CANCER TUMOR DETECTION USING MACHINE LEARNING
L.Pradeep Shaik Faisal Syed Obaid Information Technology Information Technology Information Technology Sreenidhi Institute Of ScienceSreenidhi Institute Of Science
Sreenidhi Institute Of Science Technology and Technology and Technology
Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Hyderabad, Telangana, India. Hyderabad, Telangana, India.
Dr.B.IndiraProfessor
Dr.M.Sreenivas Associate ProfessorInformation Technology Information Technology

Sreenidhi Institute Of Science and Sreenidhi Institute Of Science and Technology Technology
Hyderabad, Telanganga, India. Hyderabad, Telanganga, India. ***
ABSTRACT :
Breast tissue can develop tumours of the breast cancer variety. It is the most prevalent type of cancer infemalesaroundthe worldandoneofthemaincausesofdeathinfemales.Thispiecegivesacomparisonofthedatamining,machinelearning,and deeplearningmethodsusedtodetectbreastcancer.
Numerous researchers have worked to improve breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis; nevertheless, each technique has a distinctaccuracyratethatchangesdependingonthecircumstances,resources, anddatasetsemployed.Ourprimarygoalisto compare and contrast various Machine Learning and Data Mining approaches currently in use in order to identify the most effectiveapproachthatwillsupportthe enormous dataset with the best possible prediction accuracy. The major goal of this study is to highlightall the prior research on machine-learning algorithms that have been used to predict breast cancer, and thisarticlegivesalltheknowledgeanoviceneedstounderstandmachinelearningalgorithmsandbuild asolidfoundationfor deeplearning.
INTRODUCTION:
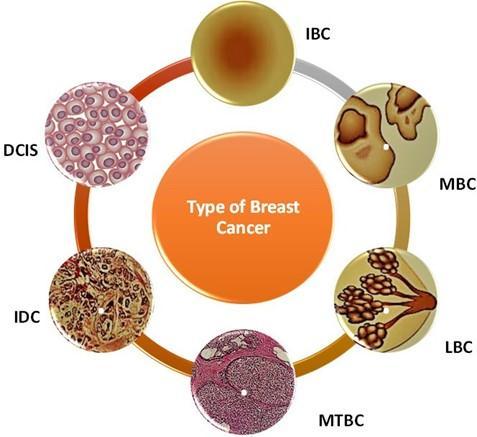
Inthemodernday,breastcancerisoneofthemostdeadlyanddiversediseases,killingahugenumber ofwomenalloverthe world.Itisthesecondmostcommonillnessthatkillswomen.Differentmachine learninganddataminingmethodsarebeing appliedforbreastcancerprediction.Oneofthekeytasksistofindthemostacceptableandsuitablealgorithmforbreastcancer prediction. Malignant tumours, which form when a cell's development spirals out of control, are the cause of breast cancer. Breast cancer is brought on by the abnormal proliferation of numerous fatty and fibrous breast tissues. Tumors that cause variousstagesofcancerhavecancercellsthathavespreadthroughoutthem.Breastcancer cantakemanydistinctforms,and it develops when damaged cells and tissues are dispersed all across the body. DCIS, commonly referred to as non-invasive cancer, is a kind of breast cancer that develops when abnormal cells move outside the breast. The second kind is Infiltrative DuctalCarcinoma(IDC),whichissometimesreferredtoasInvasiveDuctalCarcinoma(IDC).IDCcanceristypicallyobserved in men,anditdevelopswhenbreastaberrantcellsexpandthroughoutallbreasttissues.Thethirdsubtypeofbreastcanceris knownasMixedTumorsBreastCancer(MTBC),whichisalsoreferredtoasinvasivemammarybreastcancer.Suchcancersare broughtonbyabnormalductandlobularcells.
Lobular Breast Cancer (LBC) [11] is the fourth form of cancer and develops inside the lobule. It raises therisk of developing moreinvasivemalignancies.Colloidbreastcancer,alsoknownasmucinousbreastcancer(MBC)[12],isthefifthkindofbreast cancer that arises from invasive ductal cells. When aberrant tissues surround the duct, it happens [13]. IBC (Inflammatory BreastCancer)isthemostrecentformthatresultsinswellingandbreastreddeningWhenlymphaticchannelsbecomeblocked inbreakcells,abreastcancerofthistypebeginstodevelopquickly[14].
Dataminingistheprocessofextractingusefulinformationfromlargedatasets.Data miningfunctions andtechniquescanbe used to identify any type of disease. For example, machine learning, statistics, databases, fuzzy sets, data warehouses, and neuralnetworkscanbeusedtodiagnoseandpredicttheprognosisofvariouscancerdiseases,includingprostatecancer,lungs cancer, and leukaemia [15]. The "goldstandard"approach,whichentailsthreeprocedures(clinicalexamination,radiological imaging,andpathologytest),formsthefoundationoftraditionalcancerdetectionmethodology[18].Whilethelatestmachine learning approaches and algorithms are based on model creation, the conventional method uses regression to signal the existenceofcancer.Themodeliscreatedtopredictunknowndataand deliversthepredictedresultswellthroughouttraining and testing [19]. Preprocessing, features selection or extraction, and classification are the three primary methodologies on which machine learning is founded [20]. The main component of machine learning, feature extraction, aids in the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer and may distinguish between benign and malignant tumours [21]. We can diagnose and anticipate certain types of breast cancer, like the one depicted in Figure 1, thanks to data mining and machine learning algorithms. Classification,regression,andclusteringareafewdataminingtechniques [22] that assist us in obtaining useful data on breast cancer patients. These algorithms [23] include trainingdatasets,andby usingthesedatasets,wecandeterminethelikelihoodofpredictingvarioustypesofbreastcancer[24].
II.MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS FOR BREAST CANCER PREDICTION:

Weinputavastamountofdata,themachinelearningmodelanalysesthatdata,andonthebasisofthattrainedmodel,wecan makeapredictionaboutthefuture[24],[26],[27].Machinelearningisan automaticlearningmethod[25].Thefollowingare themainmachinelearningalgorithmsforpredictingbreastcancer:
A. ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK (ANN):
Anefficientapproachfordata miningistheartificial neural network [28].Input, hidden,and output layersmakeupaneural network.Thismethodisemployedtoextractthetoo-complexpatterns[29].The algorithm is based on network architecture [32]–[34],distributedmemory[31],collaborativesolutions,andparallelprocessing[30].
B. LOGISTICS REGRESSION (LR):

The algorithm is supervised learning and has more dependent variables. This algorithm's output takes theformofa binary number.Regressioninlogistics[35]canofferacontinuousresultforacertaindata. A statistical model with binary variables makesupthismethod[32].
C. K-NEAREST NEIGHBOR (KNN)
In order to recognise patterns, this method is utilised. It is an effective strategy for predicting breast cancer. Every class receivedthesameamountofattentioninordertospotthetrend.Fromasizable dataset,KNearestNeighbor[36]extractsthe relatedhighlighteddata.Weclassifyasizabledatasetonthebasisoffeaturesimilarity[32].
D.DECISION TREE (DT)
Classificationandregressionmodelsarethefoundationofdecisiontree[37].Thedatasetisbrokenupintofewersubsets.The best degree of precision in prediction may be achieved using these smaller sets of data. CART [38], C4.5 [39], C5.0 [40] and conditionaltree[32,[41]areamongthedecisiontreemethods.
E. NAIVE BAYES ALGORITHM (NB)
With this approach, a sizable training dataset is assumed. The Bayesian approach is employed in the algorithm tocalculate probability[42].Whendeterminingtheinputprobabilitiesofnoisydata,itoffers the maximum accuracy [43]. This classifier usesanalogiestocomparetrainingdatasetsandtrainingtuples[32].
Both classification and regression issues are addressed by this supervised learning system [44]. It uses mathematical and theoretical functions to address the regression issue. When making predictions using a huge dataset, it offers the highest accuracyrate.Basedon3Dand2Dmodelling,itisapowerfulmachinelearningtechnique[32],[45].
G. RANDOM FOREST (RF)
The supervised learning-based Random Forest algorithm [46] is used to address classification and regression issues. It is a machinelearningbuildingcomponentthatisusedtopredictnewdatabasedonhistoricaldatasets[32].
Withthehelpoftheclustering methodK mean,data canbe dividedintosmall groups. Todeterminethe degree of similarity between various data points, algorithms are used. The most appropriate cluster forevaluating a large dataset is present in everydatapoint[48].
Itistheunsupervisedlearningmethodthatismostwidelyused.Themethodofcomputingthelikelihood of various forms of clustered data is referred to as the soft clustering methodology. This algorithm's implementation is based on expectation maximisation[51].
III. ENSEMBLE TECHNIQUES FOR BREAST CANCER PREDICTION
Both homogeneous and heterogeneous ensemble techniques can be used; homogeneous ensemble techniques [52] combine one base method with two or more configuration methods, such as bagging and boosting technique, while heterogeneous ensembletechniques [53]-[55]combinetwoormorebase methods. Ensemble techniques are based on supervised learning, whichoffersaccuratepredictionsbasedonspecifichypotheses.
A. BAGGING
Theothernameofthebaggingtechniqueisbootstrapaggregationwhichisusedforthepredictionofanydisease.Itisbasedon multiplemodels,[54]eachmodelistrainedseparatelyandthencombinedtogetherforprediction[52].
B. BOOSTING
Boostingishomogenousweeklearnerthatcreatesonestrongclassifierfromsomeweakclassifiers[52].Itisbasedonstepby stepstrategiesforbuildingupthemodelfromsometrainingdata[54],[55].
C. STACKING
For prediction on the same dataset, stacking is a heterogeneous [52] weak learner that integrates many machine learning techniques.Itismadeupoftwoormorebasicmodelsandcombinestheirpredictions[54,55].
V. SURVEY ON BREAST CANCER
Theworld'smostpopulousnationisChina.Maleshavebreastcanceratarateof8.6%,whilstfemales experienceitatarateof 19.2%,according toa recent organisation report(GLOBOCAN-2018)[65].Everyyear,1.2 million people passawayfromthis illness. The American Cancer Society identified 48,100 incidences ofDCID cancerin femalepatients. Accordingtoa US2019 study,41,760womenand500menareanticipatedtopassawayfrombreastcancer[66].AccordingtoaUSsurvey,thereare 3.8millionwomenwhoarestilllivingbutarebattlingbreastcancer.2019saw59,838incidencesofDuctal CarcinomainSitu (DCIS)breastcancer inUS women [67].458,000 peoplehavedied frombreastcancer worldwide.Chinesewomendiedfrom breastcanceratarateof48%in2012,comparedtoaglobal deathrateof52%[68].Datafrom1,517womenwereexamined in 2015 to determine the breast cancersurvival and recurrence rates; the breast cancer recurrence rate was 100 and the mortalityratewas132[69].
VI. REVIEW OF MACHINE LEARNING ALGORITHMS FOR BREAST CANCER PREDICTION

Themajorgoalofthisstudyistoevaluateseveralmachinelearninganddataminingmethodsthathave aidedinbreastcancer prediction. Finding the most precise and appropriate algorithm for breast cancer prediction is our main goal. In order to do this,we'vegoneoverandexaminedpreviousresearchonbreastcancerpredictionalgorithms.additionallyexaminedresearch publications based on linear, nonlinear, naive bayes, K-nearest neighbour, support vector machine, and certain ensemble algorithms (Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, Linear Discriminant Analysis) (Decision Tree, Random Forest, Boosting and AdaBoost). The vast majority of researchers combined linear and nonlinear or nonlinear and ensembletechniques.Asa result, we have divided our review article into sections thatwill compare andcontrast each algorithm based on its accuracy level.Followingthatcomparison,wewillhighlightthebestmachinelearningmethodforpredictingbreastcancer.
CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have examined various data mining, machine learning, and deep learning methods for the prediction of breastcancer.Findingthebestalgorithmtomoreaccuratelyforecasttheonsetof breastcancerisourkeygoal.Thisarticle's maingoalistoshowcaseallofthepriorresearchonmachinelearningalgorithmsthathavebeenusedtopredictbreastcancer. Italsogivesnewcomersalltheinformationtheyneedtounderstandmachinelearningalgorithmsandprovidethegroundwork fordeeplearning.Thereviewofthisarticlebeginswithadiscussionofthemanyformsofbreastcancer.Tolearnmoreabout the main forms, symptoms, and causes of breast cancer, fourteen research publications were examined. Following that, a reviewofthemostimportantmachinelearning,ensemble,anddeep learningapproacheswasgiven.Thesetechniquesgreatly elaboratethealgorithmsthatareusedtoforecastbreastcancer.Therearestillcertainproblemsthatwillneedtoberesolved infuturedevelopment.Researcherscanuseseveraldataaugmentationstrategiestoaddresstheproblemofthe smallamount ofavailabledataset.Researchersshouldtakeintoaccounttheissueofthedisparitybetweenpositiveandnegativedatasinceit can result in bias towards either a positive or negative prediction. For accurate breast cancer diagnosis and prognosis, an essentialproblemwithanunevennumberofbreastcancerphotosagainstafflictedpatchesneedstoberesolved.
REFERENCES:
Wang,D.ZhangandY.H.Huang“BreastCancerPredictionUsingMachineLearning”(2018),Vol.66,NO.7.
B.Akbugday,"ClassificationofBreastCancerDataUsingMachineLearningAlgorithms,"2019Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO),Izmir,Turkey,2019,pp.1-4.
Keles, M. Kaya, "Breast Cancer Prediction and Detection Using Data Mining Classification Algorithms: AComparative Study." Tehnicki Vjesnik - Technical Gazette, vol. 26, no. 1, 2019, p. 149+. [4] V. Chaurasiaand S. Pal, “Data Mining Techniques: To PredictandResolveBreastCancerSurvivability”,IJCSMC,Vol.3,Issue.1,January2014,pg.10–22.
Delen,D.;Walker,G.;Kadam,A.Predictingbreastcancersurvivability:Acomparisonofthreedataminingmethods.Artif.Intell. Med.2005,34,113–127.
R. K. Kavitha1, D. D. Rangasamy, “Breast Cancer Survivability Using Adaptive Voting Ensemble Machine Learning Algorithm AdaboostandCARTAlgorithm”Volume3,SpecialIssue1,February2014[7]P.Sinthia,R.Devi,S.GayathriandR.Sivasankari, “BreastCancerdetectionusingPCPCETandADEWNN”,CIEEE’17,p.63-65
VikasChaurasiaandS.Pal,“UsingMachineLearningAlgorithmsforBreastCancerRiskPredictionandDiagnosis”(FAMS2016) 83(2016)1064–1069
N. Khuriwal, N. Mishra. “A Review on Breast Cancer Diagnosis in Mammography Images Using Deep Learning Techniques”, (2018),Vol.1,No.1.
Y.KhourdifiandM.Bahaj,"FeatureSelectionwithFastCorrelation-BasedFilterforBreastCancerPredictionandClassification UsingMachineLearningAlgorithms,"2018InternationalSymposiumonAdvancedElectricalandCommunicationTechnologies (ISAECT),Rabat,Morocco,2018,pp.1-6.
R. M. Mohana, R. Delshi Howsalya Devi, Anita Bai, “Lung Cancer Detection using Nearest Neighbour Classifier”,International JournalofRecentTechnologyandEngineering(IJRTE),Volume-8,Issue-2S11,September2019

Ch. Shravya, K. Pravalika, Shaik Subhani, “Prediction of Breast Cancer Using Supervised Machine Learning Techniques”, InternationalJournalofInnovativeTechnologyandExploringEngineering(IJITEE),Volume-8Issue-6,April2019.
HaifengWangandSangWonYoon,“BreastCancerPredictionUsingDataMiningMethod”,Proceedings ofthe2015Industrial and Systems Engineering Research Conference, [14] Abdelghani Bellaachia, Erhan Guven, “Predicting Breast Cancer SurvivabilityUsingDataMiningTechniques”
