforAutomaticDetection ofBrainTumours in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Images by (Ahmed S. Musallam,AhmedS.Sherifetal.),Theproposeddesignhasa fewconvolutional,max-poolinglayersandtrainingrounds, makingitacomputationallylightmodel.Whenevaluatedon adatasetof3394MRIpictures,anexceptionalaccuracyof 98.22% is obtained, in recognising glioma, meningioma, pituitary,andnormalimages[10].BrainTumourandGlioma Grade Classification using Gaussian Convolutional Neural Networkby(MuhammadRizwan,AyshaShabbiretal.),They proposed a method to identify different types of brain
cancersutilisingtwodatasetsandaGaussianConvolutional Neural Network (GCNN). To categorise tumours into pituitary, glioma, and meningioma, one of the datasets is employed.TheotheronedistinguishesbetweenGrades1,2, and 3 of gliomas [11]. Data Augmentation and Transfer LearningforBrainTumourDetectioninMagneticResonance Imagingby(AndresAnaya-IsazaandLionelMera-Jimenez), inthispaper,theyevaluatehowseveralconventionaldata augmentation techniques affect the ResNet50 network's ability to identify brain tumours. And they included a principalcomponentanalysis-basedtechnique.Thenetwork trainedfromzerosandtransferlearningfromtheImageNet datasetwereusedforthetraining.Theywereabletoacquire anF1detectionscoreof92.34%[12].MachineLearningand Deep Learning Approaches for Brain Disease Diagnosis: PrinciplesandRecentAdvancesby(ProtimaKhan,MDFazlul Kaderetal),Thegoalofthisstudywastodiscoverthebest effectivemethodforidentifyingvariousbrainillnessesthat may be used to further treatment in the future. And they have suggested very good techniques [13]. Towards RealTimeComputingofIntraoperativeHyperspectralImagingfor BrainCancerDetection
Using Multi-GPU Platforms by (Giordana Florimbi, Himar Fabelo,etal.),Themosteffectiveapplicationcreatedinthis researchthatmakesuseofGraphicProcessingUnit(GPU) technology is that, it can effectively fulfil the real-time limitation set at one minute for surgical operations by classifyingthelargestpictureinthedatabaseinlessthan3 seconds. [15]. Combining Noise-to-Image and Image-toImage GANs: Brain MR Image Augmentation for Tumour Detection by (Changhee Han, Leonardo Rundo, et al.), To enhance the DA impact with the GAN configurations, they developedatwo-stepGAN-basedDAthatcreatesandrefines brain Magnetic Resonance (MR) pictures with or without tumours independently. They carefully examine the outcomes of CNN-based tumour classification, taking into accountpre-trainingonImageNetandremovingodd-looking GAN-generatedpictures.Thefindingsdemonstratethat,in tumouridentificationaswellasothermedicalimagingtasks, theirtwo-stepGAN-basedDAcanconsiderablyoutperform the standard DA alone [16]. Segmentation C- Means ClusteringwithSpatialInformationforImage
Segmentationby(MalathiHong-Longet.al),inthispaper,for the categorization of Brain MRI, a desegregation wave entropy technique based mostly on spider net plots and probabilistic neural networks was presented. For classification,theproposedapproachemploystwosteps:a wavelet entropy-based mainly spider net plot for feature removalandaprobabilisticneuralnetworkforclassification [17]. Transfer Learning Based Image Visualization Using CNN by(Santosh Giri and Basanta Joshi)Computefeature vectors using a feature extraction component of the Inception v3 model and retrained the classification layer usingthesefeaturevectors.WiththeCaltech101dataset,the artificial neural network architecture's mean testing
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page122

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
precisionwas98%,whilewiththeOxford17Flowerpicture dataset, it was 92.27% [20]. A Study on CNN Transfer Learning for Image Classification by (Mahbub Hussain, JordanJ.Bird,andDiegoR.Faria),Inordertodetermineif such a CNN architectural model (i.e. Inception-v3) will performbestintermsofaccuracyandefficiencywithfresh imagedatasetsusingTransferLearning,thisworksuggests theresearchandexaminationofit.Theretrainedmodelis assessed, and the outcomes are contrasted with several cutting-edge methods [21]. All these are works that are related to the system we are referring to in this research paper.
Classifying images of brain tumours is a crucial step in medical image processing. It helps physicians develop precise diagnoses and treatment regimens. One of the primary imaging methods used to examine brain tissue is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MR imaging). Magnetic ResonanceImaging(MRI)generateshigh-qualityimagesof theintracranial,andthemethodwehaveusedinthissystem isthat,afterthemagneticresonance(MR)imaginggenerates theimages,thesystemwillacceptthemandfirsttrytocheck ifanyareaintheimageiscancerous,secondly,ifthesystem detectsthearea,itwillfurtherclassifywhichtypeofcancer isthereintheimage.Otherwise,itwillgenerateareportthat theimageisnormal.Hismethodintroducedanovelstrategy for distinguishing four unique classifications: glioma, meningioma,pituitary,andnormalimages.
Convolutional Neural Network:Adeep learning algorithm called ConvNet or CNN in short can take photos as input, identifydistinctobjectsintheimage,andthendistinguish one image from another. In order to categorize the MRIproducedinputimages,weemployedtheConvNetapproach.
TransferLearning:Implementingamodelthathasalready beenlearnedtosolveanewproblemiscalledtheTransfer Learning (TL). Therefore, in this model, we used the approachoftheTLandalsobespokeCNNtotrainthemodel to compare accurate findings. This is highly prevalent in deep learning since it can be used to train deep neural networksthathavealittlequantityofdata.
Prediction:Simplysaid,thepredictionentailshighlighting the aspects of the data that have the most bearing on the results of the model. Each row from the prediction array, whichcontainsfouralternativevaluesforthecorresponding labels, has been processed using the argmax function. by using the argmax function, we are able to determine the indexassociatedwiththeprojectedoutcomeasseenbelow. Thelargestvaluethatisin eachrow reflectsthe expected outputoutofthefourpotentialpossibilities.
Dataset:Weutilizedalmost1500imagesofvarioustypesof braintumourstotrainthemodel,andwealsodevelopeda testmodelwith500relatedimages.Ateamoffourpersons
(Sartaj Bhuvaji, Ankita Kadam, Prajakta Bhumkar, and Sameer Dedge) created the dataset and posted it to the Kaggle website. [17]. The dataset comprises images of all three kinds of brain cancer, as well as the normal images indicatedinthemethodologysection.
(a)Glioma(b)Pituitary(c)Meningioma(d)Normal
Fig.4. Sampleofimagesfromeachclassofbraintumours generatedfromtheMRI.
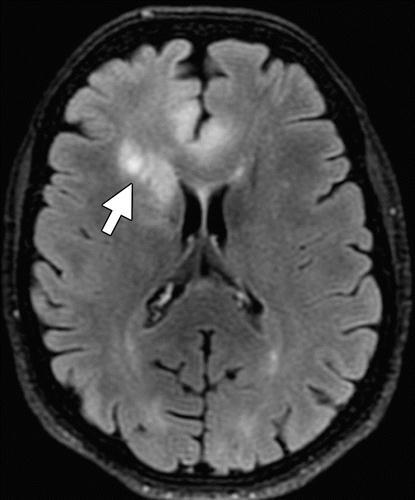
Thisapproachdividesitsworkintosomestepstocreatean effective structure for identifying cancerous and noncancerous images; these stages are critical for achieving greater classification accuracy. The phases are described below.
i. Datacollection:Theinitialstepafterloggingintothe system is to upload high-quality intracranial images produced by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Additionally, the system will store every image that is submittedandmaintainacopyofitinaseparatefolder.
ii. Pre-Processing: The process of transforming unstructured data into a form that can be used by a deep learning or machine learning model is called data preprocessing. An essential part of the workflow is data preparation, based on the fact that the data needs to be alteredsothatacomputercanuseit.Inordertopreparethe
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
data for training and testing, the pre-processing stage is helpful.
iii. Segmentation: The clipped area of the Magnetic ResonanceImageisutilizedastheROI(RegionofInterest) oncethebraintumourhasbeen found.UsingthisROI,the ActiveContourSegmentationAlgorithm,sometimesknown as"snakes,"dividesthetumourregion[19].Whencreatinga contouralgorithm,theboundaryisthefirststep.Theyoften taketheformofsplinecurvesandaredistributedinacertain way according to the application being used. The curve is drawn, producing a picture with various sections and the growthproceduresusedinthisprocessarecarriedoutusing theenergyfunction.
iv. Feature Extraction: In this stage, we consider the pre-trained network as an independent feature extractor whenexecutingdeeplearningfeatureextraction,lettingthe incoming picture to progress further, pausing at the prespecifiedlevel,andusingtheoutcomesofthatlayerasour features. So, we can still use the powerful, discriminative properties that Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) has learned.TheycanalsobeusedtoidentifysubjectsthatCNN wasnotinstructedon.
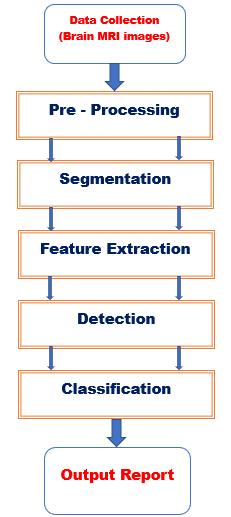
v. Detection: In the detection step, it begins when intracranial MRI images are uploaded to the system, the systemwillattempttoidentifythepresenceoftumoursin the input image among the three different types of brain tumours gliomas,meningiomas,andpituitary aswellas inthenormalimagesthataretumour-free.’
vi. Classification:Givingalabelfromapredetermined list of categories to an input image is known as image classification.Therefore,atthisstage,thesystemwillhaveto identify the type of tumour present in the picture after identifyingcancersfromthe inputimages.Andit will also notice that there isn't a tumour if there isn't one in the image.
vii. OutputReport:Theinputpicturewillreachthisstep afterpassingthroughallthepreviousstagesofthesystem, where the outcome will beformed. Ifaninfectedimage is discovered, the system will provide a report outlining the specific ailment. The system will then provide the final resultsanda recommendationaboutthetumourthatwas foundsuchasthetumour’sname,itssigns,andthestepsyou needtofollowtotreatit.
Fig.5. Architectureofthesystem.
Software used:
1. Computerwithacorei-3processor.
2. Framework:FlaskandStreamlit.
3. IntegratedDevelopmentEnvironment(IDE): Data scientists can create and share documents that incorporateequations,livecode,andcomputational output using the open-source Jupyter Notebook online tool. We have picked it for the system's constructionbecauseitisutilizedformanydifferent data science activities, such as deep learning, machine learning, and many more. Secondly, we deployed the model after it was created in the Jupyter notebook with the help of a sublime text editorandvisualcodestudio,whichcomprisesthree separateprogramminglanguages(HTML,CSS,and JavaScript).
The results of this system'simplementation are displayed below.Priortoperformingtheillnessclassification,thehighquality brain cancer pictures produced by Magnetic
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ResonanceImaging(MRI)areanalysedandthenfeaturesare extractedusingConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(ConvNet).
Extracted image Detected image
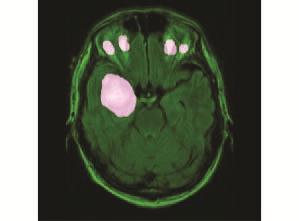
Fig.6 Demonstrationofresultwithfivedetectedtumours
Sensitivity and specificity are two metrics used in machinelearningtoassessamodel'sperformance.Specificity is the proportion of genuine negatives that the model properlypredicts,whereassensitivityisthefractionoftrue positivesthatthemodelcorrectlypredicts.
Terms;
a. TP(TruePositive):Tumourexistsanddetected.
b. FN(FalseNegative):Tumourexistsandnotdetected.
c. FP (False Positive): Tumour does not exist and is detected.
d. TN(TrueNegative):Tumourdoesnotexistandhas notbeendetected.
Sensitivity=TP/(TP+TN);whichmeansthereissuccessful detectionofatumour.
Specificity = TN / (TN+FP); it means there is successful detectionofahealthyimage.
Accuracy = TN+TP / (TN+TP+FN+FP); it means there is successfuldetectionofatumour.
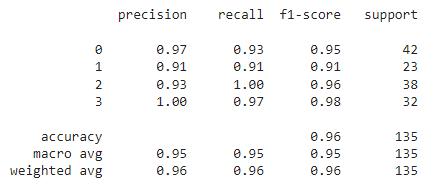
Fig.7. ThePerformanceofthesystem
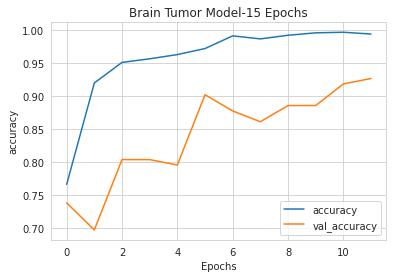
Figure7illustratesthesystem'sperformancebyevaluating the model on the support, precision, recall, and f1-score metrics. The precision, recall, and f1-score metrics all acquired scores of 0.95, or 95% when multiplied by 100. Additionally, the model's total accuracy was 96%. Fig 8 showstheactualaccuracyofthesystem.
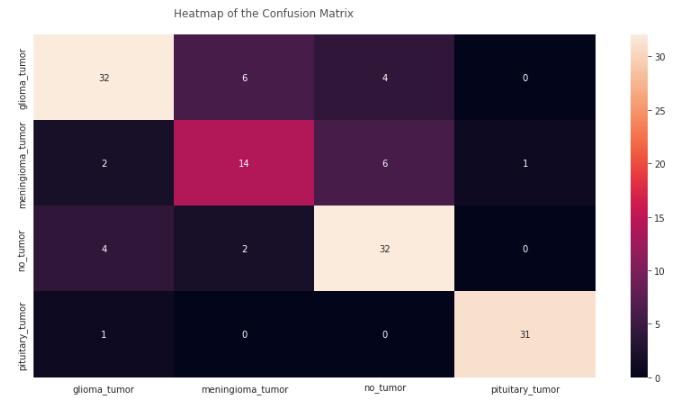
Fig.9 TrainingandValidationLossCurvesoftheproposed model.
Fig. 10 Confusionmatrixoftheproposedmodel.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Inthetablebelow,wegatheredinformationontheprevious models for brain tumour detection and their respective accuraciesaswell.Thetableshowsthecomparisonofthis oursystemandthosealreadyexisting.
Latifetal.[23] SVM 96% Khanetal.[24] VGG-19 94% Yahyaouni et al. [25] DenseNet 92%
Bhatheleetal.[26] HybridEnsemble 95.2% Murthlyetal.[27] CNNEnsemble 95%
Table 1. Comparisonoftheexistingsystems.
Prediction: I'veusedtheargmaxfunctionsinceeachrowof the prediction array below contains four values for the correspondinglabels.Thehighestnumberineachrowisthe expectedresultoutofthefourpotentialscenarios.
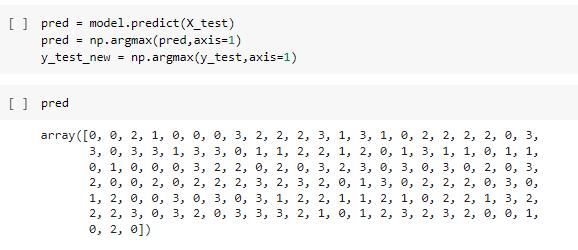
Icanthusdeterminetheindexlinkedtotheexpectedresult usingargmax.
willperformallthetasks,includinggeneratinghigh-quality images,detectingdiseases,andclassifyingdifferenttypesof diseasesdetectedallatatime.
[1] D. Y. Lee, ``Roles of mTOR signaling in brain development,'' Experim. Neurobiol., vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 177_185,Sep.2015.
[2] F. Islami, C. E. Guerra, A. Minihan, K. R. Yabroff, S. A. Fedewa, K. Sloan, T. L.Wiedt, B. Thomson, R. L. Siegel, N. Nargis,R.A.Winn,L.Lacasse,L.Makaroff,E.C.Daniels,A.V. Patel,W.G.Cance,andA.Jemal,``AmericanCancerSociety's reportonthestatusofcancerdisparitiesintheUnitedStates, 20210,''CA,CancerJ.Clinicians,vol.72,no.2,pp.112_143, Mar.2022.
[3]G.Raut,A.Raut,J.Bhagade,J.Bhagade,andS.Gavhane, ``Deep learning approach for brain tumor detection and segmentation,''inProc.Int.Conf.Converg.Digit.WorldQuo Vadis(ICCDW),Feb.2020,pp.1_5.
[4] F. Saeed, A. Paul, P. Karthigaikumar, and A. Nayyar, ``Convolutionalneuralnetworkbasedearly_redetection,'' MultimediaToolsAppl.,vol.79,nos.13_14,pp.9083_9099, Apr.2020.
[5] F. Saeed, A. Paul, W. H. Hong, and H. Seo, ``Machine learningbasedapproachformultimediasurveillanceduring _re emergencies,'' Multime-dia Tools Appl., vol. 79, nos. 23_24,pp.16201_16217,Jun.2020.
[6]Aidoc ``Algorithms and AI: Deep learning medical imaging'' https://www.aidoc.com/blog/deep-learningmedical-imaging/
[7] Z. Jia and D. Chen, "Brain Tumor Identification and ClassificationofMRIimagesusingdeeplearningtechniques," inIEEEAccess,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3016319.
Inthisstudy,asystemisdevelopedthatwouldassistdoctors todiagnosebraindisordersfromthepicturesproducedby MRI while resolving concerns with human intracranial tumours.TheMRIpicturesareoftenevaluatedbydoctors; thusthissystemwillnowbeveryhelpfulinloweringload andlabourtothedoctorsastheywilljustneedtousethis systemtodetectandclassifycancerswhenevertheyreceive imagesfromtheMRI.
This system could be enhanced in the future to become a standard physical machine and will be recommended to attachittotheMRIphysicallytocreateasinglemachinethat
[8]H.A.Shah,F.Saeed,S.Yun,J.-H.Park,A.PaulandJ.-M. Kang, "A Robust Approach for Brain Tumor Detection in MagneticResonanceImagesUsingFinetunedEfficientNet," in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 65426-65438, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3184113.
[9] A. H. Abdel-Gawad, L. A. Said and A. G. Radwan, "Optimized Edge Detection Technique for Brain Tumor DetectioninMRImages,"inIEEEAccess,vol.8,pp.136243136259,2020,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3009898.
[10]A.S.Musallam,A.S.SherifandM.K.Hussein,"ANew Convolutional Neural Network ArchitectureforAutomatic DetectionofBrainTumorsinMagneticResonanceImaging Images,"inIEEEAccess,vol.10,pp.2775-2782,2022,doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3140289.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page126

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[11]M.Rizwan,A.Shabbir,A.R.Javed,M.Shabbir,T.Baker and D. Al-Jumeily Obe, "Brain Tumor and Glioma Grade Classification Using Gaussian Convolutional Neural Network,"inIEEEAccess,vol.10,pp.29731-29740,2022, doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3153108.
[12] A. Anaya-Isaza and L. Mera-Jiménez, "Data Augmentation and Transfer Learning for Brain Tumor DetectioninMagneticResonanceImaging,"inIEEEAccess, vol. 10, pp. 23217-23233, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3154061.
[13] P. Khan et al., "Machine Learning and Deep Learning Approaches for Brain Disease Diagnosis: Principles and RecentAdvances,"inIEEEAccess,vol.9,pp.37622-37655, 2021,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3062484.
[14] National Brain Tumor Society (NBTS), “Signs and Symptoms of Brain Tumor” in https://www.braintumor.org/brain-tumors/diagnosistreatment/signs-symptoms/
[15] G. Florimbi et al., "Towards Real-Time Computing of Intraoperative Hyperspectral Imaging for Brain Cancer DetectionUsingMulti-GPUPlatforms,"inIEEEAccess,vol.8, pp.8485-8501,2020,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2963939.
[16]C.Hanetal.,"CombiningNoise-to-ImageandImage-toImage GANs: Brain MR Image Augmentation for Tumor Detection,"inIEEEAccess,vol.7,pp.156966-156977,2019, doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947606.
[17] Malathi Hong-Long , , “Segmentation C- Means Clustering With Spatial Information For Image Segmentation,”ComputerizedMedicalImagingAndGraphics 30(2006)9–15.
[18] Sartaj Bhuvaji, Ankita Kadam, Prajakta Bhumkar and Sameer Dedge “Brain Tumor Classification (MRI)” https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sartajbhuvaji/braintumor-classification-mri?resource=download
[19] Maham Khan, Syed Adnan Shah et al. “Brain Tumor Detection and Segmentation Using RCNN” in Computers, Materials&Continua,doi:10.32604/cmc.2022.023007.
[20] Santosh Giri and Basanta Joshi. “Transfer Learning Based Image Visualization Using CNN” In International Journal of Artificial Intelligence and Applications (IJAIA), Vol.10,No.4,July2019.DOI:10.5121.
[21]MahbubHussain,JordanJ.Bird,andDiegoR.Faria“A Study on CNN Transfer Learning for Image Classification” Contributions Presented at the 18th UK Workshop on Computational Intelligence, September 5-7, 2018, Nottingham, UK. January 2019 DOI: 10.1007/978-3-31997982-3_1
[22]ArnaudA,ForbesF,CoqueryN,CollombN,LemassonB, Barbier EL. Fully Automatic Lesion Localization and Characterization:ApplicationtoBrainTumorsusingMulti parametricQuantitativeMRIData,TransactionsonMedical Imaging.
[23]G.Latif,G.B.Brahim,D.N.F.A.Iskandar,A.Bashar,and J.Alghazo,``GliomaTumors'classificationusingdeep-neuralnetwork-based features with SVM classifier,'' Diagnostics, vol.12,no.4,p.1018,Apr.2022.
[24] A.R.Khan,S.Khan,M.Harouni,R.Abbasi,S.Iqbal,and Z. Mehmood, ``Brain tumor segmentation using K-means clustering and deep learning with synthetic data augmentationforclassification,''Microsc.Res.Tech-nique, vol.84,pp.1389_1399,Feb.2021.
[25] H. Yahyaoui, F. Ghazouani, and I. R. Farah, ``Deep learning guided by an ontology for medical images classificationusingamultimodalfusion,''inProc.Int.Congr. Adv.Technol.Eng.(ICOTEN),Jul.2021,pp.1_6.
[26] K. R. Bhatele and S. S. Bhadauria, ``Machine learning applicationingliomaclassification:Reviewandcomparison analysis,''Arch.Comput.MethodsEng.,vol.29,pp.247_274, Apr.2021.
[27] M. Y. B. Murthy, A. Koteswararao, and M. S. Babu, ``AdaptivefuzzydeformablefusionandoptimizedCNNwith ensemble classification for automated brain tumor diagnosis,''Biomed.Eng.Lett.,vol.12,no.1,pp.37_58,Feb.2
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
