A Progressive Review: Early Stage Breast Cancer Detection using Ultrasound Imaging Modality as well as Machine Learning
Jinal Patel1, Himanshu Patel2
1Student, Department of Biomedical Engineering, U.V.Patel College of Engineering, Ganpat University, 2Professor, Department of Biomedical Engineering, U.V.Patel College of Engineering, Ganpat University, Mehsana, India
Abstract- Breast cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed diseases in women and is the leading cause of cancerrelated death in women. The early detection of cancerous tissue can aid in the recovery and treatment of the disease and save more lives. The detection of breast cancer can be challenging using mammography, as dense tissues can overlap in screening. Ultrasound and MRI have also been used for breast cancer growth screening. Numerous methods have been used for the detection of abnormalities in the breast. Here I am only using ultrasound screening modality for the deection of breast cancer at the early stage. For the detection of breast cancer at the early stage, many research works have been carried out. Machine learning is frequently used for detection. Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that provides computers with the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. For the classification of images, Machine learning algorithms like Convolutional neural networks can be used. In this study, we have presented a comprehensive review of Machine learning algorithmsforearly-stage breastcancer detection using imaging modalities.
Key Words: Breast cancer, image processing, ultrasound, early stage detection, machine learning, deep learning.
1. INTRODUCTION
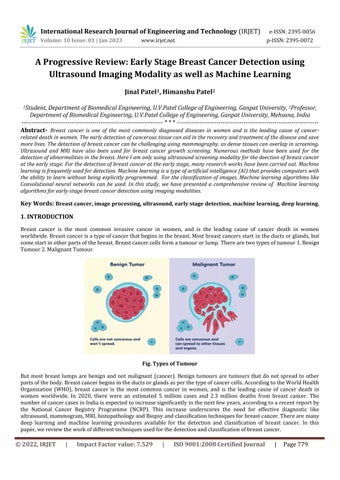
Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women, and is the leading cause of cancer death in women worldwide.Breastcancerisatypeofcancerthatbeginsinthebreast.Mostbreastcancersstart intheductsorglands,but somestartinotherpartsofthebreast.Breastcancercellsformatumourorlump.Therearetwotypesoftumour1.Benign Tumour2.MalignantTumour.
Fig. Types of Tumour
But most breast lumps are benign and not malignant (cancer). Benign tumours are tumours that do not spread to other partsofthebody.Breastcancerbeginsintheductsorglandsasperthetypeofcancercells.AccordingtotheWorldHealth Organization (WHO), breast cancer is the most common cancer in women, and is the leading cause of cancer death in women worldwide. In 2020, there were an estimated 5 million cases and 2.3 million deaths from breast cancer. The numberofcancercasesinIndiaisexpectedtoincreasesignificantlyinthenextfewyears,accordingtoarecentreportby the National Cancer Registry Programme (NCRP). This increase underscores the need for effective diagnostic like ultrasound,mammogram,MRI,histopathologyandBiopsyandclassificationtechniquesforbreastcancer.Therearemany deep learning and machine learning procedures available for the detection and classification of breast cancer. In this paper,wereviewtheworkofdifferenttechniquesusedforthedetectionandclassificationofbreastcancer.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW

Early stage breast cancer detection is a vital topic in the medical field and various methods have been proposed for detectionanddiagnosis.Inthisprogressivereviewsection,theauthorshavediscusseddifferentsegmentationprocesses, featuresandclassifiersalongwiththeirmeritsanddemeritsforearlystagebreastcancerdetection.Machinelearningand deep learning approaches have been discussed for early‐stage breast cancer detection and their role for detection and diagnosis of breast cancer and assistance in the treatment, recovery and decrease the chances of critical situations has beendiscussed.
Narumi Harada-Shoji et al. [1] have discussed in this research work, the use of Ultrasonography in combination with mammographyscreeningisexploredasameanstodetectearly-stageandinvasivebreastcancersinasymptomaticwomen withbothdenseandnondensebreasts.Itissuggestedthatthiscombinationofscreeningmethodsmaybemoreaccurate indetectingbreastcancersthanmammographyalone.
KushangiAtreyetal.[2]havediscussedinthisresearchwork, toinvestigateamultimodalapproachtothedetectionand validationofbreastcancerimages,combiningbothultrasonographyandmammography.segmentationapproachthatcan accuratelydetectbreastlesionsusingadual-modalitysystem.Tothisend,experimentwithandevaluatetheperformance of three popular techniques, namely Fuzzy-c-Means (FCM), K-means (KM) and Darwinian Particle Swarm Optimization (DPSO),fordetectinglesionsusingthecombinedultrasonographyandmammography.ThefuzzyC-meansalgorithmgives accurateresults.
Eduardo Reyes et al. [3] have discussed in this research work, the radiologic characteristics, histology, and prognostic factorsofbreastcancerinpregnantwomen.Itaimstoassesstheimpactofthesefactorsontheprognosisofthedisease.
etal.[4]have discussedinthisresearchwork,machinelearning-baseddiagnosis techniquetoaddressthe Ul Haq, Amin challenge of early diagnosis of breast cancer. The SVM model was utilized to classify malignant and benign cases. To enhance accuracy, the Minimal Redundancy Maximal Relevance and Chi-square algorithms were employed to select relevantfeaturesfromthebreastcancerdataset.
Kiran Jabeen et al. [5] have discussed in this research work, This proposed approach is evaluated on a publiclyavailable ultrasound image dataset and results demonstrate its effectiveness for breast cancer classification. The proposed framework is composed of five key steps: (i) data augmentation is used to increase the size of the original dataset for improvedtrainingofConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(CNN)models;(ii)apre-trainedDarkNet-53modelisselectedandits outputlayermodifiedaccordingtotheclassesintheaugmenteddataset;(iii)themodifiedmodelistrainedusingtransfer learning,withfeaturesextractedfromtheglobal averagepoolinglayer;(iv) theoptimal featuresareidentifiedusingtwo improvedoptimizationalgorithms,namelyreformeddifferentialevaluation(RDE)andreformedgraywolf(RGW);and(v) the best selected features are fused together using a novel probability-based serial approach and classified by machine learningalgorithms.
GelanAyanaetal.[6]havediscussedinthisresearchwork,TransferLearning(TL)isamethodofleveragingapre-trained model to construct an efficient model using limited training data. In this work, propose a multistage Transfer Learning (MSTL) algorithm which utilizes three pre-trained models: EfficientNetB2, InceptionV3, and ResNet50 with three optimizers: Adam, Adagrad, and Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), to improve the performance of classification of microscopic cancer cell line images in ultrasound breast cancer image classification. The MSTL algorithm combines knowledgefrombothnaturalandmedicaldatasets.
RoxanaIacobetal.[7]havediscussedinhisresearchwork,inordertoachievethemostbeneficialoutcomeforthepatient, we should use all available imaging techniques to the fullest extent. Mammography and 3D tomosynthesis should be employedforthescreeningandinitialdiagnosis,withtheassistanceofultrasound.Additionally,ultrasound,MRI,andPETCTcanbeusedtogetherfortheassessmentofthetumor'sstage.
R. Karthiga et al. [8] have discussed in his research work, In this work, the performance of a machine learning (ML) classifier is evaluated using deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and transfer learning models (Alexnet, VGG-16, VGG-19,Resnet-50,andResnet-101).BeforetheMLclassificationprocess,ananisotropicdiffusionfilterisusedtoextract tumoralfeaturesfromthedata.
MehediMasudetal.[9]havediscussed in his research work, Thisresearchimplements pre-trained convolutional neural networks for identifying breast cancer through ultrasounds. The models were fine-tuned to detect key features from the imagesanda classifier wasappliedto the toplayer.Fivefoldcross validationwasusedtomeasuretheaccuracyofseven popularmodelswithdifferentoptimizersandhyper-parameters.Inaddition,Grad-CAMandocclusionmappingwereused to evaluate how well the models captured the relevant features in the images. After fine tuning, DenseNet201 and ResNet50achievedperfect accuracywithAdamandRMSpropoptimizers.StochasticGradientDescentoptimizer enabled VGG16tohave100%accuracy.
Pratiksha Joshi et al. [10] have discussed in his paper reviews the use of machinelearning and deep learning techniques for the early detection of breast cancer. It is found that deep learning is more effective than machine learning when it comes to detecting tumors and classifying breast cancer images. The convolutional neural network (CNN) model is used forclassificationandprovidesmoreaccurateoutcomesthanothermachinelearningapproaches.Thus,deeplearningcan be a reliable tool for detecting breast cancer in its early stages, which can be beneficial for successful treatment and recovery.
YaghoubPourasadetal[11]havediscussedinhisresearchwork,todesignamethodforidentifyinganddiagnosingbreast tumors based on ultrasound images. For this purpose, six techniques have been performed to detect and segment ultrasound images. Features of images are extracted using the fractal method. Moreover, k-nearest neighbor, support vector machine, decision tree, and Naïve Bayes classification techniques are used to classify images. Then, the convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture is designed to classify breast cancer based on ultrasound images directly.
Viswanatha Reddy Allugunti et al [12] have discussed in his research work, a Computer-aided Diagnosis (CAD) for categorizingpatientsinto3distinctclasses(cancer,nocancer,andnon-cancerous)utilisingadatabase.CADisasystemfor computer-assisteddiagnosis.TheyexploreConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(CNNs),SupportVectorMachines (SVMs),and Random Forests (RFs), which are all powerful classifiers, for the classification stage. The three robust classifiers that investigateandevaluateareConvolutionNetworks,SupportVectorMachines,andRandomForest.
Mahmoud Ragab et al [13] have discussed in his research work, an Ensemble Deep-Learning-Enabled Clinical Decision Support System for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Classification (EDLCDS-BCDC) was designed to detect the presence of breast cancer through the use of USIs. The EDLCDS-BCDC consists of two pre-processing stages, Wiener filtering and contrast enhancement, followed by image segmentation with Chaotic Krill Herd Algorithm (CKHA) and Kapur's Entropy (KE). Lastly, an ensemble of three deep learning models, VGG-16, VGG-19, and SqueezeNet, were employed for feature extraction.
Epimack Michael etal [14] havediscussedinhis researchwork,anautomatedCAD systemthat formulatesan optimized algorithm.Thirteenfeatureswerechosenfromthetotal185featurestotrainmachine learning.Fiveclassifierswereused to distinguish between malignant and benign tumors. The results of 10-fold cross-validation revealed Bayesian optimization with a tree-structured Parzen estimator. LightGBM classifier showed the best performance with 99.86% accuracy,100.0%precision,99.60%recall,and99.80%FIscore.
Ye-Jiao Mao et al [15] have discussed in his review paper, to analyze the use of machine learning models in ultrasound elastographysystemsfortheclassificationofbreasttumours.Literaturedatabases PubMed, WebofScience,CINAHL and EMBASEweresearchedandthirteenstudieswerefoundtobeeligibleforreview.Ofthese,sixstudiesinvestigatedshearwaveelastography,whilesevenstudiesfocusedonstrainelastography(fivefreehandandtwoAcousticRadiationForce). Traditional computervision workflowswerecommonlyusedinstrain elastography whichincludedimagesegmentation, feature extraction and classifier functions implemented by means of different algorithms, neural networks or support vector machines (SVM). Shear-wave elastography, on the other hand, tended to adopt the deep learning model of convolutional neural networks (CNN), which combines multiple functional tasks. All the articles included in the review achieved sensitivity of at least 80%, though only half of them yielded acceptable specificity of 95%. Surprisingly, deep learningmodelsdidnotnecessarilyoutperformtraditionalcomputervisionworkflows.

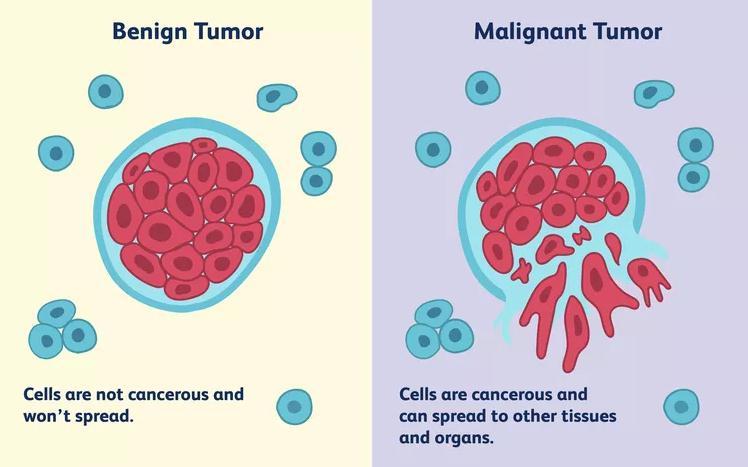
3. PROPOSED BLOCK DIAGRAM
Digital Image processing has been a great benefit to the medical profession, enabling more accurate diagnosis and treatment of diseases. It has been especially effective in early breast cancer detection, making it possible to identify the diseaseinitsearlieststages.Thisreviewwillcoverthemostrecentadvancesinthefieldofbreastcancerdiagnosis,suchas
segmentation methods, feature selection and classifier. These advancements have made it possible to enhance the accuracyandeffectivenessofearlydetectionandtreatment.
4. TECHNIQUES
The current section of the progressive review paper outlined various segmentation, feature extraction and classifier methods, evaluating their respective strengths and weaknesses in terms of noise sensitivity, accuracy, sample size and simplicity.TableIthensummarisedthesignificantcontributionstothefieldmadebetween2018and2022.
Table -1: Summaryofsegmentationmethods,featureextractionandclassifiersmethodandsomeofthekeymeritsand demerits
Segmentation methods
Techniques Merits Demerits
Threshold-based segmentationmethods

Regionbasedsegmentation method
Edgebasedsegmentation methods
Fuzzy theory basedimage segmentation
Artificialneuralnetwork basedimagesegmentation
Uncomplicate,effortless,and economical.
Itiseasytoobtainresultswithfewer noisewhenapplyingmultiplecriteria
Thistechniqueissuitableforimages havingprominentedges.
Thistechniquecanbeusedtoprocess imagesandeliminateanyunwanted noise.
Fewerdataareneededand implementationisstraightforward.
K-meansclusteringmethod Simplicity,fastandifdatais recognizable,providesbetterresult.
Active Contours Algorithm
DarwinianParticleSwarm Optimization(DPSO)
Computationallyefficient,versatile, robust,andcapableofhandling multipleobjects
Foroptimizingaspecificfunction
Itisnotsuitableformulti-channelimagesandcan beeasilyaffectedbynoiseintheimages.
Atime-consumingmethod,thisonecannotbeused fornoisyimagesanddoesnotprovideaccurate shadingresultsforactualmammograms.
Imageswithsmoothedgesarenotsuitablefor applyingedgedetectiontechniques,whichcanalso leadtoadecreaseintheimage'scontrast.
Itcannotbeapplieddirectlytograyscaleimages.
Aquantityofpixelsshouldbespecified.
Thenumberofclustersmustbepredetermined.
Requiresgoodinitialcontour,sensitivetoerrors, notsuitableforsegmentingobjectswithlarge intensityvariations,andcomputationallyexpensive forlargeimages.
Lessaccurate
Feature extraction/selection
Techniques Merits Demerits
GraylevelCo-occurrence matrix(GLCM)
Second-orderstatisticaltexture characteristicscanprovide enhancedperformanceonbasic textures
PrincipalComponentAnalysis Givesclearervisualsandboosts performance.
Linear DiscriminantAnalysis Supervisedlearning,Simpleto executeandrapidcategorization
WaveletTransform
WaveletTransformisableto representsignalsinbothtimeand frequencydomains
Classifiers
Verysensitivetothedimensionsofthetexture samples.
Suitableforstandardizeddata,Noteasytointerpret
samplesize
WaveletTransformiscomputationallyintensive andrequiresmorememoryforstorage
Techniques Merits Demerits
Convolutional
NeuralNetwork
SupportVector Machine
ArtificialNeuralNetwork
RandomForestclassifier
DecisionTree classifier
K-NearestNeighbor algorithm
5. PROBLEM STATEMENT
Supervisedlearning,Highaccuracy
Itnecessitatesavastamountofdata
Suitableforbinarydata
Providehighaccuracy
Provideshigheraccuracythan Decisiontreeclassifier
Categorizesthedatasetintopredeterminedclasses
Simpleandsupervised learning
Itcannotbeusedformultipledatasimultaneously
Dataneedstobeconvertedintonumericalformat.
Complicatedasitgeneratesmultipletrees
Lessaccuratecompareto
Randomforestclassifier
Timeconsumingalgorithm
Early-stage breast cancer screening is an important step to preventing potentially fatal consequences. There are various diagnostic imaging techniques available to detect breast tumours, such as ultrasound, mammography (X-ray), magnetic resonanceimaging(MRI),andcomputedtomography(CTscan).Additionally,physicalexaminationsarealsoconductedto identifyanyabnormalities.Mammographyisparticularlyeffectiveindetectingbreastcancer,butoverlappingtissuescan obscuretheresults.Anultrasoundcanprovideamoreaccurateresult,buthasalowerresolutionandcontrast.
For early-stage breast cancer detection, mammography is the preferred screening test, however, it can have some potentialharms.Falsepositivescanleadtoanerroneousdiagnosisofbreastcancerinahealthypersonandfalsenegatives can lead to a misdiagnosis of a patient having cancer as healthy. Furthermore, mammography can be uncomfortable and causepain.Incontrast,ultrasoundimagingisa non-invasivetechniquewithnoradiationrisk,however,theresolutionof the images is not as accurate as that of a mammogram. Mammography is quite expensive and absorbs more radiation, makingittakelongertodiagnose. Toimprovetheaccuracyofthe results,wesuggesta methodwhereinonly ultrasound screeningmodalityisusedandtheresolutionoftheimageisincreasedbyusingasuperresolutiontechnique.
6. CONCLUSION
The purpose of this research is to detect breast cancer at its early stage and reduce the number of fatalities. Therefore, ultrasound imaging is used as the modality for initial diagnosis and image processing techniques are utilized for further

assessment.Thisstudyexaminedtheuseofmachinelearninganddeeplearningtechniquestoidentifyearly-stagebreast cancer, thereby providing the opportunity for early treatment and improved recovery chances. The results revealed that machine learning techniques, such as artificial intelligence, provide improved accuracy and precision. Specifically, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) were used to classify breast cancer images, which showed a greater degree of accuracythanothermachinelearningtechniques.Inconclusion,machinelearningisa viableapproachtoearlydetection anddiagnosisofbreastcancer,thusaidinginreducingfatalities.
REFERENCES
[1] Harada-Shoji, N., MD PhD. (2021, August 18). Evaluation of Adjunctive Ultrasonography for Breast Cancer Detection Among Women Aged 40-49 Years With Varying https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2783177
[2] Breast cancer detection and validation using dual modality imaging. (2020, January 1). IEEE Conference Publication|IEEEXplore.

[3] Reyes,E.,Xercavins,N.,Saura,C.,Espinosa-Bravo,M.,Gil-Moreno,A.,&Cordoba,O.(2020).Breastcancerduring pregnancy:matchedstudyofdiagnosticapproach,tumorcharacteristics,and prognosticfactors. Tumori Journal, 106(5),378–387.
[4] Haq,U.A.(2020,January1). Anovel integrated diagnosis methodfor breastcancer detection - IOSPress.
[5] Jabeen, K. (n.d.). Breast Cancer Classification from Ultrasound Images Using Probability-Based Optimal Deep LearningFeature Fusion.MDPI.
[6] Ayana,G.(n.d.). ANovelMultistageTransfer Learningfor Ultrasound BreastCancerImageClassification.MDPI.
[7] Iacob,R.,Manolescu,D.L.,Stoicescu,E.R.,Fabian,A.,Malita,D.,&Oancea,C.(2022,June22).
[8] Narasimhan, K. (2022). Automated diagnosis of breast cancer from ultrasound images using diverse ML techniques. MultimediaToolsand Applications, 81(21),30169–30193.
[9] Masud,M.,Hossain,M.S.,Alhumyani,H.,Alshamrani,S.S.,Cheikhrouhou,O.,Ibrahim,S.,Muhammad,G.,Rashed, A. E. E., & Gupta, B. B. (2021). Pre-Trained Convolutional Neural Networks for Breast cancer detection using Cancer Detection Using Ultrasound Images. ACM Transactions on Internet Technology, 21(4), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1145/3418355
[10]
[11]
Journal, I. (2022, April 22). A Progressive Review on Early Stage Breast Cancer Detection.https://www.academia.edu/77263822/A_Progressive_Review_on_Early_Stage_Breast_Cancer_Detectio n
Pourasad, Y., Zarouri, E., Salemizadeh Parizi, M., & Salih Mohammed, A. (2021). Presentation of Novel Architecture for Diagnosis and Identifying Breast Cancer Location Based on Ultrasound Images Using Machine Learning. Diagnostics, 11(10),1870.https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101870
[12] ReddyAllugunti,V.(2022).Breastcancerdetectionbasedonthermographicimagesusingmachinelearningand deeplearningalgorithms. Researchgate,49–51.
[13] Ragab, M. (n.d.). Ensemble Deep-Learning-Enabled Clinical Decision Support System for Breast Cancer Diagnosis andClassificationon UltrasoundImages.MDPI.
[14] Michael,E.,Ma,H.,Li,H.,&Qi,S.(2022).AnOptimizedFrameworkforBreastCancerClassificationUsingMachine Learning. BioMedResearch International, 2022,1–18.
[15] Mao, Y. J., Lim, H. J., Ni, M., Yan, W. H., Wong, D. W. C., & Cheung, J. C. W. (2022). Breast Tumour Classification Using Ultrasound Elastography with Machine Learning: A Systematic Scoping Review. Cancers, 14(2), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14020367
[16] https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer

[17] https://www.indiatoday.in/information/story/world-cancer-day-2021-breast-cancer- scenario-in-india1765496-2021-02-03
[18] https://www.verywellhealth.com/what-does-malignant-and-benign-mean-514240