Parkinson’s Disease Detection By MachineLearning Using SVM
Doneti Sowmya1, Dodla Kavya2, J. Rashmitha3 , V. Satheesh kumar4 , Preethi Jeevan54,5 Professor, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering,SNIST,Hyderabad-501301,India

1,2,3B.TECH Scholars, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Hyderabad-501301,India
***
Abstract:-
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neuro degenerative movement disorder in which the signs initially appear as a mild tremor in one hand and a general sense of stiffness, but gradually get worse. Over 6 million people are impacted globally. Currently, nonspecialist clinicians have not been able to definitively diagnose this disease, especially in the early stages of the illness when it is very challenging to identify the symptoms. The issue can be resolved with a low mistake rate by utilising machine learning techniques. As a result, data mining offers a prediction method for systematically identifying Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism cannot be diagnosed using a traditional test, hence we suggest a statistical method based on the most prevalent PD symptoms, Given that there is no established test to identify Parkinsonism, we suggest a statistical method based on the three most prevalent PD symptoms gait, tremors, and micrographia. In order to determine the classification method that provides the maximum accuracy in diagnosing PD patients, this involves studying the correlation between the symptoms and classifying the obtained data using several classification algorithms. By combining inputs from Parkinson's sufferers and healthy individuals, our suggested method produces reliable results for the data sets obtained as the input. Our work will demonstrate how early disease identification can extend a patient's life and lead to a serene existence through appropriate medical care andmedication.
Keywords: Machine learning; SVM; Parkinson’s disease; Gaitanalysis.
INTRODUCTION:
Parkinson's disease is characterized by the death of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain. Coordination problems, bradykinesiaandvoicealterationsareamongthesignsof thisneurodegenerativedisease.Parkinson'sdisease (PD) patients can also develop dysarthria, an impairment of the motor-speech system that affects respiratory, phonatory, articulatory and prosodic functions. Parkinson's disease symptoms can be different for everyone. Early signs are mild that goes unnoticed. Symptoms usually begin on one side ofyour body and
gets worsen on that side, afterwards it affects both the sides.Parkinson'ssymptomsmayinclude:
• Tremor
• Slowedmovement
• Rigidmuscles.
• Impairedpostureandbalance.
• Lossofautomaticmovements
• Speechchanges
• Writingchanges butseveralfactorsappeartoplayarole, including:
• Genes
• Environmental
• Triggers
BACKGROUNDSTUDY(LITERATURE)
The cause of Parkinson's disease is still a question mark, Parkinson's illness is generally incurable, however Medication can frequently help control the symptoms. dramatically. Surgery may be required in some more severe situations. Additionally, yourhealthcare physician could counsel lifestyle adjustments, particularly consistent aerobic activity. In a few instances,physical treatment that emphasises balance and Exercising is crucial. A therapist for speech-languagedisorders help withspeechissues.
Medicines may be able to assist you control tremor, mobility, and walking issues. Dopamine-boosting or dopamine-substitutingdrugs.thosewithBraindopamine levels are low in those with Parkinson's disease. However, because it cannot enter the body directly, dopamine the mind. Your performance could significantly improve. symptomsfollowing the start of treatment for Parkinson's disease.However, over time, the advantages of medicationsfrequently decreasing or losing consistency .Usually, youstill have good control over your symptoms. The following are current methodsforidentifyingParkinson'sdisease:
PET scans are utilised to evaluate the function andactivityofthebrain'smovement-relatedareas.

SPECTscansareabletospotalterations inbrain chemistry,includingadropindopamine.
MRI or CT scan - Conventional MRI is unable to identifyParkinson'sdisease'searlysymptoms.
Parkinson's disease can be detected using voiceandspeechdata.
These procedures result in unwelcome bias (up to 25%), mistakes, high medical expenses, and late PD diagnosis, which may have an impact on the patient's qualityoflife.
METHODOLOGY:
By using machine learning techniques, the problemcan be solved with minimal error rate. Parkinson’sdisease detectionusinggait,tremorsandhandwritingsamplesas the dataset, in order to increase the accuracy by finding theco-relationbetweenthesesymptoms.Sinceindividual analysis of every symptomhas some drawback attached toit,forexamplehandwritingisacomplexactivitywhere other factors can influence motor movement, in speech recognition additional steps such as noise removal and speech segmentation are required, using breath samples hasbeenprovedtofailtomeetclinicallyrelevantresults. Thus, in order to avoid the above problems, we have includedmultiplesymptomsratherthanrelyingononeof them.
Our proposed system provides accurate results by integrating the input data of healthy and Pd affected patients. Thus, by the results, doctor can conclude normally or abnormality and prescribe the medicine based on the affected stage. It saves time and helps in early detection. No need to spend a lot over hospitals. This study represents the experimental process (figure 3.1) of the experiment, including machine learning techniques. Parkinson's Disease data sets have been considered in this work. Firstly, wefocused on preparing and combining data from the main datasets. 30 characteristics were also taken out of the Parkinson datasets.
Next, we looked at the co-related and missing values. Second, a key task in this machine learning-based industry isdatasetseparation. Wewereunabletolocate splitandtestdatasetsinthisdataset.TheParkinsondata sethasbeendividedintotrainsetandtestsets,asshown in Figure 3.1. Three supervised- based classifiers then went into operation. After these algorithms were successfully implemented, SVM showed the best performance.
Keep meticulous records of attendance. If no match is detected, the system will simply resume looking for the next visitor, suggesting that the person's photo has not yetbeenenteredintothesystem.
Untilthesystemisshutoff,thiscontinues.Byvisiting the configuredhomepagewithpropercredentialsAdmincan view the attendance and details of employee or student. We update the attendance in real time into a local excel sheetthatcanbereadbyadmin.
ALGORITHMS:
4.1SupportVectorAlgorithm:
Support vector machines have been first introduced by Vladimir Vapnik and Alexey Chervonenkis (Chervonenk is, 2013)(Vapnik, Guyon, Learn, & 1995, n.d.). SVMis a method of machine learning that can solve both linear andnonlinear problems. It provides goodperformance to solvebothregressionandclassification problems. The SVM classification technique inspects forthe optimal separable hyperplane to classify the dataset between two classes (Smola & Schölkopf, 2004). Finally, the model can estimate noisy data problems for newcases.
A Support Vector Machine is a supervised learning algorithm. An SVM models the data into k categories, performing classification and forming an N- dimensional hyperplane. These models are very similar to neural networks. Consider a dataset of N dimensions. The SVM plots the training data into an N-dimensioned space. Following that, using hyper- planes with n various dimensions, the training data points are split into k distinctregionsbasedontheir labels. Thetest points are shown in the same N- dimensional plane following the testing phase. The points are correctly classified in the respective regioninwhichtheyareplaced.Dividedintoa trainandtest set,our datasetwasthen fittedtothe SVM modelasseenbelow.
X_train X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X_all, y_all) clf = svm.LinearSVC()clf.fit(X_train,Y_train) pred = clf.predict(X_test)
Result is stored in csv file by using below code result2=open("Output/resultSVM.csv","w") result2.write("ID,PredictedValue"+"\n") forjin range(len(pred)): result2.write(str(j+1) + ","
+str(pred[j])+"\n")result2.close();
Support vector machines (SVMs) are regarded as effective learning techniques and are frequently used to issuesinbiomedicalandhealthinformatics[49].AnSVM model's output after training is an ideal hyperplane that can increase the distance between any class and the
closest training data points. The following are the main factorsthatdrivemachinelearningresearcherstoutilise SVM for their issues. (1) The first justification is that SVMs are very good at generalising to new data. (2) SVMs' reliance on a relatively small set of hyperparametersisthesecondfactor.
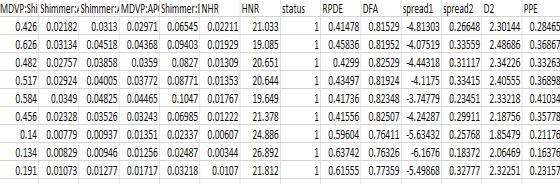
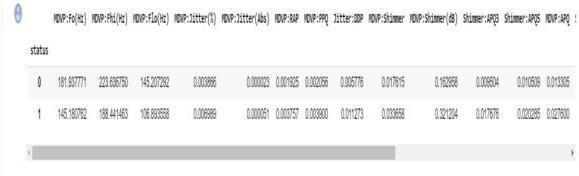
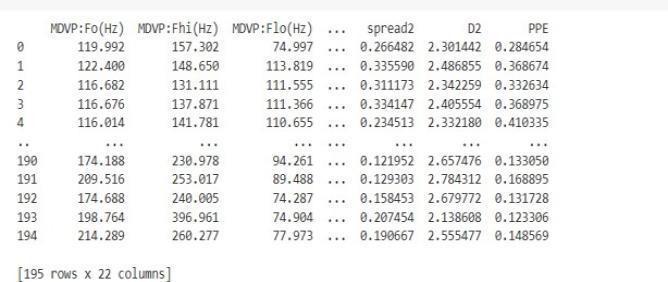
Data Set Information: This dataset includes various biologicalvoicemeasurementstakenfrom31individuals, 23ofwhomhaveParkinson's disease(PD). Each row in the table corresponds toone of the
195voicerecordingsfromthesepeople,andeachcolumn in the table represents a specific voice measure("name" column). According to the "status" column, which is set to 0 for healthy and 1 for PD, the maingoalofthedata is to distinguish between healthy individuals and those with PD. The information is in CSV ASCII format. One instance per voice recordingispresentineachrowofthe CSV file. Each patient hasabout six recordings, and the firstcolumnliststhepatient'sname.
IMPLIMENTATION:
Any project's implementation phase is a real showcasefor the turning points that determine whether it will succeed or fail. The installation and operationalizationof the system or system modifications in a production environment is referred to as the implementation step. The Support Vector Machine (SVM) technique is employed to create the prediction system, and Python is thelanguageused.
Libraries/AlgorithmsUsed:
➢ NUMPY: which stands for Numerical Python, is a library consisting of multidimensional array objects and acollectionofroutinesforprocessingthosearrays.
➢ PANDAS: is a Python library. Pandas is used to analyzedata,LearningbyReading.
➢ SK-learn: Scikit-learn is a free machine learning library for Python. It features various algorithms like support vector machine, random forests, and kneighbours, and it also supports Python numerical and scientificlibrarieslikeNumPyandSciPy.
DATASET:
Number of Instances: 197 Number of Attributes: 23
MissingValues?N/A
Source: Max Little of the University of Oxford generated the dataset in association with the National Centre for VoiceandVoiceinDenver, Colorado,whichcapturedthe speech signals. The feature extraction techniques for general voice problems were published in the original paper.
PROCEDURE/ALGORITHM:
➢ Start
➢ CREATINGAMACHINELEARNINGMODEL{
IMPORTINGDEPENDENCIES; DATACOLLECTIONANDANALYSIS{ loadingthedatafromcsvfiletoaPandas DataFrame;
DataNormalization(removinginconsistentvalues);
DATAPREPROCESSING{
Separatingthefeatures&Target;
Splittingthedatatotrainingdata&Testdata;

DataStandardization;ModelTraining;Model Evaluation{
calculatingaccuracyoftrainingdataset;calculating accuracyoftestdataset;
Volume: 10 Issue:01 | Jan 2023
➢ BUILDINGAPREDICTIVESYSTEM{ user_input_data(parameters/attributes); user_input_datatonumpy.array;standardizationof data:
std_data=scaler.transform(input_data); #predicting
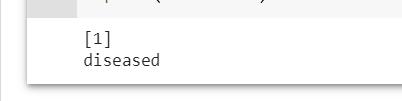
prediction=predict(std_data)print(prediction);
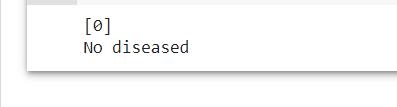
ifpredictionis‘0’thendo
print("ThePersondoesnothaveParkinsons Disease");
elsedo
print("ThePersonhasParkinsonsDisease");
Results(Accuracy)/OutputScreens
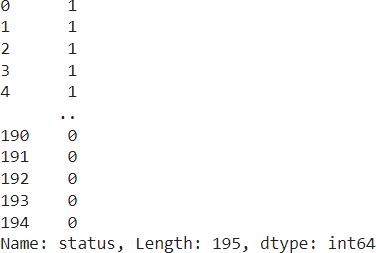
Targetdata

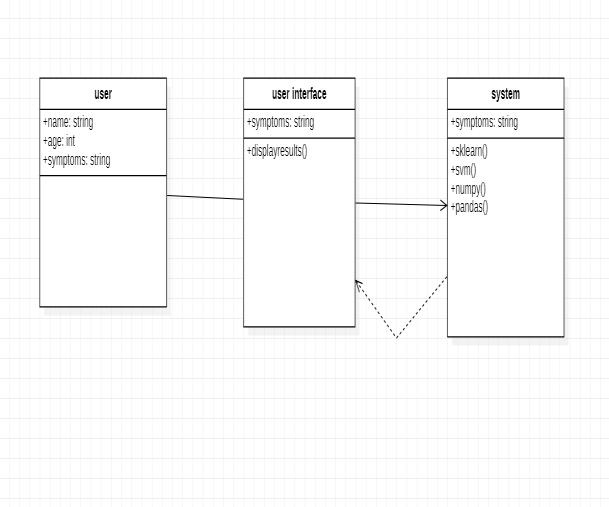
UML DIAGRAMS
ClassDiagram
The visual depiction of a class object in a model system, arranged according to class types, is calledaclassdiagram. Withthreecompartmentsfortheclassname,attributesand
operations each class type is shown as a rectangle. Ovals areused to represent objects, and inside each oval are compartmentswith class names.
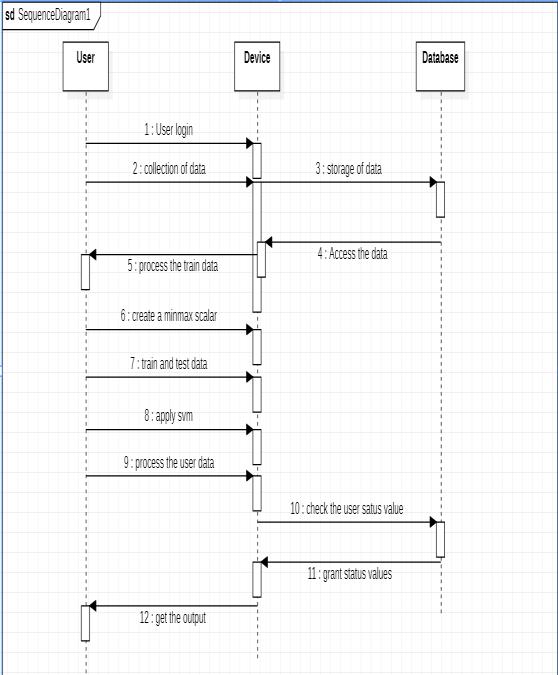
SequenceDiagram
Theproject'ssequencediagramfordiseasepredictionusing machine learning includes all the different elements that a typical sequence diagram needs. This flow chart demonstrates how the model progresses from the initial steptothelast.
ADVANTAGESOFTHESYSTEM:
The suggested system uses a much more straight forwardandeffectivemethod.Theusageofaneasy-touse Frame work makes the system simpler. It has fewer complicated database setups and a more effective algorithm. Dueto its platform independence, the system ismoreeffective.
CONCLUSION
Parkinson's disease, which affects the brain's CNS, is incurable unless it is caught early. Lack of treatment and life loss result from late discovery. Therefore, it is important to diagnose it early. We used the machine learning technique Support Vector Machine for early illnessidentification.
SVMisthebestmethodthatdeliversthe best accuracy(up to 86%) comparison to other algorithms to forecast the commencement of the disease, allowing for early treatment and perhaps saving a life. We checked our Parkinsondiseasedataanddiscoveredthis.
FUTURE ENHANCEMENT
Usecasediagram
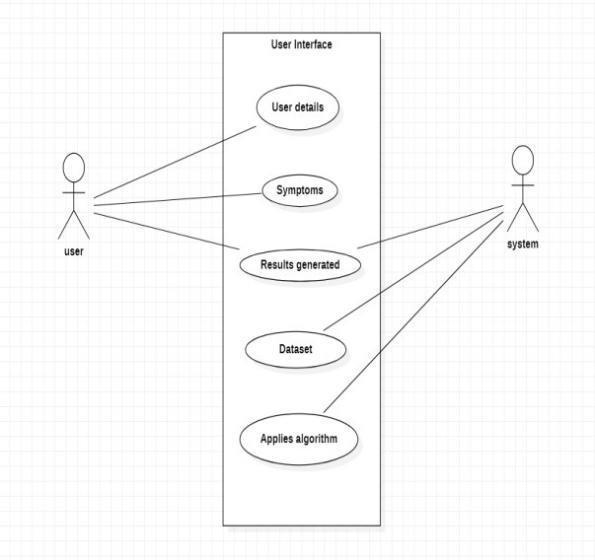
The Use Case diagram of the project disease prediction using machine learning consist of all the various aspects a normal use case diagram requires. This use case diagram shows how from starting the model flowsfrom onesteptoanother.
Future research can concentrate on various methods for anticipating Parkinson's disease utilizing various datasets. In this study, we classify patients using a binary attribute (1- diseased patients, 0- non-diseased patients). The classification of patients and the distinct stages of Parkinson'sdiseasewillbedoneinthefutureusingvarious typesoffeatures.

ACKNOWLDEMENT
For his insightful suggestion, knowledgeable counsel, and moral support during the writing of this work, we would liketoexpressourgratitudetoMr.V.SatheeshKumar.
REFERENCES
[1] DraganaMiljkovicetal,“MachineLearningandData Mining Methods for Managing Parkinson’s Disease” LNAI9605,pp209-220,2016.
[2] Arvind Kumar Tiwari, “Machine Learning based Approaches for Prediction of Parkinson’s Disease,” Machine Learning and Applications- An International Journal(MLAU)vol.3,June2016.
[3] Dr. Anupam Bhatia and RaunakSulekh, “Predictive Model for Parkinson’s Disease through Naive Bayes Classification” International Journal of Computer Science&Communicationvol.9,March2018.
[4] M. Abdar and M. Zomorodi-Moghadam, “Impact of Patients’ Gender on Parkinson’s disease using Classification Algorithms” Journal of AI and Data Mining,vol.6,2018.
[5] Md. Redone Hassan et al, “A Knowledge Base Data Mining based on Parkinson’s Disease” International Conference on System Modelling& Advancement in ResearchTrends,2019
[6] I. Cantürk and F. Karabiber, ‘‘A machine learning system for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease from speech signals and its application to multiple speech signal types,’’ Arabian J. Sci. Eng., vol. 41, pp. 5049–5059,Dec.2016
[7] Ho, A.K., Iansek, R., Marigliani, C., Bradshaw, J.L. and Gates, S. (1998) Speech Impairment in a Large Sample of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Behaviour Neurology, 11, 131-137. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/1999/327643.
[8] Gil, D. and Johnson, M. (2009) Diagnosing Parkinson by Using Artificial Neural Networks and Support Vector Machines. Global Journal of Compute ScienceandTechnology,9,63-71
[9] Logemann, J.A., Fisher, H.B., Boshses, B. and Blonsky, E.R. (1978) Frequency and Co-Occurrence of Vocal-Tract Dysfunctions in Speech of a Large Sample of Parkinson Patients. Journal of Speech HearingDisorder,43,47-57.
[10]L.M.deLauandM.M.Breteler,“Epidemiologyof Parkinson’s disease,” The Lancet Neurology, vol.5, no.6,pp.525
535,2006.
[11]L.Ali,C.Zhu,M.Zhou,andY.Liu,“Earlydiagnosis of Parkinson’s disease from multiple voice recordings by simultaneous sample and feature selection,” ExpertSystemswithApplications, vol.137, pp.22–28,2019.
[12] L. Ali, C. Zhu, Z. Zhang, and Y. Liu, “Automated detection of Parkinson’s disease basedon multiple types of sustained phonations using linear discriminant analysis and genetically optimized neural network,” IEEE Journal of Translational Engineering in Health and Medicine, vol. 7, pp. 1–10, 2019.
[13]J. Rusz, M. Novotny, J. Hlavnivcka, T. Tykalova, and E. Ruuvzivcka, “High-accuracy voice-based classification between patients with Parkinson’s disease and other neurological diseases may be an easy task with inappropriate experimental design,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, vol. 25, no. 8, pp. 1319–1321,2016.

[14] Z. A. Dastgheib, B. Lithgow, and Z. Moussavi, “Diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease using electrovestibulography,” Medical & Biological Engineering&Computing,vol.50,no.5,pp.483–491, 2012.
[15]L.Naranjo,C.J.Pérez,andJ.Martín,“Addressing voice recording replications for tracking Parkinson’s disease progression,” Medical & Biological Engineering&Computing,vol.55,no.3,pp.365–373, 2017.
