International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Gaurav Kadam1, Aman Tobaria2 , Sahil Arya3, Asst. Prof. Sudha Narang(Guide) 4
1Gaurav kadam, Dept. of Computer Science Engineering, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Delhi, India
2Aman Tobaria, Dept. of Computer Science Engineering, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Delhi, India
3Sahil Arya, Dept. of Computer Science Engineering, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Delhi, India
4Professor Sudha Narang, Dept. of Computer Science Engineering, Maharaja Agrasen Institute of Technology, Delhi, India ***
Abstract - Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. It is a serious illness that can lead to death, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with compromised immune systems. There have been several studies that have used deep learning and machine learning techniques to detect pneumonia from medical images such as chest X-rays or CT scans. These techniques involve training a model on a large dataset of labeled images, where the model learns to recognize patterns and features that are indicative of pneumonia. One example of a study that used deep learning for pneumonia detection was published in the journal Radiology in 2017. In this study, the authors trained a convolutional neural network (CNN) on a dataset of chest X-rays and found that the CNN was able to accurately classify images as normal or pneumonia with an AUC (area under the curve) of 0.97. Another example is a study published in the journal Chest in 2018, which used a machine-learning approach called a random forest classifier to detect pneumonia from chest X-rays. The authors found that their model had an accuracy of 89.6% and an AUC of 0.94. Overall, the use of deep learning and machine learning for pneumonia detection shows promising results and has the potential to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the diagnosis process.
Words: Machine Learning, Deep Learning, CNN, TransferLearning,ChestX-RayImages.
Pneumonia is a common respiratory infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. It is a serious illness that can lead to death, especially in vulnerablepopulationssuchastheelderlyandthosewith compromised immune systems. Early diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia is important to prevent complicationsandimproveoutcomes.
Traditionally, pneumonia has been diagnosed using clinical symptoms, physical examination, and imaging testssuchaschestX-rays.However,thesemethodscanbe subjectiveandmaynotalwaysprovideaccurateresults.
Deep learning and machine learning techniques offer a potential solution to improve the accuracy and efficiency ofpneumoniadiagnosis.Thesetechniquesinvolvetraining a model on a large dataset of labelled images, where the model learns to recognize patterns and features that are indicative of pneumonia. One approach that has been widely used is transfer learning, which involves pretrainingamodelonalargedatasetandthenfine-tuningit onasmaller,specificdatasetforaparticulartask.
Transfer learning has been applied to pneumonia detection using chest X-rays with promising results. For example, a study published in the journal Radiology in 2017 used a convolutional neural network (CNN) trained on a large dataset of chest X-rays and found that the CNN was able to accurately classify images as normal or pneumoniawithanAUC(areaunderthecurve)of0.97.
Overall,theuse of deep learning and transferlearning for pneumonia detection using chest X-rays as the dataset shows promise as a way to improve the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis and has the potential to benefit patientsandhealthcaresystems.
The Lung Infection in Chest X-ray Images (Kaggle) dataset: This dataset contains over 5,863 chest X-ray images, including a large number with pneumonia. It was created as part of a Kaggle competition and has been widely used in research studies. Overall, these datasets provide a diverse range of chest X-ray images that can be usedtotrainandevaluatemodelsforpneumoniadetection.
Thedatasetisorganizedinto3folders(train,test, val)and contains subfolders for each image category (Pneumonia and Normal). There are 5,863 X-Ray images (JPEG)and2 categories(PneumoniaandNormal).
ChestX-rayimages(anterior-posterior)wereselectedfrom retrospectivecohortsofpediatricpatientsonetofiveyears old from Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center, Guangzhou. Analysis of chest x-ray images was done on all chest radiographs that were initially screened for quality control by removing all low-quality or unreadable x-ray images. The diagnoses for the images
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
were then graded by two expert physicians before being clearedfortraining intheAIsystem. Tocheck thegrading errors,theevaluationsetwasconfirmedbyathirdexpert.
4. Model training: The next step is to train a machine learning or deep learning model on the dataset. This may involve selecting a model architecture, such as a convolutional neural network (CNN) or random forest classifier,andchoosingappropriatehyperparameterssuch asthelearningrateandregularizationstrength.
5. Model evaluation: Once the model is trained, it is important to evaluate its performance on a separate test dataset to assess its accuracy and generalizability. This may involve calculating metrics such as accuracy, precision,recall,andtheareaunderthecurve(AUC).
6.Modeldeployment:Ifthemodelperformswell,itcanbe deployed in a clinical setting to assist with a pneumonia diagnosis. This may involve integrating the model into a computer-aideddiagnosissystemorusingittogeneratea probabilityscorethatcanaiddecision-making
Overall, the methodology for pneumonia detection using machinelearning and deep learning involves a number of steps that require careful consideration and optimization toachievegoodperformance.
The methodology for using machine learning and deep learning techniques to detect and predict pneumonia varies depending on the specific approach and data sources used. Here is a general outline of the steps that maybeinvolvedinthisprocess:
1. Data collection: The first step is to collect a dataset of chest X-ray images that include both normal images and images with pneumonia. This dataset may be obtained from a hospital or clinical setting, or it may be obtained from online repositories such as the Kaggle Chest X-ray dataset.
2. Data preprocessing: The next step is to preprocess the databyselectingasubsetoftheimagestousefortraining and testing the model, and by resizing and cropping the imagesasneeded.Itmayalsobenecessarytocorrectany errorsorbiasesinthedata.
3. Feature extraction: In this step, features are extracted from the images that are relevant for pneumonia detection.Thesefeaturesmayincludepatternsandshapes in the lung tissue, abnormalities in the appearance of the heartandbloodvessels,andothercharacteristicsthatare indicativeofpneumonia.
Several types of machine learning and deep learning modelshavebeenusedforpneumoniadetection. Wehave usedthefollowingmethodsforpneumoniadetection:
These are a type of deep learning models that are particularlywell-suitedforimageclassificationtasks.They consistofmultiplelayersofinterconnectednodesthatare trainedtorecognizepatternsandfeaturesinimages.CNNs havebeen widelyusedfor pneumonia detectionandhave achievedgoodresultsinanumberofstudies.
We Build a separate generator for valid and test sets. We cannot use the same generator for the previously trained databecauseitnormalizeseachimageperbatch,meaning that it uses batch statistics. We should not be able to do batchtestsandvalidations ofdata,becauseinthereal-life scenario we don't process input images in a batch as it is not possible. We will have the advantage of knowing the averageperbatchoftestdata. Thatiswhyweneedtodo is to normalize input test data using the statistics functionsfromthetrainingdataset.
DenseNetisatypeofconvolutionalneuralnetwork(CNN) that has been used for various image classification tasks, including pneumonia detection. It was introduced in a paper published in the journal Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition in 2017. One of the key features of DenseNet is that it uses dense connectivity, which means
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
that each layer in the network is connected to all of the preceding layers. This allows the network to learn more efficiently and reduces the risk of overfitting. There have been a number of studies that have used DenseNet for pneumonia detection using chest X-ray images. For example, a study published in the journal Biomedical Signal Processing and Control in 2019 used DenseNet to classify chest X-ray images as normal or pneumonia Overall, DenseNet has shown good performance for pneumoniadetectionusingchestX-rayimagesandmaybe a promising approach for this task. However, it is important to carefully evaluate the performance of different models and choose the one that is most suitable foraparticulardatasetandtask.
VGG-16 is a type of convolutional neural network (CNN) that was introduced in a paper published in the journal ComputerSciencein2014.ItwasdevelopedbytheVisual Geometry Group at the University of Oxford and has been widely used for various image classification tasks, includingpneumonia detection. Oneofthekeyfeaturesof VGG-16isitsuseofsmall,3x3convolutionalfilters,which allows it to capture fine-grained details in images. It also uses a large number of layers, which allows it to learn complex patterns and features in the data. There have been a number of studies that have used VGG-16 for pneumonia detection using chest X-ray images. For example, a study published in the journal Biomedical Signal Processing and Control in 2018 used VGG-16 to classify chest X-ray images as normal or pneumonia affected Overall,VGG-16hasshowngoodperformancefor pneumoniadetectionusingchestX-rayimagesandmaybe a promising approach for this task. However, it is important to carefully evaluate the performance of different models and choose the one that is most suitable foraparticulardatasetandtask.
ResNet is a type of convolutional neural network (CNN) that has been used for various image classification tasks, including pneumonia detection. It was introduced in a paper published in the journal Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition in 2015. One of the key features of ResNet is its use of residual connections, which allow the network to learn more efficiently and reduce the risk of overfitting. It also has a very deep architecture, with over 50 layers, which allows it to learn complex patterns and features in the data. Overall, ResNet has shown good performance for pneumonia detection using chest X-ray images and may be a promising approach for this task. However, it is important to carefully evaluate the performance of different models and choose the one that ismostsuitableforaparticulardatasetandtask.
InceptionNet is a type of convolutional neural network (CNN) that has been used for various image classification tasks,includingpneumoniadetection.Itwasintroducedin a paper published in the journal Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition in 2014. One of the key features of InceptionNet is its use of inception modules, which allow the network to learn multiple scales and sizes of features in the data. It also has a relatively shallow architecture compared to some other CNNs, which makes it more efficient and easier to train. Overall, InceptionNet has shown good performance for pneumonia detection using chest X-ray images and may be a promising approach for thistask.However,itisimportanttocarefullyevaluatethe performance of different models and choose the one that ismostsuitableforaparticulardatasetandtask.
There are several evaluation metrics that can be used to assess the performance of a model for pneumonia detection True positive and true negative are terms used to describe the performance of a classifier in a binary classificationtask.Truepositives(TP)areinstanceswhere the classifier correctly predicts the positive class. True negatives(TN)areinstanceswheretheclassifiercorrectly predicts the negative class False positives (FP) are instances where the classifier predicts the positive class but the instance is actually negative. False negatives (FN) are instances where the classifier predicts the negative class but the instance is actually positive. Some common metricsinclude:
1. Accuracy: This is the percentage of images that are correctly classified by the model. It is calculated by dividingthenumberofcorrectpredictionsbythetotal numberofpredictions.
Accuracy = (True Positives + True Negatives) / Total Predictions
2. Precision:Thisisthepercentageofpredicted positive cases (i.e., cases where the model predicts pneumonia) that are actually positive. It is calculated bydividingthenumberoftruepositivepredictionsby thetotalnumberofpositivepredictions.
Precision = True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives)
3. Recall: This is the percentage of actual positive cases (i.e.,caseswherethepatienthaspneumonia)thatare correctly predicted by the model. It is calculated by dividing the number of true positive predictions by thetotalnumberofactualpositivecases.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Recall = True Positives / (True Positives + False Negatives)
4. F1 score: This is the harmonic mean of precision and recall. It is calculated by taking the average of the precision and recall, with higher weights given to lowervalues.
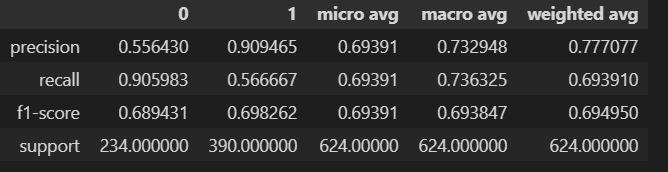

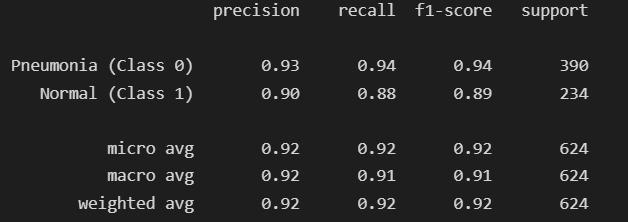
Fig-6: CNNmodel
Fig-3: CNNEvaluationMetrics
Fig-4: CNN_2EvaluationMetrics
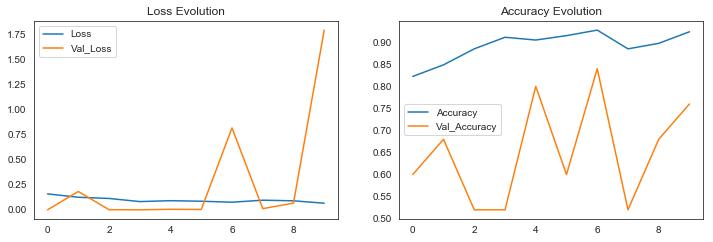
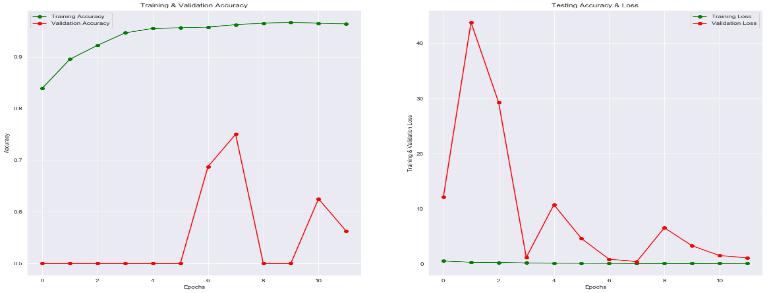
Fig-5: DenseNetEvaluationMetrics
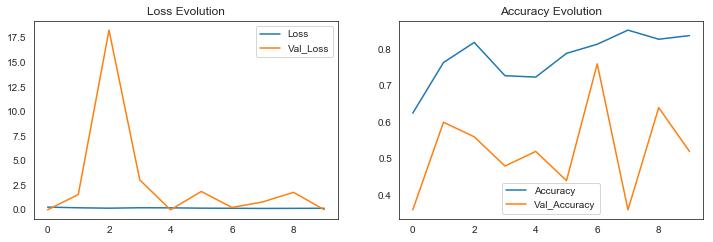
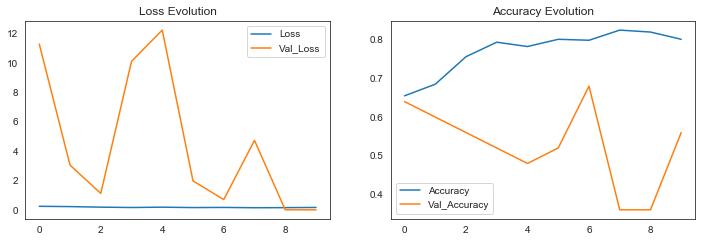
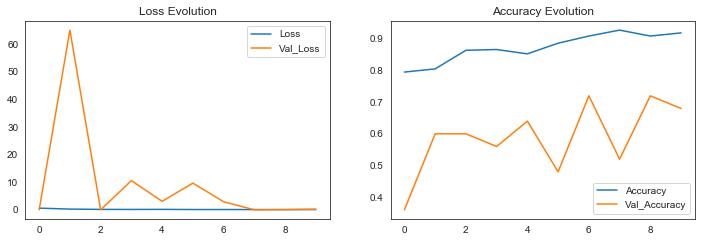
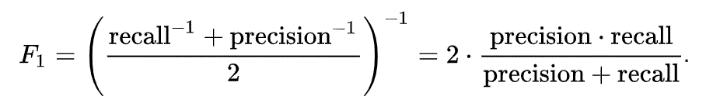
In this section, we attempt to analyze the classification using metrics such as accuracy and loss. There have been numerous studies that have analyzed the use of machine learning for pneumonia detection. Overall, the results of thesestudieshavebeenpromising,withmachinelearning models demonstrating high accuracy in identifying pneumonia from medical images. We try to put Training andValidationAccuracyintoagraphrepresentationusing accuracy on the y-axis and epochs on the x-axis. The results came out to be as following for the different models:
Fig-7: CNN_2model Fig-8: DenseNetmodel Fig-9: VGG-16model
Fig-10: ResNetmodel
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 10 Issue: 01 | Jan 2023 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

In this section, we try to compare the different preprocessed models based on their performance such as accuracy and loss. Ultimately, the best model for pneumonia detection will depend on the specific characteristicsofthedatasetandthedesiredperformance. It may be necessary to try several different models in order to find the one that works best. We are comparing thedifferentmodelsontestingandtrainingaccuracy. The accuraciescameouttobeasfollowing:
limitations to consider when using CNNs for pneumonia detection. One potential issue is the need for a large amountofannotateddatatotrainthemodel,whichcanbe time-consuming and expensive to collect. In the future, further research is needed to better understand the strengths and limitations of CNNs for pneumonia detectionandtoidentifythemosteffectiveapproachesfor different typesofdatasets This work can be extended for the classification and detection of the dataset of Dicom(.dcm) images. This would be our next approach to increasetheaccuracyusingDicomimages.
We would like to acknowledge the contribution of the following people without whose help and guidance this research would not have been completed. We acknowledge and counsel and support of faculty from MaharajaAgrasenInstituteofTechnologyforprovidingus a platformto researchon thetopic“Pneumonia Detection using CNN” and alsowould to thank our HOD Dr. Namita Gupta for giving us the opportunities and time to conduct and research on our topic. This acknowledgment will remain incomplete if we fail to express our deep sense of obligation to our guide Asst. Prof. Sudha Narang (CSE Department). We are indeed fortunate and proud to be supervised by them during our research, which would have seemed difficult without their motivation, constant support,andvaluablesuggestion. Weshall ever remain in debt of our parents and friends for their support and encouragement during the research. It would’ve been impossiblewithouttheircooperationandsupport.
[1] Kaggle Dataset accessed on 10 October 2022: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/paultimothymooney/c hest-xray-pneumonia
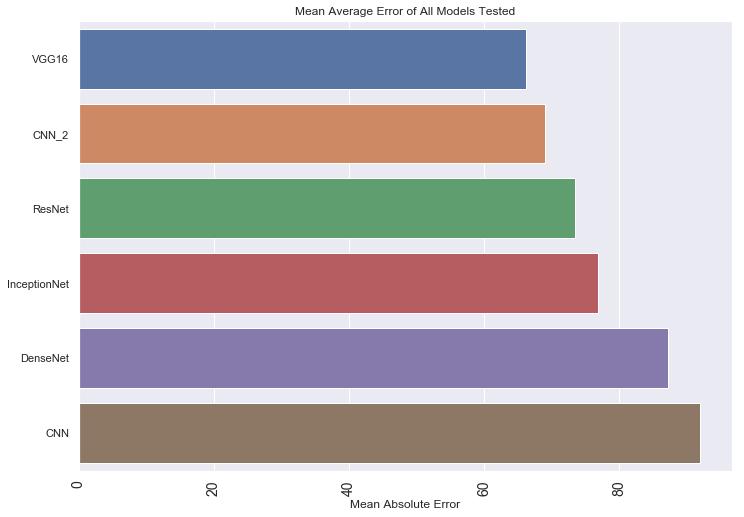
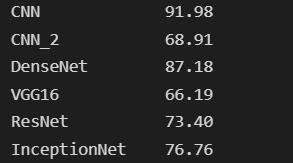
Fig-12: MeanAverageErrorofallmodelstested
[2] Alom MZ, Hasan M, Islam MT, et al. Automatic pneumonia detection from chest X-ray images using a deep convolutional neural network. In 2018 International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision (ICIEV) (pp.1-6).IEEE,2018
[3] Han B, Kim Y, Kim H, Lee S. A deep learning-based approach for detecting pneumonia from chest X-rays. ComputersinBiologyandMedicine,98:58-64,2018.
Fig-13: Accuracyofallmodelstested(in%)
We have proposed various models that detect pneumonia from chest x-ray images. We have made this model from scratch and all the models are purely based on transfer learning and CNN models. However, there are also some
[4] Tulabandhula S, Mehta K, Elgendy IY, et al. Deep learning-based automated detection of pneumonia from chest radiographs. Journal of Medical Systems, 43(2): 31, 2019.
[5] Li Q, Zhang L, Chen M, et al. Automated detection of pneumonia in chest X-ray images using a deep learning model.Radiology,291(3):673-681,2019