An Outline on Various Methods Used in Formulation and Evaluation of Lansoprazole of Liposome & Pro-Liposome.
Manisha Dubey1 , Priyanka Tyagi2 , Mr. Chandan Yadav3 , Lavkush Kumar Pal41Lecturer, Sherwood College of Pharmacy Barabanki, U.P, India.
2 Assistant Professor, Sherwood College of Pharmacy Barabanki, U.P, India.

3 Assistant Professor, Sherwood College of Pharmacy Barabanki, U.P, India.
4 Assistant Professor, Sherwood College of Pharmacy Barabanki, U.P, India. ***
Abstract - The medication lansoprazole is used to treat stomachandintestineulcers,erosiveesophagitis(esophageal damage caused by stomach acid), and other disorders including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome that involve excessive stomachacid.Frequentheartburnthatoccursatleasttwicea week is treated with over-the-counter (OTC) lansoprazole. Thismedicationisnotmeanttoprovideimmediaterelieffrom heartburn symptoms. A medicine that lowers stomach acid is marketedunderthetradenamesPrevacidandothernames.It is usedto treat Zollinger-Ellisonsyndrome, gastroesophageal refluxdisease,andpepticulcerdisease.Comparabilitytoother proton pump inhibitors of efficacy (PPIs). It is consumed orally. Pro-liposome applications are highlighted along with various formulation techniques (Film-deposition carrier method, Spray drying method, Fluidized-bed method, and Supercritical anti-solvent method), evaluation criteria (Hydrationstudy,Zetapotential,Flowproperty,Releasestudy, Particle Size, Entrapment Efficiency), and formulation techniques. This might aid in the development and testing of lansoprazole further. There have also been reports of distinct lansoprazolecharacteristicsconnectedtoitspharmacological profile and mechanism of protection in treating various illnesses. White crystalline powder, lansoprazole is very little soluble in water and easily soluble in ethanol, methanol, and acetone.Thegoalistocreatelansoprazole inabiocompatible and low-toxic form that may be utilised to treat ulcerative colitis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, gastric, duodenal, and peptic ulcers.
Key Words: Lansoprazole, Liposome, Pro-liposome, method,releasestudy.
1. INTRODUCTION
Themedicationlansoprazoleisused totreatstomachand intestine ulcers, erosive esophagitis (esophageal damage caused by stomach acid), and other disorders including Zollinger-Ellisonsyndromethatinvolveexcessivestomach acid.Frequentheartburnthatoccursatleasttwiceaweekis treated with over-the-counter (OTC) lansoprazole. This medication is not meant to provide immediate relief from heartburnsymptoms.Amedicinethatlowersstomachacidis marketedunderthetradenamesPrevacidandothernames. [1] It is used to treat Zollinger-Ellison syndrome,
gastroesophagealrefluxdisease,andpepticulcerdisease.[2] Comparability to other proton pump inhibitors of efficacy (PPIs).[3]Itisconsumedorally.Pro-liposomeapplications arehighlightedalongwithvariousformulationtechniques (Film-deposition carrier method, Spray drying method, Fluidized-bed method, and Supercritical anti-solvent method),evaluationcriteria(Hydrationstudy,Zetapotential, Flow property, Release study, Particle Size, Entrapment Efficiency),andformulationtechniques.Thismightaidinthe developmentandtestingoflansoprazolefurther.Therehave also been reports of distinct lansoprazole characteristics connectedtoitspharmacologicalprofileandmechanismof protection in treating various illnesses. White crystalline powder, lansoprazole is very little soluble in water and easilysolubleinethanol,methanol,andacetone.Thegoalis tocreatelansoprazoleinaformthatislowintoxicityand biocompatibleandmaybeusedtotreatconditionsincluding ulcerative colitis, inflammatory bowel syndrome, gastric, duodenal,andpepticulcers.[3]Effectsmayendureforafew days and begin over the course of a few hours. [1]. Constipation, stomach discomfort, and nausea are typical adverseeffects.[2][5]Osteoporosis,lowbloodmagnesium, a Clostridium difficile infection, and pneumonia are examplesofseriousadverseeffects.[4][5]Thesafetyofuse duringpregnancyandbreast-feedingisquestionable.[1]It operates by inhibiting the stomach parietal cells' H+/K+ATPase.[2]Inmedicalpractisesince1992,lansoprazolewas firstpatentedin1984.[6]Itisaccessibleasagenericdrug. [7] With more over three million prescriptions written, it wasthe188thmostfrequentlyprescribeddrugintheUSin 2017.Alansoprazoleisreportedlyexcretedintheurinein amountsbetween14to23%,andthisrangeincludesboth conjugatedandunconjugatedhydroxylatedmetabolites. A Drugs of the proton pump inhibitor family are typically recommendedforconditionswherethereisanexcessofacid inthebody.CYP2C19andCYP3A4oftenmetabolisethem.It isnotshownthatP-glycoproteinactivityislikewiseinhibited by proton pump inhibitors. Therefore, the purpose of our work was to describe lansoprazole as substrates and inhibitorsofP-glycoprotein.InCaco-2andL-MDR1cellsthat expresstheP-glycoprotein,polarisedtransportofthedrugs wasevaluated.UsingdigoxinasaP-glycoproteinsubstrate, lansoprazole's ability to inhibit efflux transport was evaluated. In conclusion, our findings show that proton
pump inhibitors are P-glycoprotein substrates and inhibitors.
Pro-liposomesareaflexiblesystemsincetheyareaccessible in dry form, which makes them simple to distribute, measure, transport, and store. The liposomes produced during reconstitution are more homogeneous in size and resemble traditional liposomes[15]. The pro-liposomes' solidformatteststotheirimprovedstabilityandpracticality.
1.1. Merits of Pro-Liposome:

1.Highhydrophilicmaterialtrapping.
2. Improved bioavailability is one of pro-liposomes' therapeuticadvantages.
3.PreventingmedicationdeteriorationintheGIT
4.Fairlyinexpensive.
5. Pro-liposomes, which are employed for controlled medicationreleaseandtargeteddrugdelivery.
6.Protonpumpinhibitortargeting.
Table 1 Comparison between liposome’s and proliposome’s
Liposome Pro-liposome
Liposomes are Unilamellar or multilamellar spheroid structures.
Composed of phospholipid andcholesterol.
The solubility of liposomes increaseswithoxidationand they have a propensity to clump together or fuse duringhydrolysis.
PLs are used as alternatives for liposomes.
Composed of water soluble porous powderascarrierphospholipids
In order to create free-flowing granular material that exhibits superior stability, increased solubility, and controlled release, drug and phospholipid material is coatedoncarriermaterial.
Table 2.Morphological characters of Lansoprazole.
IUPAC name RS)-2-([3-methyl-4-(2,2,2trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2yl]methylsulfinyl)-1Hbenzo[d]imidazole.
Molecular
Route
Excretion Kidneyandfecal
Melting point
The melting point is approx 166 °C
Molecular weight 369.36g.mol-1
Solubility freely soluble in ethanol and methanol slightly solubleinacetoneandvery lesssolubleinwater.
Colour whitecrystallinepowder
2. METABOLISM AND MECHANISM OF ACTION OF LANSOPRAZOLE

It works by specifically inhibiting the membrane enzyme H+/K+ATPaseintheparietalcellsofthestomach.Inclinical studies, the treatment of reflux oesophagitis with lansoprazole was superior to placebo or histamine (H2)receptorantagonists.Lansoprazoleisaprotodrugthatmust undergoprotonationinanacidicenvironmentinordertobe activatedasaPPI.Whenlansoprazoleisprotonated,itmay interactwiththecysteineresiduesCys813andCys321on theparietalH+,K+-ATPasetoproducestabledisulfides.PPIs in general have the capacity to bind covalently to their targets,whichallowsthemtoofferpersistentsuppressionof acidsecretion.
CYP3A4andCYP2C19metaboliselansoprazolemostlyinthe liver.Thetwomainmetabolitesthatareproducedarethe lansoprazolesulfonederivativeand5-hydroxylansoprazole.
3. MATERIALS AND METHODS
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents.
Twokindsoffood-gradesoybeanlecithinsfromLipoidGmbH (Ludwigshafen,Germany)wereusedtomakeproliposomes: phosphatidylcholine from hydrogenated, purified soy Phospholipon 90H (P90H), which contains a minimum of 90% weight-for-weight phosphatidylcholine (PC), a maximumof4%weight-for-weightlysophosphatidylcholine (LPC),and2%weight-for-weighttriglycerides(TG),andfatfree powder lecithin Lipoid S40 (LS40), which contains a minimum of 40% weight-for-weight phosphatid (PI).
Curcuminthatwascrystallisedandpurifiedwaspurchased fromSigma-Aldrich(St.Louis,MO,USA).Guargum(GG)was purchasedfromxodoCientifica(Hortolândia,SP,Brazil)and xanthan gum (XG) (Grindsted Xanthan 80) was provided courtesy of DuPont (Cotia, SP, Brazil). From Synth, we obtainedsucrose,dimethyl sulfoxide(DMSO),andsodium benzoate(Diadema,SP,Brazil).Thecompoundsutilisedin this investigation were all of the reagent grade kind. Throughoutthestudies,deionizedwater(fromaDirectQ3 system,Millipore,Billerica,MA,USA)wasutilised.
4. METHODS OF PREPARATION
Pro-liposomes(PLs)arepreparedbytwomethods-

Film-depositioncarriermethod.
Handshakingmethod
4.1.Film Deposition Carrier Method
Pro-liposomesarecreatedusingthefilmdepositioncarrier technique.Thisprocedureinvolvesdischargingacoatingof pharmaceuticals and phospholipids onto a permeable, water-solublecarriermaterial.AsshowninFigure1,afeed tubeinjectsanevaporativesolutiondropbydropontoacore of carrier material that is stored in a vessel of a rotary flashevaporator under vacuum. The evaporative solution containsasolutionofmedicationandphospholipids.Whena free-flowingpowdermatrixisobtained,overwettingofthe matrixispreventedatanytimeandasubsequentaliquotof organicmixtureisfed[9].Tocontroltheamountofcarrier that is required to help the lipids, chosen carriers should have high surface area and permeability. Additionally, it permitsahighsurfactanttocarriermassproportionforthe generationofpro-liposomes.Duetotheirwatersolubility, they may produce liposomal dispersion quickly after hydration, and by properly regulating the size of the previouspowder,arelativelysmallrangeofreconstituted liposomes can be obtained. Maltodextrin, sorbitol, microcrystallinecellulose,magnesiumaluminiumsilicates, mannitol,andothersarethemostoftenutilisedcarriers[16]. Sluggishsolventinclusionandevaporationsteps[17].Modify the process by spreading the carrier component in an organic medicine and phospholipid combination in the rotary evaporator vessel before managing the vacuum evaporationtoeliminatethisproblem.Incontrasttothereal technique,thisresultsinastableandlesstime-consuming lipiddispersionthatisveryconsistentandwell-organized.
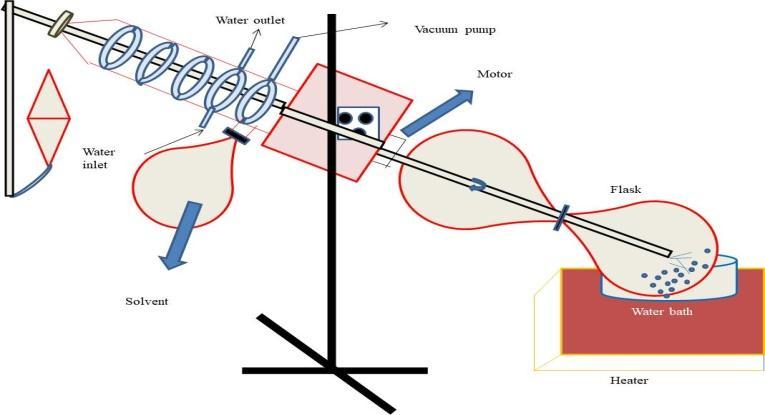
5. EVALUATION OF PRO-LIPOSOME
5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy(SEM):
Basically, it's utilised to study the PL powder's surface structure. Additionally, it is utilised to compare the appearance of liposomes and pure carrier material. Proliposomeformulationconfirmsaftercarriermaterialinthe formulation approves the disposition of phospholipids on thecarrier.
5.2. Transmission electron microscopy(TEM):
This technique is often used to examine the liposome's structureafterPLpowderhydration.Inthisprocedure,the pro-liposomepowderishydratedwithdistilledwaterbefore being examined under a microscope to determine its lamellarityandform.
5.3. Hydration Study:
Studiesonhydrationarebasedonthefactthatliposomesare created when they come into contact with an aqueous environment.Thismethodinvolvesaddingasmallamount ofdrypro-liposomepowdertoaglassslide,graduallyadding water,andusingamicroscopetoobservevesicleformation. Assoonashydrationstarts,dissolutionanddisintegration start happening quickly. When water comes into contact with the lipid surface of pro-liposomes, liposomes are created.Thisprocedurecontinuesuntilthecarrierandlipid layerhavecompletelydissolved.
5.4.Zeta Potential:
Surfacechargeoftheparticlemaybeusedtocalculatezeta potential.Itisthepotentialdifferencebetweenthesolution's electro-neutralzoneanditsdenselybondedlayer'ssurface (shearplace).
5.5. Flow Property:
The flow feature of a powder formulation may be used to describe satisfied homogeneity and handling processing operations. It is necessary to examine the pro-properties liposome's for formulations based on solid powder. The parameters Angle of repose, Carr's Index, and Hausner's ratiomaybeusedtoevaluateit.
6. CONCLUSION
The use of liposomes and pro-liposomes has been a significantcontributortotheresolutionofissues withthe stability,bioavailability,andsolvabilityofmedicationsthat are only partially soluble. There has been tremendous progress made toward the creation of pro-liposomes as viableoraldosageforms;nevertheless,therearecurrently nomedicinesthatareavailableonthemarket.
REFERENCES
1. "LansoprazoleUseDuring Pregnancy". Drugs.com.
Retrieved3March2019.
2. Jump up to:a b c d e f "Lansoprazole Monograph for Professionals" Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved3 March2019
3. Jump up to:a b British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 79–80. ISBN9780857113382
4. Jump up to:a b "[99] Comparative effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors |TherapeuticsInitiative". 28 June 2016.Retrieved14July2016.
5. Jump up to:a b c d e "Lansoprazole capsule, delayed release pellets" DailyMed. 11 October 2016
Retrieved31December2019
6. Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analoguebased Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 445. ISBN9783527607495
7. "The Top 300 of 2020" ClinCalc. Retrieved11 April2020
8. "Lansoprazole - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc.
Retrieved11April2020.
9. Pauli-MagnusC,RekersbrinkS,KlotzU,FrommMF: Interaction of omeprazole, lansoprazole and pantoprazole with P-glycoprotein. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;364(6):551-7.
10. S. P.Vyas and R. K Khar,; Niosomes, Target and controldrugdelivery1stedition:249-279,(2002). Rolland, “ Pharnmaceutical particulates carriers therapeutic application” Marcel Dekkar: 107-117, (2003).

11. Shin JM, Kim N: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamicsoftheprotonpumpinhibitors.J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013 Jan;19(1):25-35. doi: 10.5056/jnm.2013.19.1.25. Epub 2013 Jan 8. (PubMedID23350044)
12. BosnjakT,SolbergR,HematiPD,JafariA,KassemM, Johansen HT: Lansoprazole inhibits the cysteine protease legumain by binding to the active site. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Mar 27. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13230.(PubMedID30916878)
13. JangaKY,JukantiR,VelpulaA,SunkavalliS,Bandari S, et al. 2012; Bioavailability enhancement of zaleplonviaproliposomes:Roleofsurfacecharge. EuroJPharBiop80:347-357.
14. SongKH,ChungSJ,ShimCK(2002)Preparationand evaluation of proliposomes containing salmon calcitonin.JConRel84:27-37.
15. JangaKY,JukantiR,VelpulaA,SunkavalliS,Bandari S, et al. 2012; Bioavailability enhancement of zaleplonviaproliposomes:Roleofsurfacecharge. EuroJPharBiop80:347-357.
16. RojanaratW,ChangsanN,TawithongE,PinsuwanS, Chan HK, et al. 2011;Isoniazid proliposome powders for inhalation preparation, characterization and cell culture studies. Intern J MolSci12:4414-4434.
17. Xu H, He L, Nie S, Guan J, Zhang X, et al. 2009; Optimizedpreparationofvinpocetineproliposomes by a novel method and in vivo evaluation of its pharmacokineticsinNewZealandrabbits.JConRel 140:61-68.
18. Yan-YuX, YunMeiS,Zhi-PengC,Qi-NengP2006; Preparationofsilymarinproliposome:anewwayto increaseoralbioavailabilityofsilymarininbeagle dogs.InterPhar319:162-168.
19. Payne NI, Browning I, Hynes CA 1986; Characterization of proliposomes. J Phar Sciences 75:330-333.
20. Martin A 1993; Physical pharmacy: physical chemicalprinciplesinthepharmaceuticalsciences: BIWaverlyPvt.Ltd.
21. Burgess DJ, 2005; Injectable dispersed systems: Formulation, processing, and performance. Boca Raton:Taylor&FrancisVemuriS,RhodesC1995; Preparation and characterization of liposomes as therapeutic delivery systems: a review. Pharm Ac Hel70:95-111.

